Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Migrant Di China
Uploaded by
agusCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Migrant Di China
Uploaded by
agusCopyright:
Available Formats
Nature Environment and Pollution Technology ISSN: 0972-6268
An International Quarterly Scientific Journal
Vol. 15 No. 1 pp. 81-86 2016
Original Research Paper
Game Theory Analysis on Agricultural Ecological Compensation in Rural
Areas Around Beijing-A Case of Zhangcheng District
Guo Ping and Chen Huiqing
School of Economics and Management, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, Shijiazhuang-050043, China
Corresponding author: Guo Ping
ABSTRACT
Nat. Env. & Poll. Tech.
Website: www.neptjournal.com The environment of Beijing, the capital of China, has deteriorated, which need to be managed in the areas of
Received: 10-10-2015 the city and the neighboring rural areas. Zhangcheng district is the main soil and water conservation area of
Accepted: 12-11-2015 Beijing. Agricultural-ecological environmental problems of Zhangcheng district are increasingly serious,
because of conflict between different benefit of each main body in the agricultural ecosystem. Agricultural-
Key Words: ecological compensation, as an institutional arrangement to adjust the damage and the protection of
Returning farmland to forests agricultural-ecological environment interest relations, is an effective measure to protect the ecological
Compensation mechanism environment. This paper takes Zhangcheng district as an example, using the game theory to study its
Farmers payment function agroecological compensation mechanism theory model, as well as the compensation policy decisions and
Compensation policy behaviour process between subject and object in the compensation practice process. The analysis shows
that: (1) The ecological compensation policy effect is not entirely depending on the amount of compensation
in size, and only by improving the standard of compensation to protect environment is not wise; (2) Ecological
compensation policy made by government should also be included in the scope of compensation limit policy;
(3) The level of development of the third industry and the income of migrant workers directly affects the level
of ecological construction project implementation effect.
INTRODUCTION pants, during agro-ecological compensation.
As the agro-ecological environment is deteriorating today, The two districts of Zhangjiakou and Chengde are lo-
long-term excessive use of ecological resources will result cated in the north-west of Hebei Province, and at the junc-
into widespread phenomenon of ecological damage. The tion of four provinces of Beijing, Hebei, Shanxi, and Inner
meaning of agro-ecological compensation is obvious, which Mongolia. Zhangjiakou and Chengde districts, lying on the
can reduce the pressure on the agricultural economy by means north of Beijing, and because of the low-lying northwest to
of financial compensation in the fragile ecological areas and the southeast, they form a natural ladder as a natural barrier
protect the environment (Jia 2014). On government and to the Beijing-Tianjin area. Also, this district is rich in natu-
farmer behaviour, Douglas (2006) discussed that, the suc- ral resources, and as Beijings reservoir, vegetable bas-
cess of any agricultural development project must not only ket and energy supply base, has an important significance
attempt to balance the economic costs and benefits for the for Beijing. Due to the fragile ecological environment in
participants involved in the change, but also take into ac- Zhangjiakou and Chengde region, it is difficult to withstand
count the political, agricultural, ecological, economic and large-scale development. Especially indiscriminate discharge
cultural consequences of such change. Lack of eco-compen- of waste gas and water pollution from heavy industries, soil
sation system is an important reason for ecological degrada- erosion caused by deforestation, which has led to outstand-
tion in China to solve the problem on conservation (Zhiwei ing environmental problems in the Zhangjiakou and Chengde
2011). On agro-ecological compensation issues, lot of re- districts. Therefore, there is a need to develop a reasonable
searches have focused on the evaluation of the ecological and perfect agro-ecological compensation mechanism to pro-
benefits (Lebon et al. 2014), the source of the ecological com- mote ecological construction and social and economical co-
pensation funds, compensation standards and remedies, etc. ordinated development (Liu et al. 2012).
(Renard et al. 2012). Salla (2013) presents an analytical MATERIALS AND METHODS
framework for studying the social impacts of conservation
interventions, and factors affecting post-intervention liveli- In this paper, Zhangjiakou and Chengde districts are selected
hood rehabilitation. Li & Li (2013) and Dong et al. (2014) as the research objects, through game theory, taking return-
have analysed the acts of decision-making, of the partici- ing farmland to forest policy as an example, to examine the
82 Guo ping and Chen Huiqing
effect of the implementation of ecological compensation vegetation, weak soil corrosion resistance, soil erosion, deser-
system, analyse the behavioural and decision-making proc- tification, etc. Area of soil erosion in the region, accounts
esses of ecological compensation policy implementation for about 50 percent of the mountain area, wetland area cuts
process of the different benefit parties, in order to develop a more than half of the early days of about 60 years ago, which
reference of future development of relevant government ag- not only leads to low productivity of arable land, and pro-
ricultural compensation policy. duce sediment deposition problem, but also threats the wa-
ter conservancy facilities of Miyun, Guanting, Panjiakou res-
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ervoirs.
The poor socio-economic environment and worrying eco- Severe sandstorms: Due to the large population, the land in
logical environment of Zhangcheng district: Zhangjiakou this area cannot withstand the pressure resulting from un-
and Chengde regions economy progress lags behind at pro- sustainable human activities, and the area faces serious
vincial average level. In 2014, there were 10 state-level pov- desertification, currently desertification area accounts for
erty-stricken counties in 13 counties of Zhangjiakou, and 5 more than 20% of land area. Zhangjiakou and Chengde there-
state-level poverty-stricken counties in 8 counties of fore become a source of sandstorms and wind duct in Beijing
Chengde, and many poor people, particularly concentrated and Tianjin. In the spring of 2010, in Beijing, blowing sand
in the adverse natural conditions of the dam area. The econo- and dust storms have occurred 12 times, including four from
my gross of Zhangjiakou and Chengde area is behind, over Zhangjiakou and Chengde dam area, high frequency of oc-
the years within the region, and the GDP and fiscal revenues currence, large scope, heavy intensity, which is rare in re-
are difficult to exceed 10% of the total in Hebei Province. cent decades.
Also, the industrial development is uneven, the major share Pollution of water source: Although Zhangjiakou and
of the primary sector, secondary and tertiary industries, es- Chengde districts are severe water shortage areas, but are
pecially the service sector, lag behind. In addition, there is a still committed to providing clean water to Beijing and
huge contradiction between the local regional economic de- Tianjin. From 2003, Zhangjiakou City has provided a total
velopment and ecological environment protection. Primary of 251 million cubic meters of water to Beijing (excluding
industry in Zhangjiakou and Chengde districts, mainly agri- natural water). Since the building of Miyun Reservoir and
culture and animal husbandry, and the secondary industry is Panjiakou Reservoir, Chengde City has supplied a total of
mainly mining industry. Over-development of mineral re- 79.1 billion cubic meters of water to the two reservoirs.
sources will destroy the ecological balance of the natural However, due to the development of industry, the increase
environment, cause soil erosion, land desertification and en- of the population and township enterprises in recent years,
vironmental pollution problems. The poor economic envi- water and reservoirs in Zhangjiakou and Chengde areas have
ronment in Zhangjiakou and Chengde area has led to no fi- suffered a certain degree of pollution, water quality has
nancial resources for government to resolve the local envi- eutrophication trend, particularly serious agricultural pollu-
ronmental problems, and in order to accelerate the develop- tion caused from extensive use of fertilizers and pesticides.
ment of the regional economy, it will lead to further damage According to the statistics of pesticides and fertilizer use per
to the ecological environment. This vicious circle even af- year, the amount of usage growth is at 10% annually, which
fects the ecological environment and economic development makes agricultural water eutrophication, and cause serious
of Beijing-Tianjin region. damage to the water. Without timely treatment, water pollu-
After years of treatment, ecological environment of tion is a threat to the water security of the Beijing-Tianjin
Zhangjiakou and Chengde region has been improved. Re- area.
turning farmlands to forests, planting trees and grass, pro- Returning farmland to forest project of Zhangcheng dis-
moting forest grass, increase vegetation cover, preventing trict: Returning farmland to forest is the most favourable
sandstorm, meadowland management, protection of water and major ecological compensation policy projects (Fu et
sources and other measures mitigates the environmental de- al. 2013), a Chinese first major move in the cross-regional
terioration in Zhangjiakou and Chengde district, and ecological compensation areas. Returning farmland to for-
achieved results in the construction of the Beijing-Tianjin est project began in 2000, the first pilot in Zhangjiakou and
green belt areas. However, considering the overview of the Chengde city dam areas, two years after being promoted to
status of rural ecological environment, the situation is still the whole Hebei province. 2002-2006 was a comprehensive
worrying, the main environmental problems are as follows: construction period, and after 2006 the period was to con-
Serious soil erosion: Zhangjiakou and Chengde area lies at solidate the results. Zhangjiakou and Chengde regions as a
Yellow River downstream, with serious problems of sparse key areas of returning farmland to forest project, has com-
Vol. 15, No. 1, 2016 Nature Environment and Pollution Technology
GAME THEORY ANALYSIS ON AGRICULTURAL ECOLOGICAL COMPENSATION 83
pleted the forest green area of 2370000 hm, and completed arable farmland, can choose to return farmland to protect
with a total area of grassland management as 1300000 hm; the environment, and good ecological environment is the
the average growth of the forest coverage rate is 3.77 per- product of all residents to share, that all residents may get
centage points, and has the good control effect in the pre- the benefit from returning farmland behaviour. Clever Pig
vention of sand and dust, prevention of soil erosion, local Game story gives ideas for the weak (little pig) to wait in
production and living environment in rural areas has im- the competition as the best strategy. In practice, returning
proved. farmland areas are more in the economically under-developed
Agro-ecosystem services provide significant economic regions, and those who obtain more ecological compensation
value, which is the theoretical basis of ecological econom- benefits are residents in economically developed areas. This
ics of agro-ecological compensation. Returning farmland to leads to lack of enthusiasm to return farmland to forest for
forest project promoted the adjustment of agricultural struc- farmers in economically under-developed regions. Also, the
ture and increased farmers income. For the Hebei province, residents in economically developed areas do not understand
the economic benefit is amazing from this project. Total area sacrifices of other people, when they enjoy the ecological
of the new fruit garden is more than three hundred thousand protection benefits, naturally there will be no sense of
hectares in the province, the total area of fodder forest is ownership for consciously safeguarding the ecological
more than two hundred and sixty thousand hectares, raw ma- protection.
terials (paper) forest area is close to one hundred and thirty Construction and analysis of game model of compensa-
thousand hectares, and generates economic benefits of nearly tion mechanism
nine billion RMB yuan. On this basis, the number of the
Construction of the game theory model:
provinces agricultural and forestry products processing en-
terprises, surges to about five hundred, with an annual out- G = {P, S, I, U},
put amount per year close to four hundred million RMB yuan. the players: P=Pi(i=1,2),
The project has made important contributions to rural eco- P1 stands for farmers,
nomic development. Project implementation makes a lot of
rural labour force enter into the tertiary industry, related in- P2 stands for the government.
come generated close to four billion RMB yuan. Meanwhile, During the agro-ecological compensation process, espe-
forestry, especially private forestry of Hebei province has cially in the case of returning farmland to forests, farmers
made great progress. In the implementation of returning farm- will choose the right whether to carry out forest resources
land to forest policy, government support private enterprise ecological protection in Zhangjiakou and Chengde area, ac-
contract to invest in barren mountains and waste lands. As cording to the degree of government compensation made
of 2012, there were more than six hundred thousand hec- (Niu et al. 2010), specifically according to the government
tares private forests in Hebei woodland returning farmland compensation standards for each hectare farmland. The gov-
to forest. Private enterprise contract reforestation projects, ernment needs to pay a certain price in order to achieve the
both achieve the aim to increase jobs, transfer the labours, protection of the ecological value of the forest (Ulbrich et
increase farmers incomes, and improve the quality of con- al. 2008), while the governments available resources are lim-
struction of returning farmland to forest project. ited (Villarroya et al. 2014), so the government has the right
Applying game model in the study of agro-ecological com- to decide whether to compensate for forest conservationists
pensation: Game theory is the study of the relationship that in Zhangjiakou and Chengde area. The strategies collection
occurs when behaviour subjects make decisions and the bal- is constituted as Table 1.
ance of decision-making and behaviour, to solve practical Empirical function of various factors: Government usually
problems that contradiction by a mathematical model. The follows some sort of compensation criteria established to
purpose of game theory analysis is to use game plan to de- develop compensation policy of returning farmland to for-
termine the balance of all participants involved in the opti- ests (Wang et al. 2013). According to the compensation
mal strategy combination. Ecological compensation belongs policy improved by the State Council in 2007, subsidy cri-
to the cooperative game, because ecological compensation teria of returning farmland to forests is 2250 kg grain (unpro-
is made on the perspective of the collective interest (Zhao et cessed) per hectare, equivalent funds of 3150 RMB Yuan,
al. 2014), its implementation and the beneficiaries are all living allowance as 300 RMB Yuan, a total of 3450 RMB
participants. Yuan/ha. The returning ecological forest is eight years at the
In an ecological compensation project of returning moment. After the expiry of the existing subsidies, accord-
farmland to forest, farmers living in areas that need to return ing to the current subsidy standards (in Yangtze River and
Nature Environment and Pollution Technology Vol. 15, No. 1, 2016
84 Guo ping and Chen Huiqing
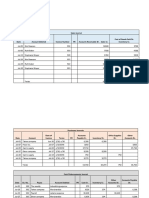
Table 1: The strategies collection of the government and farmers.
Government
Compensation Q1 No compensation Q2
Farmers Returning farmland S1 Returning farmland of farmers Returning farmland of farmers
Compensation of government No compensation of government
No returning farmland S2 No returning farmland of farmers No returning farmland of farmers
Compensation of government No compensation of government
Table 2: Government and farmers payment matrix.
Government
Compensation Q1 No compensation Q2
Farmers Returning farmlandS1 (2379 + pI, -2379 + 0.61a) (2379 + pI, -0.61a)
No returning farmlandS2 (3341.85, -0.61a) (3341.85, -0.61a)
southern regions 1575 RMB Yuan per hectare of returning U 2' (Q1 ) 3900 0.61 0.61a 2379 0.61a
farmland every year, in the Yellow River and the northern U 2' (Q2 ) 0.61a
regions 1050 RMB Yuan per hectare of returning farmland Before farmers returning farmland, the value of labour
every year) add a cycle cash grant for returning farmland is implied in total output per hectare: the main output crop
farmers, and 300 RMB Yuan living allowance per hectare in Zhangjiakou and Chengde region is the corn, the output
per year will be linked to the management and protection was 4313.7 kg/ha, the total output was 5478.45 RMB Yuan
tasks, direct subsidies to farmers. According to inspection per hectare; assuming there are two labours in every house-
results, the government pays cash subsidies. hold, in which one labour needs to deal with familys daily
According to the governments compensation policy, the life, and do preservation and maintenance for forests return-
government compensates for Zhangjiakou and Chengde dis- ing farmland, the other one labour may choose to go out to
trict, the compensation amount for 3900x, in which x is the work or engage in other non-farming activities such as ani-
actual area of returning farmland to forests; at the same time, mal husbandry, etc. Assuming that the average income of
the ecological benefits of forests are value in return enjoyed migrant workers is I, the probability of obtaining migrant
by the public, this value in return has a huge economic ben- income chance is p, the farmers payment function can be
efits and ecological value, its value shown as A. A divided expressed as:
by the total area is ecological benefits of forest per unit area, U1(S1)=39000.61+pI=2379+pI
and is denoted by a.
U2(S2)=5478.450.61=3341.85
The payment function to all households in Zhangjiakou
According to the above described analysis, a payment
and Chengde area by government is:
matrix (Table 2) is formed.
U2(Q1)= 3900x + A
For the government, when farmers choose the returning
U2(Q2)= A farmland strategy for ecological protection, as the value of
This paper takes an example of individual farmer for ecological compensation is a large positive value, namely:
analysis. In 2014 Statistical Yearbook of Hebei Province, 2379 + 0.61a> 0.61
actual arable area in Zhangjiakou and Chengde area was
At this point, the government will choose the compensa-
992.88 thousand hectares, total rural population was 4883
tion strategy. While when farmers choose no returning farm-
thousand persons, which can be calculated as an average of
lands strategy without ecological protection, the government
0.2 hectares of arable land per capita; if assuming the stand-
preference is same for the two strategies. So compared to
ard of an average 3.54 people per household, the average
non-compensation policy, the government is more willing
arable land per household is approximately 0.61 hectares.
to choose the compensation policy.
Therefore, the government payment function for single
household in Zhangjiakou and Chengde area can be expressed Because the government has ecological compensation
as follows: preferences, and premise for farmers to returning farmland,
Vol. 15, No. 1, 2016 Nature Environment and Pollution Technology
GAME THEORY ANALYSIS ON AGRICULTURAL ECOLOGICAL COMPENSATION 85
is clearly aware of the contents of the compensation policy, and is more favourable to promote the transfer entrepreneur-
so in case the government chooses compensation strategy, ship of farmers.
the farmers will repeatedly compare their actual income that Except the above advantages of policy implementation
can be achieved with 3341.85 RMB Yuan to make decisions. of returning farmland to forests, there are some problems
That is, if the government wants to make farmers choose that need to be improved, such as the implementation of some
returning farmland, it must satisfy the condition as follows: projects do not implement a publicity system with opaque-
2379 + pI 3341.85 ness. In addition, there is a slow disbursement of project funds
Then, pI 962.85 in some areas even insufficient funds situation and so on.
These issues need to be addressed and settled.
pI is a non-farming income of migrant workers or en-
gage in cultivation, etc., that is, when migrant farmers in- Policy implementation of returning farmland gives a lot
come is greater than 962.58 RMB Yuan, the farmers and the of inspiration and advice for the construction of other eco-
government will choose the strategy that farmers do return logical compensation mechanism by government. First, the
farmland and government do compensate, which is the development of the project policy should consider the bal-
games dominant strategy. ance of interests of various actors of policy implementation,
so that policy implementation can play to maximize effec-
In above dominant equilibrium, income plays an impor- tiveness; secondly, in the process of policy implementation
tant role for farmers to choose the behaviour of returning it should strengthen organization and leadership, improve
farmland to forest, the specific impact is by the income that the implementation and enforcement of policies; finally, the
farmers work outside the home, including the level of in- construction of ecological compensation mechanism is based
come, and other efforts required access to income. Because on a long period, involving a wide range, it should increase
the State Department grants for ecological forests allowance the support efforts to ensure that investment funds play the
period is eight years, since it started in 2008, government biggest role.
allowance becomes 0 RMB Yuan from 3900 RMB Yuan
per hectare. At this point, farmers returning farmland condi- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
tions change accordingly.
The paper is the part research results of project Study on
pI 3341.85 Coordinated Development of Poverty Alleviation and Eco-
Because if government subsidies stop, the necessary con- logical protection in the Rural Areas around central capital
ditions for farmers to returning farmland adjust such that (No: HB13JJ023), which accepted the fund of 2013 Social
migrant farmers income must be at or over 3341.85 RMB Science Project in Hebei Province in China; and the part re-
Yuan, which also reflects the important role of income fac- search results of project Research on mechanism and coun-
tor for farmers to choose a strategy. termeasure of ecological compensation around Capital
Beijing (No: 14454213D), which accepted the fund of Soft
CONCLUSION Science Research Proposal Project in Hebei province; and
After the above analysis, researchers found that the imple- received the fund of school of economics and management
mentation of ecological protection mechanisms of returning in Shijiazhuang Tiedao University.
farmland to forests has a significant impact on farmland REFERENCES
household income and rural economy. Specific features are
as follows: Baojin, J. 2014. On the legal research of the rural collective land expro-
priation compensation for ecological conservation fee. WIT Transac-
First, households have benefited from policy of return- tions on the Built Environment, 145: 283-290.
ing farmland to forests, the income increases steadily. In Dong, X.B., Yu, B.H., Brown, M.T., Zhang, Y.S., Kang, M.Y., Jin, Y.,
addition to directly subsidize farmers in the choice of re- Zhang, X.S. and Ulgiati, S. 2014. Environmental and economic con-
sequences of the overexploitation of natural capital and ecosystem
turning farmland, after returning farmland, the government services in Xilinguole league, China. Energy Policy, 67: 767-780.
implements basic food grain farmland, rural energy, ecologi- Douglas, William Hume 2006. Swidden agriculture and conservation in
cal migration, skills training and other initiatives to consoli- eastern Madagascar: stakeholder perspectives and cultural belief sys-
date the achievements of returning farmland to ensure an tems. Conservation and Society, 4(2): 287-303.
Haipeng, N. and Anlu, Z. 2010. Method of measuring ecological and so-
increase in household income. cial benefits of cultivated land and its application. Nongye Gongcheng
The second is to promote the transfer of rural labour to Xuebao/Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineer-
urban areas or the secondary and tertiary industries, which ing, 26(5): 316-323.
Lebon, A., Mailleret, L., Dumont, Y. and Grognard, F. 2014. Direct and
stimulate the enthusiasm of households returning farmland, apparent compensation in plant-herbivore interactions. Ecological
Nature Environment and Pollution Technology Vol. 15, No. 1, 2016
86 Guo ping and Chen Huiqing
Modelling, 290: 192-203. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.02.020. developments. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 45:
Li, Xian E. and Li, Qian 2013. The barriers and countermeasures of im- 54-62.
plementing ecological poverty alleviation in concentrated poverty Wang, Y., Feng, Q., Chen, L. and Yu, T. 2013. Significance and effect of
areas. Advanced Materials Research, 734-737: 1976-1980. ecological rehabilitation project in inland river basins in Northwest
Liu, Yuqing, Xu, Zhongmin and Nan, Zhuotong 2012. Study on ecologi- China. Environmental Management, 52(1): 209-220.
cal compensation in upper stream of Heihe river basin based on Yicheng, F., Ting, G., Lijuan, Y., Aijing, Z. and Benqing, R. 2013. Agro-
SWAT model and minimum-data approach. Nongye Gongcheng ecological compensation standard based on energy analysis in
Xuebao, 28(10): 124-130. (in Chinese) Yongding River basin. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Transactions of
Renard, D., Iriarte, J., Birk, J.J., Rostain, S., Glaser, B. and McKey, D. the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(1): 209-217. (in
2012. Ecological engineers ahead of their time: The functioning of Chinese)
pre-Columbian raised-field agriculture and its potential contributions Yuqing, L., Zhongmin, X. and Zhuotong, N. 2012. Study on ecological
to sustainability today. Ecological Engineering, 45: 30-44. compensation in upper stream of Heihe river basin based on SWAT
Salla, E. Rantala, Heini, Vihemki, Brent, M. Swallow and George, model and minimum-data approach. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/
Jambiya 2013. Who gains and who loses from compensated displace- Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,
ment from protected areas? the case of the Derema Corridor, Tanza- 28(10): 124-130. (in Chinese)
nia. Conservation and Society, 11(2): 97-111. Zhao, G., Wang, Y., Tang, X., Li, C. and Wu, W. 2014. Evaluation of
Ulbrich, K., Drechsler, M., Wtzold, F., Johst, K. and Settele, J. 2008. A sustainability for intensive farmland ecosystem based on energy eco-
software tool for designing cost-effective compensation payments logical footprint. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Transactions of the
for conservation measures. Environmental Modelling and Software, Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 30(18): 159-167. (in
23(1): 122-123. Chinese)
Villarroya, A., Persson, J. and Puig, J. 2014. Ecological compensation: Zhiwei, Xiong 2011. Research on eco-compensation system in China.
from general guidance and expertise to specific proposals for road Journal of Agricultural Science, 3(2): 255-267.
Vol. 15, No. 1, 2016 Nature Environment and Pollution Technology
Copyright of Nature Environment & Pollution Technology is the property of Technoscience
Publications and its content may not be copied or emailed to multiple sites or posted to a
listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission. However, users may print,
download, or email articles for individual use.
You might also like
- Isuzu 4be1 Engine Manual KolesooreDocument5 pagesIsuzu 4be1 Engine Manual KolesooreRaymart Dealca75% (8)
- December + Yearly ReviewDocument2 pagesDecember + Yearly ReviewNick FabrioNo ratings yet
- In-Film BrandingDocument27 pagesIn-Film BrandingSantosh Parachuri0% (1)
- Quiz 1 - Domain Modeling With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 - Domain Modeling With Answer Keyprincess100267% (3)
- Sustainability 10 00006Document23 pagesSustainability 10 00006Katherine JonesNo ratings yet
- Water 10 01653 PDFDocument18 pagesWater 10 01653 PDFAlvaroPereiraNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Water Management 243 (2021) 106417Document9 pagesAgricultural Water Management 243 (2021) 106417camus CaNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S1470160X23002728-main P8Document8 pages1-s2.0-S1470160X23002728-main P8Saengsuree Lamei WardwijitNo ratings yet
- Social, Economic, and Ecological Impacts of The Grain For Green'' Project in China: A Preliminary Case in Zhangye, Northwest ChinaDocument11 pagesSocial, Economic, and Ecological Impacts of The Grain For Green'' Project in China: A Preliminary Case in Zhangye, Northwest ChinaPablo CalviNo ratings yet
- How Human Activity Has Changed The Regional Habitat Quality in An Eco-Economic Zone: Evidence From Poyang Lake Eco-Economic Zone, ChinaDocument21 pagesHow Human Activity Has Changed The Regional Habitat Quality in An Eco-Economic Zone: Evidence From Poyang Lake Eco-Economic Zone, Chinanardifebri00No ratings yet
- Ma 2020Document9 pagesMa 2020safikahNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Science of The Total EnvironmentDocument37 pagesJournal Pre-Proofs: Science of The Total EnvironmentCleyby DavilaNo ratings yet
- WTP SungaiDocument7 pagesWTP SungaiYnandar NandarNo ratings yet
- Ecological Engineering: A A B CDocument8 pagesEcological Engineering: A A B Cbunga djasmin ramadhantyNo ratings yet
- Deep 5565@1Document3 pagesDeep 5565@1Kirethik BNo ratings yet
- Development Strategy Research of Modern Eco-Agriculture On The Basis of Constructing The Rural Circular Economy-For The Example of Shandong ProvinceDocument5 pagesDevelopment Strategy Research of Modern Eco-Agriculture On The Basis of Constructing The Rural Circular Economy-For The Example of Shandong ProvincezewpadNo ratings yet
- Eco Eco 3Document21 pagesEco Eco 3Kelmaisteis CorreaNo ratings yet
- Environment Mangament Notes 1Document40 pagesEnvironment Mangament Notes 1jayeshpereNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Evaluation of Agricultural Land Suitability For Irrigation in Osijek County CroatiaDocument23 pagesCriteria For Evaluation of Agricultural Land Suitability For Irrigation in Osijek County Croatianirmal kumarNo ratings yet
- 2019 Zhaomin Hu Zhe Zhao Yue Zhang Haichun Jing Shuqin Gao Jingyun FangDocument7 pages2019 Zhaomin Hu Zhe Zhao Yue Zhang Haichun Jing Shuqin Gao Jingyun FangVitor Ferreira LinsNo ratings yet
- Dilemma Analysis of China Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Based On Peasants' Household SurveysDocument10 pagesDilemma Analysis of China Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Based On Peasants' Household SurveysDwirapi TirtoNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Hydrological Consequences of Agriculture Activities: General Review & Case StudyDocument20 pagesEnvironmental and Hydrological Consequences of Agriculture Activities: General Review & Case Studyengrijaz786No ratings yet
- FahadDocument9 pagesFahadSaleh ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Contoh Literatur Review 1Document34 pagesContoh Literatur Review 1Muhammad Fathi Al GhifariNo ratings yet
- Strategic Approach For Controlling Soil PDFDocument12 pagesStrategic Approach For Controlling Soil PDFNischal NarayanNo ratings yet
- Mitigating Climate Change Through The Utilisation of BiomassDocument7 pagesMitigating Climate Change Through The Utilisation of BiomassMarina FiliposkaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Indicators: Original ArticlesDocument19 pagesEcological Indicators: Original ArticlesMaria Luisa VarillasNo ratings yet
- Agriculture, Ecosystems and EnvironmentDocument12 pagesAgriculture, Ecosystems and EnvironmentTalión WhbNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Synergy Management in Response To Climate Change in ChinaDocument14 pagesWater Resource Synergy Management in Response To Climate Change in ChinaUndrah TsogooNo ratings yet
- GE 8291 Unit IV Social Issues & The Environment (Student Print Out 27.2.20)Document27 pagesGE 8291 Unit IV Social Issues & The Environment (Student Print Out 27.2.20)IT GirlsNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Assessment Using STIRPAT Approach To Environmental Quality: An Extended Panel Data AnalysisDocument13 pagesSustainability Assessment Using STIRPAT Approach To Environmental Quality: An Extended Panel Data AnalysisWadar BalochNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - The Path AheadDocument6 pagesClimate Change - The Path AheadUmesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- s11356 019 06343 ZDocument17 pagess11356 019 06343 ZnhoctydangtapdiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Their Mitigation Measures of Irrigation ProjectDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Their Mitigation Measures of Irrigation ProjectInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Ecological Indicators: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesEcological Indicators: SciencedirectRaíssa Tayná KlasmanNo ratings yet
- CC Swat QnamDocument12 pagesCC Swat QnamMeobeobu MisonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Environmental AssessmentDocument13 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Environmental AssessmentJenny Guarda JudanNo ratings yet
- Osama BSDocument15 pagesOsama BSyasir.ali7018No ratings yet
- Malin Songa, Xin Cui, Shuhong Wang-Simulation of Land Green Supply Chain Based On System Dynamics and Policy OptimizationDocument11 pagesMalin Songa, Xin Cui, Shuhong Wang-Simulation of Land Green Supply Chain Based On System Dynamics and Policy OptimizationfaradibafarukzubediNo ratings yet
- Back Ground - Climatic ChangeDocument3 pagesBack Ground - Climatic ChangeleozalkiNo ratings yet
- The Valuation of Chinas Environmental DegradationDocument10 pagesThe Valuation of Chinas Environmental DegradationMonica VaronaNo ratings yet
- L02-Water Reclamation and Sludge RecyclingDocument10 pagesL02-Water Reclamation and Sludge RecyclingNicolas MedinsNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1470160X2200019X MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1470160X2200019X MainAruni KarinaNo ratings yet
- Jia 2019Document12 pagesJia 2019MuletaNo ratings yet
- Dalin 2016 Environ. Res. Lett. 11 035012Document10 pagesDalin 2016 Environ. Res. Lett. 11 035012taqweemulhaq258No ratings yet
- 1.1 Background of The Study: Et Al (2018) Was Elaborate That The Time Trends For Countries and The World Have StayedDocument5 pages1.1 Background of The Study: Et Al (2018) Was Elaborate That The Time Trends For Countries and The World Have StayedIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Ecological Indicators: A B C D D A A DDocument11 pagesEcological Indicators: A B C D D A A DbibrevNo ratings yet
- Socioeconomic and Environmental Effects of China's Conversion of Cropland To Forest Program After 15 Years: A Systematic Review ProtocolDocument12 pagesSocioeconomic and Environmental Effects of China's Conversion of Cropland To Forest Program After 15 Years: A Systematic Review Protocola20201540No ratings yet
- Jia2018 Regionalization of Water Environmental Carrying Capacity For Supporting TheDocument12 pagesJia2018 Regionalization of Water Environmental Carrying Capacity For Supporting TheBarney StinsonNo ratings yet
- Water Scarcity in The Context of ChinaDocument20 pagesWater Scarcity in The Context of ChinaMsa-Management Sciences JournalNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentDocument15 pagesEnsuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentJJNo ratings yet
- OYEBODEO.J. StrategicApproachforContDocument13 pagesOYEBODEO.J. StrategicApproachforContDragón Shiryu ShyriuNo ratings yet
- E C and ImpactsDocument17 pagesE C and ImpactsLaxmi LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Madhya Pradesh State Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument152 pagesMadhya Pradesh State Action Plan On Climate ChangeRahul Kumar AwadeNo ratings yet
- Peatland Policy and Management Strategy To SupportDocument11 pagesPeatland Policy and Management Strategy To SupportardikaNo ratings yet
- Ijiem 283Document10 pagesIjiem 283Jabir ArifNo ratings yet
- Ijiem 283Document10 pagesIjiem 283Jabir ArifNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Trade Liberalization On Productivity Distribution Under The Presence of Technology Diffusion and InnovationDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Trade Liberalization On Productivity Distribution Under The Presence of Technology Diffusion and Innovationduyenntk21408cNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 18 07111 v2Document23 pagesIjerph 18 07111 v2anam asharfNo ratings yet
- Economical EnvironmentDocument6 pagesEconomical Environmentstudyquora.inNo ratings yet
- Wue DryDocument12 pagesWue DryGabriel Brito CostaNo ratings yet
- Greater Mekong Subregion Environmental Performance Assessment 2006–2016From EverandGreater Mekong Subregion Environmental Performance Assessment 2006–2016No ratings yet
- Payments for Ecological Services and Eco-Compensation: Practices and Innovations in the People's Republic of ChinaFrom EverandPayments for Ecological Services and Eco-Compensation: Practices and Innovations in the People's Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Transforming Urban–Rural Water Linkages into High-Quality InvestmentsFrom EverandTransforming Urban–Rural Water Linkages into High-Quality InvestmentsNo ratings yet
- Unified HACKTBDocument15 pagesUnified HACKTBKali PentesterNo ratings yet
- Modern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesDocument10 pagesModern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesCristina AronNo ratings yet
- Abstract 2 TonesDocument8 pagesAbstract 2 TonesFilip FilipovicNo ratings yet
- Boat, Time Speed and DistanceDocument5 pagesBoat, Time Speed and DistanceAnmol AswalNo ratings yet
- Asus P8Z68-V PRO GEN3 ManualDocument146 pagesAsus P8Z68-V PRO GEN3 ManualwkfanNo ratings yet
- 100 Free Fonts PDFDocument61 pages100 Free Fonts PDFzackiNo ratings yet
- 201805graphene PDFDocument204 pages201805graphene PDFMohammad RezkyNo ratings yet
- Create New Project CodeVision AVR (LED)Document5 pagesCreate New Project CodeVision AVR (LED)calvinNo ratings yet
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument1 pageSpecial Power of Attorneywecans izza100% (1)
- RBA Catalog Maltby GBR Aug 16 2023 NL NLDocument131 pagesRBA Catalog Maltby GBR Aug 16 2023 NL NLKelvin FaneyteNo ratings yet
- L8 Logistics ManagementDocument41 pagesL8 Logistics ManagementShahmien SevenNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis FormulasDocument4 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis FormulasVaishali Jhaveri100% (1)
- CHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryDocument30 pagesCHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryLeo Archival ImperialNo ratings yet
- 5 GR No. 93468 December 29, 1994 NATU Vs TorresDocument9 pages5 GR No. 93468 December 29, 1994 NATU Vs Torresrodolfoverdidajr100% (1)
- C&DS Lab Manual UpdatedDocument182 pagesC&DS Lab Manual UpdatedJesmin MostafaNo ratings yet
- MyFlixer - Watch Movies and Series Online Free in Full HD On MyFlixerDocument1 pageMyFlixer - Watch Movies and Series Online Free in Full HD On MyFlixerGeanina OlteanuNo ratings yet
- Cbseskilleducation Com Digital Presentation Class 9Document11 pagesCbseskilleducation Com Digital Presentation Class 9riscomputersirNo ratings yet
- Annexure - IV (SLD)Document6 pagesAnnexure - IV (SLD)Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Train Details of New DelhiDocument94 pagesTrain Details of New DelhiSiddharth MohanNo ratings yet
- Contracts Act, 2010Document59 pagesContracts Act, 2010Sam KNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. WHAT IS AGROTECHNOPRENEURSHIPDocument23 pagesLesson 2. WHAT IS AGROTECHNOPRENEURSHIPRhea Jane DugadugaNo ratings yet
- Hyperformance Plasma: Manual GasDocument272 pagesHyperformance Plasma: Manual GasSinan Aslan100% (1)
- Cbi LNG Storage US Rev8 LoresDocument4 pagesCbi LNG Storage US Rev8 LoresVilas AndhaleNo ratings yet
- Yesenia Acc SjournalsDocument7 pagesYesenia Acc SjournalsFileon ChiacNo ratings yet
- Soal PAS-UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 11 SMADocument10 pagesSoal PAS-UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 11 SMAAlexander TristanNo ratings yet
- Maxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportDocument3 pagesMaxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportCarlos Cobaleda GarcíaNo ratings yet