Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TP5 Language Analysis
Uploaded by
puravidayblessOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TP5 Language Analysis
Uploaded by
puravidayblessCopyright:
Available Formats
International Training Institute
Language Analysis
Language Area/Skill: Context:
Mysteries and oddities
MODAL VERBS
SKILLS (Which productive or receptive skills will be practised/focused on? How? Be specific with sub-skills: e.g. The Ss will
practise reading for gist by skimming the text and choosing the best title for the it and show which sub-skills you will practise in each stage.)
The Ss will be practicing reading for gist by skimming the text and choosing the correct modal(s) for various sentences.
LANGUAGE ANALYSIS: (Analyse all relevant language areas here for grammatical structures, function or vocabulary. If your
main aim is skills, you should still have some supporting language in the lesson, e.g. vocabulary)
MEANING/FORM
What is the meaning conveyed by the language you are covering? Provide model sentences.
How can you break down the form?(example sentences and highlighting of form, e.g. S + will + have + past participle)
For vocabulary, list all items you will teach, provide definitions, and parts of speech e.g. information (n - uncountable)
S + modal verb + main verb
- Should / Shouldnt / - Ought to used for obligations that are not strong it is not necessary but is a good idea or the right thing(eg You
should be nervous. You ought to be nervous.)
- Must / mustnt expresses necessity (obligation or logical necessity) (eg I mustnt go in there. Hes not answering his phone, so he must be
asleep.)
*have to and have got to are similar but usually express external obligation versus musts normal internal obligation.
* dont have to expresses that something is not necessary. Mustnt expresses not allowed to.
* Cant expresses the logically impossible.
- Can expresses ability (She can scream), permission (You can go), general possibility (It can be a sign of stress.)
- Could expresses ability (She could disappear when she wanted), permission (Could you leave us alone for a minute?), or present/future
possibility (He could be gone.)
- May - generally expresses possibility in two ways: permission (first person, formal) (May I go now?) or present / future possibility (He may
be coming now.)
- Might expresses present/future possibility (We might see you again.) and reported speech as the past of may (He said she might come.)
*Also, old-fashioned permission (Might I?)
When the continuous form follows these modals it indicates that the action is happening now.
Checking meaning script any Concept Questions & responses that you will use, including timelines, clines etc where appropriate,
or refer to visuals to be used, e.g. for vocabulary.
CCQs
With should, is the obligation strong or not? (not strong) Is it a good idea though? (yes) Is ought to the same or different than
should?
With must, is the obligation strong or weak? (strong) Is this only for commands or can it also be used for logical necessity?
(both)
With can, how many things can be expressed? (3) What are they? Ability, permission, general possibility
With could, how many things can be expressed? (3) What are they? Ability, permission, present/future possibility
With may, how many things can be expressed? (2) What are they? Permission or present/future possibility
With might, how many things can be expressed? (2) What are they? Present/future possibility & reported speech of (past) may
PRONUNCIATIONconsider weak forms, stress and intonation. For vocabulary, transcribe items phonemically, and show stress as
appropriate when you list items in meaning and form. How will you focus on pronunciation? e.g. drilling, conducting stress
e.g. information /nfmenn |/
International Training Institute
d (weak form - d)
t t
mst
hv t
kn (weak form kn)
kd
me
mat
International Training Institute
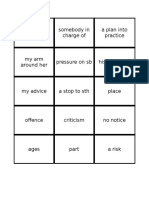
WHITEBOARD PLANS (show your overall w/b plan here or break it down for stages of
the lesson
Vocabulary
Model Sentences and Grammar
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- DMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFDocument305 pagesDMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFpooja100% (1)
- Teaching and Learning ResourcesDocument4 pagesTeaching and Learning ResourcesTey Lee PohNo ratings yet
- Boat DesignDocument8 pagesBoat DesignporkovanNo ratings yet
- Singular and Plural NounsDocument3 pagesSingular and Plural NounsJosé BulquesNo ratings yet
- Lease of Residential HouseDocument4 pagesLease of Residential HousedenvergamlosenNo ratings yet
- RPH Sains DLP Y3 2018Document29 pagesRPH Sains DLP Y3 2018Sukhveer Kaur0% (1)
- For/Against Essay TopicsDocument2 pagesFor/Against Essay TopicspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- For/Against Essay TopicsDocument2 pagesFor/Against Essay TopicspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- F2F Oral PT Question Bank PDFDocument3 pagesF2F Oral PT Question Bank PDFpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- The Beggar's Opera - Character ListDocument4 pagesThe Beggar's Opera - Character ListpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Clothes CrosswordDocument1 pageClothes CrosswordpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Moll Flanders' MarriagesDocument2 pagesMoll Flanders' MarriagespuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- FCE Reading Part 1Document8 pagesFCE Reading Part 1puravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Bingo NumbersDocument4 pagesBingo NumberspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- I Get To Meet Lots of People. (The Potter)Document8 pagesI Get To Meet Lots of People. (The Potter)puravidayblessNo ratings yet
- I Get To Meet Lots of People. (The Potter)Document8 pagesI Get To Meet Lots of People. (The Potter)puravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Reyes UK Mundos AnglofonosDocument16 pagesReyes UK Mundos AnglofonospuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Cambridge First Essay ChecklistDocument1 pageCambridge First Essay ChecklistpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Yet/alreadyDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Yet/alreadypuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Review of Present Tenses + Grammar CasinoDocument5 pagesReview of Present Tenses + Grammar CasinopuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Action Plan For ESSAY WritingDocument1 pageAction Plan For ESSAY WritingpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Uptown GirlDocument1 pageUptown GirlpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Hot Cross Buns b2 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHot Cross Buns b2 Lesson PlanpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Review of Present Tenses + Grammar CasinoDocument5 pagesReview of Present Tenses + Grammar CasinopuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZDocument2 pagesABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Fce PrepDocument1 pageFce PreppuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Snakes and LaddersDocument1 pageSnakes and LadderspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- PYRAMID GAME Relative ClausesDocument1 pagePYRAMID GAME Relative ClausespuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- 1B Grammar Psimple PcontinuousDocument1 page1B Grammar Psimple PcontinuouspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Getting to know each other: short conversationsDocument1 pageGetting to know each other: short conversationspuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) in Foreign Language TeachingDocument12 pagesLearning Management Systems (LMS) in Foreign Language TeachingpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Focus 1A Character AdjectivesDocument1 pageVocabulary Focus 1A Character AdjectivespuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- Business ConvDocument4 pagesBusiness ConvbarliyanNo ratings yet
- How British Is Your English? - A Test of Where Your English Comes FromDocument8 pagesHow British Is Your English? - A Test of Where Your English Comes Fromİrem BayrakNo ratings yet
- Hot Verbs Take and Put Bingo and PokerDocument5 pagesHot Verbs Take and Put Bingo and PokerpuravidayblessNo ratings yet
- DRUG LISTDocument45 pagesDRUG LISTAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- CuegisDocument2 pagesCuegisTrishaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Placement Paper Interview Questions 48072Document3 pagesAxis Bank Placement Paper Interview Questions 48072Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Regional Office X: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesRegional Office X: Republic of The PhilippinesCoreine Imee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Long Standoff Demolition Warheads For Armor, Masonry and Concrete TargetsDocument27 pagesLong Standoff Demolition Warheads For Armor, Masonry and Concrete Targetsahky7No ratings yet
- Baella-Silva v. Hulsey, 454 F.3d 5, 1st Cir. (2006)Document9 pagesBaella-Silva v. Hulsey, 454 F.3d 5, 1st Cir. (2006)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Organized Educator Seeks New OpportunityDocument1 pageOrganized Educator Seeks New OpportunityCaren Pogoy ManiquezNo ratings yet
- Reference Letter For Employment AustraliaDocument8 pagesReference Letter For Employment Australiabcqy21t7100% (2)
- Springhill Suites by Marriott / Houston Brookhollow Remit To:2750 N.Loop West, Houston TX 77092 713.290.9242Document1 pageSpringhill Suites by Marriott / Houston Brookhollow Remit To:2750 N.Loop West, Houston TX 77092 713.290.9242Josué SalazarNo ratings yet
- Adjective: the girl is beautifulDocument15 pagesAdjective: the girl is beautifulIn'am TraboulsiNo ratings yet
- BS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsDocument26 pagesBS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsBorn ToSinNo ratings yet
- Weakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDDocument38 pagesWeakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDabdisalaan hassanNo ratings yet
- Active Sound Gateway - Installation - EngDocument9 pagesActive Sound Gateway - Installation - EngDanut TrifNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice: DescriptionDocument3 pagesProforma Invoice: Descriptionanon-690278No ratings yet
- Hydroponics SummaryDocument4 pagesHydroponics SummaryJose NovoaNo ratings yet
- C++ Practical FileDocument15 pagesC++ Practical FilePreetish ChandraNo ratings yet
- GTA Max Profit Bunker Locations Update v1.4Document1 pageGTA Max Profit Bunker Locations Update v1.4Sam FarrelNo ratings yet
- Construction Internship ReportDocument8 pagesConstruction Internship ReportDreaminnNo ratings yet
- VNACS Final Case ReportDocument9 pagesVNACS Final Case ReportVikram Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- MCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutDocument3 pagesMCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutPR.comNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis (ELEN-1100) : Lecture # 13: More On Mesh Current AnalysisDocument11 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis (ELEN-1100) : Lecture # 13: More On Mesh Current AnalysisPhD EENo ratings yet
- Blocked threads jstack analysisDocument69 pagesBlocked threads jstack analysisMike TNo ratings yet
- jk2 JAVADocument57 pagesjk2 JAVAAndi FadhillahNo ratings yet
- All Paramedical CoursesDocument23 pagesAll Paramedical CoursesdeepikaNo ratings yet