Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Strategies
Uploaded by
Mohsin JuttCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Strategies
Uploaded by
Mohsin JuttCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 05: Types of Business Strategies
A. Integration Strategies
1. Horizontal Integration
2. Vertical Integration
i. Backward Integration
ii. Forward Integration
B. Intensive Strategies
1. Market Penetration
2. Market Development
Even if 3. Product Development
C. Diversification Strategies
1. Related Diversification
youre on
2. Un-related Diversification
D. Defensive Strategies
1. Retrenchment
the right
2. Divestiture
3. Liquidation
E. Michael Porters Generic Competitive Strategies
1. Cost Leadership ----- Low Cost
track, youll 2. Cost Leadership ----- best Value
3. Differentiation
4. Focus ----- Low Cost
get run over 5. Focus ----- Best Value
if you just
sit there.
A. Integration Strategies 1. Horizontal Integration
When the company seek to purchase its Seeking ownership or increased control over competitors.
competitors, suppliers or distributors to Examples:
gain economies of scale in VMS or HP purchased Compaq.
Guidelines to use:
market leadership.
1. Company wants to create monopoly.
2. Company needs diverse Managerial skills
3. Market share
4. Economies of scale
5. Competing in growing industry.
2.1 Backward Integration
Seeking ownership or increased control of
Examples:
Nishat Mills Purchased MCB.
PTC purchased Tobacco fields in NWFP.
Guidelines to use:
1. When suppliers are expensive and
2. High growth industry.
3. Number of suppliers is small an
large in numbers.
4. Present suppliers have high profit m
2. Vertical
5. When stable price and suppliers
Integration
importance.
2.2 Forward Integration
Seeking ownership or increased control o
retailors.
Examples:
Pepsi Co. launched hostile merger to acq
Group.
Guidelines to use:
1. Present distributors are expensive
irregular to meets firms needs.
2. Availability of quality distributors is
3. High growth industries.
4. Present distributors have higher pro
5. When benefits of less price and sta
of much importance.
B. Intensive Strategies 1. Market Penetration
These require firms intensive efforts Seeking increased market share for present products or s
and resources to gain and maintain its markets through greater marketing efforts
competing position in markets served. Examples:
Coke spending millions of dollars on marketing campaign.
Guidelines to use:
1. Current market has growth means not saturated.
2. Usage rate can be increased by marketing efforts.
3. Competitors sale is decreasing.
2. Market Development
Introducing present products or services into new geographic a
Examples:
When gourmet entered in Faisalabad market.
Guidelines to use:
1. Untapped or unsaturated market.
2. New channels of distributions are reliable and inexpensive.
3. Excess production capacity.
4. Company and its products are in growing phase.
3. Product Development
Seeking increased sales by improving present products or serv
new ones
Examples:
McDonalds started breakfast products and services.
Guidelines to use:
1. Present products are in maturity stage.
2. Rapid technological changes in industry.
3. Major competitors offering products at low price.
4. High growth industry.
5. Strong R & D department.
C. Diversification Strategies 1. Related Diversification
Adding new, but related, products or services
--- Changing industry because you dont Examples:
want your all eggs in one basket. Sony and Samsung introduced smart phones.
Guidelines to use:
--- Becoming less popular as 1. Compete in low or no growth industry.
2. New products would increase overall sales.
organizations are finding it more
3. Related technological and human expertise.
difficult to manage diverse business 4. Current products are in declining phase of product life cycle
activities. 5. Strong management team.
2. Un-related Diversification
Adding new, unrelated products or services
Examples:
Pepsi introducing LAYS.
Sony going in insurance industry.
Guidelines to use:
1. Existing market for present products is saturated.
2. Declining revenues and profit margins.
3. Financial synergy.
4. Capital and managerial expertise.
D. Defensive Strategies 1. Retrenchment
When companies are at back foot. Regrouping through cost and asset reduction to reverse declin
Examples:
Ericsson, Intel retrenched thousands of employees.
Guidelines to use:
1. Firm failed to its financial goals consistently over the years.
2. We are the weaker competitor in the industry.
3. Inefficiency, low profitability, low employee morale,
stakeholders to improve performance.
4. Strategic management is failed.
5. Rapid growth to a large organization where major interna
needed.
2. Divestiture
Selling a division or part of an organization
Examples:
Rafhan selling its consumer products wing to Unilever Pakistan
Guidelines to use:
1. When firms tried retrenchment but not improved.
2. Division needing more resources than company can provide
3. Division is responsible for overall poor performance.
4. Division is a misfit in organization.
5. A large amount of cash is needed to finance other growing
3. Liquidation
Selling all of a companys assets, in parts, for their tangible wo
Examples:
Nokia and Compaq.
Guidelines to use:
1. When both retrenchment and divestiture has been failed.
2. If the only option is bankruptcy, liquidation is the suitable p
3. Stockholders can minimize their lose by selling the firms a
E. Michael Porters Generic Cost Leadership Type 1 --- Low Cost
Competitive Strategies These strategies emphasize A strategy that offers produc
Beyond above discussed options, producing standardized wide range of customers at
Professor Porter from Harvard product or service at a very price available on the mark
Business School identified five basic low-per unit cost for quality may be sacrifice
strategies for all business types consumers who are price customers are highly price se
covering all areas of strategic sensitive. Type 2 --- Best Value
options. There are two further types: A strategy that offers produc
Type 1 ----- Low Cost wide range of customers at t
Competitive strategy is about Type 2 ----- Best Value available on
being different. It means the market; the best-value
deliberately choosing to perform Note: offer customers a range of p
activities differently or to Both type 1 and 2 strategies at the lowest price availab
perform different activities than are aimed to be used at large rivals products with similar a
rivals to deliver a unique mix of market. The element of quality isn
value. because we are to generate
(Michael E. Porter) option.
Differentiation (Type 3) A strategy aimed at produ
services considered unique
Note: Note: difficult for the competitor to
. Type 3 strategy can be used in
small as well as large market.
Larger firms with greater access to Focus Type 4 --- Low Cost
resources typically compete on a cost Focus means producing Type 4 is a low-cost focus s
leadership and/or differentiation basis, products or services that fulfill products or services to a s
whereas smaller firms often compete on the needs of small groups of group) of customers at
a focus basis. consumers. (niche) available on the market.
There are two further types: Again quality isnt a matter o
Note that a differentiation strategy
Type 4 ----- Low Cost Type 5 --- Best Value
(Type 3) can be pursued with either a
Type 5 ----- Best Value Type 5 is a best-value focus
small target market or a large target
products or services to a
market. However, it is not effective to
customers at the best price
pursue a cost leadership strategy in a Note: the market. Sometimes
small market because profits margins Both type 4 and 5 strategies differentiation, the best-va
are generally too small. Likewise, it is are aimed to be used at small aims to offer a niche gro
not effective to pursue a focus strategy market.
products or services that me
in a large market because economies of
requirements better than riva
scale would generally favor a low-cost
Quality is the name of game
or best-value cost leadership strategy
are to generate a best price v
to gain and/or sustain competitive
advantage.
You might also like
- HamdanDocument17 pagesHamdanMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Sdarticle 2Document34 pagesSdarticle 2OKS BANGETNo ratings yet
- FPSC Senior Auditor Past Paper 2018 PDFDocument6 pagesFPSC Senior Auditor Past Paper 2018 PDFIrfan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Uvvis 1Document4 pagesUvvis 1AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Bae 2012Document24 pagesBae 2012Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Honda Alts CarDocument37 pagesHonda Alts CarMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Teacher Accountant CV 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesTeacher Accountant CV 40 CharactersMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionsDocument18 pagesSampling DistributionsYuleta Puspa MelatiNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Cotton and Textile IndustryDocument119 pagesPakistan's Cotton and Textile IndustryNajeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Bae 2012Document24 pagesBae 2012Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Store Stock Report Arshad Corporation (PVT) Ltd. : GarmentsDocument2 pagesStore Stock Report Arshad Corporation (PVT) Ltd. : GarmentsMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Rana Adil CVDocument2 pagesRana Adil CVMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Teacher Accountant CV 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesTeacher Accountant CV 40 CharactersMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Monthly Report Dec-19 (Printing, Dying & Garment UnitsDocument21 pagesMonthly Report Dec-19 (Printing, Dying & Garment UnitsMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Transcript Scan ImageDocument1 pageTranscript Scan ImageMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- MohsinDocument18 pagesMohsinMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
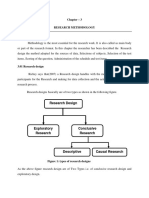
- 11 - Chapter 3 Research MethodologyDocument54 pages11 - Chapter 3 Research MethodologyMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Quantum mechanics solution manual downloadDocument3 pagesQuantum mechanics solution manual downloadMohsin Jutt17% (6)
- Application FormDocument34 pagesApplication FormMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 3 Research MethodologyDocument10 pages11 - Chapter 3 Research MethodologypradeepNo ratings yet
- Garments (Cash) PDFDocument1 pageGarments (Cash) PDFMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- CBVCBDocument2 pagesCBVCBMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Cash (Printing) 22 NOV 19Document1 pageCash (Printing) 22 NOV 19Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Punjab Group of Colleges: Recruitments 2017Document1 pagePunjab Group of Colleges: Recruitments 2017ehsanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Orthogonality of Sines and CosinesDocument2 pages1.4 Orthogonality of Sines and CosinesMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document3 pagesLecture 14Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Orthogonality of Sines and CosinesDocument1 page1.4 Orthogonality of Sines and CosinesShinaolordNo ratings yet
- Corporate Risk-taking and Firm Performance in Pakistan (35Document13 pagesCorporate Risk-taking and Firm Performance in Pakistan (35Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- 5 Tahir Saleem I ArshadDocument9 pages5 Tahir Saleem I ArshadMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- KSE data sample for ownership-capital structure studyDocument1 pageKSE data sample for ownership-capital structure studyMohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Zenith HDTV Marketing StrategyDocument4 pagesZenith HDTV Marketing StrategyArpit KanodiaNo ratings yet
- He - Caregiving - EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesHe - Caregiving - EntrepreneurshipAllis CanadaNo ratings yet
- The Timing of Merger ActivityDocument28 pagesThe Timing of Merger ActivityZackyNo ratings yet
- APM 10. 1 - Sales PromotionDocument42 pagesAPM 10. 1 - Sales PromotionMadhu BalaNo ratings yet
- Al Rifai PanamaDocument2 pagesAl Rifai PanamaAliElneserNo ratings yet
- Hero Motocorp Industry & Market Leader AnalysisDocument20 pagesHero Motocorp Industry & Market Leader AnalysisNivetha0% (1)
- Marketing 5th Edition Grewal Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesMarketing 5th Edition Grewal Solutions Manualaureliaeirayetu6s100% (26)
- Bank of MunteniaDocument13 pagesBank of MunteniaZahara GaniNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis MicrosoftDocument3 pagesCase Analysis MicrosoftkaransangarNo ratings yet
- Marketing DossierDocument38 pagesMarketing DossierTigran WadiaNo ratings yet
- Food Packaging IndustryDocument7 pagesFood Packaging IndustrySanjay Kumar ShahiNo ratings yet
- Retail franchise-LEVI'SDocument14 pagesRetail franchise-LEVI'Snealabrata200867% (3)
- Sona Chandi's unique positioning on immunity and mind powerDocument3 pagesSona Chandi's unique positioning on immunity and mind powerdr_sristiNo ratings yet
- Template Road Carbon Style XL A4 TubeMiterDocument26 pagesTemplate Road Carbon Style XL A4 TubeMiterRahul ManavalanNo ratings yet
- Current Focus On Management AccountingDocument3 pagesCurrent Focus On Management AccountingGêmTürÏngånÖ0% (2)
- Fusertech QuotationDocument1 pageFusertech QuotationSammy ChivasaNo ratings yet
- Revised Exam Time Table May 2011Document8 pagesRevised Exam Time Table May 2011nclpjalgaonNo ratings yet
- International Marketing Strategy - Case StudyDocument4 pagesInternational Marketing Strategy - Case StudyndumieNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For EILDocument4 pagesBusiness Plan For EILVikas ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document3 pagesUnit 6api-271339973No ratings yet
- List of 80+ FREE Classified Ad Websites!Document5 pagesList of 80+ FREE Classified Ad Websites!BizMarketing360No ratings yet
- Internship GAUDocument10 pagesInternship GAUBashar Abu HijlehNo ratings yet
- Xenot Garri Processing Industry Executive SummaryDocument27 pagesXenot Garri Processing Industry Executive SummaryAgboola Bamidele100% (1)
- Bhavna CV Dec'19Document12 pagesBhavna CV Dec'19bhaawanaanambiearrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Critical Thin...Document7 pagesChapter 1 Critical Thin...sameh06No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document9 pagesChapter 11oranghebat0% (1)
- Post Event Evaluation ChecklistDocument5 pagesPost Event Evaluation ChecklistbrendaNo ratings yet
- Media Management Unit 1 Organizational Behavior: Importance of OBDocument48 pagesMedia Management Unit 1 Organizational Behavior: Importance of OBRosariomerko100% (1)
- 2b Jun7 13Document14 pages2b Jun7 13MediaMassageNo ratings yet