Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arp, Its Challenges & Solutions: Study: Mohit Jani
Uploaded by
IJRAEROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arp, Its Challenges & Solutions: Study: Mohit Jani
Uploaded by
IJRAERCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
ARP, ITS CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS: Study
Mohit Jani
Ad hoc Lecturer, Bhavnagar University
Abstract: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) lives in the Network layer. In a LAN, each PC has a
real (IP) address and a physical (MAC) address. To impart something particular from one machine to
other in the same or unmistakable network(s), MAC area of the destination machine is required by
the source machine. Thusly to get the MAC area of destination if truant in ARP store of source, a
mapping is ought to have been developed between the IP address and the MAC address. Thus ARP is
used. From this it can be grasped that ARP is a basic part of the framework layer and a stateless
tradition. As a result of stateless property, ARP have some basic security defects which make it
vulnerable against different ARP save hurting ambushes, for instance, MITM and DoS attacks
inciting spillage or mischief of information. In light of the essentialness of this issue, there have been
a couple of game plans Studied to comprehend it. We have separated that no course of action offers
an achievable plan. So in this paper we present an Enhanced type of ARP that can adjust up to
different sorts of attacks in ARP besides feasible game plan. This changed tradition will hold most of
the colossal motivations behind the first for ARP [4], yet will shut off its security inadequacies
inciting a more adjusted framework than existing by making it stateful. We term this balanced
tradition the "Overhauled Address Resolution Protocol (EARP)". It is a stateful tradition, by securing
the information of the Request layout in the ARP store, to diminish the chances of various sorts of
strikes in ARP. It is more changed by TV ARP Reply layout in the framework and securing related
entries in the ARP save each time when correspondence happen.
I.
INTRODUCTION
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) stays in the Network layer. In a LAN, each PC has a true blue
(IP) address and a physical (MAC) address. To convey something particular from one machine to
other in the same or unmistakable network(s), MAC area of the destination machine is required by
the source machine. Thusly to get the MAC area of destination if missing in ARP store of source, a
mapping is ought to have been developed between the IP address and the MAC address.
Consequently ARP is used. From this it can be appreciated that ARP is a basic part of the framework
layer and a stateless tradition. As a result of stateless property, ARP have some trademark security
flaws which make it feeble against different ARP store hurting ambushes, for instance, MITM and
DoS attacks provoking spillage or damage of information. Due to the essentialness of this issue,
there have been a couple of courses of action Studied to disentangle it. We have separated that no
plan offers a conceivable course of action. So in this paper we show an Enhanced interpretation of
ARP that can adjust up to different sorts of strikes in ARP besides conceivable course of action. This
balanced tradition will hold most of the considerable reasons for the first for ARP [4], yet will shut
off its security weaknesses provoking a more adjusted framework than existing by making it stateful.
We term this balanced tradition the "Enhanced Address Resolution Protocol (EARP)". It is a stateful
tradition, by securing the information of the Request plot in the ARP store, to reduce the chances of
various sorts of ambushes in ARP. It is more modified by TV ARP Reply diagram in the framework
and securing related sections in the ARP save each time when correspondence happen.
I.
BACKGROUND
A. Address Resolution Protocol
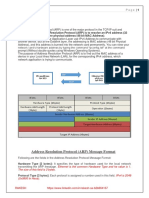
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) abides in the base bit of the Network layer of TCP/IP suite. In
this layer, a host C is perceived by its 32-bit IP address. Regardless, the Medium Access Control
15
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
(MAC) layer of the TCP/IP suite takes after a substitute having a tendency to scheme [5]. An
interface in the MAC layer is recognized by a 48-bit MAC address.
Exactly when Network layer gets a bundle from the higher layers it checks the IP area of the
destination machine. In case the destination machine is in the same neighborhood framework as that
of the sending machine, the package can be sent particularly to the destination machine; else the IP
group must be directed by method for a switch [5]. To send the group particularly to the destination
machine, the framework layer needs to know the MAC area of the destination machine. The
framework layer of the TCP/IP suite plays out this by using ARP. ARP effectively maps the 32-bit IP
area of a machine to its 48-bit MAC address in a short lived memory space called the ARP store.
There are two sorts of ARP messages that may be sent by the ARP tradition. One is ARP Request
and other is ARP Reply.
Framework as that of the sending machine, the package can be sent particularly to the destination
machine; else the IP group must be directed by method for a switch [5]. To send the group
particularly to the destination machine, the framework layer needs to know the MAC area of the
destination machine. The framework layer of the TCP/IP suite plays out this by using ARP. ARP
effectively maps the 32-bit IP area of a machine to its 48-bit MAC address in a short lived memory
space called the ARP store. There are two sorts of ARP messages that may be sent by the ARP
tradition. One is ARP Request and other is ARP Reply.
FIG 1. Host A broadcasts request for Host D.
FIG 2. Host D Replies to Host A (unicast).
ARP RequestWhen a host sends an ARP request, it fills in the ARP Request layout its IP address,
MAC address, sort of ARP message and the target IP address. By then the ARP sales is broadcast to
each one of the hosts in the same LAN as the sending host [5]. The target MAC address field is left
clear for the host with the target IP area to fill in.1. Machine A needs to send a parcel to D, yet An
exclusive knows IP location of D.
2. Machine A broadcasts ARP Request with IP address of D as shown in Fig. 1.
3. All machines on the local network receive the ARP Request which is broadcast.
4. Machine D replies with its MAC address by unicast of ARP Reply as shown in Fig. 2 and update
its ARP cache with MAC of A.
16
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
5. Machine A adds MAC address of D to its ARP cache.
6. Now Machine A can delivers packet directly to D.
II. SECURITY ISSUES WITH ADDRESS RESOLUTION PROTOCOL (ARP)
A.
ARP cache poisoning attacks [1]:
ARP hold hurting is the strategy by which an assailant perniciously changes the mapping of an IP
area to its relating MAC address in the ARP store of another host by sending mock ARP answer. So
this system is also called ARP mocking. In FIG 3, the aggressor is Host C. It executes the ARP
Cache Poisoning ambush by sending a false ARP answer to Host A saying that 'IP area of Host B
maps to MAC area of Host C' and a spoofed ARP answer to Host B saying that 'IP area of Host A
maps to the MAC area of Host C'. ARP is a stateless tradition and answers are not checked against
pending requesting. In this manner Host An and Host B will update their ARP hold with the mapping
got in the ARP answers
.
FIG 3. Host C performing ARP cache poisoning attack on Host A & Host B.
1)Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack:
Once the ARP stores of Host An and Host B are hurt, Host A will send all the development destined
for Host B, to Host C. So additionally Host B will send all development headed for Host A, to Host
C. Host C can now read all the development between Host An and Host B. In the wake of
scrutinizing the development, If Host C propels the packs to the genuine destination machine, then
Host An and Host B won't perceive that they are being struck. This is a Man-in-the-Middle attack by
which the attacker can divert the development going between two machines to go through him.
2)Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack:
A Denial-of-Service assault is marginally not quite the same as MITM assault, when the assailant
does not forward the bundles, in the wake of understanding them, to the real destination machine; it
is called Denial-of-Service assault.
III. ENHANCED ARP (EARP)
From past trades on ARP evidently the crucial deficiency of ARP lies in the way that it is all-trusting
i.e. it doesn't separate between messages got and trusts any got answer heedlessly. This happens in
view of the way that ARP is a stateless tradition. It doesn't keep any information regarding the sales
it passes on to the framework or the answers it gets. This loophole is used by attackers to send
exaggeration up answers which are trustingly recognized by the ARP. In this way these answers lead
to ARP save hurting
17
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
.
FIG 4. Host D Replies to Host A (broadcast).
Our execution of the Enhanced Address Resolution Protocol (EARP) will be in, such a way, that
both ARP answer and ARP requesting is appeared. We wish to make EARP stateful by securing the
information of the Request plot in the ARP hold. In this tradition regardless of hosts from the source
host will store the areas in the ARP save while the broadcast of both ARP Request and Reply.
Instance of ARP Request and ARP Reply in EARP is according to the accompanying [1]:
1. Machine A wants to send a packet to D, but A only knows IP address of D.
2. Machine A broadcasts ARP Request with IP address of D as shown in Fig. 1.
3. All machines on the local network receive the ARP Request which was broadcasted and update
their ARP cache with the MAC of A.
4. Machine D replies with its MAC address by broadcasting ARP Reply as shown in Fig. 4.
5. All machines add the MAC address of D to their ARP cache.
6. Now Machine A can delivers packet directly to D.
These adjustments in the primary ARP makes it considerably more secure and efficient.In the
Studied stateful tradition, at whatever point any ARP answer will land to source host, it will check in
its ARP store whether the destination host area is accessible or not. In case the segment is accessible,
then simply the source host will recognize the answer, else it will fundamentally discard the ARP
answer plot. This figuring will check for a genuine mix of IP and MAC area of the destination
present in the ARP Reply plot, with the made hosts in network(s), before TV Reply frame.For
adequacy, this count broadcasts ARP answer diagram too, so upgrading of the ARP store will happen
twice i.e. first time when ARP request edge is appeared (IP and MAC of source host will be secured)
and second time when ARP answer packaging is broadcasted (IP and MAC of destination host will
be put away).Mathematically:
Let us suppose , if there are N number of hosts in a network(s), then total number of transactions
require for the complete updating of ARP cache of all hosts in EARP is given by,
N is even, No. of transaction = N/2.
N is odd, No. of transaction = (N+1)/2.
In case of existing ARP,
No. of transaction = N (N-1)/2.
The TV of ARP answer layout also gives security against ARP store hurting, just as any attacker
send disparaged ARP answer, then this answer moreover got by the concentrated on host whose IP
area is used to outline MAC area of aggressor. So this host distinguishes that this ARP answer is
spoofed by the attacker. Thusly we can say the segment of TV of ARP answer diagram makes EARP
more secure furthermore beneficial.
IV.
ARP REFINEMENTS: ARP WITHDRAWAL AND POPULARIZATION
Operationally, ARP message is of two types viz. ARP Request (OPERATION filed value=1) and
ARP Reply (OPERATION filed value=2).
18
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
However, two more optimization is possible by inclusion of two more ARP message types viz.
1) ARP Withdrawal
2) ARP Popularization
The above two enhancement or refinements are clearly conceivable since the "OPERATION" field
of the ARP message arrangement is 16-bit whose exclusive a couple of bits are essentially being
used for ARP and RARP reason. Along these lines, effortlessly two more piece grouping can be
utilized to incorporate the aforementioned two extra ARP message sorts.
1)
ARP Withdrawal message: When a machine goes for close down or when a machine should
be separated from the framework it is at this moment on or when a machine needs to pull back itself
for some other reason, the machine will demonstrate an ARP Withdrawal message setting the
OPERATION FIELD to a particular worth, say X for this circumstance, where X is a positive entire
number and not used as a piece of present ARP message bunch. This message is broadcast to educate
everybody in the LAN that it no more open. Getting this message, all machines, beside the proprietor
of the message, will expeditiously delete the entry from their individual ARP Cache. None will give
any response to this message.ARP Popularization message: In the present case, when a machine
boots, it telecasts its own IP-MAC mapping as an ARP ask. There ought not be a reaction. Entirely,
the machine, which sends this AREQ, will answer to itself. Nonetheless, the symptom of this telecast
is to make a passage in everybody's ARP Cache. In the event that a reaction arrives, two machines
more likely than not been alloted the same IP address. The new one ought to illuminate the
framework supervisor and not boot
1) The Studied arrangement prescribes that instead of doing such Self ARP Request, another kind of
ARP show message, called ARP Popularization, could be joined by taking the upside of epic no. of
unused piece gathering in the OPERATION FIELD of the ARP message position. This new kind of
ARP message sort is fundamental in light of the fact that, since in this Studied arrangement, the ARP
Reply message is appear, along these lines, doing Self ARP Request may make undesirable
movement in the framework hurled by the Requester. In any case, the arrangement can be made
more savvy altering a machine doing Self ARP Request will never reply in light of the sales made by
it.
This advancement message utilized by a machine when booted or rebooted, will help the machine to
promote its nearness (recently) in the system and everyone in the system will extricate the IP-MAC
mapping and reserve the section in their particular ARP store without giving any answer. Mimic for
this situation is unrealistic because of the telecast way of the promotion message. The second
preferred standpoint of this kind of message is to increase most recent information about the status of
a newcomer, which was unrealistic in before plan.
V.
CONCLUSION
The Studied EARP has a couple purposes of interest. A couple of changes to the present ARP system
are prescribed to fabricate execution and to make ARP free from low-level security threat like ARP
store hurting, Man in the Middle, Women in the Middle and Denial of Service attacks. EARP is a
stateful tradition, by securing the information of the Request layout in the ARP store, to diminish the
chances of various sorts of ambushes in ARP. It is more modified by TV ARP Reply layout in the
framework and securing related segments in the ARP store, each time when correspondence
happens. It holds most of the colossal motivations behind the ARP however close off its security
deficiencies.
19
International Journal of Recent Advancement in Engineering & Research
Volume 2, Issue 2 February; -2016
REFERENCES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Md. Ataullah, Naveen Chauhan, ES-ARP: an Modified Address Resolution Protocol, IEEE 2012
Santanu Kr. Sen, Debraj Roy, Sinthia Roy, Shirsankar Basu, Poojarini, Design and Development of an Enhanced
Address Resolution Protocol to Overcome Security Threats, IJARCSSE 2014
D. Bruschi, A. Omaghi and E. Rosti, S-ARP: a secure address resolution protocol, in Proceedings of the 19th
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, December 2003.
D.Shrinath, S.Panimalar, A.Jerrin Simla, J.Deepa, Detection and Prevention of ARP Spoofing using Centralized
Server, International Journal ,March 2015
Seung Yeob Nam, Dongwon Kim, and Jeongeun Kim, Enhanced ARP: Preventing ARP Poisoning-Based Man-inthe-Middle Attacks, IEEE2010
20
You might also like
- CST 3607 ARP LabDocument7 pagesCST 3607 ARP Labericherrera09No ratings yet
- MAC ARP ExDocument3 pagesMAC ARP ExNayla GreigeNo ratings yet
- Trade Secrets Lawsuit V ReebokDocument17 pagesTrade Secrets Lawsuit V ReebokDarren Adam HeitnerNo ratings yet
- Engaging The Powers Discernment and Resistance in A World of Domination by Walter Wink - MagnificentDocument3 pagesEngaging The Powers Discernment and Resistance in A World of Domination by Walter Wink - MagnificentMiroslavNo ratings yet
- IHL ReviewerDocument22 pagesIHL ReviewerMaria Reylan GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Arp Protocol Survey PPRDocument3 pages2 - Arp Protocol Survey PPRIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Arp SpoofingDocument14 pagesArp SpoofingAvita KatalNo ratings yet
- Preventing ARP Cache Poisoning Attacks - A Proof of Concept Using OpenWrt PDFDocument9 pagesPreventing ARP Cache Poisoning Attacks - A Proof of Concept Using OpenWrt PDFclu5t3rNo ratings yet
- Prevent ARP Spoofing with MAC Filtering and ARPserverDocument13 pagesPrevent ARP Spoofing with MAC Filtering and ARPserverAlejo HerzferzNo ratings yet
- A Solution For Arp Spoofing: Layer-2 Mac and Protocol Filtering and ArpserverDocument12 pagesA Solution For Arp Spoofing: Layer-2 Mac and Protocol Filtering and ArpserverNeba Neba NebaNo ratings yet
- ARP SpoofingDocument6 pagesARP SpoofingDileep Kumar ManjhiNo ratings yet
- Spoofing and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Date Assigned: Mm/dd/yyyy Time Due: Mm/dd/yyyy by HH:MM Educational ObjectivesDocument12 pagesSpoofing and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Date Assigned: Mm/dd/yyyy Time Due: Mm/dd/yyyy by HH:MM Educational ObjectivesSimbad MNo ratings yet
- Subverting ARP Protocol SecurityDocument16 pagesSubverting ARP Protocol SecurityWilliam WangNo ratings yet
- Arp 1Document15 pagesArp 1محمد فتح اللهNo ratings yet
- ARP Poisoning: An Investigation Into Spoofing The Address Resolution ProtocolDocument5 pagesARP Poisoning: An Investigation Into Spoofing The Address Resolution ProtocolUmang KediaNo ratings yet
- Publication 5 19295 300Document7 pagesPublication 5 19295 300AsankaNo ratings yet
- Protection To ARP From Attackers Based On Timer Tables and VotingDocument5 pagesProtection To ARP From Attackers Based On Timer Tables and Votingsurendiran123No ratings yet
- Protection To ARP From Attackers Based On Timer Tables and VotingDocument5 pagesProtection To ARP From Attackers Based On Timer Tables and Votingamitmsh1995No ratings yet
- Seed Lab SolutionDocument11 pagesSeed Lab SolutionMalik ShahidNo ratings yet
- Arp Spoof Detection System Using Icmp Protocol An Active Approach IJERTV3IS051581Document3 pagesArp Spoof Detection System Using Icmp Protocol An Active Approach IJERTV3IS051581lijigirishNo ratings yet
- All About ARPDocument15 pagesAll About ARPazrul asreeNo ratings yet
- NetcutDocument3 pagesNetcutRajveer NandaNo ratings yet
- Attacking The Arp Attacking Thattacking The Arp E ArpDocument8 pagesAttacking The Arp Attacking Thattacking The Arp E ArpAnkit KomarNo ratings yet
- ARP Storm Detection and Prevention MeasuresDocument5 pagesARP Storm Detection and Prevention MeasuresRenato SilvaNo ratings yet
- ARP POISONING ATTACK ReportDocument11 pagesARP POISONING ATTACK ReportSidNo ratings yet
- ARP Mapping: in A Frame With The MAC Address of The Local Host, or Next-Hop RouterDocument17 pagesARP Mapping: in A Frame With The MAC Address of The Local Host, or Next-Hop RoutermuseNo ratings yet
- Detecting ARP Spoofing: An Active Technique: Abstract. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Due To Its StatelessDocument2 pagesDetecting ARP Spoofing: An Active Technique: Abstract. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Due To Its Statelessshaahin13631363No ratings yet
- Wireless Access Points and ARP Poisoning:: Wireless Vulnerabilities That Expose The Wired NetworkDocument12 pagesWireless Access Points and ARP Poisoning:: Wireless Vulnerabilities That Expose The Wired NetworkNajeeb AbduNo ratings yet
- Gratuitous ARP ExplainedDocument28 pagesGratuitous ARP ExplainedEmilio A. RosendoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4 (Arp & Rarp)Document8 pagesUnit 3 & 4 (Arp & Rarp)rohit2636No ratings yet
- Lab No. 9-UpdatedDocument4 pagesLab No. 9-Updatedmayashamaim72002No ratings yet
- Understanding Arp (Address Resolution Protocol) Spoofing For Usage in Control and SurveillanceDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Arp (Address Resolution Protocol) Spoofing For Usage in Control and SurveillanceAyush ParthNo ratings yet
- CS425 ARP, RARP, ICMP ProtocolsDocument7 pagesCS425 ARP, RARP, ICMP ProtocolsAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- An ICMP Based Secondary Cache Approach F PDFDocument6 pagesAn ICMP Based Secondary Cache Approach F PDFJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Network Traffic & Flow AnalysisDocument41 pagesNetwork Traffic & Flow AnalysisAdu SinghNo ratings yet
- Configure Dynamic ARP Inspection on Catalyst 6500Document22 pagesConfigure Dynamic ARP Inspection on Catalyst 6500PA2 ksplNo ratings yet
- Address Resolution Protocol: Finding Feature InformationDocument18 pagesAddress Resolution Protocol: Finding Feature InformationBenny FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ARP PoisoningDocument8 pagesUnit 4 ARP PoisoningJovelyn Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- What Is An ARP Entry ?: KarishmaDocument2 pagesWhat Is An ARP Entry ?: Karishmavijay6996No ratings yet
- Introduction To Routing: Destination AddressDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Routing: Destination AddressB RaoNo ratings yet
- Ethernet (LAN) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)Document55 pagesEthernet (LAN) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)Sigra JisawNo ratings yet
- The Audiovisual LAN Series Theory in PracticeDocument4 pagesThe Audiovisual LAN Series Theory in PracticeGustavo Rincon PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Acn NotesDocument79 pagesAcn NotesShubNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Lab 9.8.1 Address Resolution Protocol ARPDocument8 pagesCisco CCNA Lab 9.8.1 Address Resolution Protocol ARPBms AgNo ratings yet
- Using Arp in WiresharkDocument7 pagesUsing Arp in Wiresharkapi-418424782No ratings yet
- Web Technology and Commerce Unit-1 by Arun Pratap SinghDocument38 pagesWeb Technology and Commerce Unit-1 by Arun Pratap SinghArunPratapSinghNo ratings yet
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection: Understanding DAIDocument22 pagesConfiguring Dynamic ARP Inspection: Understanding DAInggianglx100% (2)
- An Introduction To Arp Spoofing Sean WhalenDocument7 pagesAn Introduction To Arp Spoofing Sean Whalenlsdn1No ratings yet
- CN - Unit3.3Document55 pagesCN - Unit3.3Nishant BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- Understanding ARP Spoofing For: Usage in Control and SurveillanceDocument13 pagesUnderstanding ARP Spoofing For: Usage in Control and SurveillanceAyush ParthNo ratings yet
- Ex ArpDocument3 pagesEx ArpFAIZ AHMED H 17CSNo ratings yet
- CISCo - P ARPDocument4 pagesCISCo - P ARPpantelimon11No ratings yet
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol Options: First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: May 2, 2008Document22 pagesConfiguring Address Resolution Protocol Options: First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: May 2, 2008elephant1961No ratings yet
- Cisco Cyberops Final ExamDocument44 pagesCisco Cyberops Final ExamSebaNo ratings yet
- Preventive Approaches Towards ARP SpoofingDocument6 pagesPreventive Approaches Towards ARP SpoofingpritheshNo ratings yet
- ARP ProtocolDocument29 pagesARP Protocolmeo_omhtNo ratings yet
- Unit:2 ARP (Operation, Format, Proxy Arp) : Presented by Baljit ChaudharyDocument17 pagesUnit:2 ARP (Operation, Format, Proxy Arp) : Presented by Baljit ChaudharysainibaljeetNo ratings yet
- CN - Unit3.4 PDFDocument27 pagesCN - Unit3.4 PDFKanika TyagiNo ratings yet
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol Options: Finding Feature InformationDocument20 pagesConfiguring Address Resolution Protocol Options: Finding Feature InformationNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- Multicast Routing Protocols: A Survey: Student, Sikkim Manipal UniversityDocument4 pagesMulticast Routing Protocols: A Survey: Student, Sikkim Manipal UniversityIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Wireless Sensor Network Safety & ChallengesDocument8 pagesWireless Sensor Network Safety & ChallengesIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Captcha For Security in WWWDocument3 pagesCaptcha For Security in WWWIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 4Document4 pages4IJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review of Cache Problem With ARP: S.Balasubrahmanyam, P BalasubrahmanyamDocument3 pagesReview of Cache Problem With ARP: S.Balasubrahmanyam, P BalasubrahmanyamIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 3Document7 pages3IJRAERNo ratings yet
- Survey On Use of Bet in Medical Diagnosis As Support System: Kashvi MunjaparaDocument4 pagesSurvey On Use of Bet in Medical Diagnosis As Support System: Kashvi MunjaparaIJRAERNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Simple Network Management Protocol: Kumar SatakarniDocument5 pagesA Review Paper On Simple Network Management Protocol: Kumar SatakarniIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 3 SMTPDocument4 pages3 SMTPIJRAERNo ratings yet
- High Speed Mobile Wireless TechnologyDocument5 pagesHigh Speed Mobile Wireless TechnologyIJRAERNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Intrusion Finding SystemsDocument5 pagesA Survey On Intrusion Finding SystemsIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Surveying & Evaluating Various Multicasting Protocols: Vihang PatelDocument4 pagesSurveying & Evaluating Various Multicasting Protocols: Vihang PatelIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Method For Huge Data Insertion: AbstractDocument4 pagesEnhanced Method For Huge Data Insertion: AbstractIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review On Protocols For Routing in Network With Sensing CapacityDocument4 pagesReview On Protocols For Routing in Network With Sensing CapacityIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2IJRAERNo ratings yet
- A Complete Review On SMTP Protocol: Sheena Aggrawal AbstractDocument8 pagesA Complete Review On SMTP Protocol: Sheena Aggrawal AbstractIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Private Cloud Server Applicationsfor Data StorageDocument5 pagesPrivate Cloud Server Applicationsfor Data StorageIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Study of WSN Clustering & Routing ProtocolDocument5 pagesStudy of WSN Clustering & Routing ProtocolIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Working of Asynchronous Teller Machine With Parent and Foreign OrganizationDocument4 pagesWorking of Asynchronous Teller Machine With Parent and Foreign OrganizationIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review On High Bandwidth Network For Man: Praita BhattDocument7 pagesReview On High Bandwidth Network For Man: Praita BhattIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Router Level Load Matching Tools in WMN - A SurveyDocument2 pagesRouter Level Load Matching Tools in WMN - A SurveyIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 1 - A Review Paper of ZRPDocument6 pages1 - A Review Paper of ZRPIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Modeling Radar On Global Positioning System: Department of Electronics, RTU, IndiaDocument7 pagesModeling Radar On Global Positioning System: Department of Electronics, RTU, IndiaIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review On DNS (Domain Name System)Document2 pagesReview On DNS (Domain Name System)IJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review On Ipv4 To Ipv6 Transition MechanismsDocument4 pagesReview On Ipv4 To Ipv6 Transition MechanismsIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Black Hole Attack in Wireless Mobile Adhoc NetworksDocument4 pagesBlack Hole Attack in Wireless Mobile Adhoc NetworksIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Review On Extraction of Information From Stream Data Using Data Mining TechniqueDocument7 pagesReview On Extraction of Information From Stream Data Using Data Mining TechniqueIJRAERNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1IJRAERNo ratings yet
- Deepsea WSN Working: A Study: Pratiksha JaniDocument5 pagesDeepsea WSN Working: A Study: Pratiksha JaniIJRAERNo ratings yet
- Bridge To LifeDocument11 pagesBridge To LifeRandy LandaoNo ratings yet
- People Vs Isleta PDFDocument9 pagesPeople Vs Isleta PDFheyoooNo ratings yet
- 1718-Level I Genghis Khan Vocab and Spelling ListsDocument5 pages1718-Level I Genghis Khan Vocab and Spelling ListsAdriana DimaNo ratings yet
- Prosperity Gospel and The Catholic Errol FernandesDocument3 pagesProsperity Gospel and The Catholic Errol FernandesFrancis LoboNo ratings yet
- An Impasse in SAARC - ORFDocument4 pagesAn Impasse in SAARC - ORFTufel NooraniNo ratings yet
- Corporate Computer Security Chapter 1Document9 pagesCorporate Computer Security Chapter 1a128128No ratings yet
- 10 Rel. Clause-3Document1 page10 Rel. Clause-3TC Melis ERNo ratings yet
- History Nicula Monastery Wonderworking Icon of The Mother of GodDocument2 pagesHistory Nicula Monastery Wonderworking Icon of The Mother of Godlilianciachir7496No ratings yet
- Eth 2Document6 pagesEth 2111111No ratings yet
- Letter of Quarantine of EmployeesDocument3 pagesLetter of Quarantine of EmployeesSample BakeshopNo ratings yet
- Bellefonte Walkout Letter To ParentsDocument1 pageBellefonte Walkout Letter To ParentsMatt StevensNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review 3Document1 pageChapter Review 3riya patelNo ratings yet
- JA Physician 1Document2 pagesJA Physician 1JFANo ratings yet
- United States v. Rashella Reed, 11th Cir. (2014)Document5 pagesUnited States v. Rashella Reed, 11th Cir. (2014)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Nuisance - 7 - Zorilla - Ramcar V MillarDocument13 pagesNuisance - 7 - Zorilla - Ramcar V MillarRalph Christian ZorillaNo ratings yet
- People V Aca-AcDocument11 pagesPeople V Aca-AcJoy NavalesNo ratings yet
- 5.implantasi & PlasentasiDocument111 pages5.implantasi & PlasentasiherdhikaNo ratings yet
- Aznar V YapdiangcoDocument1 pageAznar V YapdiangcoMJ FloresNo ratings yet
- Tantuico Seeks Bill of Particulars in Ill-Gotten Wealth CaseDocument21 pagesTantuico Seeks Bill of Particulars in Ill-Gotten Wealth CaseKinitDelfinCelestialNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drug Overdose The Death of The Hollywood Celebrity Heath LedgerDocument5 pagesPsychotropic Drug Overdose The Death of The Hollywood Celebrity Heath LedgerlalipredebonNo ratings yet
- Passport Apply InfoDocument12 pagesPassport Apply Infoybbvvprasada raoNo ratings yet
- Learner Recognition CertificateDocument10 pagesLearner Recognition CertificateOmengMagcalasNo ratings yet
- (L4) Nullity - Void and Voidable MarriagesDocument20 pages(L4) Nullity - Void and Voidable MarriagesRoberto GuiseppiNo ratings yet
- MBBS Second Year Books and Syllabus GuideDocument15 pagesMBBS Second Year Books and Syllabus GuideUma MounaNo ratings yet
- 76-07-12Document2 pages76-07-12Francisco VallejoNo ratings yet
- Guide to the Circuit Court of Cook CountyDocument22 pagesGuide to the Circuit Court of Cook CountysuescorpionNo ratings yet
- American Atheist Magazine March 2009Document32 pagesAmerican Atheist Magazine March 2009American Atheists, Inc.No ratings yet