Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Grammar Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
api-341767113Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Grammar Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
api-341767113Copyright:
Available Formats
English Grammar Cheat Sheet
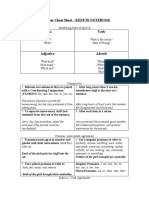
Adjective vs. Adverb
Conjunctions
Adjectives an adjective points out or describes a noun.
Example:
Conjunctions a word that
joins two words, or groups of
works together.
That dog is hungry.
Adverb a word that modifies (changes) a verb, an
adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs indicate time, place,
manner, degree, affirmation, or negation. Examples:
Sometimes my family
goes to the zoo. (time)
Capitalization
and
We like to watch the animals
there. (place)
Apostrophes
()
We stroll slowly along the paths. (manner)
Coordinating Conjunctions
join words that are SIMILAR. Ex:
and, but, nor, or, so, and yet.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Punctuation
used to connect words that have
equal importance. Ex: both/and,
used to show possession.
Singular: before the s Subject-Verb Agreement:
Gerunds and Infinitives The mans coat
Plural: after the s
A subject must agree with its verb.
Gerunds- a verb that ends in ing
The boys jacket
that is used as a noun.
Examples:
Singular subject = singular verb
Capital Letters
Plural subject = plural verb
First
Word:
Reading is his
favorite
My dad asked
pastime. (noun)
Rule 1: Subject comes before of
First word in quotes:
A bouquet of yellow roses lends color to the room.
Infinitives a verb form that
Would you
starts with to.
Proper Noun/Proper Adjectives:
Rule 2: Two singular subjects connect by or, either/or, or
Abraham
Lincoln
neither/nor require a singular verb.
went to study in the
Pronoun IUsage
State
Capitol
Library.
Neither Juan nor Carmen is available.
Directions:
Pronoun = word that takes
the place of a
Northrefers
noun. The noun to which a pronoun
Rule 3: Use a plural verb when there are two subjects
is its antecedent. A pronoun must agree
connected by and.
Colonsand
(:)number.
with its antecedent in person
and
a bike are
myfollows
means are
of transportation.
before a list when terms such Aascar
the
following
or as
used.
Third person personal, Used
possessive,
Id like
visit
cities: Paris, London, Rome, and Berlin.
intensive, and reflexive pronouns
must
alsothe following
Rule 4: When the subject is separated from the verb by
Commas (,)
agree in gender.
such words as along with, as well as, etc. keep the tense
Separate 3 or more words
the same.
Personal Pronouns: I, you, they,
her, two
its, dogs, three
She has
cats, and one bird.
ours and others.
Separate adjectives
He was
kitten.
Relative Pronouns: who, which,
thata fluffy, white
Verb Tenses
Direct Quotations
Interrogative: who, whose, what,
whichHe doesnt
She said,
like green
beans.
The tense
of the verb
expresses the time of the action or
and others
Before a coordinating conjunction
state of being.
I read the directions, but Sally built the model car.
Demonstrative: this, these, that, those
Present: I eat a lot of fruit.
Semicolons
(;)
Past: I ate a lot of melon for lunch yesterday.
Double Negatives - Using
two negative
Separate clauses in a compound sentence when they are not joined by a
words in the same sentence.
Future: I am going to eat cherries for lunch today.
conjunction
It rained all afternoon; the game was cancelled.
Separate clauses in a compound
sentence
that is connected with a conjunctive
Funky
Sentences:
Parallelism Similar elements have
adverb
similar
form.
Fragments
when
a sentence lacks
a main verb.
The water washed out the
flowerbeds;
furthermore,
it flooded
the
basement.
Misplaced modifier an adverb/adjective is in the wrong
place in a sentence.
You might also like
- Grammar ACT Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesGrammar ACT Cheat Sheetshare2gain100% (1)
- EnglishGrammar Cheat Sheet For TeachersDocument2 pagesEnglishGrammar Cheat Sheet For TeachersAA11mm2289% (9)
- Grammar Cheat Sheet 2016Document3 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet 2016임민수No ratings yet
- + Gerund: Will, Going ToDocument7 pages+ Gerund: Will, Going ToTeresa De Jesús Juárez GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs GuideDocument5 pagesModal Verbs GuideCésar Muñoz NicolásNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar Cheat Sheet (Draft #1)Document2 pagesBasic English Grammar Cheat Sheet (Draft #1)MEG60% (5)
- Phan Loai Grammar Theo LevelDocument1 pagePhan Loai Grammar Theo LevelleviboNo ratings yet
- Collocations List: Collocations Are Very Common in English, and Learning Them Is Important. ADocument50 pagesCollocations List: Collocations Are Very Common in English, and Learning Them Is Important. AVillMa ABNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument39 pagesTenseVien Pearl LagpaoNo ratings yet
- Useful Collocations For IELTS, ToEFL and PTEDocument34 pagesUseful Collocations For IELTS, ToEFL and PTEPratik Paudel83% (6)
- Grammar Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheetapi-243050568No ratings yet
- IELTS General Writing Task 1 - Advanced Vocabulary For LettersDocument7 pagesIELTS General Writing Task 1 - Advanced Vocabulary For LettersShalva SamkharadzeNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Types GuideDocument14 pagesPronouns Types GuideYokNo ratings yet
- English Tenses PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish Tenses PDFRizwan GhaniNo ratings yet
- 700 Daily Spoken English DialougeDocument55 pages700 Daily Spoken English DialougeMd nishad100% (2)
- English Tenses: Tense Signal Words Use Form Examples Affirmative Examples Negative Examples InterrogativeDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses: Tense Signal Words Use Form Examples Affirmative Examples Negative Examples InterrogativeKhalifa ChilifiannooNo ratings yet
- Prepositional Phrase FunctionsDocument5 pagesPrepositional Phrase FunctionsMar Nie Morales ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Structure and Written ExpressionDocument50 pagesTOEFL Structure and Written ExpressionDaniel Perez VillaseñorNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument1 pageEnglish Tensesapi-3737801No ratings yet
- English Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterRamin ShamsNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet To Use With BellworkDocument8 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet To Use With Bellworksaed ahmad100% (1)
- 7 Sentences - PTE ESSAYSDocument2 pages7 Sentences - PTE ESSAYSPramodh KumarNo ratings yet
- Forming Nouns and AdjectivesDocument10 pagesForming Nouns and AdjectivesGlenpptNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialDocument9 pagesNamma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialdeviNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookDocument119 pagesGrammar BookBetsabe Tejada100% (3)
- GERUND and INFINITIVE Verb Forms ExplainedDocument17 pagesGERUND and INFINITIVE Verb Forms ExplainedSidiq WiranataNo ratings yet
- A To Z Verbs List Learning EnglishDocument4 pagesA To Z Verbs List Learning Englishpadmanabham0% (1)
- 12 Tenses in English Grammar - Tenses Table With Examples - 1Document13 pages12 Tenses in English Grammar - Tenses Table With Examples - 1Santhosh AbinavNo ratings yet
- Tenses FormulaDocument1 pageTenses Formularrusmita75% (4)
- English Grammar, Learn English Verbs, Learn English Verb Forms, Verb List, FormDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar, Learn English Verbs, Learn English Verb Forms, Verb List, FormAshish Singh0% (1)
- PTE Writing EssayDocument7 pagesPTE Writing EssayAceNo ratings yet
- Preposition LorenDocument12 pagesPreposition LorenJude SampangNo ratings yet
- Identifying Sentence ErrorsDocument11 pagesIdentifying Sentence ErrorsNéè RozNo ratings yet
- صفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةDocument79 pagesصفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةbewarkootcher100% (1)
- Ron's Examples by RakibDocument136 pagesRon's Examples by RakibEd S Andy KrNo ratings yet
- Line Graph: Ielts WritingDocument41 pagesLine Graph: Ielts WritingTu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument156 pagesEnglish GrammarSelfhel100% (1)
- Easy English Grammar GuideDocument129 pagesEasy English Grammar GuideVusala HasanovaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesActive and Passive VoiceCatalin CiubotariuNo ratings yet
- ACT Grammar Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesACT Grammar Cheat SheetsuriyadaruwaNo ratings yet
- PrepScholar TOEFL CommonWords PDFDocument156 pagesPrepScholar TOEFL CommonWords PDFCai_waiBeioanNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument5 pagesPart of Speech OverviewJayana SujayanoNo ratings yet
- ChartofEnglishTenses 1558525337663Document1 pageChartofEnglishTenses 1558525337663Ingrid DiazNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 2 Useful PhrasesDocument7 pagesIelts Writing Task 2 Useful PhrasesJagan BoseNo ratings yet
- English Tenses Summary - Lingolia EnglishDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses Summary - Lingolia EnglishCharity N N LwinNo ratings yet
- SuffixesDocument3 pagesSuffixesrichardoentaryoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument38 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated Actionssabine111No ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument26 pagesEnglish Tense SystemJordan CruzNo ratings yet
- What are Phrasal Verbs? (EnglishClubDocument5 pagesWhat are Phrasal Verbs? (EnglishClubJAA 2019100% (1)
- Tenses Table PDFDocument5 pagesTenses Table PDFPeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Basic Spelling RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Spelling Rulesmadrb_amlfNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech 1Document3 pagesPart of Speech 1María Luisa BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Hanah Mae G. RiveraDocument7 pagesSubmitted By:: Hanah Mae G. Riverahannah riveraNo ratings yet
- Parts of speech guideDocument13 pagesParts of speech guideDiana Laura Valdez AldereteNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsnarutothunderjetNo ratings yet
- How To Use Parts of Speech PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Use Parts of Speech PDFIrish Dyan CataquizNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizDocument5 pagesParts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizlanrrayNo ratings yet
- Word classes in 40 charactersDocument7 pagesWord classes in 40 charactersTarik AlicNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Lessons and Self QuizzesDocument11 pagesParts of Speech Lessons and Self QuizzesNermine MouallemNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes Power PointDocument34 pagesGrammar Notes Power PointMrsAndersonLHSSNo ratings yet
- Old Latin PDFDocument14 pagesOld Latin PDFthersitesNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Last AntecedentDocument32 pagesDoctrine of Last Antecedentdrumbeater79No ratings yet
- Sanskrit Case EndingsDocument5 pagesSanskrit Case EndingsJayalakshmi Devi Neeta JaglalNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar: Christian Schrade, Attorney-At-Law TESOL, College of TeachersDocument13 pagesBasic Grammar: Christian Schrade, Attorney-At-Law TESOL, College of Teacherslaki binicikguNo ratings yet
- Spoken English Guru PDF Ebook PDFDocument400 pagesSpoken English Guru PDF Ebook PDFShubhi Sharma75% (4)
- Objective Type: Q.1: Choose The Correct Form of Verb. Questions (A) (B) (C) (D) 1 2 3 4 5Document2 pagesObjective Type: Q.1: Choose The Correct Form of Verb. Questions (A) (B) (C) (D) 1 2 3 4 5Arooj ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Simple and Past Perfect ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast Perfect Simple and Past Perfect ContinuousOctavia MirunaNo ratings yet
- Minitest Week 2Document3 pagesMinitest Week 2trothu264No ratings yet
- Verb14Document9 pagesVerb14olivareginaNo ratings yet
- Active-Passive Verb FormsDocument2 pagesActive-Passive Verb FormslmartinaNo ratings yet
- Ing Form ConstructionDocument9 pagesIng Form ConstructionRizky RosdianaNo ratings yet
- CT3Document2 pagesCT3IsabelitaPintoNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument6 pagesMixed ConditionalsKarina FernandesNo ratings yet
- How to change sentences from active to passive voiceDocument19 pagesHow to change sentences from active to passive voiceFazza MozzaNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Dictionary of The Bobangi LanguageDocument533 pagesGrammar and Dictionary of The Bobangi LanguageGarvey LivesNo ratings yet
- Rules of Grammar NarrationDocument27 pagesRules of Grammar Narrationapi-373125786% (7)
- Cohesive DevicesDocument32 pagesCohesive DevicesMuhammad SyafieNo ratings yet
- Omplete English Grammar: by Purushottam PandeyDocument26 pagesOmplete English Grammar: by Purushottam PandeyNaveen SNo ratings yet
- Homework English III Module 7 8 9Document5 pagesHomework English III Module 7 8 9graicellNo ratings yet
- Complements: (Direct and Indirect Objects) - Practice 1Document2 pagesComplements: (Direct and Indirect Objects) - Practice 1Bang SipoholonNo ratings yet
- Army Writing Style QuizDocument3 pagesArmy Writing Style QuizacNo ratings yet
- UNAD English Course Writing Task and Grammar ChartDocument23 pagesUNAD English Course Writing Task and Grammar ChartMauricio CostaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives - Order - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument8 pagesAdjectives - Order - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionarynsliskovNo ratings yet
- Describing Pictures in ICAO Aviation English TeDocument4 pagesDescribing Pictures in ICAO Aviation English TeCelal BozdoganNo ratings yet
- Yle Movers WorksheetsDocument1 pageYle Movers WorksheetsalejandroNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Pasado SimpleDocument4 pagesEjercicios Pasado Simplejoaquin perez gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Diego Collado's Grammar of The Japanese Language by Collado, Diego, - 1638Document118 pagesDiego Collado's Grammar of The Japanese Language by Collado, Diego, - 1638Gutenberg.org100% (7)
- He Does, She Does File Folder GameDocument5 pagesHe Does, She Does File Folder GameDarko SpasojevićNo ratings yet
- Too and EnoughDocument4 pagesToo and Enoughwindya rizkiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hindi GrammarDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Hindi GrammarParul KhannaNo ratings yet