Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flowes and Germination Work Sheet
Uploaded by
api-2386434120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
698 views6 pagesOriginal Title
flowes and germination work sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
698 views6 pagesFlowes and Germination Work Sheet
Uploaded by
api-238643412Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Flowers and plant reproduction |
Flower cut in half te show the main structures
Key:
1 Patal {Veliow) Attrects insects with eplour and scent
2 Sepal (Oark green) Protects flower in bud and when closed
3 Aeesptwcle tigrtareen) — Supportsall the other parts of the flower
4 Hactary (Grange) Produces nectar to attract and reward insects
5 Ovary (Wambrown) Contains one or mora OVULES
6 Gvule (Purple) Contains an OVUM
7 Style (Light rea) Supporis the STIGMA
8 Stigma (Dark reef) Catches POLLEN on ite sticky surface:
9 Carpel Unit containing all the female parts of the flower
10 Anther (Dark ou} POLLEN producing structure
11 Filament (light ued Stalk supporting the ANTHER,
12 Stamen Unit cantaining all the male parts of the flower
Flowers and plant reproduction
ltyou opaned alfower bud {ofthe type shown) by peeling off eaai layer separately, in which order
‘would the various structures appear?
How many petals would there ba in a completa Mower ef the type shown?
Insects fead on pollen, which is rch in protein, on what eico do thay ofen foed when wieling
flowers, andl in whet isa rich?
Flowers are not usualy set pollinated (solHtertised) despite having beth sale and femate
reproductive structures. What is the advantage of erass-pollination aid haw do you think that
flowers ensuee that it happens?
Complete the fllowing paragraph using ihe words provided below. Each wordmay be used mara
than once oF not at all,
‘style - potien - receptacie - anthers - scented - nectaries - sepals - stamens - transfer -
coloured - stigma nectar - ovaries - petals - reproduetive
Flowers re plants. structures, Thase which recruft Insects to...
pollen trom the. Of en Bower to tha
atactive to them. They tend to have
and reward the right visitors wah sugary
excess vinen a fowar Is In bud the actual reproductive sbuctures, the
andthe <8 hrmature, an he Goged petals ae pretectt
comnes THE wha ower supparted bythe .
°
280,
Hope
2248
a9
“ Bollem grein | Pollen gratn
Dark blue) Wry ht Light biue) suck te
and cantied by wird | abdomen of INSECT
‘estried pretom (fi@80 are Brown - rat wings)
‘Canes lgo qoartiles ony ptien pans out Pick up polen from one Bowe 3
‘sl espoted enters on one plan ard Gt 11h ‘caries # urinary Wo others (also
ssa of ote = role raredom cop by a Bia an rae)
Feritisaion -to FUSIONal fie male muclous from a pole grain ard ths fomale muciaus trom anvovury |
Peltier gratin @ark bo) SS —— Pella grain cigm pie
From anothetypa of war. There i ‘uch o rice of STIOMA ol same
not COMPATIBLE and HO growth of a type of ower, tergfora COMPATIBLE,
polis nse ard gona @ POLLEN TUBE
Shgona pare ray
‘icky sures lo cach POLLEN ——— Bolen tube cigt peo
‘Grows dome theough stigma, tye
‘anc ovary wall. Delivers MALE
Stylo wigneresy —— NUCLEUS wo the OVUM theaigh
ihe MICROPYLE
Guery gm prow) —_
o lale nucleus
Syl (Purple ‘GAMETE mucteus earning hat the
‘Usual number of CHROMOSOMES
Deum (ore by
Female nucleus ~
GAMETE NUCLEUS cantaining =~ Micropyle
hall the ysual number of IROVULE through wich
CHROVOSOMES, POLLEN TUBE grows,
Carpe’ of insect-pollinated flower - cid ope to show how lerisalan takes plac
‘Summ
-r Foailisalion
Fomale nucleus + Male nucleus - > ZYGOTE => EMBRYO
(FUSION) (SEED)
Distinguish clearly betwoen sell- and crose-pellinatlon.
Expiain briefly how Inseets end atter animals can pollinate flawers.
‘Why do wind-ollinated plants tand to be less brightly coloured. unscented, and preduce much
larger quantities of pallon then insect-pollinated onde?
‘Outline the raute taken by te male nucleus tron a polen grain arriving on the stigma ot flower,
ta its fusion with the famale nucieus in the ovurn.
Winy do some pollen grains landing on the stigma af a lower not graw a palien tube?
How is a zygote toemod, and what dose it develop into, in a seed?
Sexual repraduction, using flowers, is] complicated procass compared to the various forme at
sexual reproduction (og wsing runnars or bubba). Wht Is the great aovantago of aseKust
reproduction? Try ta wxolain your answer care‘uly.
Why do most plants encourage cross-polination? Try to find out how they have avalvad to
prevent self-potiinatien.
Complete the folowing paragraph using the words provided Belew. Each word may be used more
than one oF wot at al
hucleus - vast - anthers - embrya - sticky - grain - wind - cross - tube - exposed - correct -
ovuie -7ygote - flowering - random. ovary. stigma -fuee -ingect -femako- nectar -transier.
enleropyle - unintentionally - animals
Ma Bt econ PRAMS BE. Painted. This involves the _. ol palloe from
the ofene plant to Bie. of anther, . inated lowers producs
- ‘quantities of ight pollen it... anthers. The winds: action 1g relatively
OOO. making the process wasteful pollinated towers reward the insects or
otrer Dwi. ‘and pollen for cn Wranstering paller,
stuck to thair bodliss, as they feed. Once om tr . surface of the sigma Me
type of pelien will begin togrow a pollen . Thisgrows dawn through the:
ad, carrying Blemale 0...» Entering te owute via the
nucteusis able to... fe. RbelBUs.i fhe OVUM fo fo
This develops to Become the wa sonueue i Be 6
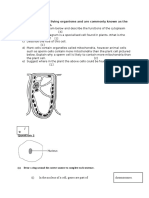
Seed structure and germination
_--— Mieropyle
|) Abrosdibeanseed FAA ea mm (etsex) Poin ot amachment to pod
> Twxarf@ (Lignterowny Tough prowecive
win
— Plwcnale (Greeny
‘Brose bean seed - Becomes SHOOT of new plant
‘cut open to how main parts: Reade! 9 (Orange) Embryo
Becomes COT of née plant
> Golyledon cretiew
Le" ENERGY sloro to tel gosh curing
2 Sennen
ood bean son ,
ce — Puomate (reer .
Leioly em
LC }——— Radel orange) rye
[Germination of abroad basn seed
Phunowle_
‘Ground level
1
Key: (Orange)
V DORMANT sseatburied inthe sail,
2 S00L becomes WARMER and WETTER and GERMINATION starté - WATER absorbed, TESTA spits. a
seed cxpands, fotd resarvos in the COTYLEDOM are mobifsed and RADIGLE grows downs
3 _ WATER continues ta ba absorbed, ROOT SYSTEM develops ancertamges, PLUMULE begins 10 grow
4
upwards; COTYLEDONS stl footing all graat
[ROOTS now abeorbing water rectly, EMBRYONIC LEAVES of PLUMULE nom clmar of the ground and
beginning io PHOTOSYNTHESISE. GOTYLEOONS naw much less importa,
[This type of GERMINATION seated HYPOGEAL, because the GOTYLEOONS and TESTA remain
vreorgrourd |
8.
Seed structure and germinat ion
Name the main parts ofa brosa bean seed,
‘Outline the role seeds play in the Ile eyele of a plant, and explain ie importance of the tough
pprotectiva skin or testa,
Why is the broad bean called a dicolyledanous plant, and what de the estyledons de during
germination?
Wat does the teem dormant mean, and why sees a busiad sued only germinate when ee
Cconeitions bacome eultably warm and wat?
How can jou sirlate te conditions nekossary foe garmination, without sel, at hama or in the
laboratory?
Plants tondto produce large numbers of sends, why ls thls necessary?
When aflower is feniieed, azygate is formed, Which pat ol the seecidoes tis develop into, what
are the twa main parts ofthe structure, and whet do they forms dusing germination?
Complete the fotowing paragraph using the words provided bela. Each word may be used mor
than ones er nat at all
plumule - released - shoot - testa -fertllsed - absorption - soll - hilum - two - warm = water
= reserves-germinates- wet-pads -radicle-energy-tuel - embrye-germinate -cotyledans
= food
‘Seods are ormedirom
‘each seed altached by its
Hlowers. Inbrosd beans the sueds are groupedin
Insige he tough, protective.
‘and roo! fegpectively, if the saed
stores from wtih... .
~ sondlions ood wif start 1 nn
of water, COUSIN THE ooo tO SBM, aN the
TRB errr OQUEE 1, - this
shrnk as theirfoad. .
growth of the radiele-and then
‘growth igpre idee by the oaty
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Heart Key Words Match UpDocument1 pageHeart Key Words Match Upapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta Genetic FingerprintingDocument2 pagesTa Genetic Fingerprintingapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Heart TaDocument3 pagesHeart Taapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta 2017 Session RevisionDocument2 pagesTa 2017 Session Revisionapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Respiration TaDocument1 pageRespiration Taapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF AlveoliDocument2 pagesPDF Alveoliapi-238643412No ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument2 pagesWorksheetapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesTa Dna Replicationapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF HaemoglobinDocument3 pagesPDF Haemoglobinapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Level Ladder RespirationDocument1 pageLevel Ladder Respirationapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta KaryogramDocument1 pageTa Karyogramapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pagePDF Mitosis and Meiosisapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Structures Part 1Document10 pagesStructures Part 1api-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF ProteinsDocument1 pagePDF Proteinsapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesPDF Protein Synthesisapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF PubertyDocument1 pagePDF Pubertyapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta Lactobacilus and PasteurDocument3 pagesTa Lactobacilus and Pasteurapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Crocodile Haemoglobin Article QuestionsDocument1 pageCrocodile Haemoglobin Article Questionsapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta Gills ExpDocument1 pageTa Gills Expapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Spot The Difference Worksheet ReproductionDocument4 pagesSpot The Difference Worksheet Reproductionapi-238643412No ratings yet
- PDF ReproductionDocument1 pagePDF Reproductionapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Fermentation of YeastDocument2 pagesFermentation of Yeastapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Rods and Cones TaDocument1 pageRods and Cones Taapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Flowering Plants WorksheetDocument2 pagesFlowering Plants Worksheetapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Ta Fish AnatomyDocument2 pagesTa Fish Anatomyapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Term Test 1 PracticeDocument11 pagesTerm Test 1 Practiceapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Practice TestDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet Practice Testapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Hyperopia Myopia TaDocument1 pageHyperopia Myopia Taapi-238643412No ratings yet
- Accomodation and Lens TaDocument2 pagesAccomodation and Lens Taapi-238643412No ratings yet