Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electro Magnetic Waves M@trix Foundation
Uploaded by
djbabuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electro Magnetic Waves M@trix Foundation
Uploaded by
djbabuCopyright:
Available Formats
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
In electromagnetism, displacement current is a
quantity appearing in Maxwell's equations that is
defined in terms of the rate of change of electric
displacement field. Displacement current has
the units of electric current density, and it has an
associated magnetic field just as actual currents
do.
The idea was conceived by James Clerk Maxwell in
his 1861 paper On Physical Lines of Force, Part
III in connection with the displacement of electric
particles in a dielectric medium. Maxwell added
displacement current to the electric current term
in Ampre's Circuital Law. In his 1865 paper A
Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic
Field Maxwell used this amended version of
Ampre's Circuital Law to derive
the electromagnetic wave equation. This
derivation is now generally accepted as a
historical landmark in physics by virtue of uniting
electricity, magnetism and optics into one single
unified theory. The displacement current term is
now seen as a crucial addition that completed
Maxwell's equations and is necessary to explain
many phenomena, most particularly the existence
of electromagnetic waves.
M@trix
Maxwells Equations
Lets summarize all the electromagnetic
equations we have learned so far, both integral
and differential forms:
1.
Gauss Law for electric field:
E
E dA
S
E
0
or
2.
Gauss Law for magnetic field:
B
B dA 0
S
B 0
or
charges)
The electric displacement field is defined as:
3.
(no magnetic monopole
Faradays Law of Induction:
D= 0 E + P
E ds
where:
B dA
t S
0 is the permittivity of free space
E is the electric field intensity
P is the polarization of the medium
4.
defines the displacement current density, which
JD= 0
E P
+
t t
Amperes Law and Maxwells Law of
Induction:
B ds 0 0
C
d
E dA 0ienc
dt S
B 0 0
or
Electromagnetic Wave - radiation consisting of
waves of energy associated with electric and
magnetic fields resulting from the acceleration of
B
t
or
Differentiating this equation with respect to time
therefore has two components in a dielectric.
qenc
0
E
0 j
t
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
M@trix
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
M@trix
Uses of X-ray
1. Medical uses (to see the bones, teeth etc)
2. Crystallography : to determine the molecular
structure of various metals & crystals
3. Metallurgy : to see the hidden (or unseen)
flaws, cracks, malformations in structural bodies.
4.Airport security scanners use X-rays for
inspecting the interior of luggage for security
threats before loading onto an aircraft.
5.In the treatment of skin diseases.
5.Many things that are invisible to the human eye
become visible under UV light.
UV rays
Uses
1.Ultraviolet waves are effective in killing
bacteria and viruses.
2 To preserve food.
3. To investigate finger prints.
4.To study atomic structure.
5. To study sample in the earth.
6. To clean surgical apparatus .
Ultraviolet light is a type of electromagnetic
radiation, as are radio waves, infrared
radiation, X-rays and gamma-rays. UV light,
which comes from the sun, is invisible to the
human eye. It makes black-light posters glow,
and is responsible for summer tans and
sunburns.
Ultraviolet (UV) is an electromagnetic
radiation with a wavelengthfrom 10 nm (30 PHz)
to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible
light but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is
present in sunlight. It is also produced by electric
arcs and specialized lights such as mercury-vapor
lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights.
Facts
1- UV light can damage the human skin.
2- UV light or phototherapy vitiligo treatment can
help create repigmentation.
3- Possible eye damage can result from high
doses of UV light, particularly to the cornea which
is a good absorber of UV light.
4- High doses of UV light can cause a temporary
clouding of the cornea; called 'snow-blindness'
and chronic doses have been tentatively linked to
the formation of cataracts.
Visible light is a form of electromagnetic (EM)
radiation, as are radio waves, infrared radiation,
ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and microwaves.
Generally, visible light is defined as the
wavelengths that are visible to most human
6.Sun tanning describes a darkening of the skin
(especially of fair-skinned individuals) in a natural
physiological response stimulated by exposure to
ultraviolet radiation from sunshine (or a sunbed).
7.A positive effect of UVB exposure is that it
induces the production of vitamin D in the skin.
Visible Light
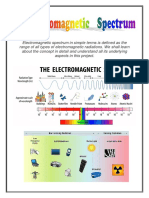
The spectrum of electromagnetic
radiations consists radiations of all ranges. This
spectrum is shown different radiations according
to their wavelength or frequency. The energy of
radiations is reciprocal to the wavelength of
radiations. So, the energy of radiations is
increased with decreasing the wavelength of
radiations. From all radiations, we cannot see all
by our eyes. Some are harmful rays like IR rays
but some are useful in various fields like X-rays
are used for X-rays treatments, radio waves are
communication rays etc. some part of this
spectrum is visible for us. These rays are
called visible rays. This is a small portion of the
electromagnetic spectrum.
Color
Wavelength
Frequency
violet
380450 nm 668789 THz
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
M@trix
eyes. ... This broad range of wavelengths is
known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
What is Visible Light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Human eye has the capability to detect or sense
some part of the complete electromagnetic
spectrum.
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
which is sensed by our human eye having
wavelength in the range between 380nm and
750nm is called Visible light. Visible Light travels
in straight line and the speed of light in vacuum is
equal to c = 2.99792458 108 m s1. This is
approximately taken as 3 108 m s1
Wavelength of visible is defined as the distance
between the two consecutive crests or between
two consecutive troughs. Wavelength of the
Visible Light Ranges from 380nm to 750 nm. In
the electromagnetic spectrum, Infrared rays has
higher wavelength than the visible rays and the
ultraviolet rays has smaller wavelength as
compared to the visible light.
Visible light facts
Wavelength: 380 to 750nm.
It travels in straight line.
Speed of light in vacuum is approx 3
108 m s1.
Light shows both types of nature, particle
as well as wave.
Light shows the properties like reflection
refraction, absorption, diffraction etc.
Uses of IR Ray
Infrared radiation is used to de-ice the
wings of aircraft
It is used in cooking and heating food
In industries they are used for welding
plastics, drying prints, curing (process of
hardening) coatings etc.
Used in locating missing people and
people trapped under collapsed buildings
blue
450495 nm 606668 THz
green
495570 nm 526606 THz
yellow
570590 nm 508526 THz
orang
e
red
590620 nm 484508 THz
620750 nm 400484 THz
Infrared radiation
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic
radiation, as are radio waves, ultraviolet
radiation, X-rays and microwaves. Infrared(IR)
light is the part of the EM spectrum that people
encounter most in everyday life, although much
of it goes unnoticed. It is invisible to human eyes,
but people can feel it as heat.
Infrared (IR) light is electromagnetic radiation with
longer wavelengths than those of visible light,
extending from the nominal red edge of the
visible spectrum at 0.74 micrometres (m) to 300
m. This range of wavelengths corresponds to a
frequency range of approximately 1 to 400 THz,
and includes most of the thermal radiation
emitted by objects near room temperature.
Infrared light is emitted or absorbed by molecules
when they change their rotational-vibrational
movements.
*** infrared radiation was first discovered in 1800
by astronomer William Herschel.
4. The infrared radiations lie in between
visible and microwave regions of the
EM spectrum.
5. The infrared can be used in
astronomical study of stars and
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
(Infrared imaging devices are used)
Used by fire-fighters to find people inside
smoke filled buildings (Infrared imaging
devices are used)
Used in archaeology to study ancient
civilizations.
Used in night vision devices to observe
animals or people using the
phenomenon called infrared illumination.
The observant will not know that they are
being observed.
Used in body heating of a patient.
To heat plants in green house.
To send signals from pone place to other.
The infrared radiation or waves can be
defined as waves with the wavelength in the
range of 0.75 m to 1 mm in the EM
spectrum.
Infrared Waves Facts
Back to Top
1. Infrared Waves can be used for
muscle relaxation and pain reliever.
2. The IR detector needs to cool by
helium so as to avoid the
interference due to heat generated
by the detector itself.
3. It is used in several areas of our day
to day life.
5.Heating:
Infrared are increasing the popularity as the rays
used in cooking for heating. The infrared can heat
the opaque objects instead of the air around
them. These are also used in industries for
wielding, drying, etc.
6. There are other uses of the infrared in the field
of astronomy, meterology, Spectroscopy, History,
Biological systems.
Microwave
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic
radiation with wavelengths ranging from one
M@trix
galaxies.
Uses of IR technique wise
1.Communications:
Some of these wavelengths are used in optical
communication to carry the information from one
place to another. It is also used in remote control,
mobile phone, laptop, PDAs, etc. to have a
channel for short range communication, like
between the mobile and laptop or between TV
and remote control.
2.Thermal imaging:
Thermal imaging or thermography is used to
determine the temperature of an object remotely.
This is used mostly in industries and military
operations.
3.Night vision:
The night vision, which is seeing in night (or dark
black) without the use of external light, is a
device which uses the ambient light of the
atmosphere. It amplifies the ambient light and
helps to see things in dark without the use of light
to illuminate the area of interest.
4.Missile Tracking:
It is used in missile technology to follow its target,
since everything emit infrared rays so the missile
seeks the infrared and hit the target based on the
heat emitted by it. these types of missile are
known as heat seekers.
Later Marconi found a way of using these radio
waves to carry sound. In 1907 he was able to
transmit the first sound signal across the Atlantic.
Marconi's discovery was the key to the
widespread use of radio waves for
communication.
Waves with relatively law frequencies, or
long wavelengths are known as radio
waves.
The Radio Wave Wavelength lies in 1 millimeter to
100,000 kilometers. And the Radio Wave
Frequency lies between as low as 3 Hz to as high
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
millimeter to 30cm ; with frequencies between
300 MHz (100 cm) and 300 GHz (0.1 cm).
The existence of radio waves was predicted
by James Clerk Maxwell in 1864 from his
equations. In 1888, Heinrich Hertz was the first to
demonstrate the existence of radio waves.
M@trix
as 300 GHz. The radio waves are generally used
in communication systems. The Radio Wave
Frequency band is generally divided into several
categories according to their wavelength and
uses.
Uses of Microwaves
1. In Navigation
2. In Radar uses of microwave radiation to detect
the range, speed ,and other characteristics of
remote objects.
3. Most radio astronomy uses microwaves.
4. In Heating and power application like
Microwave Owen.
5. In Spectroscopy
Radio Waves
In 1887 Heinrich Hertz was experimenting with a
spark coil. He noticed that whenever it produces a
spark, another spark operated across the ends of
an open metal ring several metres away. Radio
waves, produced by the first spark, had been
transmitted across the room.
Long Wave Radio
The long wave radio refers to those parts of the
radio spectrum which lies in the longer
wavelength region. The definition of the long
wave radio is different in different countries. Like
in U.S. the long wave radio lies in the frequency
upto 550 KHz. The long wave radio travels
between two points due to surface wave or sky
wave propagation. These waves attenuated to a
large extent when covering larger distance and
are hence suitable only for the short distance
communications.
Short Wave Radio
The short wave radio refers to those parts of the
radio spectrum which lies in the short wavelength
region of the radio wave spectrum. The short
wavelength region is region above the Medium
frequencies. The short wave have the properties
The Radio Wave Speed is equal to the speed of
the light since the radio wave also comes under
the category of EM waves. The speed of the radio
wave also depends on several factors when they
are travelling through the medium.
Radio Wave Uses
There are several uses of the radio wave. The
important one is the transfer of the information
from one place to another without the use of the
wires.
1.
2.
3.
The radio waves are used in
communication systems like TV
broadcasting, radio broadcasting, mobile
communication, etc.
The radio waves are used in navigation of
the ships and aircrafts.
The radio waves are used by Global
Positioning Satellite to precisely pin point
the location of the targets.
Electro Magnetic Waves
Foundation
of travelling the longer distance with the lesser
attenuation than that of the long wave radio
waves. These waves travel by the reflection
between earths surface and the ionosphere.
These waves can travel any distance on the earth.
It is not unusual to pick a radio station of a distant
country when a person is tuning a radio set on
short waves.
4.
Radio Wave Facts
1. The radio waves are used to carry
information from one place to another by
the use of air as a medium.
2. The speed of radio waves is equal to the
speed of the light.
3. The radio wave can travels larger distance
with very less attenuation and hence can
be used for communication without the
need of the wired medium.
7.
5.
6.
8.
9.
M@trix
The radio telescopes are used to study
the radio waves emitted by the far flung
galaxies and the star to understand their
origins and characteristics.
The radio waves (20 Hz to 2000 Hz) are
used by us to communicate with each
other.
The radio waves are also used in remote
control of toys.
The radio waves in the ultrasonic region
are used by bats to navigate, since bats
do not have eyes and they can only
navigate by the use of listening the echo
of the ultrasonic wave which they emit.
The radio waves in the ultrasonic region
are used to detect the sea objects and
also used to detection of flaws in the
manufactured products.
Ultrasound, which lies in the radio wave
range, is used in medical science to
detect several diseases. The ultrasonic
waves are also used in cleaning the teeth.
You might also like
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Light: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 pagesLight: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchRonaldNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument11 pagesEM WavesHomok Noki100% (1)
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Effect of Electromagnetic Radiation On Human BeingsDocument26 pagesEffect of Electromagnetic Radiation On Human Beingsdrmarwayaseen85No ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesputri_latifah100% (3)
- What Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarDocument18 pagesWhat Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarAndrei Cojanu100% (1)
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAk R71No ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 1Document20 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 1Ma'am LeiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- Source of EnergyDocument6 pagesSource of Energypg2No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzJuan Carlos Isaza JacomeNo ratings yet
- 8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesDocument3 pages8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesRamananNo ratings yet
- Physics1101 - Course MaterialDocument332 pagesPhysics1101 - Course MaterialAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 2Document138 pagesElectrotherapy 2nagyrashad123No ratings yet
- Light: Modern PhysicsDocument5 pagesLight: Modern PhysicsJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument34 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumShinpay doodles100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Waves ProjectDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Waves ProjectDiya Kumar79% (53)
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceseradillajoshgabrielNo ratings yet
- Document (4) - 1Document9 pagesDocument (4) - 1Justin DugangNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic PDFDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic PDFkanishksajankar735No ratings yet
- Alziya Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesAlziya Physics ProjectMohammad AyanNo ratings yet
- 104 Lec 1Document27 pages104 Lec 1Rezwan RashikNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumKuruluş OsmanNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Charging of Mobile PhonesDocument18 pagesWireless Charging of Mobile PhonesChakraPaniNo ratings yet
- Wireless Charging of Mobile PhonesDocument18 pagesWireless Charging of Mobile PhonesChakraPaniNo ratings yet
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Definition of Light WavesDocument9 pagesDefinition of Light WavesJF BatucalNo ratings yet
- Physics - Electromagnetic WavesDocument3 pagesPhysics - Electromagnetic WavesALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Radiasi Non PengionDocument13 pagesRadiasi Non PengionNurul Ekawati PNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Input 1 To 5Document57 pagesInput 1 To 5Starskie MonacarNo ratings yet
- Elecromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElecromagnetic SpectrumTIJIN ABE THOMASNo ratings yet
- Light: "Visible Light" Redirects Here. For Light That Cannot Be Seen With Human Eye, See - For Other Uses, See andDocument2 pagesLight: "Visible Light" Redirects Here. For Light That Cannot Be Seen With Human Eye, See - For Other Uses, See andMatías Navarro PricolliNo ratings yet
- Wave Nature of Light: Basic Properties of Waves: Amplitude, Wavelength, and FrequencyDocument4 pagesWave Nature of Light: Basic Properties of Waves: Amplitude, Wavelength, and FrequencyJaden MoniezNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics ProjectGanesh harkalNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic WavesNjike ChigbuNo ratings yet
- 9042 EMWavesDocument11 pages9042 EMWavescheukhin ngNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Document7 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Nur-shima SakilinNo ratings yet
- Waves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pagesWaves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument20 pagesLesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumsubaldojenniferNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic WavegabezneNo ratings yet
- Ec Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesEc Seminar ReportDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Module - 1 Lecture Notes - 2: Remote Sensing: Introduction and Basic Concepts EMR SpectrumDocument9 pagesModule - 1 Lecture Notes - 2: Remote Sensing: Introduction and Basic Concepts EMR SpectrumYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Integrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiDocument49 pagesIntegrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiFabricio Echeverri LondoñoNo ratings yet
- n3 Physics Revision Notes - Waves and Radiation Farr HsDocument10 pagesn3 Physics Revision Notes - Waves and Radiation Farr HsNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: PropertiesDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: PropertiesdjbabuNo ratings yet
- Physics em WavesDocument1 pagePhysics em WavesdjbabuNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch15 Communication SystemsDocument4 pages12 Physics Notes Ch15 Communication SystemsMayank Saini100% (1)
- Maxwell EquationsDocument5 pagesMaxwell EquationsdjbabuNo ratings yet
- Metal Spinning PDFDocument86 pagesMetal Spinning PDFloosenut100% (1)
- Plastics - Polyacrylamide Materials - Designation System and SpecificationDocument20 pagesPlastics - Polyacrylamide Materials - Designation System and SpecificationDevesh Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- DR Perla D Santos OcampoDocument2 pagesDR Perla D Santos OcampoAiza CabolesNo ratings yet
- MISC - MSDS - 3 in 1 Oil PDFDocument4 pagesMISC - MSDS - 3 in 1 Oil PDFFifi UmmahNo ratings yet
- INDENTIFICATIONDocument6 pagesINDENTIFICATIONMomina HaiderNo ratings yet
- A 1033 - 04 Qtewmzm - PDFDocument14 pagesA 1033 - 04 Qtewmzm - PDFTiến Lượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Assignment 2013Document10 pagesThermal Physics Assignment 2013asdsadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Eccentricity On Analysis and Design of Isolated FootingsDocument18 pagesEffect of Eccentricity On Analysis and Design of Isolated Footingsप्रभु नाथ सिंहNo ratings yet
- ChemBioEng Reviews - 2019 - BL Ker - Characterization of Activated Carbon Adsorbents State of The Art and NovelDocument20 pagesChemBioEng Reviews - 2019 - BL Ker - Characterization of Activated Carbon Adsorbents State of The Art and NovelgueabdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Dissertation TitlesDocument5 pagesMechanical Engineering Dissertation TitlesCustomPaperServicesUK100% (1)
- Agip Eni Alaria-2 - 3 - 7Document2 pagesAgip Eni Alaria-2 - 3 - 7Andre WantoNo ratings yet
- TelusDocument3 pagesTelusGembonz Crew Gon'z SpeedNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Part 1Document19 pagesElectrochemistry Part 1Jenny ArutaNo ratings yet
- Students Guide For Entry Test Info)Document13 pagesStudents Guide For Entry Test Info)Sunny MudassarNo ratings yet
- Sand To Silicon 22nm VersionDocument18 pagesSand To Silicon 22nm VersionDavid Rubio SaezNo ratings yet
- I - Grades & Materilas InfoDocument32 pagesI - Grades & Materilas InfoEswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Batubara Dari Channel-Pit Menuju Stockpile: Pt. Kuasing Inti MakmurDocument10 pagesQuality Control Batubara Dari Channel-Pit Menuju Stockpile: Pt. Kuasing Inti MakmurDiiNo ratings yet
- Lec8 RTMDocument31 pagesLec8 RTMmoonrock1No ratings yet
- 158 Unibar 700 2 I8Document1 page158 Unibar 700 2 I8Selvaraji MuthuNo ratings yet
- Electronics - 1 Lecture 13Document37 pagesElectronics - 1 Lecture 13rizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Tl-Isover S en PDFDocument2 pagesTl-Isover S en PDFBogdan MucenicaNo ratings yet
- Thumb RuleDocument13 pagesThumb RuleAtiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9869 0099 01e Grouting Solutions Technical Specification EnglishDocument7 pages9869 0099 01e Grouting Solutions Technical Specification Englishignacio.garcia11No ratings yet
- Lip SealDocument31 pagesLip SealVineet ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- High Frontier 3rd Card ListDocument14 pagesHigh Frontier 3rd Card ListfireheartNo ratings yet
- Uniform Mechanical Code - 2009 Chapter 5Document34 pagesUniform Mechanical Code - 2009 Chapter 5memosplumbingNo ratings yet
- Cyberware AlternityDocument25 pagesCyberware Alternitycymru devourer100% (1)
- Can Man Alter MarsDocument1 pageCan Man Alter MarsJan Gabriel Gimao100% (2)
- TFP330 10 2013Document4 pagesTFP330 10 2013Mihai CatalinNo ratings yet
- Eurovent Energy Efficiency CalculatorDocument1 pageEurovent Energy Efficiency CalculatorPradeep Sukumaran100% (1)