Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Methods
Uploaded by
Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Methods
Uploaded by
Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.
Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
Topics: Chemistry C2 : Method Of Separation
(A) Methods of Separation
Threshing
Winnowing
Sifting/Sieving
Hand Picking
Solid Solid Separation
Sublimation
Magnetic separation
Fractional
crystallization
Sedimentation
Decantation
Insoluble solid from
Coagulation or loading
liquid Separation
Filtration
Centrifugation
Soluble solid from liquid Evaporation
Separation Distillation
Separation of liquid Separating funnel
from Liquid Separation
Fractional Distillation
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
(1) Solid Solid Separation:
Following are the method of separation for Solid-Solid Separation
a. Threshing: Is the method to separate the grain from ears. Act of removing grain or seeds from hulls or husks
b. Winnowing: Is the method to separate lighter part from heavier part of mixture
c. Sifting/Sieving: Method of separating mixture based on size of particles.
d. Hand Picking: Method of separating mixture based on size of particles.
e. Sublimation: Method of separating sublimative substance.
Sublimation is the process where solid gets converted into gas after heating.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
f. Magnetic separation: Method Used to separate particles out based on magnetic properties
g. Fractional crystallization Separation of two soluble solid.
In this both the solid is dissolved in a particular liquid(Solvent).After cooling, hot
saturated solution ,crystals of less soluble substance is first formed. Using filtration
method they are separated from solution.
e.g. Common salt and potassium nitrate
(2) Insoluble solid from liquid
a. Sedimentation: Method of separation heavy insoluble solid from liquid. We allow the mixture to settle down
for some time. Settling of heavy particles at bottom is called sedimentation
b.Decantation: The method of removing upper clear liquid without disturbing settled solid is called decantation
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
c. Coagulation or loading : Method of removing heavy suspended particle by adding alum or coagulating agent.
d. Filtration: Method of separating insoluble solid from liquid by using filter like filter paper ,cloth ,cotton ,sand
Bed
e. Centrifugation Removes fine insoluble suspended particles from solution by applying centrifugal force.
e.g. Butter from curd ,washing machine squeeze water
(3) Soluble solid from liquid
a.Evaporation: is used to remove liquids from solutes which cannot be done through filtration
due to the small size of the substances.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
b. Distillation: 1. The evaporation and subsequent collection of a liquid by condensation as a means of
purification: the distillation of water.2. The extraction of the volatile components of a mixture by the
condensation and collection of the vapors that are produced as the mixture is heated: petroleum distillation.
(4) Solid from Gas
Cyclone separation the cyclone technology forces air to spin round at very high speed, creating centrifugal
force and causing the dust particles to be pulled out into the bin
(5) Separation of liquid liquid mixture
a. Separating funnel For Immiscible Liquid
A separating funnel is a glass funnel with a tap at the bottom. A separating funnel is a separation technique that
is used for two liquids that do not dissolve in each other. Liquids that do not dissolve in each other are called
immiscible.
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
b. Fractional Distillation
Liquids that dissolve in each other can be separated by fractional distillation. Liquid that dissolve each other are
called as Miscible liquid
Principle is based on difference in boiling point
The solution is heated until it boils. The liquid with the lowest boiling point boils first and becomes a vapour (gas). The
vapour is cooled in the condenser until the temperature falls below the boiling point when it condenses back into a
liquid which is collected in a container. The collected liquid is called the distillate. It has been distilled. The condenser has
cold water running through a jacket around the outside to keep the temperature below the boiling point of the vapour.
After the liquid with the lowest boiling point has been collected, the temperature of the remaining mixture will rise to a
new temperature when the liquid with the next lowest boiling point will boil and be collected. The process can be
continued to separate all the liquids in the mixture.
Fractional distillation is used to separate the components of crude oil and to separate nitrogen and oxygen from liquid
air.
(6) Chromatography:
Separation of different dissolved constituent of a mixture present in a very minute Quantity
Important Definition:
Settling: Settling is the process by which particulates settle to the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. It
happens due to force which could be due to Gravitational force or centrifugal force.
E.g. Removal of solids from liquid sewage waste, Settling of solid food particles from a liquid food
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
Filtrate: The liquid or solution that has passed through a filter.
Residue: The substance that remains after evaporation, distillation, filtration or any similar process.
Sublimating substance: Ammonium chloride , Sal ammoniac, Camphor, Naphthalene, Iodine
Identify chemical instrument
1. Iron gauze: Wire gauze can be used to support a container (such as a beaker or flask) during heating. When the
bunsen burner flame is beneath it, with a tripod, the wire gauze helps to spread the flame (and heat) out evenly over the
container.
2. Tripod: Used to support and hold various flasks, beakers and other glass ware.
3. Round bottom flask:
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series
4. Condenser: One that condenses, especially an apparatus used to condense vapor to liquid
Write notes on following topics
Define
Vaporization
Freezing
Condensation
Melting Point
Boiling point
Evaporation
Fractional Distillation Principle is difference in boiling point
Crude Oil Low Boiling Point Petrol
Higher Boiling Point Diesel
Strictly for Private Circulation
www.homibhabhacompetition.com
You might also like
- The-Power-To-Visualize - Unknown PDFDocument31 pagesThe-Power-To-Visualize - Unknown PDFathanasia123100% (2)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chapter 5 - Lubrication ManagementDocument41 pagesChapter 5 - Lubrication ManagementAdinz DinNo ratings yet
- Preliminary HSC Biology - Australian Biota NotesDocument13 pagesPreliminary HSC Biology - Australian Biota Notesamy_nomNo ratings yet
- Sydney Boys 2012 3U Prelim YearlyDocument11 pagesSydney Boys 2012 3U Prelim YearlygeeeelooNo ratings yet
- Mid-to-Mega: Industry leadership key to rapid Wealth CreationDocument60 pagesMid-to-Mega: Industry leadership key to rapid Wealth CreationSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Robinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601Document32 pagesRobinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601MarcWorld100% (1)
- Lecture 1-Introduction To Transition Metals ChemistryDocument52 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To Transition Metals ChemistryFELIX ORATINo ratings yet
- Intro to MS Examples - Functional GroupsDocument5 pagesIntro to MS Examples - Functional GroupsMohamed DahmaneNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical Design Engineer Interview QuestionssuseevNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions O Level NotesDocument22 pagesChemical Reactions O Level Notesveryveryhappyfeet100% (1)
- S1 Geography NotesDocument42 pagesS1 Geography NotesKurtis ChomiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry Class-XiDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry Class-XiSatyaSaraswatNo ratings yet
- Innesting BehaviourDocument38 pagesInnesting BehaviourSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- CSA GasTrade-Ed7 Quiz U10-Ch3Document2 pagesCSA GasTrade-Ed7 Quiz U10-Ch3diegoNo ratings yet
- Equation AnswersDocument12 pagesEquation AnswersMark CalawayNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Math Send of Year Worksheet 1Document14 pagesYear 10 Math Send of Year Worksheet 1shahulNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 4Document13 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 4haha_le12No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Aqueous SolutionDocument40 pagesElectrolysis Aqueous SolutionVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its AllotropesDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its AllotropesSyed MoinNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5Document8 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5haha_le12No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY XII Model Test PaperDocument68 pagesCHEMISTRY XII Model Test PaperAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Feb ExamDocument6 pagesYear 10 Feb ExamMaogageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ChemistDocument27 pagesTutorial Chemisthujanku5915No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry 20Document15 pages12 Chemistry 20Aranyak NagNo ratings yet
- Mock 7 ResultsDocument9 pagesMock 7 ResultsAnonymousBoi136No ratings yet
- Chemistry ShipwrecksCorrosion&ConservationDocument17 pagesChemistry ShipwrecksCorrosion&ConservationMarco Huang100% (7)
- Year 10 Science: Unit - Going Downhill - Physics EEI (Extended Experimental Investigation)Document9 pagesYear 10 Science: Unit - Going Downhill - Physics EEI (Extended Experimental Investigation)Chad GardinerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDocument24 pagesChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundTiviya Tarini ManiamNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument387 pagesBiologyAaron Wong100% (1)
- Revision Physics Year 10 March 2018Document24 pagesRevision Physics Year 10 March 2018AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Reactions and Equilibrium ConstantsDocument58 pagesEquilibrium Reactions and Equilibrium ConstantsRoger WangNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemistrySandeep Yadav25% (4)
- Year 10 Practice Examination.Document4 pagesYear 10 Practice Examination.jamesedgecombeNo ratings yet
- 2010 HSC Term4 Theory PhysicsDocument9 pages2010 HSC Term4 Theory PhysicsSandy WongNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 English 2005Document14 pagesPaper 2 English 2005Kyambadde FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Year 10 - QuestDocument2 pagesYear 10 - QuestSk Balan100% (1)
- VOLCANICITY Notes Stage 8Document21 pagesVOLCANICITY Notes Stage 8Bona Noble BasingaNo ratings yet
- Complex NomenclatureDocument1 pageComplex NomenclatureYunkai DayNo ratings yet
- HSC Preliminary Chemistry Water NotesDocument27 pagesHSC Preliminary Chemistry Water NotesDrago6678100% (6)
- Year 10 Worksheet 2 PDFDocument19 pagesYear 10 Worksheet 2 PDFTavishi PragyaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument3 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Revision Schedule BookletDocument8 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Revision Schedule BookletDermot ChuckNo ratings yet
- Ideal Heat CapacityDocument12 pagesIdeal Heat CapacityDerek Lua YongweiNo ratings yet
- IBT Sample Questions: Depth of Water (CM) Volume of Water in The Jug (ML)Document2 pagesIBT Sample Questions: Depth of Water (CM) Volume of Water in The Jug (ML)SaravanaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- Comparing Properties of Alkali Metals and HalogensDocument1 pageComparing Properties of Alkali Metals and HalogensBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
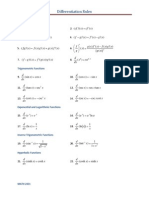
- Differentiation FormulasDocument1 pageDifferentiation Formulasslipper_crazy5335No ratings yet
- Biology ss1Document2 pagesBiology ss1Shonekan KhadijahNo ratings yet
- Latin Continuers Vocabulary List (Recovered) (Autosaved) (Recovered)Document70 pagesLatin Continuers Vocabulary List (Recovered) (Autosaved) (Recovered)thereisnousernameNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For Class 10 Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument4 pagesScience Notes For Class 10 Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elementscrazy about readingNo ratings yet
- Applications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltDocument6 pagesApplications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltSiddhartha GautamaNo ratings yet
- The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For Reproduction or DisplayDocument14 pagesThe Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For Reproduction or DisplaypsdantonioNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Electromagnetism Revision Notes 2016Document7 pagesYear 10 Electromagnetism Revision Notes 2016이다은No ratings yet
- Uses of MetalsDocument6 pagesUses of Metalsdan964No ratings yet
- Investigate How Period Varies With Length for a Simple PendulumDocument4 pagesInvestigate How Period Varies With Length for a Simple PendulumLawrence OnthugaNo ratings yet
- 5090 w01 QP 2Document12 pages5090 w01 QP 2Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Topic Practice Papers - Using QuadraticsDocument51 pagesYear 10 Topic Practice Papers - Using QuadraticsHazelNo ratings yet
- Othello EssayDocument3 pagesOthello Essayapi-356405026No ratings yet
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Kannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFDocument55 pagesKannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- CBSE X Science (Hots)Document65 pagesCBSE X Science (Hots)KKiranKumar50% (2)
- C3 Method of SeparationDocument9 pagesC3 Method of SeparationHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- SEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Document44 pagesSEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"Document20 pagesNotes of "Is Matter Around Us Pure?"SKULL XT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Separating Components of MixturesDocument2 pagesSeparating Components of MixturesAnna Dominic De RomaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch.3Document14 pagesChemistry Ch.3OmlNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 4Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 4BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- MSIL Gujarat - Project.. From ArchivesDocument28 pagesMSIL Gujarat - Project.. From ArchivesSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management Lifecycle: Guide Clients and Grow Your PracticeDocument1 pageWealth Management Lifecycle: Guide Clients and Grow Your PracticeSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Sub: Intimation of Resignation of Deputy Managing Director of HDFC Bank LimitedDocument1 pageSub: Intimation of Resignation of Deputy Managing Director of HDFC Bank LimitedSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Paul VolckerDocument3 pagesPaul VolckerSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Background Paper - Infrastructure - 27jan PDFDocument39 pagesBackground Paper - Infrastructure - 27jan PDFSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Write Up For Navneet Jan202014Document3 pagesWrite Up For Navneet Jan202014Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Tale of Two BanksDocument1 pageTale of Two BanksSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- 19 Types of Tax Deductions in IndiaDocument3 pages19 Types of Tax Deductions in IndiaSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Indias Ascent Executive BriefingDocument40 pagesIndias Ascent Executive BriefingSantanu DasmahapatraNo ratings yet
- IIFL - 2017 Investors Conference - 25 Jan 17Document11 pagesIIFL - 2017 Investors Conference - 25 Jan 17Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Sanitaryware and Faucets Sector - Sep 2014Document36 pagesSanitaryware and Faucets Sector - Sep 2014Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Principles in One Chart - Vishal Khandelwal PDFDocument1 pagePrinciples in One Chart - Vishal Khandelwal PDFSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- EPC Annual ReportDocument56 pagesEPC Annual ReportSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Satyam Daylight Robbery Theme Note 17-12-08Document4 pagesSatyam Daylight Robbery Theme Note 17-12-08Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- 19 Types of Tax Deductions in IndiaDocument3 pages19 Types of Tax Deductions in IndiaSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate CalcDocument1 pageInterest Rate CalcSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- MMS IV Final Project Marks StatementDocument2 pagesMMS IV Final Project Marks StatementSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- History: Badminton Is A Racquet Sport Played UsingDocument26 pagesHistory: Badminton Is A Racquet Sport Played UsingSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- The LeavesDocument3 pagesThe LeavesSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Metrics To Maximize ProfitabilityDocument17 pagesChoosing The Right Metrics To Maximize ProfitabilitydipanshurustagiNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesAnimal TissuesSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- 3D - The Crude ArithmeticDocument13 pages3D - The Crude ArithmeticSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Valuation BasicsDocument9 pagesValuation BasicsSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Sanjeev: Three Rules of GoldrattDocument3 pagesSanjeev: Three Rules of GoldrattSanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - 2016Document1 pageQuestion Bank - 2016Sanjeev Sadanand PatkarNo ratings yet
- Structural steel elements classification and buckling analysisDocument1 pageStructural steel elements classification and buckling analysisNeeraj DubeyNo ratings yet
- SoapsDocument7 pagesSoapsLucita P. CatarajaNo ratings yet
- Sika ViscoCrete 4203 NSDocument2 pagesSika ViscoCrete 4203 NSSantosh Kumar GoudaNo ratings yet
- EPSRC Metallurgy Research Present and FutureDocument15 pagesEPSRC Metallurgy Research Present and Futuresujit_sekharNo ratings yet
- Insulating Glass Panels With Metal Interlayer Other Glass FacadesDocument10 pagesInsulating Glass Panels With Metal Interlayer Other Glass Facadesvikina34No ratings yet
- Klubermatic FLEXDocument24 pagesKlubermatic FLEXVelibor KaranovicNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod for Medium & Thick PlatesDocument1 pageWelding Rod for Medium & Thick PlatesImmalatulhusnaNo ratings yet
- Deha Halfen Kkt-EDocument52 pagesDeha Halfen Kkt-ENandeesha RameshNo ratings yet
- Dalian Hivolt Power System Co. Glass Insulator Test ReportDocument5 pagesDalian Hivolt Power System Co. Glass Insulator Test ReportdiegoyyNo ratings yet
- Cookery Summative TestDocument10 pagesCookery Summative TestSonia CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Conformity: No. CLSAN 080567 0058 Rev. 00Document2 pagesCertificate of Conformity: No. CLSAN 080567 0058 Rev. 00annamalaiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Molecular Liquids: Chandrabhan Verma, Eno E. Ebenso, Indra Bahadur, M.A. QuraishiDocument14 pagesJournal of Molecular Liquids: Chandrabhan Verma, Eno E. Ebenso, Indra Bahadur, M.A. QuraishiterNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument27 pagesProjectAbhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Volume 1 One Mark Study Material 215342Document25 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Volume 1 One Mark Study Material 215342Aakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Safety SheetDocument6 pagesYttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Safety SheetAli Ali AsjariNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall Design and TestingDocument9 pagesCurtain Wall Design and TestingUzair SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Outokumpu Stainless Steel For Automotive IndustryDocument20 pagesOutokumpu Stainless Steel For Automotive IndustrychristopherNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ProcessDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Process056 Jatin GavelNo ratings yet
- Masterseal 909: Re-Injectable Hose For Construction and Cold Joints in ConcreteDocument2 pagesMasterseal 909: Re-Injectable Hose For Construction and Cold Joints in Concretevelmurug_balaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Law of ThermodynamicsDocument7 pages1ST Law of ThermodynamicsKen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged RemovedDocument19 pagesIlovepdf Merged RemovedNeet AspirantNo ratings yet
- Improvised Power Bank From Torn Out Electronic GadgetsDocument2 pagesImprovised Power Bank From Torn Out Electronic GadgetsJiya PalomaresNo ratings yet
- GB Catalog Threading 2014 LRDocument113 pagesGB Catalog Threading 2014 LRPrle TihiNo ratings yet
- Haselrieder 2015Document8 pagesHaselrieder 2015Daiana Medone AcostaNo ratings yet
- Hook-Up Solutions Hanley Controls Compressed AirDocument16 pagesHook-Up Solutions Hanley Controls Compressed AirAriel HughesNo ratings yet