Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Makalah Bahasa Inggris
Uploaded by
AyuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Makalah Bahasa Inggris
Uploaded by
AyuCopyright:
Available Formats
Created by:
MIRA ZAHRA FAUZIYAH
PSIKOLOGI
1 C
GRAMMAR
1.Noun
Definition:
Nouns are a part of speech typically denoting a person, place ,thing
,animal or idea. In linguistics a noun is a member of a large, open lexical
category whose member can occur as the main word in the subject of a
clause, the object of a verb or the object of a preposition.
Example:
2.Adjective
Definition:
In grammar an adjective is a describing word the main syntactic
role of which is to quality a noun or noun phrase, giving more information
about the object signified.
Example:
3.Adverb
Definition:
Is an adverb that explains how or how something happens. Adverbs of
manner are generally located after the main verb or after the object.
Example
4.Tenses
Definition:
Tenses is a grammatical category, typically marked on the verb, that
deictically refers to the time of the event or state denoted by the verb in
relation to some other temporal reverence point.
Simple past tense
Definition:the simple past or past simple, sometimes also called the
preterite, consists of the bare past tense of the verb (ending in, ed for
regular verbs, and formed in various ways for irregular ones, see
English verbs for details). In most questions (and other situations
requiring inversion) when negated and in certain emphatic statement,
a perpiphrastic construction consisting of did and the bare infinitive of
the main verb is generally used instead see do support.
Past continuous tense
Definition:we usually use the past continuous to talk about activities
that lasted for sometime in the past the actions can be interruped by
something or can be happening at the same time.
Past perfect tense
Definition:the past perfect sometimes called the pluperfect,combines
past tense with perfect aspect it is formed by combining had (the past
tense of the auxiliary have) with the past participle of the main verb.
It is used when referring to an event that took place prior to the time
frame being considered. This time frame may be stated explicitly, as a
stated time or the time of another past action.
Past perfect continuous tense
Definition:the past perfect progressive or past perfect continuous
(also known as the pluperfect progressive or pluperfect continuous)
combines perfect progressive aspect with past tense. It is formed by
combining had (the tense of auxiliary have) been (the past participle
of be) and the present participle of the main verb.
Simple present tense
Definition:present is a syntax that we use when we want to convey an
idea that is routine or occur at any time.
Present continuous tense
Definition:the present progressive or present continuous is a form
which combines present tense with progressive aspect. It thus refers
to an action or event conceived of as having limited duration, taking
place at the present time. It consists of a form of the simple present of
be together with the present participle of the main verb.
Present perfect tense
Definition:the present perfect (traditionally called simply the perfect)
combines present tense with perfect aspect, denoting the present
state of an actions being completed, that is that the action took place
before the present time. (it is thus often close in meaning to the
simple past tense, although the two are not usually interchangeable).
It is formed with the present tense of the auxiliary have (namely have
or has) and the past participle of the main verb.
Present perfect continuous tense
Definition:the present perfect progressive (present perfect
continuous) construction combines perfect progressive aspect with
present tense. It is formed with the present tense of have (have or
has) the past participle of be (been) and the present participle of the
main verb. This construction right up to the present or has recently
finished.
Simple future tense
Definition:the term simple future, as applied to English, generally
refers to the combination of the modal auxiliary verb will with the
bare infinitive of the main verb, sometimes (particulary in more formal
or old fashioned English) shall is preferred to will when the subject is
first person (I or we) see shall and will for details. The auxiliary is
often contracted to ll see english auxiliaries and contractions.
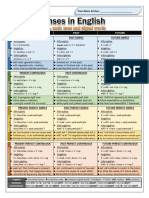
Simple Past Tense Past Continuous
Tense
(+): s+v2+o (+):cs+was/were+v.ing+o
(-) : s+did+not+been+v1+o (-) : s+was/were+not+v.ing+o
(?): did+s+v1+o? (?): was/were+s+v.ing+o?
Past Perfect
Past Perfect Tense
Continuous Tense
(+):s+had+v3+o (+):s+had+been+v.ing+o
(-) :s+had+not+v3+o (-) :s+had+not+been+v.ing+o
(?):had+s+v3+o? (?):had+s+been+v.ing+o?
Past future perfect tense
Definition:the future perfect combines perfect aspect with future time
reference. It consists of the auxiliary will (sometimes shall in the first
person, as above) the bare infinitive have and the past participle of
the main verb. It indicates an action that is to completed sometime
prior to a future time of perspective or an ongoing action continuing
up to a future time of perspective (compare uses of the present
perfect above).
Past future perfect continuous tense
Definition:the future perfect progressive or future perfect continuous
combines perfect progressive aspect with future time reference. It is
formed by combining the auxiliary will (sometimes shall, as above) the
bare infinitive have the past participle been and the present participle
of the main verb. Uses of the future perfect progressive are analogous
to those of the present pefect progressive, except that the point of
reference is in the future.
Simple Present Tense
Present Continuous
Tense
(+) : s+v1(s/es)+o (+):s+is/am/are+v.ing+o
(-) : s+do/does+not+v1+o (-) : s+is/am/are+not+v.ing+o
(?) : do/does+s+v1+o? (?) : is/am/are+s+v.ing+o?
Present Perfect
Present perfect tense
Continuous Tense
(+): s+have/has++v3+o (+): s+have/has+been+v.ing+o
(-) : s+have/has+not+v3+o (-) : s+have/has+not+been+v.ing+o
(?):have/has+s+v3+o? (?):have/has+s+been+v.ing+o?
Past future continuous
Simple future tense
tense
(+): s+will/shall+v1+o (+): s+would/should+be+v.ing+o
(-) : s+will/shall+not+v1+o (-) : s+would/should+not+be+v.ing+o
(?): will/shall+s+v1+o? (?): would/should+s+be+v.ing+o?
Past future perfect Past future perfect
tense continuous tense
(+): s+would/should+have+v3+o (+): s+would/should+have+been+v.ing+o
(-) : s+would/should+not+have+v3+o (-) :
s+would/should+not+have+been+v.ing+o
(?): would/should+s+have+v3+o? (?): would/should+s+have+been+v.ing+o?
5.Passive voice
Definition
Is a voice that indicates that the subject is the patient or recipient of the
action denoted by the verb.
Tenses Active Passive
1.simple past tense We ate rice Rice was eaten by us
2.past continuous We was eating rice Rice was being eaten by
tense us
3.past perfect tense We had eaten rice Rice had been eaten by
us
4.past perfect We had been eating rice Rice had been being
continuous tense eaten by us
5.simple present tense We eat rice Rice is eaten by us
6.present continuous We are eating rice Rice is being eaten by us
tense
7.present perfect We has eaten rice Rice has been eaten by
tense us
8.present perfect We has been eating rice Rice has been being
continuous tense eaten by us
9.simple future tense We will eat rice Rice will be eaten by us
10.past future We would be eating rice Rice would be being
continuous tense eaten by us
11.past future perfect We would have eaten Rice would have been
tense rice eaten by us
12.past future perfect We would have been Rice would have been
continuous tense eating rice being eaten by us
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- L4 B1PLUS Grammar Reference EnglishDocument9 pagesL4 B1PLUS Grammar Reference EnglishAnna Garcia VilàNo ratings yet
- General Instructions in 38 CharactersTITLE Teacher's Guide for ESL ClassDocument20 pagesGeneral Instructions in 38 CharactersTITLE Teacher's Guide for ESL ClassLeiz de FariaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 English Core by Raghav...Document80 pagesClass 11 English Core by Raghav...Raghav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tenses For Class 5 Worksheet PDFDocument21 pagesTenses For Class 5 Worksheet PDFayanyaduvanshiiNo ratings yet
- Uses of TensesDocument23 pagesUses of TensesRachkara BonifaceNo ratings yet
- Future PerfectDocument5 pagesFuture PerfectJuan Camilo Castro Mendoza100% (1)
- Shot-In-The-Dark Game Future PerfectDocument2 pagesShot-In-The-Dark Game Future PerfectRomero Laura CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Verbul: Diateza ActivaDocument16 pagesVerbul: Diateza Activaralucutza_86No ratings yet
- French - TensesDocument2 pagesFrench - TensesKane K95% (21)
- Perubahan TENSES Active Ke PassiveDocument4 pagesPerubahan TENSES Active Ke PassiveAl Arkam AlbugisyNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice ChartsDocument5 pagesPassive Voice ChartsnenoulaNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp Grammar PPT B2P U8Document10 pagesGold Exp Grammar PPT B2P U8seduction123No ratings yet
- English Grammar TensesDocument38 pagesEnglish Grammar Tensesapi-283719185No ratings yet
- PREDICTING THE FUTURE WITH WILLDocument2 pagesPREDICTING THE FUTURE WITH WILLEduardo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Past Tense VerbsDocument14 pagesPast Tense VerbsLara Mae CabangonNo ratings yet
- Robot or HumanDocument9 pagesRobot or HumanNicole BarrettoNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses PDFDocument37 pages16 Tenses PDFFatih100% (1)
- Perfect and Progressive Verb FormsDocument1 pagePerfect and Progressive Verb FormsStavros86No ratings yet
- Belajar BingDocument14 pagesBelajar BingDea Oryza SativaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctive Participles in Hindi GrammarDocument1 pageConjunctive Participles in Hindi GrammarIdasob LahariniNo ratings yet
- 0 Verb Tense Exercise 2118Document11 pages0 Verb Tense Exercise 2118Andreea ŢăranuNo ratings yet
- Future Continuous Tense - Usage of Rules - Bhavishya Kaal Kay Niyam Aur PrayogDocument5 pagesFuture Continuous Tense - Usage of Rules - Bhavishya Kaal Kay Niyam Aur PrayogBachchan MishraNo ratings yet
- EnglishTown. GramáticaDocument134 pagesEnglishTown. GramáticaSantiago Díaz MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Modulos 1 2 3 Students GuideDocument50 pagesModulos 1 2 3 Students GuideDanuil Salazar AmayaNo ratings yet
- Helping Verbs in TensesDocument9 pagesHelping Verbs in TensesUbed KudachiNo ratings yet
- Makalah 16 TensesDocument44 pagesMakalah 16 TensesPLAY FUN100% (1)
- English Grammar Tenses For English For MathDocument64 pagesEnglish Grammar Tenses For English For MathSyaifa AlifhiarizkiNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument4 pagesFuture Tenseapi-383712378% (9)
- Tenses in English Grammar Guides - 110569Document2 pagesTenses in English Grammar Guides - 110569Adri PerezNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument14 pagesActive and Passive VoicebebeioNo ratings yet