Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fractures of The Upper Limb
Uploaded by
Jim Jose AntonyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractures of The Upper Limb
Uploaded by
Jim Jose AntonyCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractures of upper extremity
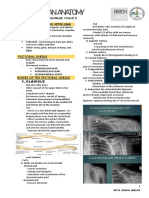
FRACTURES OF THE CLAVICLE
common fractures
fall into the shoulder
middle 3rd
evident on inspection
treated non operatively
open fracture, displaced surgically
treated
LATERAL 3RD
Less common
With coracoclavicular ligament
rupture
High risk for non-union
Displaced surgical treatment
Clavicular fracture is treated by?
A. Fixation with plate and screw
B. Open reduction and internal
fixation
C. Skeletal traction
D. Figure of eight bandage
Common injury to baby is
a) Fracture of humerus
b) Fracture of clavicle
c) Fracture of radius and ulna
d) Fracture of femur
Treatment of fracture clavicle in an
infant is best treated by
a) Cuff and sling
b) Figure of eight bandage
c) Open reduction
d) Shoulder cast
Most common complication of
clavicular fracture is?
a) Nonunion
b) Delayed union
c) Malunion
d) Neurovascular damage
Regarding the clavicle, all are correct
EXCEPT:
a. It is an example of the short bones.
b. It is the first bone to ossify in the fetal
life.
c. It ossifies in membrane.
d. It is the commonly fractured bone.
e. It has no medullary cavity.
The most common site of fracture of
the clavicle is:
a. Medial end.
b. Lateral end.
c. Midpoint of the clavicle.
d. Junction of the medial two-thirds and
the lateral third.
e. Junction of the lateral two-thirds and
the medial third.
The inferior surface of the clavicle
gives attachment to all of the
following EXCEPT:
a. Conoid ligament.
b. Trapezoid ligament.
c. Costoclavicular ligament.
d. Pectoralis major muscle.
e. Subclavius muscle.
These muscles are attached to the
medial two thirds of the clavicle
EXCEPT:
a. Sternomastoid.
b. Deltoid.
c. Pectoralis major.
d. Subclavius.
e. Sternohyoid.
Regarding the articulations of the
clavicle, one is correct:
a. The medial end articulates with the
manubrium by fibrous articulation.
b. The medial end articulates with the
manubrium by cartilaginous articulation.
c. The medial end articulates with the
body of the sternum by saddle synovial
joint.
d. The lateral end articulates with the
acromion by fibrous articulation.
e. The lateral end articulates with the
acromion by plane synovial articulation.
One of he following is not attached to
the medial border of the scapula:
a. Levator scapulae.
b. Teres minor.
c. Serratus anterior.
d. Rhombideus minor.
e. Rhomboideus major.
All of the following parts of the
scapula can be felt EXCEPT:
a. Acromion process.
b. Crest of the spine.
c. Upper border.
d. Inferior angle.
Fractures of upper extremity
The glenoid cavity articulates with the
head of the humerus by a:
a. Fibrous articulation.
b. Cartilaginous articulation.
c. Plane synovial articulation.
d. Ball and socket synovial articulation.
e. Hinge synovial articulation.
e. Tip of the coracoid process.
The surgical neck of the humerus is
related to the:
a. Radial nerve.
b. Axillary nerve.
c. Ulnar nerve.
d. Median nerve.
e. None of the above.
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint injuries
Fall on shoulder or outstretched hand
AC ligament and Coracoclavicular
ligament tears
Step off or separation of AC jointradiograph
Majority treated non operatively
Severe displacement surgery
Sternoclavicular joint
Injury is rare
Anterior dislocation is more
common than posterior
Close reduction and
immobilization by arm sling
Posterior dislocation dangerous
Pulmonary or neurovascular injury
Close reduction under anesthesia
with vascular surgeon present
Fracture of scapula
Associated head, ribs, lungs and
spine injuries
Check neurovascular injury
Mostly treated non operatively
Glenoid fracture/intra-articular
fracture open reduction by plates
or screws
Shoulder dislocation
Most commonly dislocated joint
Bankart lession injury labrum
Hill-sachs lession impression
fracture at humeral
Rotator cuff tears
Posterior dislocation seizures and
electric shock
Radiograph
Close reduction + short period
immobilization
Proximal humerus fractures
Common in elderly
Fall on shoulder/direct blow/
high energy trauma
Neer classification
Treatment
o Displacement
o Angulation
o Comminution
o Age
Proximal humerus fractures
Radiography AP, Axillary,
scapular Y view
Intra-articular fracture Computed
tomography/3d reconstruction
Treatment
o Immobilization
o ORIF
o Prosthetic replacement
elderly and osteoporotic
patient
Humeral shaft fractures
Direct blow, fall on outstretch arm
Neurovascular examination
o Radial nerve injury
(neuropraxia)
Radiography arm apl
Acceptable alignment
o Coaptation splint
o Functional bracing
2
Fractures of upper extremity
o
Close monitoring with
radiograph
Unacceptable alignment or angulation
o OR Plate fixation
o OR intramedullary nailing
o Minimally invasive plate
osteosynthesis (MIPO)
Distal Humerus Fractures
Fall on elbow/outstretch arm
Radiography elbow apl
Supracondylar fractures/
capitellum
Undisplaced LAPM
Displaced dual plating
Intraarticular goal
o Anatomic reduction with
stable fixation
o Restoration of anatomic
alignment of the joint
o Early range of motion
o ! TOTAL ELBOW
REPLACEMENT
Elbow dislocation
Fall outstretch hand
Radiography elbow apl
Posteriorly directed
Ruptured of lateral collateral ligament
Associated with fracture of radial
head, coronoid, or epicondyle
Reduced urgently with LAPM
Associated with fractures
treated surgically
TERRIBLE TRIAD
o Elbow dislocation
o Radial head fracture
o Coronoid fracture
Unstable injuries repair of LCL, fixer replace
radial head, coronoid fixation
Surgical treatment displaced
supination/pronation block
ORIF (open reduction internal
fixation)
Radial head replacement
Excission
Olecranon Fractures
Fall directly onto flexed elbow
Swelling/tenderness
Radiography elbow APL
Non-surgical undisplaced,
immobilization
o Early ROME
o Close ff-up
Surgical treatment pull of triceps
cause displaement
Tension Band Wiring (TBW) tranverse facture
Plates and screws
comminuted fracture
Forearm Fractures
High energy trauma
Deformity, swelling, tenderness
Radiography forearm APL
Non surgical undisplaced
SURGICAL restoration of radial bow
angle
Plates and screws
Intramedullary rod
Night stick fracture isolated fracture
of ulna
Monteggia fracture fracture of ulna
with radial head dislocation
Galeazzi fracture fracture of radius
with dislocation of distal radioulnar
joint (DRUJ)
Radial Head Fractures
Fall on outstretch hand
Swelling tenderness
Radiography elbow APL
Non surgical - immobilization
3
You might also like
- Fractures of The Upper LimbDocument20 pagesFractures of The Upper LimbWendy Francisca Borquez PerezNo ratings yet
- Hip Neck Fracture, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHip Neck Fracture, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocument31 pagesMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesRasjad ChairuddinNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic examination techniques and common conditionsDocument226 pagesOrthopedic examination techniques and common conditionsMandisa Ndlovu Tenego0% (1)
- By DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@: +pigmented Stones (Black Stone - Non Infected) (Brown Stone - Infected)Document11 pagesBy DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@: +pigmented Stones (Black Stone - Non Infected) (Brown Stone - Infected)Nisreen Al-shareNo ratings yet
- Meningeal SyndromeDocument2 pagesMeningeal SyndromeEmi ValcovNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument23 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjuriesUmar AzlanNo ratings yet
- Normal Pressure HydrocephalusDocument59 pagesNormal Pressure Hydrocephalusrys239No ratings yet
- Emtiaz Guide in SurgeryDocument25 pagesEmtiaz Guide in SurgeryMohamed AwadNo ratings yet
- ParaplegiaDocument7 pagesParaplegiaRigaga GopiNo ratings yet
- Fractures of Arm Forearm PDFDocument3 pagesFractures of Arm Forearm PDFjimNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord TumorsDocument23 pagesSpinal Cord TumorsTahleel AltafNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology: Diseases of The EsophagusDocument18 pagesGastroenterology: Diseases of The EsophagusKayeshiana30No ratings yet
- Combined Okell NotesDocument202 pagesCombined Okell Notessameeramw100% (5)
- Avascular NecrosisDocument3 pagesAvascular Necrosisahmad shaltoutNo ratings yet
- High Yield General Surgery Topics PDFDocument85 pagesHigh Yield General Surgery Topics PDF1031 Muhammad zaryabNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Neurosurgery Lecture NotesDocument124 pagesUndergraduate Neurosurgery Lecture NotesLuquiitas LasernaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Notes NeetpgDocument4 pagesOrthopedics Notes NeetpgGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Motor Neuron Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)Document2 pagesMotor Neuron Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)james cordenNo ratings yet
- CTEVDocument25 pagesCTEVIceBearNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Surgery for Knee Pain in Young GirlsDocument88 pagesOrthopedic Surgery for Knee Pain in Young Girlsteena6506763No ratings yet
- 008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenDocument7 pages008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenAthul GurudasNo ratings yet
- MSK Pathology For USMLE Step OneDocument6 pagesMSK Pathology For USMLE Step OneGrilled CroweNo ratings yet
- Clinical MnemonicsDocument23 pagesClinical MnemonicsMing WangNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument3 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisJohnpeter EsporlasNo ratings yet
- AV Fistula ExamDocument4 pagesAV Fistula ExamKay BristolNo ratings yet
- SC - Fracture ZMHDocument51 pagesSC - Fracture ZMHMis StromNo ratings yet
- Child With Bruises 00Document36 pagesChild With Bruises 00Awatef AbushhiwaNo ratings yet
- Dislocations and Soft Tissue InjuryDocument40 pagesDislocations and Soft Tissue InjuryAnonymousNo ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Last Minute Revision Points LMRPDocument4 pagesLast Minute Revision Points LMRPbetsyNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument3 pagesNeurology Notesdlynne23No ratings yet
- UKA: When Would I Do It?Document35 pagesUKA: When Would I Do It?neareastspineNo ratings yet
- PancytopeniaDocument9 pagesPancytopeniadrhammadtufailNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic SlidesDocument78 pagesOrthopedic SlidesAzry Mustapa100% (1)
- Anatomy TotalDocument19 pagesAnatomy TotalSnehanshNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Surgery PDFDocument15 pagesOrtho - Surgery PDFIC BNo ratings yet
- Slipped Capital Femoral EpiphysisDocument40 pagesSlipped Capital Femoral EpiphysisDrAshesh Desai100% (2)
- Intra Abdominal 2009Document8 pagesIntra Abdominal 2009Shinta Dwi Septiani Putri WibowoNo ratings yet
- Supracondylar FractureDocument53 pagesSupracondylar Fracturedesire kbpNo ratings yet
- Teratogens and Cardiac MalformationsDocument27 pagesTeratogens and Cardiac MalformationsNada AKNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis PresentationDocument15 pagesOsteomyelitis PresentationFrancis_Legasp_3667No ratings yet
- Lower Limb - Clinical AnatomyDocument18 pagesLower Limb - Clinical Anatomyewijayapala100% (2)
- Upper Limb TransDocument18 pagesUpper Limb Transashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology Case StudiesDocument10 pagesClinical Pathology Case StudiesKwadwo Sarpong JnrNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Forearm & Hand AnatomyDocument5 pagesForearm & Hand AnatomyshivnairNo ratings yet
- Amboss Hemolytic AnemiaDocument16 pagesAmboss Hemolytic AnemiaAhmed Ali100% (2)
- ABC Interpretation and Pulmonary Function TestsDocument21 pagesABC Interpretation and Pulmonary Function TestsbobiomeNo ratings yet
- Bone Tumours - I & Ii - 2015Document113 pagesBone Tumours - I & Ii - 2015Nur Atiqah Mohd AzliNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Disease by GadisaDocument128 pagesSpinal Cord Disease by GadisaGadisa DejeneNo ratings yet
- Elbow WristDocument59 pagesElbow Wristdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Localisation of Spinal Cord LesionsDocument218 pagesLocalisation of Spinal Cord LesionsGoh Sheen YeeNo ratings yet
- Surgery Signs, Triads N SyndromesDocument11 pagesSurgery Signs, Triads N Syndromesdrusmansaleem100% (1)
- Renal Pathology GuideDocument71 pagesRenal Pathology GuideSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cns PathologyDocument18 pagesCns Pathologysunnyorange8No ratings yet
- Synovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSynovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- 6min English Kids at Home PDFDocument5 pages6min English Kids at Home PDFJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorDocument11 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- 6min English Electricity PDFDocument5 pages6min English Electricity PDFJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Common Cutaneous Infections and InfestationsDocument28 pagesCommon Cutaneous Infections and InfestationsJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Immunization in Children: Fahad Al ZamilDocument44 pagesImmunization in Children: Fahad Al ZamilJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- India Today 29 June 2020 PDFDocument76 pagesIndia Today 29 June 2020 PDFJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Elham Bukhari: Aediatri Nfectious IseaseDocument56 pagesDr. Elham Bukhari: Aediatri Nfectious IseaseJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ortho Team FinalDocument221 pagesOrtho Team FinalJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument10 pagesPleural EffusionJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- Strabismus, Amblyopia Management and LeukocoriaDocument19 pagesStrabismus, Amblyopia Management and LeukocoriaJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris and Acne Related DisordersDocument12 pagesAcne Vulgaris and Acne Related DisordersJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Acute Visual LossDocument10 pagesAcute Visual LossJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument7 pagesRefractive ErrorsJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Optha: NeuroDocument13 pagesOptha: NeuroJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergenciesDocument4 pagesOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Criteria For Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Criteria For Urinary Tract InfectioncandyslibioNo ratings yet
- Chronic Visual LossDocument7 pagesChronic Visual LossJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- COPD and BronchiectasisDocument20 pagesCOPD and BronchiectasisJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions May 2006Document10 pagesMCQ Questions May 2006Jim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Investigations of Lung DiseasesDocument14 pagesInvestigations of Lung DiseasesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Hair Disorders and Pigmented Skin ConditionsDocument8 pagesHair Disorders and Pigmented Skin ConditionsJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose Nasopharynx and Paranasal Sinuses PDFDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The Nose Nasopharynx and Paranasal Sinuses PDFJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic History Taking: DR - Kholoud Al-ZainDocument30 pagesOrthopedic History Taking: DR - Kholoud Al-ZainJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument1 pageGoutJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Disease List PDFDocument139 pagesCardiology Disease List PDFJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- History and Physical Exam of Depressed College StudentDocument6 pagesHistory and Physical Exam of Depressed College StudentJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Medicine Annotated Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesMedicine Annotated Multiple ChoiceJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Paranasal SinusesDocument7 pagesParanasal SinusesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Motor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistDocument36 pagesMotor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- Pediatric History FormDocument2 pagesPediatric History FormJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Eladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel VaultsDocument18 pagesEladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel Vaultssoniamoise100% (1)
- Television: Operating InstructionsDocument40 pagesTelevision: Operating InstructionsNitin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- C++ Practical FileDocument15 pagesC++ Practical FilePreetish ChandraNo ratings yet
- Subtracting-Fractions-Unlike DenominatorsDocument2 pagesSubtracting-Fractions-Unlike Denominatorsapi-3953531900% (1)
- M and S Code of ConductDocument43 pagesM and S Code of ConductpeachdramaNo ratings yet
- PuppetsDocument11 pagesPuppetsShar Nur JeanNo ratings yet
- Barker-Choucalas, Vida PDFDocument176 pagesBarker-Choucalas, Vida PDFAnn GarbinNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument31 pagesNumerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equationschandu3072002100% (1)
- Test Engleza 8Document6 pagesTest Engleza 8Adriana SanduNo ratings yet
- 935 Ubi PBK Statement PDFDocument20 pages935 Ubi PBK Statement PDFTECHNO ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- 457 PDFDocument8 pages457 PDFAbbey Joy CollanoNo ratings yet
- The Unseelie Prince Maze of Shadows Book 1 by Kathryn AnnDocument267 pagesThe Unseelie Prince Maze of Shadows Book 1 by Kathryn Annanissa Hri50% (2)
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument13 pagesSheet Metal FormingFranklin SilvaNo ratings yet
- Protección Fuego MetalDocument16 pagesProtección Fuego MetalTracy Mora ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Document9 pagesChapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Khaerul UmamNo ratings yet
- Case NoDocument13 pagesCase NoLaurente JessicaNo ratings yet
- Oxyacetylene Welding (OAW)Document26 pagesOxyacetylene Welding (OAW)athyrahNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Hrm353 L1Document26 pagesCourse Code: Hrm353 L1Jaskiran KaurNo ratings yet
- DMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFDocument305 pagesDMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFpooja100% (1)
- Asset Valuation: Debt Investments: Analysis and Valuation: 1 2 N M 1 2 N MDocument23 pagesAsset Valuation: Debt Investments: Analysis and Valuation: 1 2 N M 1 2 N MSirSmirkNo ratings yet
- DRUG LISTDocument45 pagesDRUG LISTAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- MCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutDocument3 pagesMCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutPR.comNo ratings yet
- PP 12 Maths 2024 2Document21 pagesPP 12 Maths 2024 2Risika SinghNo ratings yet
- Admission Notice 2023-24Document2 pagesAdmission Notice 2023-24Galav PareekNo ratings yet
- Borang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2Document2 pagesBorang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2ajai1010No ratings yet
- Fisiologia de KatzDocument663 pagesFisiologia de KatzOscar Gascon100% (1)
- Isaac Asimov - "Nightfall"Document20 pagesIsaac Asimov - "Nightfall"Aditya Sharma100% (1)
- Awwa c207 Flanges Spec SheetDocument13 pagesAwwa c207 Flanges Spec SheetVincent DiepNo ratings yet
- Electronic Throttle ControlDocument67 pagesElectronic Throttle Controlmkisa70100% (1)
- CVCITC Smoke-Free Workplace Policy & ProgramDocument2 pagesCVCITC Smoke-Free Workplace Policy & ProgramKristine Joy CabujatNo ratings yet