Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forms of Inventories Notes
Uploaded by
Anonymous p8bHAAxCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Forms of Inventories Notes
Uploaded by
Anonymous p8bHAAxCopyright:
Available Formats
Forms of Inventories
1. Raw materials
2. Maintenance, repair, and operating supplies
3. Work-in-process (WIP)
4. Finished goods
Inventory-Related Costs
1. Ordering or setup costs
2. Inventory carrying or holding costs
3. Stockout costs
4. Opportunity costs
5. Cost of goods
Functions of Inventories
1. Transit Inventories
2. Buffer Inventories (safety stocks)
3. Anticipation Inventories
4. Decoupling Inventories
5. Cycle Inventories
Priorities for Inventory Management: The ABC Concept
a. A items-15-20% of items that account for 75-80% of annual inventory value
b. B items-30-40% of items that account for 15% of annual inventory value
c. C items-40-50% of items that account for 10-15% of annual inventory value
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Assumptions
1. Constant rate of demand
2. Shortages not allowed
3. Stock replenishment can be scheduled to arrive exactly when inventory drops to zero
4. Purchase price, ordering cost, and per unit holding cost are independent of quantity
ordered
5. Items are ordered independently of each other
Q = order quantity
U = annual usage
CO = order cost per order
CH = annual holding cost per unit
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- B E MechDocument363 pagesB E MechAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
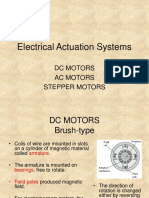
- Electrical Actuation Systems GuideDocument40 pagesElectrical Actuation Systems GuideAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design: Lecture NotesDocument61 pagesComputer Aided Design: Lecture NotesbalacoeusNo ratings yet
- B.E. Mech PDFDocument113 pagesB.E. Mech PDFarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Sections of Solids & Development of SurfaceDocument12 pagesSections of Solids & Development of SurfaceAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 MTCDocument118 pagesUnit 4 MTCAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007No ratings yet
- Projection of Points and PlanesDocument30 pagesProjection of Points and PlanesAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Iso QBDocument2 pagesIso QBAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Line Types and Dimensioning Methods in Engineering DrawingsDocument10 pagesLine Types and Dimensioning Methods in Engineering DrawingsthamaraikkannangNo ratings yet
- ED7102-Computer Applications in DesignDocument11 pagesED7102-Computer Applications in DesignLOGANTKEC100% (2)
- New Picture PDFDocument1 pageNew Picture PDFAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- L 4Document42 pagesL 4Guna RajNo ratings yet
- Ferrous MetallurgyDocument30 pagesFerrous MetallurgyGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Material Science Chapter on Polymer Types, Processing & ApplicationsDocument13 pagesMaterial Science Chapter on Polymer Types, Processing & ApplicationsVaibhav ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mn7203 Material Testing and Characterization L T P CDocument5 pagesMn7203 Material Testing and Characterization L T P CAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Handout 6Document10 pagesHandout 6Anonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Industrial RoboticsDocument47 pagesIndustrial Roboticspravdiv100% (2)
- Polymer ProcessingDocument28 pagesPolymer ProcessingMousom SomNo ratings yet
- Capd NotesDocument14 pagesCapd NotesAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- CG Lab Manual ProgramsDocument61 pagesCG Lab Manual ProgramsVivek KvNo ratings yet
- Capd 2Document7 pagesCapd 2Anonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- PLANT LOCATION FACTORS FOR NEW ORGANIZATIONSDocument2 pagesPLANT LOCATION FACTORS FOR NEW ORGANIZATIONSAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Capd Imp QuesDocument2 pagesCapd Imp QuesAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- On Equations of Motion of Elastic Linkages by FEMDocument15 pagesOn Equations of Motion of Elastic Linkages by FEMAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Electro-Hydraulic Equipment Price QuotationDocument6 pagesElectro-Hydraulic Equipment Price QuotationAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Line AlgorithmDocument62 pagesLine AlgorithmAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- FEA Simulation of Metal CuttingDocument6 pagesFEA Simulation of Metal CuttingAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- R013968998 PDFDocument10 pagesR013968998 PDFAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet