Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subject-Verb Agreement PDF
Uploaded by
Samuel Antobam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
353 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Subject-Verb Agreement.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
353 views2 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement PDF
Uploaded by
Samuel AntobamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
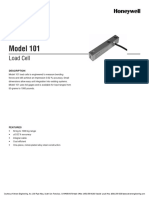
Subject-Verb Agreement
What is subject-verb agreement?
Subject-verb agreement is a grammar rule that requires the subject (noun) to agree in number and person with
the verb. So if the subject of a sentence is singular, the verb must be singular. If the subject of a sentence is
plural, the verb must be plural.
Step one: Identify the subject
In any sentence, the subject is the noun referring to the person or thing that performs an action.
Example: The disdainful badger eats eggs. (Badger is the subject, because it is the one that
performs the action of eating.)
Be careful not to confuse the subject with its compliment. A compliment is a word that renames or describes
the subject.
Example: Her biggest fear is spiders. (Fear is the subject, so the verb needs to be singular. The
word spiders is the compliment.)
Sometimes the subject comes after the verb. (This situation is particularly common in sentences that start
with there is or there are.)
Example: There is a cat on the windowsill.
Dont be misled by phrases that come between the subject and the verb.
Example: The professor, as well as all of her students, is looking forward to the weekend.
(Professor, and not students is the subject in this sentence.)
Step two: Identify the subjects person and number
Determine the subjects person.
First person I am (also first person plural: We are)
Second person You are
Third person She/He/It (or anything other than I or you) is (also third person plural: They are)
Determine if the subject is singular or plural.
Singular: I am the badger is
Plural: We are the badgers are
Some tricky subjects:
Compound subjects (those connected by and) are considered plural.
Example: Kate and Jonathan are working on their writing.
When two subjects are joined by or or nor, the verb should agree with the subject closer to it.
Example: Neither Amy nor the badgers are going to the dance. But Neither the badgers nor
Amy is going to the dance.
Titles, company names, and words mentioned as words are singular.
Examples:
Gangs of New York is a movie set in the nineteenth-century.
Einstein Brothers sells bagels.
Cacti is the plural form of cactus.
Indefinite pronouns (words like everyone, each, nobody, and anything) are usually singular.
Examples:
Anything can happen on February 29th.
Everyone needs a hug sometimes.
Gerund phrases (an ing verb followed by a noun or adjective) and noun clauses (phrases that behave like
nouns) are usually treated as singular.
Examples:
Turning orange is a side effect of eating too many carrots. (Turning orange is a gerund phrase,
and is is the verb.)
That the badgers won the election amazes me. (That the badgers won the election is a noun
clause and amazes is the verb.)
Step three: Make the number and person of the verb match those of the subject
Sources:
Hacker, Diana. A Writers Reference. 5th ed. Boston: Bedford/St. Martins, 2003.
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree. Purdue Online Writing Lab. 20 August 2006. Purdue University. 23
September 2008. <http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/599/01/>.
Rosa, Alfred and Paul Eschholz. The Writers Brief Handbook. 4th ed. New York: Pearson Education, 2002.
Undergraduate Writing Center | The University of Texas at Austin | uwc.utexas.edu | FAC 211 | 512.471.6222
Handout created by Tamara Smith, September 2008 | Last revised by Tamara Smith, March 2009
You might also like
- Quiz Grammar Gr.8Document22 pagesQuiz Grammar Gr.8hima67No ratings yet
- 6 2Document14 pages6 2Zoha AliNo ratings yet
- Phrase and ClauseDocument8 pagesPhrase and Clauseaslam844No ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Figures of Speech GuideDocument34 pages21st Century Literature Figures of Speech GuideJames Alexander DezaNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement ExcercisesDocument14 pagesSubject Verb Agreement ExcercisesEmilyn Mata CastilloNo ratings yet
- Integration Substitution Worksheet SolnsDocument16 pagesIntegration Substitution Worksheet SolnsMritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Antecedent Agreement RulesDocument9 pagesPronoun Antecedent Agreement RulesBernard Ortinero100% (1)
- Elliptical SentenceDocument13 pagesElliptical SentencePutriAuliaRamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Grammar BasicsDocument53 pagesGrammar BasicsMATHEWS V TNo ratings yet
- Active Passive Voice Simple Past Tense GuideDocument2 pagesActive Passive Voice Simple Past Tense GuideBernadette NarteNo ratings yet
- TOEFLDocument11 pagesTOEFLRirin Wahyuni PNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb-Agreement (Advanced)Document4 pagesSubject-Verb-Agreement (Advanced)Oliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Distance Training For Middle School TeachersDocument47 pagesDistance Training For Middle School TeachersMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (2)
- Subject Verb Agreement CompletedDocument4 pagesSubject Verb Agreement CompletedRaynaleese RivasNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesSubject Verb AgreementDAISYREE LORRAINE J. MONTESNo ratings yet
- Phrase: 2. Examples of Noun Phrases Example 1Document20 pagesPhrase: 2. Examples of Noun Phrases Example 1harjay padernillaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument9 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementYash JainNo ratings yet
- Writing and Grammar S1 S2 1st Year LMD PDFDocument68 pagesWriting and Grammar S1 S2 1st Year LMD PDFmima100% (6)
- Part of SpeechDocument23 pagesPart of SpeechTimilehin GbengaNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Structure Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesTOEFL Structure Bahasa InggrisYuliie WarmyNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument2 pagesSubject Verb AgreementNorlene L. MenguanNo ratings yet
- Growls Growl: Subjects VerbsDocument33 pagesGrowls Growl: Subjects VerbsNyl20No ratings yet
- The Roles Played by Referring Expression Called Participant Roles IntoDocument3 pagesThe Roles Played by Referring Expression Called Participant Roles IntoSiti FaizahNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument3 pagesSubject Verb AgreementQuân Đoàn MinhNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAccu Xii BhianNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesSubject Verb AgreementAkshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement Guide for English MajorsDocument7 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement Guide for English MajorsraffyNo ratings yet
- ENG-1N-MODULE-2Document4 pagesENG-1N-MODULE-2amandaasad3No ratings yet
- What is Concord? Understanding Subject-Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesWhat is Concord? Understanding Subject-Verb AgreementAjisafe Jerry T-moneyNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement ModuleDocument8 pagesSubject Verb Agreement ModuleJUNAID MASCARANo ratings yet
- A01 Act#1 IBALEDocument6 pagesA01 Act#1 IBALELester IbaleNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's College guide to subject-verb agreementDocument18 pagesSt. Joseph's College guide to subject-verb agreementAmritha VNo ratings yet
- ENG-1001 (GROUP 1) AssignmentDocument48 pagesENG-1001 (GROUP 1) AssignmentUmair AliNo ratings yet
- Verb Agreement Rules for Subject-Verb ConcordDocument23 pagesVerb Agreement Rules for Subject-Verb Concordabdul satarNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 Subject-Verb AgreementDocument2 pagesSEM 2 Subject-Verb AgreementJona ReyesNo ratings yet
- Campus Life GrammarDocument10 pagesCampus Life Grammarsanti setiyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement RulesDocument11 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement RulesTrianaNo ratings yet
- Eng 10 Subject Verb AgreementDocument25 pagesEng 10 Subject Verb Agreementmay beverly moralesNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Red Beans and Rice Is My Mom's Favorite DishDocument7 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement: Red Beans and Rice Is My Mom's Favorite DishAstxilNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument26 pagesSubject Verb AgreementJanelle PanizalesNo ratings yet
- VA BASIC E-BookDocument37 pagesVA BASIC E-Bookgunn RastogiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Different Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesOverview of Different Parts of Speechbenbelkacem.israaaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GuideDocument15 pagesParts of Speech GuideBEO.Teacher ChuNo ratings yet
- Grammar English for BasicDocument9 pagesGrammar English for BasicBidur KhanalNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument7 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementAlvin AdlaonNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementIan ResellozaNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument6 pagesEnglish ReviewerApril AlfaroNo ratings yet
- English Grammar RulesDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules4069-Sam ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesSubject Verb Agreementsarasajed08No ratings yet
- NounsDocument99 pagesNounsalfredo VonborstelNo ratings yet
- Problems With Subject / Verb AgreementDocument13 pagesProblems With Subject / Verb AgreementSangAnonimNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Graduate Student Writing StudioDocument4 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement: Graduate Student Writing StudioKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7Document7 pages2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Learn English Is FunDocument71 pagesLearn English Is Funika_nikanNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns Explained in DetailDocument7 pagesTypes of Nouns Explained in Detailshara santosNo ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument39 pagesLET English Major LanguageJustin Jones NotarteNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammarcontact.asif.directNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreemnet RulesDocument3 pagesSubject Verb Agreemnet RulesteebaNo ratings yet
- Finding Subjects and Verbs: ExampleDocument5 pagesFinding Subjects and Verbs: ExampleDinesh SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Construction Health and Safety PolicyDocument30 pagesConstruction Health and Safety PolicySamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Modified AxlesDocument4 pagesModified AxlesSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- What Is A Project in Project ManagementDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Project in Project ManagementSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- A Case of Project/Program Management Success Within The Office of Justice Services, Bureau of Indian AffairsDocument3 pagesA Case of Project/Program Management Success Within The Office of Justice Services, Bureau of Indian AffairsSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Terzaghi Bearing CapacityDocument6 pagesTerzaghi Bearing CapacitySamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD VBADocument19 pagesAutoCAD VBAgvgopal2No ratings yet
- Manufacturing of SteelDocument2 pagesManufacturing of SteelSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Transportation PlanningDocument87 pagesLecture - Transportation PlanningSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Terzaghi - Bearing CapacityDocument7 pagesTerzaghi - Bearing CapacitySamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Water Resources, Water Supply and Distribution: System LayoutDocument2 pagesWater Resources, Water Supply and Distribution: System LayoutSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Design of Continuous Footing-1 PDFDocument8 pagesDesign of Continuous Footing-1 PDFSamuel Antobam100% (2)
- Improving The Teaching of MultiplicationDocument20 pagesImproving The Teaching of MultiplicationSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Fixed Vs PinnedDocument2 pagesFixed Vs Pinnedgopi_ggg20016099No ratings yet
- 31loadctr PDFDocument248 pages31loadctr PDFSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Side Reinforcement in BeamsDocument5 pagesSide Reinforcement in BeamsSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- A Production Function For The Structural Steel Fabricating Indust PDFDocument58 pagesA Production Function For The Structural Steel Fabricating Indust PDFSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Car PartsDocument2 pagesCar PartsSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Footbridge Guide SetraDocument131 pagesFootbridge Guide Setraibnmessaoud10100% (1)
- Guide To Your Prescription-EYEDocument11 pagesGuide To Your Prescription-EYESamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- BS CODE Calculation ListDocument6 pagesBS CODE Calculation ListSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Characteristics of An EntrepreneurDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship: Characteristics of An EntrepreneurSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Excavation ProcessDocument5 pagesTunnel Excavation ProcessSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- 6 Projectaile MotionDocument7 pages6 Projectaile MotionSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Solving Overhanging Beam for SFD and BMD: Prob 5.5Document6 pagesSolving Overhanging Beam for SFD and BMD: Prob 5.5Samuel Antobam100% (1)
- Yield LineDocument7 pagesYield Lineisharanaveen0% (1)
- Box Culvert Design DetailsDocument5 pagesBox Culvert Design DetailsFauzankalibata100% (1)
- What Is A Project in Project ManagementDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Project in Project ManagementSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- 9 L Bridge AnalysisDocument19 pages9 L Bridge AnalysisAyodele Oluwaseyi DinaNo ratings yet
- Box Culv Draw2 PDFDocument2 pagesBox Culv Draw2 PDFSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- DeckDocument9 pagesDeckSamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- Abstract Faisal SajjadDocument1 pageAbstract Faisal SajjadMaria KhanNo ratings yet
- A1 Progress Test 05Document11 pagesA1 Progress Test 05Mar PerezNo ratings yet
- 2015 Special Matriculation ReporterDocument18 pages2015 Special Matriculation ReporterBua NyohNo ratings yet
- 0520 s14 Ms 12 PDFDocument12 pages0520 s14 Ms 12 PDFlauranistNo ratings yet
- Dll-Araling Panlipunan 2Document18 pagesDll-Araling Panlipunan 2Cheanne OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Canters' Assertive Discipline ModelDocument13 pagesCanters' Assertive Discipline ModelPretty Elka K GeorgeNo ratings yet
- CUNY Entrepreneurial Journalism CurriculumDocument19 pagesCUNY Entrepreneurial Journalism CurriculumJeff Jarvis100% (2)
- Social Learning TheoryDocument23 pagesSocial Learning TheoryJacqueline Lacuesta100% (2)
- SightwordsfcDocument28 pagesSightwordsfcapi-236498933No ratings yet
- Research Chap 1 and 2Document11 pagesResearch Chap 1 and 2AiLab YuuNo ratings yet
- A Childs Drawing Analysis PaperDocument8 pagesA Childs Drawing Analysis Paperapi-335231019No ratings yet
- Fraternity ViolenceDocument4 pagesFraternity ViolenceArmiRoseValenciaJuanNo ratings yet
- Edu 329-01 - Lesson Plan 2 - Rotations, Reflections, TransformationsDocument4 pagesEdu 329-01 - Lesson Plan 2 - Rotations, Reflections, Transformationsapi-284455411No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2api-338284745No ratings yet
- UPOU Clearance FormDocument4 pagesUPOU Clearance FormMarkie EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Cusat - Admission Notification - Cat 2018: Cochin University of Science & TechnologyDocument1 pageCusat - Admission Notification - Cat 2018: Cochin University of Science & Technologyjozf princeNo ratings yet
- REVISED STUDENT HANDBOOKDocument17 pagesREVISED STUDENT HANDBOOKSteffi ClaroNo ratings yet
- Deva Maths 1Document3 pagesDeva Maths 1Deva Rajan YadavNo ratings yet
- Outstanding Cambridge Learner Awards in Pakistan 2011Document10 pagesOutstanding Cambridge Learner Awards in Pakistan 2011Haseeb Zaman Khan0% (1)
- Minutes of The MeetingDocument3 pagesMinutes of The MeetinganirNo ratings yet
- PDPC Template CefrDocument2 pagesPDPC Template CefrTc NorNo ratings yet
- Julie Varga: Carl H. Lindner College of BusinessDocument2 pagesJulie Varga: Carl H. Lindner College of Businessapi-353790618No ratings yet
- DLL Grade 9Document5 pagesDLL Grade 9Ateneo Novy JoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 62 WritingDocument2 pagesLesson 62 WritingfaizsrbnNo ratings yet
- A. Preliminary ActivitiesDocument2 pagesA. Preliminary ActivitiesMarjoriekate EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Reflection on Behaviorism TheoryDocument5 pagesReflection on Behaviorism TheoryJem AguilarNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan 2Document2 pages5e Lesson Plan 2api-490944052No ratings yet
- Bandura and Maslow HandoutDocument5 pagesBandura and Maslow Handoutapi-296978454No ratings yet
- Spe 615 Lesson 2 PlanDocument3 pagesSpe 615 Lesson 2 Planapi-302304245No ratings yet
- Module3 PPST1 5 2-1Document37 pagesModule3 PPST1 5 2-1Vincent Librea100% (1)