Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration System
Uploaded by
Carina JL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesphysiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentphysiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesRespiration System
Uploaded by
Carina JLphysiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Rate of diffusion
Fick's Law of Diffusion R=DA (P/d)
R- rate of diffusion (amount of gas per unit) Definition Process of obtaining O2 from the external environment &
D- diffusion constant eliminating CO2
A- Area over which diffusion takes place
P- Partial pressure/ concentration difference between 2 Goal acquire O2 needed to breakdown food molecules into energy &
R can be increased if: sides of the barrier to diffusion eliminating CO2
area (A) of respiratory surface d- Distance across which diffusion takes place
difference in concentration (P) on either side of respiratory Important cellular respiration-generates energy from oxidisation of food
surface molecules
internal respiration
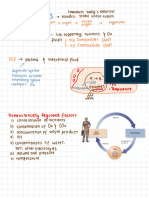
Respiration
gas exchange btw blood & the body cells
Glucose + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy
O2 + hemoglobin = oxyhemoglobin Oxygen transport external respiration
small % (>2%) dissolve in n=blood plasma
obtaining O2 from the external environment into the blood
& removing CO2 from the blood
CO2 undergo modification- bicarbonate ion (HCO3-)[~60%]
smaller % ofCO2 bound to protein (e.g.: Hemoglobin + CO2 transport
Gas exchanges
CO2 = Carbiminohemoglobin) [~20%] across bodysurface
even smaller % CO2 dissolve in blood plasma [~10%] Cnidaria
difference
cutaneous (skin)
types of respiration Annelida &
Temperature respiratory Chordata (frog)
temperature denature the bond between O2 & organ
hemoglobin, Respiration System Cnidaria Arthropoda
the dissociation curve shifts to the right & Arachnid
pH Tracheal tube system
chordata (fish)
CO2 or other acids( in pH),causes Bohr Shift internal gills
It caused more O2 to be given up as oxygen pressure gills are rich of capillary network
(countercurrent exchange system)text
The dissociation curve shifts to the right.
Factors affecting O2 binding gills Chordata
(larval fish & amphibians)
external gills
Organic phosphate feather-like arrangement gills
DPG binds to hemoglobin which rearranges the
hemoglobin into the T-state, thus the affinity of O2 for
hemoglobin (T & R state)
the curveshifts to the right
Other factors mammals
altitude, free radicals/ heavy metals, CO,etc. inhalation
alveolus on lungs ( surface area
exhalation
the sigmoid shape of O2 dissociation curve shows the
cooperative binding (hemoglobin hv > ability to bind O2) of Amphibians
O2 to 4 polypeptide chains. lungs with connective tissues
changes in temperature, pH & organic phosphates like ridges to surface area
DPG directly effect the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve Chordata (bird)
at partial pressure of O2, hemoglobin (in lungs) binds to Lungs
O2 to form oxyhemoglobin air-sac system (aerodynamical valving)
blood is saturated (oxyhemoglobin) travel to tissues Reptiles
deprived of O2, the partial pressure of O2
lung with simple sacs with
folding of wall ( surface area)
Seaturtle
lungs made up of spongy texture of faveoli
You might also like
- SEE Exam Review 1Document20 pagesSEE Exam Review 1Eric100% (2)
- LU5 TranspirationDocument28 pagesLU5 TranspirationCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Notes Form 2 Chapter 4Document4 pagesNotes Form 2 Chapter 4lembu_sihat7783% (6)
- Nso Level2 Class 6 Set 4Document8 pagesNso Level2 Class 6 Set 4Hemant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 00human Performance ATPL TeoriDocument116 pages00human Performance ATPL TeoriFlying SharkNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument255 pagesArterial Blood GasMark Joshua S CruzNo ratings yet
- Aerated Food ProductDocument22 pagesAerated Food ProductbasssingaNo ratings yet
- Basic Flow CytometryDocument37 pagesBasic Flow CytometryCarina JLNo ratings yet
- CO2 Adsorption Process Simulation in ASPEN HysysDocument5 pagesCO2 Adsorption Process Simulation in ASPEN HysysHussseinmubarkNo ratings yet
- List of Chinese RadicalsDocument5 pagesList of Chinese RadicalsCarina JLNo ratings yet
- 11 17Document68 pages11 17Estela HirataNo ratings yet
- ETP Design CalculationDocument6 pagesETP Design Calculationmanuel.hernandez100% (1)
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Document41 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Sandeep ManuNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Transport of Gases in The BloodDocument25 pagesTransport of Gases in The BloodValentinaNo ratings yet
- Physio Paramed Complete 2009 NewDocument69 pagesPhysio Paramed Complete 2009 NewJose Luis BlancoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Carbon Cycle Through Climate Science LecturesDocument54 pagesUnderstanding the Carbon Cycle Through Climate Science LecturesNicole Maite SANTIAGO APARINo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases - NotesDocument4 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide transport mechanismsDocument9 pagesOxygen and carbon dioxide transport mechanismspuchio100% (1)
- Hudson 2012Document10 pagesHudson 2012Rin4lNo ratings yet
- Respiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)Document4 pagesRespiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)PkernNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration and Gas Exchangenajmi_munirahNo ratings yet
- CE-105 Module-2 Atmosphere Water InteractionDocument39 pagesCE-105 Module-2 Atmosphere Water InteractionakashNo ratings yet
- Exchange of Gases in Alveoli & TissuesDocument26 pagesExchange of Gases in Alveoli & TissuesValentinaNo ratings yet
- SH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Document131 pagesSH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Shuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Document29 pagesGas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Fatiha TamadNo ratings yet
- Respiration PHYSIO (MediCallAcademy - Org) - 11-13Document3 pagesRespiration PHYSIO (MediCallAcademy - Org) - 11-13Tauseef AfridiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Capture and Air Quality: July 2011Document29 pagesCarbon Dioxide Capture and Air Quality: July 2011Tamara NwaserNo ratings yet
- Ransport Of: Dr. Roopa Kotha Dr. Shaji MathewDocument36 pagesRansport Of: Dr. Roopa Kotha Dr. Shaji MathewRenganathan SockalingamNo ratings yet
- Removal of Carbon Dioxide From Indoor Air Using A - 1QWDWQDQWDQWDQDocument7 pagesRemoval of Carbon Dioxide From Indoor Air Using A - 1QWDWQDQWDQWDQ16061977No ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide TransportDocument3 pagesCarbon Dioxide TransportAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CO Mitigation in Thermo-Chemical Hydrogen Processes: Thermo-Environomic Comparison and OptimizationDocument9 pagesCO Mitigation in Thermo-Chemical Hydrogen Processes: Thermo-Environomic Comparison and OptimizationLaura Cristina BrandNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications of Teh Veno Arterial Pco2 Gap, ReviewDocument9 pagesPathophysiology and Clinical Implications of Teh Veno Arterial Pco2 Gap, ReviewDeisy Marcela Reyes ParraNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - Water InteractionsDocument43 pagesAtmosphere - Water InteractionsakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter-04 (RESPIRATION)Document9 pagesChapter-04 (RESPIRATION)shivaNo ratings yet
- Notes: Ideal (General) Gas LawDocument8 pagesNotes: Ideal (General) Gas LawFakultas Kedokteran UnhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Gaseous Exchange Through The Respiratory Membrane.Document23 pages3 Gaseous Exchange Through The Respiratory Membrane.Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument25 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For Scientiststopspeed1No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange L1Document13 pagesGas Exchange L1delicata.benNo ratings yet
- L11 Respiratory and Skeletal Systems 2Document41 pagesL11 Respiratory and Skeletal Systems 2rs8kd4kvwhNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Gas Exchange CC PDFDocument18 pagesGr11 Gas Exchange CC PDFAsma DhoodhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Respiratory SystemDocument56 pagesChapter 9 The Respiratory SystemNurarief AffendyNo ratings yet
- 1A Ocean Carbon 2022Document7 pages1A Ocean Carbon 2022g9ydjynjqyNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Mass Transfer-IntroDocument25 pagesCH - 1 Mass Transfer-IntroDivyamNo ratings yet
- Notes Concept-of-OxygenationsdfDocument5 pagesNotes Concept-of-OxygenationsdfRandomly SelectedNo ratings yet
- 1993 - Kikkinides - Conc and Recovery of CO2 From Flue Gas by PSADocument7 pages1993 - Kikkinides - Conc and Recovery of CO2 From Flue Gas by PSAAashi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Respiration - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 10 Respiration - Lecture Notesapi-372850886% (7)
- Chemical Engineering Science: Helei Liu, Moxia Li, Raphael Idem, Paitoon (PT) Tontiwachwuthikul, Zhiwu LiangDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering Science: Helei Liu, Moxia Li, Raphael Idem, Paitoon (PT) Tontiwachwuthikul, Zhiwu LiangJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- Properties of CO2Document36 pagesProperties of CO2andiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - RevisionDocument5 pagesUnit 7 - RevisionusbdetailsNo ratings yet
- Volumes, Spirometry and Gas ExchangeDocument33 pagesVolumes, Spirometry and Gas ExchangeAnshikaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: The Exchange of Gases: Concepts & ConnectionsDocument13 pagesRespiration: The Exchange of Gases: Concepts & ConnectionsAlicia CatalanNo ratings yet
- Ventialtion Perfusion Relationships1Document1 pageVentialtion Perfusion Relationships1DewanggaWahyuPrajaNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Gas Exchange in Plants and Animals 2Document3 pages7.4 Gas Exchange in Plants and Animals 2yiuzz hcyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument188 pagesRespiratory SystemgeorgeanthonyarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4- Gaseous Exchange-convertedDocument46 pagesLecture 4- Gaseous Exchange-converted7mb767gqyvNo ratings yet
- 2nd Set Air-Water-Soil InteractionDocument53 pages2nd Set Air-Water-Soil InteractionShrilalraghudevNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 NotesDocument54 pagesExam 4 NotesAnonymous qaAbg65dCNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesThe Respiratory System5130022035 ARINA DINANANo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument2 pagesUntitled NotebookNajwa Faradila yuvitriNo ratings yet
- Universidad de la Sabana study examines gas-liquid separationDocument7 pagesUniversidad de la Sabana study examines gas-liquid separationMaria Alejandra OtavoNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Co2 Capture With Diethyl SuccianteDocument13 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Co2 Capture With Diethyl SuccianteJohn Jairo RamosNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Journal of PetroleumDocument12 pagesEgyptian Journal of PetroleumFarrasNo ratings yet
- Waste Disposal and Stream Self PurificationDocument26 pagesWaste Disposal and Stream Self PurificationsupriyapandeyNo ratings yet
- Water Quality and Organic PollutionDocument31 pagesWater Quality and Organic PollutionRoshineeNo ratings yet
- Obatpernapasan PDFDocument32 pagesObatpernapasan PDFrike adlianaNo ratings yet
- CO Separation From Purge Gas and Flue Gas in The Methanol Process, Using NLP Model OptimizationDocument10 pagesCO Separation From Purge Gas and Flue Gas in The Methanol Process, Using NLP Model OptimizationAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical3A 3B RDT 2016-17Document5 pagesPractical3A 3B RDT 2016-17Carina JLNo ratings yet
- E-Coli Competent Cells Protocol & TransformationDocument1 pageE-Coli Competent Cells Protocol & TransformationCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Ligation and TransformationDocument6 pagesLigation and TransformationCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Electrocompetent BacteriaDocument2 pagesPreparation of Electrocompetent BacteriaCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation PDFDocument1 pageThermoregulation PDFCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Bioanalysis in Drug Discovery and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesBioanalysis in Drug Discovery and DevelopmentCarina JLNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography For Clinical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography For Clinical ApplicationsCarina JLNo ratings yet
- TDMDocument68 pagesTDMCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36Document7 pagesLecture 36Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument2 pagesGuidelines For Therapeutic Drug MonitoringCarina JLNo ratings yet
- STT2073 Lect 1 Plant Breeding OverviewDocument9 pagesSTT2073 Lect 1 Plant Breeding OverviewCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxin - VetscanDocument6 pagesTherapeutic and Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxin - VetscanCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxin - VetscanDocument6 pagesTherapeutic and Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxin - VetscanCarina JLNo ratings yet
- CleavageDocument1 pageCleavageCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Integrated Solid Waste Management ISWMDocument9 pagesIntegrated Solid Waste Management ISWMCarina JLNo ratings yet
- The Role of WOX Genes in Flower DevelopmentDocument9 pagesThe Role of WOX Genes in Flower DevelopmentCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Embryonic CleavageDocument2 pagesPatterns of Embryonic CleavageCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Botulinum ToxinDocument9 pagesBotulinum ToxinCarina JLNo ratings yet
- The Four Phases of Mitosis in A CellDocument1 pageThe Four Phases of Mitosis in A CellCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Cleavage in Human ZygoteDocument3 pagesCleavage in Human ZygoteCarina JLNo ratings yet
- ABC Model of Flower Development - WikipediaDocument9 pagesABC Model of Flower Development - WikipediaCarina JLNo ratings yet
- InterphaseDocument1 pageInterphaseCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of Flower Development: An Armchair GuideDocument11 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of Flower Development: An Armchair GuideCarina JLNo ratings yet
- STF1103 - Kruskal-Wallis & Friedman Test Assignment v2Document1 pageSTF1103 - Kruskal-Wallis & Friedman Test Assignment v2Carina JLNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument2 pagesMini ProjectCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Petrol StationDocument123 pagesFire Fighting Petrol StationNazeer HaqNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Rain GaugeDocument11 pagesMini Project Rain Gaugeamin shukriNo ratings yet
- Two-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolDocument197 pagesTwo-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolSanchez JorgeNo ratings yet
- Adv Chem Q2 W2Document9 pagesAdv Chem Q2 W2Trexia SingsonNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Main Campus, Victoria, Oriental MindoroDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Main Campus, Victoria, Oriental MindoroAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Paratherm Diathermic Oil OR MSDSDocument4 pagesParatherm Diathermic Oil OR MSDSADITYA_PATHAKNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Part 2 EdexcelDocument2 pagesGroup 2 Part 2 EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- Man has continually sought to improve quality of life through technology and its environmental impactDocument13 pagesMan has continually sought to improve quality of life through technology and its environmental impactNestor Navarro Jr.No ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Adsorption Studies On Modified MontmorilloniteDocument10 pagesCarbon Dioxide Adsorption Studies On Modified MontmorilloniteJulian De BedoutNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Sample ExamDocument26 pagesEarth Science Sample ExamCatherine Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rockstrom Et Al 2009 - Planetary BoundariesDocument33 pagesRockstrom Et Al 2009 - Planetary Boundariestemp tempNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis A, General: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesApplied Catalysis A, General: Sciencedirectcholila_tamzysiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Gasoline To HumanDocument3 pagesBenefits of Gasoline To HumanErnest Glenn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse BurgerDocument1 pageGreenhouse Burgerapi-238016123No ratings yet
- Stoichiometric CombustionDocument3 pagesStoichiometric CombustionKhairil MunawirNo ratings yet
- A Life-Cycle Assessment of Portland Cement ManufacturingDocument8 pagesA Life-Cycle Assessment of Portland Cement ManufacturingLucero MamaniNo ratings yet
- Intech200906 FocusDocument29 pagesIntech200906 FocusMauro Sánchez100% (1)
- Unity 4 BiosphereDocument9 pagesUnity 4 BiosphereFredson kalindaNo ratings yet
- Appendix E Preliminary Hazard AnalysisDocument66 pagesAppendix E Preliminary Hazard Analysissusa2536No ratings yet
- IB Eassessment N20 Biology MarkschemeDocument11 pagesIB Eassessment N20 Biology MarkschemelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- 4386-MV Ocean Love - Vessel Moisture LotsDocument16 pages4386-MV Ocean Love - Vessel Moisture LotsakloioNo ratings yet
- AIR QUALITY MONITOR CONTENTSDocument9 pagesAIR QUALITY MONITOR CONTENTSÁrea de IngenieríaNo ratings yet
- Cp2245 Finish Paint Ea4-5991 MsdsDocument11 pagesCp2245 Finish Paint Ea4-5991 MsdsPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- Spe 195802 MS PDFDocument17 pagesSpe 195802 MS PDFhijoetigreNo ratings yet