Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statement Class 3 Fluid Circulation
Uploaded by
kikiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statement Class 3 Fluid Circulation
Uploaded by
kikiCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Chemistry 2016-2017
Technologies Degree
4 Course Engineering in Industrial
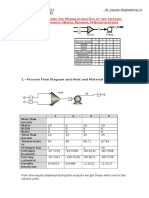
EXERCISE 3: FLUID CIRCULATION
The sewerage system of a Chemical Industry requires to collect the different types
of water into a homogenization tank previously to be sent to a wastewater plant
that is attached to the plant facilities.
Homogeneization
TANK
Figure 1. Wastewater plant.
In this industry, there are three types of residual waters to be collected: cooling
water, cleaning equipment water and sanitary water. The initial conditions of the
waters are:
1. Cooling water: Inlet conditions: 20.000 kmoles/h of water at 545 kPa y 47 C
2. Cleaning equipment water: 2500 kmoles/h of water at 22 C and 250 kPa.
3. Sanitary water: 980 kmoles/h of water at 300 kPa and 17 C.
Each of this type of water follow a different process before enter the homogenization
tank:
1. Cooling water
Before being recirculated to the process, the inlet stream must cool down to 20
C by a two-streams heat exchanger that operates with a flowrate of 25.000
kmol/h of water at 15 C and 500 kPa. The pressure drop in the hot stream is
50 kPa.
Later, the stream enters into a splitter where is split into two lines; 90% of
water will return to the industrial plant, while the rest goes the homogenization
tank. This second stream leaves the splitter at 470 kPa pressure.
2. Cleaning equipment water:
It flows through a section of pipe equivalent length of 320 m, internal diameter
of 15 cm and absolute roughness of 4.10 -4 cm. Inside the pipe there is no heat
1
Industrial Chemistry 2016-2017
Technologies Degree
4 Course Engineering in Industrial
exchange (duty = 0). Then, this type of water goes to a pump to increase the
pressure up to 300 kPa. Pump efficiency is 80%.
3. Sanitary water:
It circulates through a system of 390 m of equivalent length, internal diameter
of 8 cm and roughness of 5. 10 -4 cm. Inside the pipe there is no heat exchange
(duty = 0). Later the stream goes to a pump to achieve a pressure of 440 kPa.
The effectiveness of the pump is 75%.
Finally, after the homogenization tank, the mixed stream goes through a valve to
decrease the pressure to 60kPa. Thermodynamic method RK-SOAVE.
Questions:
1. Determines the flowrate (kmol/h), pressure (atm) and temperature (C) of the
product stream.
2. Indicate which pump does more work (W) and why.
3. Indicate on that line the pressure drop is higher (atm) and why.
4. Indicates the heat exchanged (cal/s) in the heat exchanger.
5. Indicates the outlet temperature ( C) of cool stream in the two streams
exchanger.
6. Reynolds number in pipes inside.
7. Indicates the type of flow (liquid or vapor).
8. Change the thermodynamic method: STEAMNBS and indicate the conditions of
the product stream.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Subject 5.4 Distillation and Absorption 2016-2017Document14 pagesSubject 5.4 Distillation and Absorption 2016-2017kikiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Statement Class 1. Example 1 and 2Document4 pagesStatement Class 1. Example 1 and 2kikiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Ricardo ZamoraDocument1 pageRicardo ZamorakikiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- RobotsDocument1 pageRobotskikiNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- EXAMPLE I: Calculate The Mixing Properties of Two Streams With Three Components (Water, Butanol, N-Butyl-acetate)Document6 pagesEXAMPLE I: Calculate The Mixing Properties of Two Streams With Three Components (Water, Butanol, N-Butyl-acetate)kikiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Subject 5.1 Equipment Sizing and Costing. Introduction 2016-2017Document8 pagesSubject 5.1 Equipment Sizing and Costing. Introduction 2016-2017kikiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Tabla Normal PDFDocument1 pageTabla Normal PDFkikiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Practice1 AbrahamCozDocument6 pagesPractice1 AbrahamCozkikiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Statement Class 4. Compression TrainDocument3 pagesStatement Class 4. Compression TrainkikiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Statement Class 4. Compression TrainDocument3 pagesStatement Class 4. Compression TrainkikiNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE I: Calculate The Mixing Properties of Two Streams With Three Components (Water, Butanol, N-Butyl-acetate)Document6 pagesEXAMPLE I: Calculate The Mixing Properties of Two Streams With Three Components (Water, Butanol, N-Butyl-acetate)kikiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- TryhrestyDocument1 pageTryhrestykikiNo ratings yet
- Coolrunner II Reference Manual PDFDocument16 pagesCoolrunner II Reference Manual PDFImanol LasaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- AbrhamCoz - Statement Class 3 Fluid CirculationDocument3 pagesAbrhamCoz - Statement Class 3 Fluid CirculationkikiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- E 310Document1 pageE 310kikiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Statement Class 4. Compression TrainDocument3 pagesStatement Class 4. Compression TrainkikiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3: Fluid Circulation: Homogeneization TankDocument5 pagesExercise 3: Fluid Circulation: Homogeneization TankkikiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Diagram ADocument1 pageDiagram AkikiNo ratings yet
- Subject 4a. - Application of LMB Algorithm To Case StudyDocument5 pagesSubject 4a. - Application of LMB Algorithm To Case StudykikiNo ratings yet
- Tabla NormalDocument1 pageTabla NormalkikiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- E 310Document1 pageE 310kikiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Supplemental Infovis128Document14 pagesSupplemental Infovis128kikiNo ratings yet
- Statement Class 4. Compression TrainDocument3 pagesStatement Class 4. Compression TrainkikiNo ratings yet
- Statement Class 3 Fluid CirculationDocument2 pagesStatement Class 3 Fluid CirculationkikiNo ratings yet
- Bloque 3 Tema 3.1Document59 pagesBloque 3 Tema 3.1kikiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Aspen Simulation ToolDocument27 pagesIntroduction To The Aspen Simulation ToolkikiNo ratings yet
- Coolrunner II Reference Manual PDFDocument16 pagesCoolrunner II Reference Manual PDFImanol LasaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Ansi C80-5Document11 pagesAnsi C80-5Andres Antonio Moreno CastroNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Innovative Turbulence Modeling - SST Model in ANSYS CFXDocument2 pages10.0 Innovative Turbulence Modeling - SST Model in ANSYS CFXกี้ บางพระNo ratings yet
- 5 Viscosity PDFDocument8 pages5 Viscosity PDFDENY MOL BENNYNo ratings yet
- Catalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunDocument40 pagesCatalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunHà Văn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Piping Flexibility Analysis (B 31.3)Document151 pagesPiping Flexibility Analysis (B 31.3)Majid Sattar100% (1)
- Rate ListDocument13 pagesRate ListUsamaQadirNo ratings yet
- Anexo I - Típicos de Soportes Metálicos PDFDocument174 pagesAnexo I - Típicos de Soportes Metálicos PDFAngely CanalesNo ratings yet
- Boldrocchi ESP Conversions 2013Document19 pagesBoldrocchi ESP Conversions 2013Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Dossier Teca A BDocument20 pagesDossier Teca A Bpeter2002No ratings yet
- NanoDocument10 pagesNanoRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Webbing & Round Sling Acceptance CriteriaDocument3 pagesSynthetic Webbing & Round Sling Acceptance CriteriarustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Design, Fabrication, and Testing of A Composite Side Door For A Mid SuvDocument24 pagesDesign, Fabrication, and Testing of A Composite Side Door For A Mid SuvtechfiNo ratings yet
- Alloy Selection For Dilute and Medium Concentration Sulfuric Acid NACE CORROSION OnePetroDocument5 pagesAlloy Selection For Dilute and Medium Concentration Sulfuric Acid NACE CORROSION OnePetroYaroo YarooNo ratings yet
- Load Calculation For TrussDocument40 pagesLoad Calculation For Trussk varalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Bandejas Portacables Aluminio Acero B LineDocument46 pagesBandejas Portacables Aluminio Acero B LineJose NavíoNo ratings yet
- Guest ListDocument6 pagesGuest ListindzarazizyNo ratings yet
- Cupones Astm D2688-05 PDFDocument7 pagesCupones Astm D2688-05 PDFJorge Iván Garcia SozaNo ratings yet
- Crusher Dust As Partial Cement Replacement Materrial in ConcreteDocument138 pagesCrusher Dust As Partial Cement Replacement Materrial in ConcreteZELALEMNo ratings yet
- 01.technical Specifications With P&ID - 1Document176 pages01.technical Specifications With P&ID - 1MayankDubeyNo ratings yet
- Australian Castolin Eutectic: Flame Spray Equipment and PowdersDocument18 pagesAustralian Castolin Eutectic: Flame Spray Equipment and PowdersАлмаз КенжетаевNo ratings yet
- Cavitation DamageDocument18 pagesCavitation Damagescata1117No ratings yet
- Heat PumpDocument87 pagesHeat PumpAugusto MoisesNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Carbon FiberDocument10 pagesThesis On Carbon Fiberbrendapotterreno100% (2)
- THE SHARD High Performance Structure Le PDFDocument10 pagesTHE SHARD High Performance Structure Le PDFkitstonNo ratings yet
- ACI 336.2R-88 R02 Suggested Analysis and Design Procedures For Combined Footings and Mats - MyCivil - IrDocument11 pagesACI 336.2R-88 R02 Suggested Analysis and Design Procedures For Combined Footings and Mats - MyCivil - IrRenjith S AnandNo ratings yet
- Worksheet OneDocument4 pagesWorksheet OneRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- ASTM GradesDocument4 pagesASTM GradesSaurabh MundheNo ratings yet
- State Highway and Transportation Department Concrete Plant Inspector'S ChecklistDocument2 pagesState Highway and Transportation Department Concrete Plant Inspector'S ChecklistGrafi EinsteinNo ratings yet
- External CladdingDocument32 pagesExternal CladdingMarcos PansaniNo ratings yet
- Apa Plywood Diaphragms Report 138 ReDocument59 pagesApa Plywood Diaphragms Report 138 ReJeffrey HuntNo ratings yet
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (81)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)