Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 20 PDF
Uploaded by
oscarbecOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 20 PDF
Uploaded by
oscarbecCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ________________________
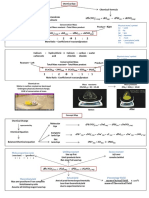
The positive anode reaction Date: _______________
with copper electrodes
Its the copper anode that is the crucial difference than electrolysing copper sulfate solution with a inert
carbon/graphite/platinum electrode.
electron discharge Cu2+(aq electrodes positive
reduced sulfate copper purification plating
negative mass coated
The ________________ sulphate ions SO42- (from copper sulfate) or the traces of hydroxide ions OH
(from water) are attracted to the ________________ electrode. But both the sulfate ion and hydroxide ion
are too stable and nothing happens to them because the copper anode is preferentially oxidised to
__________________ Cu2+ copper ions.
An oxidation electrode reaction at the positive anode
(+) Cu(s) 2e ==> ______________) (copper dissolves, oxidation - 2 electrons lost)
or Cu(s) ==> Cu(s) + 2e
atom oxidation by ________________ loss
A balancing act !
copper atoms oxidised to copper(II) ions: dissolving of copper in its electrolytic purification or electroplating
(must have positive copper anode). The change involves two electrons per copper atom.
copper(II) ion ______________ to copper atoms: deposition of copper in its electrolytic
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 1
________________________ or electroplating using copper(II) sulphate solution, so the electrode can be
copper or other metal to be plated OR any other conducting material. The change involves two electrons
per copper ion.
This means for every ____________ atom that gets oxidised, one copper ion is reduced, therefore ...
When copper electrodes are used in the electrolysis of copper ______________ solution, the mass loss of
copper from the positive anode electrode should equal the mass of copper gained and deposited on the
negative cathode electrode.
You can show this by weighing both ____________________ at the start of the experiment. After the
current has passed for some time, carefully extract the electrodes from the solution, wash them, dry them
and reweigh them. The gain in mass of the cathode should be about the same as the loss of ________ from
the anode.
Metal electrodes dipped in aqueous salt solutions
For electroplating in general: The negative cathode electrode is made the metal/conducting surface to be
____________, and the positive anode electrode is made of the ______________ metal which dissolves
and replaces any deposit formed on the cathode -which is the conducting article to be electroplated.
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 2
TEACHER ANSWER SHEET
The positive anode reaction
with copper electrodes
Its the copper anode that is the crucial difference than electrolysing copper sulfate solution with a inert
carbon/graphite/platinum electrode.
electron discharge Cu2+(aq electrodes positive
reduced sulfate copper purification plating
negative mass coated
The negative sulphate ions SO42- (from copper sulfate) or the traces of hydroxide ions OH (from
water) are attracted to the positive electrode. But both the sulfate ion and hydroxide ion are too stable
and nothing happens to them because the copper anode is preferentially oxidised to discharge Cu2+
copper ions.
An oxidation electrode reaction at the positive anode
(+) Cu(s) 2e ==> Cu2+(aq ) (copper dissolves, oxidation - 2 electrons lost)
or Cu(s) ==> Cu(s) + 2e
atom oxidation by electron loss
A balancing act !
copper atoms oxidised to copper(II) ions: dissolving of copper in its electrolytic purification or electroplating
(must have positive copper anode). The change involves two electrons per copper atom.
copper(II) ion reduced to copper atoms: deposition of copper in its electrolytic purification or
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 3
electroplating using copper(II) sulphate solution, so the electrode can be copper or other metal to be plated
OR any other conducting material. The change involves two electrons per copper ion.
This means for every copper atom that gets oxidised, one copper ion is reduced, therefore ...
When copper electrodes are used in the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution, the mass loss of copper
from the positive anode electrode should equal the mass of copper gained and deposited on the negative
cathode electrode.
You can show this by weighing both electrodes at the start of the experiment. After the current has
passed for some time, carefully extract the electrodes from the solution, wash them, dry them and reweigh
them. The gain in mass of the cathode should be about the same as the loss of mass from the anode.
Metal electrodes dipped in aqueous salt solutions
For electroplating in general: The negative cathode electrode is made the metal/conducting surface to be
coated , and the positive anode electrode is made of the plating metal which dissolves and replaces
any deposit formed on the cathode -which is the conducting article to be electroplated.
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 4
You might also like
- 7 +Electrolytic+CellsDocument17 pages7 +Electrolytic+Cellsadairyoung946No ratings yet
- Gcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Document9 pagesGcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Takudzwa ChademanaNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument30 pagesElectro ChemistryPower booster100% (1)
- Design Process in ElectrochemistryDocument92 pagesDesign Process in ElectrochemistryWulan SariNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project ChemistryDocument17 pagesInvestigatory Project ChemistryRishav PatraNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument52 pagesElectrochemistryBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisMrNutie12No ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and CorrosionDocument25 pagesUnit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and Corrosion320126512165 VSAICHARANGUPTANo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemical ChangeDocument20 pagesElectricity & Chemical ChangeGautam DayalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument51 pagesUnit 3 Electrochemistrysukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Electrode PotentialDocument24 pagesElectrode PotentialZoeNo ratings yet
- 3 MergedDocument92 pages3 MergedDev LohaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Document9 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Electrochemistry Theory EDocument30 pagesElectrochemistry Theory Ethinkiit100% (2)
- Electrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisDocument9 pagesElectrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisTopikHamdanNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Redox EquilibriumDocument17 pagesBab 1 Redox EquilibriumJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy SystemsDocument21 pages1 Energy Systemsadwar1807No ratings yet
- Analysis Questions: Part 1Document3 pagesAnalysis Questions: Part 1Celyn Millano50% (2)
- Analysis MidsDocument155 pagesAnalysis MidsAdia ChatthaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellsDocument32 pagesElectrolytic CellsHendi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch-2 Electrochemistry (CBSE Class 12)Document23 pagesChemistry Ch-2 Electrochemistry (CBSE Class 12)AyushiNo ratings yet
- Report 2 ElectrolysisDocument19 pagesReport 2 ElectrolysisOmar SamirNo ratings yet
- IGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2Document35 pagesIGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2dung luongtuanNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesKey Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisKim KatNo ratings yet
- Materi 13 - Kimia Teknik - Electrochemistry-Redox Processes-Corrosion of Metal-By Waluyo Nuswantoro 2021Document14 pagesMateri 13 - Kimia Teknik - Electrochemistry-Redox Processes-Corrosion of Metal-By Waluyo Nuswantoro 2021yosepNo ratings yet
- (18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFDocument99 pages(18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFAnuragPandey100% (1)
- MM 2008 Version Standard Grade Chemistry Topic 10 Making Electricity Page 1Document10 pagesMM 2008 Version Standard Grade Chemistry Topic 10 Making Electricity Page 1Anant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chm221 Chapter 5Document42 pagesChm221 Chapter 5Badrudin JundailiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- 4.2 ElectrolysisDocument5 pages4.2 Electrolysis211273wNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument58 pagesElectrochemistryWatan SahuNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 eDocument23 pagesChap 6 emarlina4No ratings yet
- أ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرDocument9 pagesأ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرMmm 123No ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Electrochemical Cell SLDocument27 pagesElectrochemical Cell SLRyan BoukaaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document64 pagesChap 2Swe Zin Zaw MyintNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Chm271Document63 pagesChapter 4 Chm271Amirah AdlinaNo ratings yet
- Electrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Document76 pagesElectrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Victor100% (8)
- Dr. SB Arya, NITK Surathkal, Mangalore 1Document18 pagesDr. SB Arya, NITK Surathkal, Mangalore 1Athlur Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PDFDocument13 pagesElectrolysis PDFShaikh Irad100% (1)
- Electrolysis Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesElectrolysis Cheat Sheet: by Viaaziz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Voltaic CellDocument32 pagesVoltaic CellMahijar Jarullhayati Hassan50% (2)
- Electrochemistry: GCE Study Buddy Chemistry NotesDocument38 pagesElectrochemistry: GCE Study Buddy Chemistry Notesdela2No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 1Document9 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1Imazahra Badaruddin25% (4)
- CHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long Questionssomerakhan2023No ratings yet
- Objectives: - Describe - Identify - Describe - CalculateDocument29 pagesObjectives: - Describe - Identify - Describe - CalculateJanaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument66 pagesElectrochemistryDeepti JainNo ratings yet
- Chemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutDocument5 pagesChemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutYISHAK ABRHAMNo ratings yet
- Philsslides Ig IonsandelectrolysisDocument13 pagesPhilsslides Ig Ionsandelectrolysisapi-181176018No ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electrochemical CellsDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Electrochemical CellsNieva Aldiano LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell LabDocument9 pagesElectrochemical Cell Labribots0% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument10 pagesElectrolysisFaithNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell.Document9 pagesElectrochemical Cell.Maku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Class13 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkDocument37 pagesClass13 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkAndy Rei KouNo ratings yet
- G10 worksheet for ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesG10 worksheet for Electrolysismuaz0% (2)
- Electrolysis - SLDocument10 pagesElectrolysis - SLRyan BoukaaNo ratings yet
- Drawing Laboratory Equipment WorkbookDocument4 pagesDrawing Laboratory Equipment WorkbookoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Extended Essay Rubric and NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry Extended Essay Rubric and Notesoscarbec100% (1)
- Flashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument99 pagesFlashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Using A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameDocument2 pagesUsing A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Curt Farnham, Mirjam Berghuis and Karin FischerDocument32 pagesCurt Farnham, Mirjam Berghuis and Karin FischeroscarbecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Design Experiment For Voltaic Cell and Nernst EquationDocument16 pagesTutorial On Design Experiment For Voltaic Cell and Nernst EquationoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Bonding - Reflection GuideDocument9 pagesTest 1 Bonding - Reflection GuideoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11.1: Identification of A Solvent Using Fractional DistillationDocument6 pagesExperiment 11.1: Identification of A Solvent Using Fractional DistillationoscarbecNo ratings yet
- ATL Presentation at To StaffDocument42 pagesATL Presentation at To StaffoscarbecNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Mole Concept, RAM, RMM Isotopes and Empirical/Molecular FormulaDocument23 pagesIB Chemistry Mole Concept, RAM, RMM Isotopes and Empirical/Molecular FormulaoscarbecNo ratings yet
- G11 Chemistry Test - HLTopic 5,6& 7Document11 pagesG11 Chemistry Test - HLTopic 5,6& 7oscarbecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical SeriesDocument8 pagesTutorial on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical SeriesoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Shanghai Singapore International School G11 Chemistry Test - Bonding SL Mark Out of .. Name Target Grade . Best Grade 1Document10 pagesShanghai Singapore International School G11 Chemistry Test - Bonding SL Mark Out of .. Name Target Grade . Best Grade 1oscarbecNo ratings yet
- 3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)Document24 pages3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)oscarbecNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsDocument26 pagesIB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocument27 pagesTutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationDocument13 pagesIB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Standard Electrode Potential, Standard Reduction Potential and Electrochemical SeriesDocument42 pagesTutorial On Standard Electrode Potential, Standard Reduction Potential and Electrochemical SeriesoscarbecNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationDocument13 pagesIB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodDocument2 pagesExtended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Redox Titration CalculationsDocument33 pagesAcid Base and Redox Titration CalculationsoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay Checklist: Aspect Criterion Descriptor Check CommentDocument3 pagesExtended Essay Checklist: Aspect Criterion Descriptor Check CommentoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Redox Titration, BOD and Biological Oxygen Demand Using Winkler MethodDocument35 pagesTutorial On Redox Titration, BOD and Biological Oxygen Demand Using Winkler MethodoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodDocument2 pagesExtended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodoscarbecNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Activity For G11 - Week 10th To 14thDocument3 pagesE-Learning Activity For G11 - Week 10th To 14thoscarbecNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Activity For February For G11 24-28Document2 pagesE-Learning Activity For February For G11 24-28oscarbecNo ratings yet
- G11 E-LearningDocument1 pageG11 E-LearningoscarbecNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Activity For February For G11 24-28Document2 pagesE-Learning Activity For February For G11 24-28oscarbecNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Activity For February 17-19Document4 pagesE-Learning Activity For February 17-19oscarbecNo ratings yet
- Condensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationDocument3 pagesCondensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationoscarbecNo ratings yet