Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factors Affecting Creep - Type of Cement
Uploaded by
brp4315170 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesFactors Affecting Creep - Type of Cement
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFactors Affecting Creep - Type of Cement
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesFactors Affecting Creep - Type of Cement
Uploaded by
brp431517Factors Affecting Creep - Type of Cement
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
FACTORS AFFECTING CREEP
Type of Cement
Creep is defined as the increase in strain under a sustained
constant stress after taking into account other time-dependent
deformations not associated with stress, viz. shrinkage, swelling
and thermal deformations.
Type of cement affects creep in a manner as it influences
strength of concrete at the time of application of load. On this
basis, both Portland cement lead to sensibly the same creep, but
the rate of gain of strength has same effect.
The finer the cement higher is its gypsum required, so
that regrinding a cement in laboratory without addition of gypsum
produce an improper and retarded cement, which exhibits high
shrinkage and high creep.
Extremely fine cement with specific surface up to 740
kg/m lead to high early creep but lower creep after one or two
2
years under load. This is probably due to the high gain of strength
of the finest cement with resultant rapid drop in actual
stress/strength ratio.
Creep increases in order for following type cements:
1) Rapid hardening cement,
2) Low heat cement,
3) Ordinary Portland cement.
Use of blast furnace slag leads to a lower basic creep but
higher drying shrinkage. Creep of concrete made with expansive
cement is longer than that of concrete made with Portland
cement.
FACTORS AFFECTING SHRINKAGE
Type of Cement
Shrinkage is caused by loss of water by evaporation or by
hydration of cement, and also by carbonation.
The effect of shrinkage is to cause cracks in the concrete.
Ordinary Portland cement does not show good extensibility. In this
respect low heat cement or Portland pozzolana cement will have
higher extensibility. It may not be out of place to point out that
addition of a certain quantity of lime will improve the extensibility
of ordinary cement concrete. The superiority of lime mortar for
internal plaster over cement mortar is from the point of view of
the superior extensibility of lime mortar over cement mortar by
about 7 times. A continuous surface, like plaster on the wall,
undergoes tremendous change in volume and as such cements
mortar having low extensibility, is not able to withstand the
volume change without cracking, where lime mortar or gauged
mortar having higher extensibility gives better performance.
Thus, we can conclude that Ordinary Portland cement has
lower tendency to shrink than low heat cement and Portland
pozzolana cement. Lime or gauged cement has high tendency to
shrink without forming any cracks.
You might also like
- Combined Footing Design ReportDocument9 pagesCombined Footing Design Reportbrp431517No ratings yet
- DR Fixit Samshield XL 1500 PDFDocument3 pagesDR Fixit Samshield XL 1500 PDFNational WaterproofingNo ratings yet
- LBO IndtabDocument32 pagesLBO IndtabAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- PM Modi With Coep Satellite TeamDocument1 pagePM Modi With Coep Satellite Teambrp431517No ratings yet
- Beam Reinforcement Schedule PDFDocument2 pagesBeam Reinforcement Schedule PDFbrp431517No ratings yet
- LBO IndtabDocument32 pagesLBO IndtabAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- LBO IndtabDocument32 pagesLBO IndtabAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- QuickDAQ 2013 PDFDocument132 pagesQuickDAQ 2013 PDFbrp431517No ratings yet
- Plinth BeamDocument2 pagesPlinth Beambrp431517No ratings yet
- Sardar Statue - Structural-Design-1 PDFDocument15 pagesSardar Statue - Structural-Design-1 PDFjagadeshNo ratings yet
- Beam Reinforcement ScheduleDocument82 pagesBeam Reinforcement Schedulebrp431517No ratings yet
- PM Modi With Coep Satellite TeamDocument1 pagePM Modi With Coep Satellite Teambrp431517No ratings yet
- Prof Ashok Jain - A Critical Review of Is 13920Document11 pagesProf Ashok Jain - A Critical Review of Is 13920kukadiya127_48673372No ratings yet
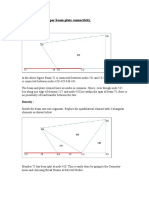
- Examples of Improper Beam Plate ConnectivityDocument4 pagesExamples of Improper Beam Plate Connectivitybrp431517No ratings yet
- Cow Shed Staad Pro ModelDocument3 pagesCow Shed Staad Pro Modelbrp431517No ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngineering Properties of Materialspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Plates CONNECTED IMPROPERLYDocument2 pagesPlates CONNECTED IMPROPERLYbrp431517No ratings yet
- Modelling of Diaphrams in STAAD Pro PDFDocument13 pagesModelling of Diaphrams in STAAD Pro PDFragalwarNo ratings yet
- Settlement in Sand Is Sudden Type of SettlementDocument1 pageSettlement in Sand Is Sudden Type of Settlementbrp431517No ratings yet
- 2006 SEM BeamColumnJoints PDFDocument19 pages2006 SEM BeamColumnJoints PDFMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- IS-13920 2016 AmendmentsDocument14 pagesIS-13920 2016 AmendmentsShakil Akhter100% (4)
- Final Result 67-2017 PDFDocument84 pagesFinal Result 67-2017 PDFbrp431517No ratings yet
- Shear Wall IS13920Document19 pagesShear Wall IS13920Parag KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Staircase DesignDocument13 pagesStaircase Designbrp431517No ratings yet
- r0-Dbr Head Regulator ConduitDocument11 pagesr0-Dbr Head Regulator Conduitbrp431517No ratings yet
- Transco 2017Document13 pagesTransco 2017pravin_3781No ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngineering Properties of Materialspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- ESE Time Table Nov-Dec 2017Document9 pagesESE Time Table Nov-Dec 2017brp431517No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Kingspan Kooltherm K7Document1 pageKingspan Kooltherm K7Diaconu FlorinNo ratings yet
- Manage Waste & Resources with WastivityDocument21 pagesManage Waste & Resources with WastivitybhishmNo ratings yet
- IJBE-9-3-2021 Bahrami Guillot 13 30Document18 pagesIJBE-9-3-2021 Bahrami Guillot 13 30Elina EsfandiariNo ratings yet
- Structural Optimization of Composite Railway SleepersDocument6 pagesStructural Optimization of Composite Railway SleepersijaertNo ratings yet
- Wax Glue2Document6 pagesWax Glue2Gamal FouadNo ratings yet
- Act 3 ConclusionDocument13 pagesAct 3 ConclusionVon A. DamirezNo ratings yet
- MECH466 Lecture 4 PDFDocument28 pagesMECH466 Lecture 4 PDFSaran ArunNo ratings yet
- Bjorn Tore Lovfall TriallectureDocument45 pagesBjorn Tore Lovfall Triallecturegreenhen15No ratings yet
- Leonard - Kabondo 1584967491 A PDFDocument2 pagesLeonard - Kabondo 1584967491 A PDFMabvuto Banda the son of the Consuming fireNo ratings yet
- A574m PDFDocument7 pagesA574m PDFLeonardo GomideNo ratings yet
- Elex ReviewerDocument3 pagesElex ReviewerJhomel EberoNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Sensing Temperature Sensors Line Guide 0 1109480Document12 pagesHoneywell Sensing Temperature Sensors Line Guide 0 1109480X'mix ĐreamerNo ratings yet
- Ultragel II Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageUltragel II Technical Data Sheetjess, cNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Copper Alloy Matrix Composites Reinforced With Wc-Xni Powders Prepared by Spontaneous InfiltrationDocument9 pagesMicrostructure Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Copper Alloy Matrix Composites Reinforced With Wc-Xni Powders Prepared by Spontaneous Infiltrationnorthpole_plNo ratings yet
- Design of Flat Slab Using Equivalent Frame MethodDocument41 pagesDesign of Flat Slab Using Equivalent Frame Methodabadittadesse100% (2)
- Tds CPD Sika ViscoCrete 2100 UsDocument2 pagesTds CPD Sika ViscoCrete 2100 UsSamirHashimNo ratings yet
- Production of Cyclohexane From BenzeneDocument151 pagesProduction of Cyclohexane From BenzeneGerald Lim60% (5)
- Bearing Capacity of Square Footing On Reinforced Pond AshDocument6 pagesBearing Capacity of Square Footing On Reinforced Pond AshHUGINo ratings yet
- Seeing NPR Material From The Mechanic Point of ViewDocument14 pagesSeeing NPR Material From The Mechanic Point of View施元No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Interpretation For Orthopedic Plate With Titanium AlloyDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of Interpretation For Orthopedic Plate With Titanium AlloyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Sustainable StationeryDocument34 pagesSustainable StationeryMonica Cortina72No ratings yet
- Extraction and Purification of Bioactive CompoundsDocument22 pagesExtraction and Purification of Bioactive CompoundsamirahNo ratings yet
- CHM 1025c Final Exam Practice WCDocument5 pagesCHM 1025c Final Exam Practice WCMiguel SuarezNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Cementing Instruments Data Acquisition and Control SystemDocument2 pagesOil Well Cementing Instruments Data Acquisition and Control Systemसागर फुकटNo ratings yet
- Tankguard StorageDocument5 pagesTankguard StorageBiju_PottayilNo ratings yet
- Congo Red Dye PDFDocument6 pagesCongo Red Dye PDFkiranpatil1014532No ratings yet
- Sodium Saccharin E-954: Material Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesSodium Saccharin E-954: Material Safety Data SheetHerdianNo ratings yet
- Merabet - Sonolytic and Ultrasound-Assisted Techniques For Hydrogen Production A Review Based On The Role of Ultrasound Review 2022Document15 pagesMerabet - Sonolytic and Ultrasound-Assisted Techniques For Hydrogen Production A Review Based On The Role of Ultrasound Review 2022Michel AertsNo ratings yet
- Design of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneDocument7 pagesDesign of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneRonin ZxxNo ratings yet
- Ultra Thin WhitetoppingDocument21 pagesUltra Thin WhitetoppingDHRUV KDMC ProjectsNo ratings yet