Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Active and Passive Voice PDF
Uploaded by
Tanupriya GoelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Active and Passive Voice PDF
Uploaded by
Tanupriya GoelCopyright:
Available Formats
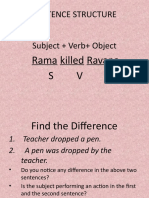
ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE
A transitive verb (a verb which depends on an object) has two voices:
1. Active Voice
2. Passive Voice
Active Voice:
It indicates that the subject of the verb is the doer of the action or is active; e.g
We help our friends.
What is the action performed? helping
What is the subject of the verb? We
Who performs the action of helping? We
So in this sentence, the subject of the verb (We) also performs the action named in the verb (helping).
This sentence is said to be in the active voice.
Passive Voice:
It indicates that the subject of the verb is the receiver of the action or is passive; e.g
Our friends are helped by us.
What is the action performed? helping
What is the subject of the verb? Our friends
Does the subject of the verb (Our friends) also perform the action of helping? No. On the contrary, the
subject (Our friends) receive the action of helping. It is the object (us) who perform the action.
So in this sentence, the subject of the verb (Our friends) is the receiver of the action named in the verb
(helping). This sentence is said to be in the passive voice.
Rules to be followed while changing from Active to Passive:
1. The lion kills a goat. (active voice)
A goat is killed by the lion. (passive voice)
The passive object, a goat (which is being killed the receiver of action), becomes the subject
while the active subject, the lion (which is the doer of action), becomes the object. And we have
used the preposition by before it.
2. The above sentences are in Present Tense and in the second sentence, the subject (A goat) is
singular so is has been used and at the same time the third form (past participle form) of kills
(i.e killed) has been used with it. The third form of verb is used in the passive voice no matter
what the tense is.
3. We have to be careful about the use of personal pronouns.
I require some papers. (active) (subject form of the pronoun I)
Some papers are required by me. (passive) (object form of the pronoun I)
The teacher taught him. (active) (object form of the pronoun he)
He was taught by the teacher. (passive) (subject form of the pronoun he)
4. When the verb in the active voice has two objects, there are two forms in the passive voice.
My friend gave me a gift. (active) ( there are two objects me and a gift)
I was given a gift by my friend.
OR
A gift was given to me by my friend.
The first form is preferred.
5. The object or subject may be a long phrase instead of a single word. But while changing from
active to passive, the whole phrase will change its position.
The parents of all the scholars attended the prize distribution ceremony. (active)
The prize distribution ceremony was attended by the parents of all the scholars. (passive)
The earthquake demolished a large number of houses and buildings. (active)
A large number of houses and buildings were demolished by the earthquake. (passive)
6. If a verb is followed by any preposition in the active voice, the preposition is retained in the
passive voice.
She did not care for me.
I was not cared for by her.
They shouted at the naughty boy.
The naughty boy was shouted at by them.
7. Sometimes the subject is not important and we may omit it.
Somebody wants Aditi on the telephone.
Aditi is wanted on the telephone.
(We have omitted the words by somebody)
Simple Present Tense:
While changing from Active to Passive, Simple Present Tense takes the form:
Object + is / are / am + third form of verb + by + subject. E.g,
Geeta sings a song. (active)
A song is sung by Geeta. (passive)
He checks all items. (active)
All items are checked by him. (passive)
He teaches me. (active)
I am taught by him. (passive)
Simple Past Tense:
While changing from Active to Passive, Simple Past Tense takes the form:
Object + was / were + third form of verb + by + subject. E.g,
Heavy rains flooded the village. (active)
The village was flooded by heavy rains. (passive)
The driver applied the brakes. (active)
The brakes were applied by the driver. (passive)
Simple Future Tense:
While changing from Active to Passive, Simple Present Tense takes the form:
Object + will / shall + be + third form of verb + by + subject. E.g,
The loud noise will disturb the child. (active)
The child will be disturbed by the loud noise. (passive)
My mother will take me to Delhi. (active)
I shall be taken to Delhi by my mother. (passive)
Other Tenses:
TENSE ACTIVE VOICE PASSIVE VOICE
Simple Present Geeta sings a song. A song is sung by Geeta.
Present Continuous Geeta is singing a song A song is being sung by Geeta.
Present Perfect Geeta has sung a song. A song has been sung by Geeta.
Simple Past Geeta sang a song. A song was sung Geeta.
Past Continuous Geeta was singing a song. A song was being sung by Geeta.
Past Perfect Geeta had sung a song. A song had been sung by Geeta.
Simple future Geeta will sing a song. A song will be sung by Geeta.
Future Continuous Geeta will be singing a song. No Passive
Future Perfect Geeta will have sung a song. A song will have been sung by Geeta.
NOTE: Passive Voice is used while writing notices, newspaper reports, in process writing and in
advertisements.
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice 082314Document9 pagesActive and Passive Voice 082314Raanya Raj NandaniNo ratings yet
- Change The VoiceDocument18 pagesChange The VoiceAshish AnandNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument43 pagesActive and Passive VoiceKanchukee KumarNo ratings yet
- Active Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesActive Passive VoiceS. Kathirvelu System AdministratorNo ratings yet
- PASSIVE VOICE - Penerapan Bentuk Kata PasifDocument5 pagesPASSIVE VOICE - Penerapan Bentuk Kata PasiftsukisakiNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Future TenseBernadette NarteNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Voicevee propaganda100% (4)
- M7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Document25 pagesM7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri Bhs - InggrisDocument31 pagesTugas Mandiri Bhs - InggrisMaria DeboraNo ratings yet
- Changing Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveDocument4 pagesChanging Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveBernadette NarteNo ratings yet
- Changing Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveDocument4 pagesChanging Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveBernadette NarteNo ratings yet
- Grammar Active and Passive FormDocument4 pagesGrammar Active and Passive FormZenZaadNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses in English GrammarDocument14 pages12 Tenses in English Grammargilgal kidsNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiveDocument6 pagesPassive VoiveToroi AritonangNo ratings yet
- Active VoiceDocument9 pagesActive VoicehamzaNo ratings yet
- UNIT V. Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesUNIT V. Passive VoiceCESAR MIERNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiveDocument6 pagesPassive VoiveToroi AritonangNo ratings yet
- 1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Document15 pages1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Sukhwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Tech - EngDocument23 pagesUnit 2-Tech - EngkarrisuryaadityaNo ratings yet
- Active PassiveDocument17 pagesActive PassiveM.Nawaz SharifNo ratings yet
- English Assignment Nadya SyaviraDocument6 pagesEnglish Assignment Nadya Syaviranadya syaviraNo ratings yet
- Class 7 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Active and Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesClass 7 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Active and Passive VoiceRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Acitve and Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesAcitve and Passive VoiceShankar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesActive and Passive VoiceNoura AttiaNo ratings yet
- Voice Change (Rules and Ex)Document7 pagesVoice Change (Rules and Ex)7a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 Active PassiveDocument5 pagesHandout 1 Active PassiveMuhammad Mubasher AliNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Tense Wise RulesDocument31 pagesActive and Passive Voice Tense Wise RulesMdMehediHasan100% (5)
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesActive and Passive VoiceSAID LADJEDELNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesActive and Passive VoiceMalik SultanNo ratings yet
- The Active and The Passive: TenseDocument4 pagesThe Active and The Passive: TenseratatecheraNo ratings yet
- Passive and ActiveDocument7 pagesPassive and Activeapi-304729893No ratings yet
- Active & Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesActive & Passive VoicesdNo ratings yet
- Passive Active VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive Active VoiceAbdennour BelarbiNo ratings yet
- Sentence TrnsformationDocument30 pagesSentence TrnsformationJoby Bang-asNo ratings yet
- Grammar PackageDocument115 pagesGrammar Packagebvvqydf5c4No ratings yet
- Acitve and Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesAcitve and Passive VoiceIlyana HaniNo ratings yet
- Open Passive and Active VoiceDocument22 pagesOpen Passive and Active VoiceMehran IbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Writing - Cici Julia Maharani - D3 A GiziDocument5 pagesWriting - Cici Julia Maharani - D3 A GiziCici Julia MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenDocument10 pagesUse of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenciciksherlyNo ratings yet
- Bismilllaaah Senjata Untuk EAPDocument166 pagesBismilllaaah Senjata Untuk EAPFathimah KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Uses of Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesUses of Active and Passive Voicehimaj42013No ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice11Document15 pagesActive and Passive Voice11f4fariha2000No ratings yet
- Book ChapterDocument8 pagesBook ChapterMisbah AwelNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice - Basic Rules With Examples PDFDocument1 pageActive and Passive Voice - Basic Rules With Examples PDFEbrahimi MJNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 THE PASSIVE NewDocument13 pagesUNIT 7 THE PASSIVE NewDINDA HUMAIRANo ratings yet
- Active & PASSIVE VOICE GRADE 8Document5 pagesActive & PASSIVE VOICE GRADE 8fathima sarahNo ratings yet
- Bab IDocument12 pagesBab IEko ServoNo ratings yet
- Active and PassiveDocument63 pagesActive and PassiveMariel MaquinianaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Practice 2.0Document12 pagesPassive Voice Practice 2.0Mario Pacheco AldapeNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice: My Grandfather Planted This Tree. This Tree Was Planted by My GrandfatherDocument10 pagesThe Passive Voice: My Grandfather Planted This Tree. This Tree Was Planted by My GrandfatherTudor MunteanNo ratings yet
- Active Passive RulesDocument8 pagesActive Passive Rulesyakshit guptaNo ratings yet
- Active PassiveDocument19 pagesActive PassiveDainy DanielNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleDocument8 pagesGrammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleYlenia BaldiviezoNo ratings yet
- Active & Passive VoicesDocument13 pagesActive & Passive VoicesKabir ChandiramaniNo ratings yet
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Active Passive Voice PDFDocument8 pagesGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Active Passive Voice PDFHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Eng Assign 1Document13 pagesEng Assign 1Muhammad WaQaSNo ratings yet
- Language Description 1 - Tenses-Voice: Active and Passive: Prepared By: Deenadevy Jessica DebbieDocument15 pagesLanguage Description 1 - Tenses-Voice: Active and Passive: Prepared By: Deenadevy Jessica DebbieJessica Debbie PeterNo ratings yet
- Barter SystemDocument11 pagesBarter SystemTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- Crop ProductionDocument1 pageCrop ProductionTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- 48.lamp Illumination Control System Using Sensor CircuitDocument4 pages48.lamp Illumination Control System Using Sensor CircuitTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- Clean Ganga Pious GangaDocument2 pagesClean Ganga Pious GangaTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- How Can I Use My Experience For Betterment of My City Oct 20th, 2016Document2 pagesHow Can I Use My Experience For Betterment of My City Oct 20th, 2016Tanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Skill Survey: 1 I Am Unable To Do This 2 I Can Do This With Help 3 I Can Do This!Document1 pagePowerpoint Skill Survey: 1 I Am Unable To Do This 2 I Can Do This With Help 3 I Can Do This!Tanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Timeline ChartDocument2 pagesVerb Tenses Timeline ChartTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- SkitDocument3 pagesSkitTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- 48.lamp Illumination Control System Using Sensor CircuitDocument4 pages48.lamp Illumination Control System Using Sensor CircuitTanupriya GoelNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 5 English Quarter 2Document9 pagesDLL Week 5 English Quarter 2ace magtanongNo ratings yet
- Badreddine Zawaka2 PDFDocument17 pagesBadreddine Zawaka2 PDFMohamed Ben kaaloulNo ratings yet
- EF4e Beg Quicktest 03Document4 pagesEF4e Beg Quicktest 03Bárbara MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Handouts - MBDocument45 pagesGrammar - Handouts - MBfruscianteNo ratings yet
- стилистикаDocument6 pagesстилистикаInessa LevinskayaNo ratings yet
- Makalah DiphtongsDocument13 pagesMakalah Diphtongsalya khasanatulNo ratings yet
- StructuralismDocument25 pagesStructuralismAlisha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Letters Of The Greek Alphabet: Notes: 1. There are seven vowels in Greek 2. γγ (gg) is pronounced as nDocument10 pages1.1 The Letters Of The Greek Alphabet: Notes: 1. There are seven vowels in Greek 2. γγ (gg) is pronounced as nImadiug AtivalledNo ratings yet
- Parent Guide To Jolly PhonicsDocument3 pagesParent Guide To Jolly Phonicsapi-370777564No ratings yet
- English Task FormDocument3 pagesEnglish Task FormAdam RiskyNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Cavite State University Don Severino de Las Alas Campus Indang, CaviteDocument29 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Cavite State University Don Severino de Las Alas Campus Indang, CaviteAubrey Shen Fidel BalicudiongNo ratings yet
- English I C2Document10 pagesEnglish I C2José Sánchez100% (1)
- Harmonize Starter My Grammar and PracticeDocument3 pagesHarmonize Starter My Grammar and PracticedolosclassroomsNo ratings yet
- Ambiguity Tests and How To Fail ThemDocument36 pagesAmbiguity Tests and How To Fail ThemO993No ratings yet
- Semiology & SemioticsDocument10 pagesSemiology & Semioticsvuksecer100% (1)
- Marked Loss in Qur'an TranslationDocument16 pagesMarked Loss in Qur'an TranslationMohammed Fahad Mohammed FirozNo ratings yet
- P1 Unit 1 LB Welcome To SchoolDocument28 pagesP1 Unit 1 LB Welcome To SchoolShyryl Annn TanNo ratings yet
- Arash The LegendDocument22 pagesArash The LegendNima ZareNo ratings yet
- Nobuyoshi Ellis - Communication Tasks and SLADocument8 pagesNobuyoshi Ellis - Communication Tasks and SLAAnna Oros BugárNo ratings yet
- E0 UoE Unit 7Document16 pagesE0 UoE Unit 7Patrick GutierrezNo ratings yet
- WEEKLY LEARNING PLAN Q1 Wk5Document3 pagesWEEKLY LEARNING PLAN Q1 Wk5Jane DagpinNo ratings yet
- Notes of The Woman On Platform No. 8 PDFDocument2 pagesNotes of The Woman On Platform No. 8 PDFloura dalal100% (2)
- Phonology Exercises1Document5 pagesPhonology Exercises1Kaouthar BazazNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument42 pagesParaphrasingDayittohin Jahid100% (3)
- English Linguistic - Prosodic Suprasegmental Phonemes - Group 6Document9 pagesEnglish Linguistic - Prosodic Suprasegmental Phonemes - Group 6Mango PieNo ratings yet
- The Top 100 Common Usage ProblemsDocument4 pagesThe Top 100 Common Usage ProblemsJayvee Puntalba Calinog100% (2)
- BHS INGGRIS Kalimat Passive Voice Cara Mengubah Kalimat Aktif KeDocument26 pagesBHS INGGRIS Kalimat Passive Voice Cara Mengubah Kalimat Aktif KeAskep geaNo ratings yet
- Sample PDF of STD 11th English Yuvakbharati Notes Book Maharashtra Board PDFDocument24 pagesSample PDF of STD 11th English Yuvakbharati Notes Book Maharashtra Board PDFmadhuri kavare38% (13)
- Providence Talks CurriculumDocument148 pagesProvidence Talks Curriculumaaron62660% (1)
- 20 Casual French PhrasesDocument5 pages20 Casual French PhrasesChandaKundaNo ratings yet
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.From EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageFrom EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (429)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundFrom Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageFrom EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (916)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideFrom EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideNo ratings yet
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllFrom EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (83)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsFrom EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (15)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneFrom EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (115)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesFrom EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (151)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingFrom EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessFrom EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (308)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- Abominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionFrom EverandAbominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Essential Spanish in 2 hours with Paul Noble: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandEssential Spanish in 2 hours with Paul Noble: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)