Professional Documents
Culture Documents
40 Minutes - Discussion - Brochure - Question and Answer - Demonstration
Uploaded by
Connie TayamenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
40 Minutes - Discussion - Brochure - Question and Answer - Demonstration
Uploaded by
Connie TayamenCopyright:
Available Formats
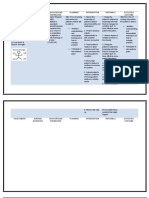
OBJECTIVES
General Objective:
At the end of the shift, the
patient and the family will
be able to gain knowledge
about CVA, and how to
care of patient with CVA.
Specific Objectives:
After 40 minutes of nursepatient
and
family
interaction, the patient
and its family will be able
to:
CONTENT
I. Cerebrovascular Accident
a. Definition of terms
b. Etiology
c. Incidence
II. Risk Factors
a. Diseases related to CVA
b. Environmental factors
contributing to CVA
III. Signs and Symptoms
a. Motor Loss
1. Define CVA
b. Communication Loss
2. Identify the risk factors
c. Perceptual Disturbances
of CVA
3. Identify the signs and
symptoms
4. Demonstrate activities
allowed for the patient
when is discharged
IV. Activities allowed when
patient is discharged
a. Hygiene and Grooming
b. Ambulation and Transferring
c. Exercises
TIME ALLOTMENT
40 minutes
TEACHING LEARNING
RESOURCES
- Discussion
- Brochure
EVALUATION
PARAMETERS
- Question and
Answer
- Demonstration
OBJECTIVES
CONTENT
TIME ALLOTMENT
General Objective:
At the end of the shift, the
patient and the family will
be able to gain knowledge
about CVA, and how to
care of patient with CVA.
Specific Objectives:
After 40 minutes of nursepatient
and
family
interaction, the patient
and its family will be able
to:
TEACHING LEARNING
RESOURCES
- Discussion
- Brochure
CVA (Cerebrovascular Accident), or
also known as brain attack is a
5 minutes
EVALUATION
PARAMETERS
- Question and
Answer
- Demonstration
1. Define CVA
2. Identify the risk factors
of CVA
3. Identify the signs and
symptoms
4. Demonstrate activities
allowed for the patient
when is discharged
sudden loss of function resulting
from disruption of blood supply to a
part of the brain.
-
Previous Transient Ischemic Attack
Hypertension
Cardiac Diseases
Congestive Heart Failure
Diabetes Mellitus
Cigarette Smoking
Obesity
Sedentary Lifestyle
High Cholesterol
Atherosclerosis
Use of Oral Contraceptives
10 minutes
- Numbness or weakness of face
and extremities
- Confusion or changes in mentation
- Problems with speech or
understanding speech
- Visual disturbance
- Difficulty in walking, loss of
balance, and dizziness
- Sudden severe headache
10 minutes
- Instruct the relative to stand on
patients weak side and place hand
under patients weak arm when the
patient is unable to walk on her
own
15 minutes
- Encourage patient to use her
stronger side of her body if
possible.
- Encourage the patient to use
ambulation devices like can or
walker when trying to ambulate by
herself
- Instruct the family of the patient
to always look after the patient
when she is trying to walk alone
- When the patient is tired of
ambulation, allow the patient to
rest
You might also like
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument13 pagesEmergency and Disaster Nursingkarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Short Version Bls - CPR 2012 (Infant&Child) OutlineDocument157 pagesShort Version Bls - CPR 2012 (Infant&Child) OutlineRandyNo ratings yet
- Medical Case 3: Vincent Brody: Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesMedical Case 3: Vincent Brody: Guided Reflection Questionsapi-546220765No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument36 pagesAttachmentgammeewaakkenneeNo ratings yet
- Possible NCP For CVDDocument6 pagesPossible NCP For CVDVincent Bulla50% (2)
- Wound care and airway clearanceDocument5 pagesWound care and airway clearanceRachel Anne Ascaño-DavidNo ratings yet
- Simman 2024Document54 pagesSimman 2024Doshi SahilNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument171 pagesFirst AidJoseph RamirezNo ratings yet
- Wolverhampton NHS Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesWolverhampton NHS Interview QuestionsChristiana OnyinyeNo ratings yet
- Work Book For NSTP Autosaved 1Document9 pagesWork Book For NSTP Autosaved 1francisromanguevaraNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document12 pagesCase Study 4kalpeshjatavNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal Worksheet Guide (Final)Document10 pagesCompetency Appraisal Worksheet Guide (Final)Shan JanoloNo ratings yet
- Hospice Care PlanDocument9 pagesHospice Care PlanAmanda SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Medsurg 3Document22 pagesMedsurg 3eyesontheskyNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument19 pagesBasic Life SupportRishabh JoshiNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIVE DISORDERSDocument10 pagesDIGESTIVE DISORDERSLeila Acero Salinas100% (1)
- Presented by Mr. NAVJYOT SINGH Choudhary M.SC Nursing 1 Year Dept. of Pediatric NursingDocument44 pagesPresented by Mr. NAVJYOT SINGH Choudhary M.SC Nursing 1 Year Dept. of Pediatric NursingMarvieMayUmpadNo ratings yet
- Faye Glenn Abdellah's influence on nursing theoryDocument80 pagesFaye Glenn Abdellah's influence on nursing theoryLonnieAllenVirtudesNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document11 pagesCase Study 1kalpeshjatavNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Abdellah TheoryDocument6 pagesAbdellah TheorySimran ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Data/Cues Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Implementation RationaleDocument6 pagesData/Cues Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Implementation RationalePong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Clinical Scenario AssessmentsDocument4 pagesClinical Scenario AssessmentsarchanaNo ratings yet
- Abdel LahDocument7 pagesAbdel LahIshaBrijeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Oxfordmedicaleducation ABCDE AssessmentDocument4 pagesOxfordmedicaleducation ABCDE AssessmentEsteban TapiaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Reviewclobregas100% (3)
- Developing Standards of Patient CareDocument9 pagesDeveloping Standards of Patient CareNaveen Eldose80% (5)
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Managing Patients with Cerebrovascular DisordersDocument3 pagesManaging Patients with Cerebrovascular DisordersJrBong Semanero50% (2)
- Alterations in the Surgical Patient: Understanding Terminology, Procedures, and Nursing CareDocument122 pagesAlterations in the Surgical Patient: Understanding Terminology, Procedures, and Nursing CarezorrotranNo ratings yet
- Test V - Cortel W-O 2Document9 pagesTest V - Cortel W-O 2PaulAliboghaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument21 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisDrishti ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Nursing Care and Education for Surgical PatientsDocument122 pagesPreoperative Nursing Care and Education for Surgical PatientshkellyrnNo ratings yet
- Presented by Mr. NAVJYOT SINGH Choudhary M.SC Nursing 1 Year Dept. of Pediatric NursingDocument44 pagesPresented by Mr. NAVJYOT SINGH Choudhary M.SC Nursing 1 Year Dept. of Pediatric NursingBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Wse Week5Document4 pagesWse Week5api-302336744No ratings yet
- Medical EmergenciesDocument32 pagesMedical EmergenciesDharani Chowdary Kilari100% (1)
- Session Module DesignDocument7 pagesSession Module DesignLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document12 pagesCase Study 5kalpeshjatavNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument7 pagesDocxShannon GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Webinar: The Ultimate Algorithm To PASS Your NCLEX On Your Very Next AttemptDocument53 pagesNCLEX Webinar: The Ultimate Algorithm To PASS Your NCLEX On Your Very Next AttemptHudson OnsareNo ratings yet
- OT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument19 pagesOT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisAnnbe BarteNo ratings yet
- Curative and Rehabilitative Nursing Care Management of Clients in Acute Biologic CrisisDocument44 pagesCurative and Rehabilitative Nursing Care Management of Clients in Acute Biologic CrisisArgee AlonsabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 029Document6 pagesChapter 029Jackie JuddNo ratings yet
- End of Life CareDocument22 pagesEnd of Life CareMkindiNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching On Ta - HbsoDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching On Ta - Hbsomecz26No ratings yet
- PCDDocument15 pagesPCDana100% (1)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJose Benit DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Possible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsDocument4 pagesPossible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsVivi rikkaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Case StudiesDocument3 pagesMetabolism Case StudiesEpoy Bantawig0% (1)
- Goals of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient'S Response Independent Assessment DoneDocument5 pagesGoals of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient'S Response Independent Assessment DoneJo Ellie MarfilNo ratings yet
- Checklist ChokingDocument8 pagesChecklist ChokingFloyd Victor F. Tipay100% (2)
- Abdulla's TheoryDocument40 pagesAbdulla's TheorysOniEh pALNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions - Neurologic FunctionDocument3 pagesPractice Test Questions - Neurologic FunctioninjilbalazoNo ratings yet
- Preboard 5Document11 pagesPreboard 5Jona BartzNo ratings yet
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseFrom EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNo ratings yet
- Mastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyFrom EverandMastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study Guide: Your Nursing Assistant To Do Well In SchoolFrom EverandNursing Study Guide: Your Nursing Assistant To Do Well In SchoolRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Classification of Placenta PDFDocument5 pagesClassification of Placenta PDFAdarsh jainNo ratings yet
- SAFETY AND LOSS PREVENTION FOR CHEMICAL PROCESS FACILITIESDocument13 pagesSAFETY AND LOSS PREVENTION FOR CHEMICAL PROCESS FACILITIESKinosraj KumaranNo ratings yet
- Dod EngDocument2 pagesDod Engvk4415003No ratings yet
- ASME B31.4-2016 Pipeline Transportation Systems For Liquids and SlurriesDocument1 pageASME B31.4-2016 Pipeline Transportation Systems For Liquids and SlurriesJose Rodrigo Salguero DuranNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Hardware and SoftwareDocument13 pages1.1 Hardware and SoftwareNurhanis SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Features General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterDocument18 pagesFeatures General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterAntonioNobregaNo ratings yet
- CDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineDocument20 pagesCDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineCherry Len FaroniloNo ratings yet
- Learning To Solve Multiple Partial Differential Equations With DNNDocument4 pagesLearning To Solve Multiple Partial Differential Equations With DNNVichara PoolsNo ratings yet
- Polycab HT XlpeDocument33 pagesPolycab HT Xlpezafrikhan875No ratings yet
- Larrabee JChem Educ 1990,67,267Document3 pagesLarrabee JChem Educ 1990,67,267κ.μ.α «— Brakat»No ratings yet
- Guide to Conducting SAFOP StudiesDocument52 pagesGuide to Conducting SAFOP Studiesokemma79% (14)
- 100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Document9 pages100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Julian BarreraNo ratings yet
- Tiger 690 Conversion PDFDocument8 pagesTiger 690 Conversion PDFGerardo Esteban Lagos RojasNo ratings yet
- ASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESDocument18 pagesASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESMuadz AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- 10 01 Breather Filters GBDocument8 pages10 01 Breather Filters GBosuengNo ratings yet
- Sanoj Kumar - OriginalDocument5 pagesSanoj Kumar - OriginalHamid SaifNo ratings yet
- Delay-Tolerant NetworksDocument66 pagesDelay-Tolerant NetworksMegi YantoNo ratings yet
- Instrument To Be CalibratedDocument3 pagesInstrument To Be Calibratedsumit chauhanNo ratings yet
- Australian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1Document32 pagesAustralian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1binoyrajcrNo ratings yet
- Kaustubh Laturkar Fuel Cell ReportDocument3 pagesKaustubh Laturkar Fuel Cell Reportkos19188No ratings yet
- NTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesDocument2 pagesNTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesFreddy SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Li-ION Battery Charger FeaturesDocument2 pagesLi-ION Battery Charger Featureshariyadi aryoNo ratings yet
- Niryana Shoola DasaDocument7 pagesNiryana Shoola DasaSuryasukraNo ratings yet
- Comparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.Document72 pagesComparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.DavldSmith100% (1)
- Capacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeDocument22 pagesCapacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeZen ZeeNo ratings yet
- Production Management Midterm ReviewDocument21 pagesProduction Management Midterm Reviewielsiu21184No ratings yet
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangDocument4 pagesJournal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangSamah SamahNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisDocument4 pagesFinite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisJin Hwan KimNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris - Narrative TextDocument21 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris - Narrative TextFenny KartikaNo ratings yet
- Vertical Jaw Relation Recording MethodsDocument17 pagesVertical Jaw Relation Recording MethodsHarish VsNo ratings yet