Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 2 1
Uploaded by
api-3437523090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pages4 2 1
Uploaded by
api-343752309Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Carter and Leila
Biomedical Sciences Experimental Design
Purpose
Scientific research requires a logical progression of steps that clearly define and
focus the work being done. These steps are guided by a specific question or a
problem. Research is rarely linear. Instead, scientists must be flexible, creative, and
willing to change strategies. Persistence is essential as there are many more failures
than successes in research. These failures often result in new strategies and new
questions re-focusing research.
When designing an experimental procedure there are guidelines that will help you
keep a logical progression of steps. Experiments have controls which allow for
comparison and help prevent incorrect conclusions being made due to inconsistent
conditions impacting the data.
The following experimental design is a guideline to be used when creating
experiments in the PLTW Biomedical Science courses. It is not a strict scientific
method protocol. It is a guide to help you create logical, thoughtful and clearly
defined procedures for investigative work. You are expected to follow these
guidelines when designing experiments.
Use your Lab Journal for recording all experimental design work. When recording
your work write the number and title of each section as shown below. Following each
design step is an explanation (shown in italics), of the format that is to be used in
your lab journal for that specific step. The evaluation rubric is based on following the
steps of design and using the correct format to record the information in your journal.
Steps of Experimental Design
1. Identify the Problem or Question
What effect a persons heart rate?
2. Predict a solution to the problem or an answer to the question.
Variations in breath will cause an increase in a persons heart rate.
3. Design the experiment to be used to test your hypothesis.
1. Plug in the LabQuest Mini into your computer
2. Plug the Bluetooth heart rate monitor into the the Lab quest mini
3. Open Logger Pro on computer
4. Open file from Human Physiology with Vernier then open 03 Heart Rate
Vital Signe file
5. Hold hands on heart rate monitor and have the Bluetooth receivers arrow
facing upwards
2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Principles of Biomedical Science Biomedical Sciences Experimental Design Page 1
Carter and Leila
6. Then click the collect button
7. Let it collect data for 60 sec while sitting and breathing normal
8. Repeat this twice
9. Collect average
10. Rest for a minute
11. Let it collect data for 60 sec while sitting and not breathing
12. Repeat this twice
13. Collect average
14. Rest for a minute
15. Let it collect data for 60 sec while sitting and breathing rapidly
16. Repeat this twice
17. Collect average
18. Rest for a minute
4. Carry out the experiment.
Effects on Heart Rate
Breathing
Carter
Leila
Average
Normal
70
96
83
None
100
105
102.5
Rapid
170
89
129
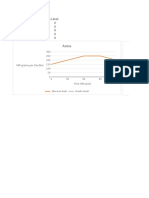
5. Analyze the data and observations.
Effects on Heart Rate
200
150
BPM 100
50
0
Normal
None
Rapidly
Rate of Breathing
carter
Leila
Average
6. State the conclusion.
2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Principles of Biomedical Science Biomedical Sciences Experimental Design Page 2
Carter and Leila
The hypothesis was correct in that variations in breathing will increase a persons
heart rate.
7. Summary Paragraph
In this experiment, the hypothesis was proven to be correct by the results in the data
table above. The reason why this happened is because a persons breathing is closely
related to a persons heart rate. Because in order for the heart to function properly it
needs and oxygen supply, and if this is affected so is the effectiveness of the heart. This
is true because any excertion on the heart will increase its rate. This experiment could
be improved by doing more trials and by having only one persons heart rate being
taken.
2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Principles of Biomedical Science Biomedical Sciences Experimental Design Page 3
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 3 2 5 A SR Client1hs 1Document2 pages3 2 5 A SR Client1hs 1api-343752309No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Patient 1 2Document8 pagesPatient 1 2api-343752309No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 2 4 3 P Exampleinteractivepresentation 1Document12 pages2 4 3 P Exampleinteractivepresentation 1api-343752309No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Biomed Presentation 1Document6 pagesBiomed Presentation 1api-343752309No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Case Reporthcandcd 3 1Document1 pageCase Reporthcandcd 3 1api-343752309No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Biochemist Project 2 - 1Document2 pagesBiochemist Project 2 - 1api-343752309No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 2 1 1 Diagnosing DiabetesDocument3 pages2 1 1 Diagnosing Diabetesapi-343752309No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 1 3 3 Case ReportDocument1 page1 3 3 Case Reportapi-343752309No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 1 1 6 Blood Splatter Analysis LabDocument2 pages1 1 6 Blood Splatter Analysis Labapi-343752309No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 20 ReadingsDocument7 pages20 ReadingstizonhanaNo ratings yet
- Educational Research Edu 309Document2 pagesEducational Research Edu 309SidraMalik100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Science in Coaching: Resource: Constraints Led Approach For AthletesDocument5 pagesScience in Coaching: Resource: Constraints Led Approach For AthletesAnomaly PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Rcms Thesis Defense Checklist: Presentation 1. Standardized Title SlideDocument2 pagesRcms Thesis Defense Checklist: Presentation 1. Standardized Title SlideZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Parts of A Whole As An Emerging PatternDocument17 pagesParts of A Whole As An Emerging PatternAiemiieee CañeteNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Menna Elsaoudy100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Islamic Education EssayDocument12 pagesIslamic Education EssaybabaneoNo ratings yet
- Letter To The Grand Duchess Christina by Galileo GalileiDocument10 pagesLetter To The Grand Duchess Christina by Galileo GalileimeNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetism? Introduction in Pictures: Branislav K. NikolićDocument14 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetism? Introduction in Pictures: Branislav K. NikolićGINNO OSMILLONo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- 2015-16 PLTW Launch Module DescriptionsDocument4 pages2015-16 PLTW Launch Module Descriptionsapi-264145284No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- RPH Scientific SkillsDocument5 pagesRPH Scientific SkillsMOHD HASRUL ASRAF BIN OTHMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Block1stsem v2-BSCSDocument4 pagesBlock1stsem v2-BSCSAngella QuisanNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Genetically Modified Organisms and Biosafety PDFDocument47 pagesGenetically Modified Organisms and Biosafety PDFrinda78No ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Perpertual Succour Academy, IncDocument4 pagesResearch Methodology: Perpertual Succour Academy, IncKen FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- PR1 Resaerch PaperDocument37 pagesPR1 Resaerch PaperKurt Marvin4No ratings yet
- Workshop Ii: Assessing Process Skills: Assessing For Learning Facilitator's GuideDocument73 pagesWorkshop Ii: Assessing Process Skills: Assessing For Learning Facilitator's Guidemutiara ramadhanNo ratings yet
- PART 1 Understanding CultureDocument24 pagesPART 1 Understanding Culturekathryn sorianoNo ratings yet
- 06 TheFinishersFormula 03 Focus Cal Newport TranscriptDocument23 pages06 TheFinishersFormula 03 Focus Cal Newport Transcriptcitad100% (2)
- One Sample T Test PDFDocument10 pagesOne Sample T Test PDFMuhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Sociology Introducing Sociology Class 11Document112 pagesSociology Introducing Sociology Class 11आरम्भNo ratings yet
- 2020 BatchprofileDocument102 pages2020 Batchprofileprasoon sahuNo ratings yet
- MICE Assignment 2 (Full Version)Document16 pagesMICE Assignment 2 (Full Version)Ting TingNo ratings yet
- For OlgaDocument16 pagesFor OlgaEscu NykuNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument24 pagesScientific MethodGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Striking Words and PhrasesDocument3 pagesStriking Words and Phrasesapi-299102530No ratings yet
- VDI2221Document8 pagesVDI2221hansen_golsvokNo ratings yet
- IOPS311 Reading Package-1Document233 pagesIOPS311 Reading Package-1Dylan BanksNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of MWM On Pain and Range of Movement in Patients With Lateral Ankle SprainDocument17 pagesEffectiveness of MWM On Pain and Range of Movement in Patients With Lateral Ankle SprainRashidkpvldNo ratings yet
- Icmr Sts Result 2011Document32 pagesIcmr Sts Result 2011Manish Chandra PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Pracrea1 Chapter 1Document36 pagesPracrea1 Chapter 1Abegail AcohonNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)