Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Valves
Uploaded by
Bagus AgungOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Valves
Uploaded by
Bagus AgungCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch.
I Introduction to Valves
1.1. Valve
Valves are mechanical devices specifically designed to
direct, start, stop, mix, or regulate the flow, pressure,
or temperature of a process fluid.
Berdasarkan atas fungsinya, aplikasinya, dan
rancangannya, valve dapat dibedakan ke dalam
beragam kelas styles, sizes, dan ragam pressure.
Tipe yang umum ditemukan adalah plug, ball, globe,
butterfly, dan gate valves.
Valve dapat dibuat dari berbagai material seperti:
steel, iron, plastic, brass, atau sejumlah material
paduan khusus lainnya.
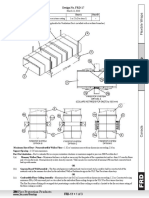
Komponen-komponen utama sebuah valve diberikan
pada Gbr. 1
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
The internal
elements of a valve
are collectively
referred to as a
valve's trim.
The trim typically
includes a disc,
seat, stem, and
sleeves needed to
guide the stem.
A valve's performa
nce is determined
by the disk and
seat interface and
the relation of the
disk position to the
seat.
Gbr. 1 Basic components of a valve
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 2
Manual Valve
Gbr.3
Control Valve
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 4
Ball Valve
Gbr. 5
Gate Valve
Gbr. 6
Plug Valve
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 7
Globe Valve
Gbr. 8
Butterfly Valve
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 9 Pinch Valve
open
throttling
closed
Gbr. 10 Diaphragm Valve
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1.2 Klasifikasi Menurut Fungsinya
Berdasarkan atas rancangan dan fungsi valve in
handling the fluid, valve dapat dibagi ke dalam 3
kelompok: on-off valves, non-return valves, and
throttling valves.
On-off valves: handle the function of blocking the
flow or allowing it to pass.
Non-return valves: allow one direction flow only.
Throttling valve: allow for regulation of the flow at
any point between fully open to fully closed.
One confusing aspect of defining valves by function
and its specific valve-body design (plug, ball, globe,
gate, butterfly, pinch, etc.)
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1. On-off Valves
Terkadang juga disebut sebagai block valve.
Kelompok valve ini yang umum dijumpai: gate, plug,
ball, pressure relief, dan tank-bottom valves.
Jenis on-off valve umumnya hand-operated, walaupun
dapat diotomasi dengan tambahan aktuator.
Pressure-relief valves adalah self-actuated on-off
valves yang dapat terbuka hanya jika preset pressure
dilampaui (mencegah over pressuration).
Pressure-relief valves dibagi menjadi 2: Relief valves,
untuk aplikasi pada fluida cair dan safety valves,
untuk aplikasi pada fluida gas.
Training on Valve Technology
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 11 Pengetesan pressure-relief valve
Training on Valve Technology
10
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
2. Non-return Valves
Nonreturn valves memungkinkan fluida untuk
mengalir ke suatu arah yang diinginkan (hanya satu
arah saja).
Semua check valves termasuk ke dalam kelompok
nonreturn valves.
Valve jenis ini digunakan untuk mencegah terjadinya
backflow yang tidak diinginkan.
Contoh aplikasi: untuk melindungi instalasi pompa
atau kompresor dari backflow saat shut down.
Nonreturn valves juga digunakan dalam sistem proses
dengan variasi tekanan yang harus dijaga secara
terpisah.
Training on Valve Technology
11
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 12 Piston check valve dalam bidang migas
Training on Valve Technology
12
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
3. Throttling Valves
Valve jenis ini digunakan untuk mengatur aliran,
temperatur, atau tekanan.
Operasi throttling valves: manual (handwheel or
lever) atau dengan kontrol otomatis, Gbr. 13(a).
Pressure regulators adalah throttling valve yang
memvariasikan posisi valve untuk menjaga tekanan di
hilir valve tetap konstan, Gbr. 13(b)
Automatic control valves atau control valves is a term
commonly used to describe valves that capable of
varying flow conditions to match the process
requirements dilengkapi dengan actuator.
Training on Valve Technology
13
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
(b) Pressure regulator
(a) Globe control valve
Gbr. 13 Contoh throttling valves
Training on Valve Technology
14
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1.3 Klasifikasi Menurut Aplikasinya
Tiga klasifikasi valve menurut aplikasinya: general
service valve, special service valves, dan severe
service valves.
General service valves: valve yang dapat
digunakan pada banyak aplikasi tanpa perlu
modifikasi.
Special service valves: valve yang dirancang
khusus untuk aplikasi tertentu/spesifik.
Severe service valves: valve yang dirancang khusus
untuk mencegah efek samping pada aplikasi yang
sulit.
Training on Valve Technology
15
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1. General Service Valves
Termasuk ke dalam kelompok ini adalah valve yang
dirancang untuk mayoritas aplikasi yang umum:
Lower-pressure: ANSI Class 150 s/d 600.
Moderate-temperature rating: -50oF s/d 650oF.
Non-corrosive fluid
Common pressure drop yang tidak menyebabkan
kavitasi atau flashing.
Dalam perancangannya, valve tipe ini dibuat dengan
level interchangeability dan flexibility yang tinggi
sehingga memiliki rentang aplikasi yang lebar.
Material body: baja karbon atau baja tahan karat.
Training on Valve Technology
16
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Manual
Otomatis
Gbr. 14 Example of two general service valves
Training on Valve Technology
17
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
2. Special Service Valves
Special service valves is a term used for customengineered valves that are designed for a single
application that is outside normal process application.
Valve jenis ini biasanya untuk aplikasi pada
temperatur tertentu, tekanan tinggi, atau medium
yang korosif.
Gbr. 15 memperlihatkan contoh sebuah control valve
yang dirancang dengan sweep-style body dan trim
dari keramik untuk aplikasi yang erosif dengan pasir
dan tekanan yang tinggi.
Training on Valve Technology
18
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 15 Sweep-style globe valve used
in erosive mining application
Training on Valve Technology
19
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
3. Severe Service Valves
Severe service valves are valves equipped with
special features to handle volatile applications, such
as high pressure drops that result in severe
cavitation, flashing, choking, or high noise levels.
Pada kondisi tertentu sering dibutuhkan special
actuation untuk mengatasi gaya yang terjadi.
Gbr. 16 shows severe service valve to handle 1100oF
(593oC) liquid-sodium application with multistage trim
to handle a high pressure drop and a bonnet with
special cooling fins.
The electro-hydraulic actuator is capable of producing
almost 89 ton of thrust.
Training on Valve Technology
10
20
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Gbr. 16 Severe service valve designed to handle highpressure drop, high temperature liquid-sodium application
Training on Valve Technology
21
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1.4 Klasifikasi Menurut Gerakan
Some users classify valves according to the
mechanical motion of the valve: linear or rotary.
Linear valves are known for their simple design, easy
maintenance, and flexibility with more size, pressure
class, and design options than other motion
classification the most common type of valves.
Linear-motion valves (linear valves) memiliki
rancangan sliding-stem yang mendorong closure
element saat valve membuka atau menutup.
Gate, globe, pinch, diaphragm, split-body, three-way,
and angle valves semuanya masuk ke dalam
kelompok linear valves.
Training on Valve Technology
11
22
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Rotary-motion valves (rotary valves) use a closure
element that rotates-through a quarter-turn or 90o
range-to open and close the flow.
Rotary valves are usually smaller in size and weigh
less than comparable linear valves.
The applications is limited to certain pressure drops
and are prone to cavitation and flashing problem.
As rotary-valve designs have matured, they have
overcome these inherent limitations and now being
used at an increasing rate.
Ball, plug, butterfly valves semuanya masuk ke dalam
kategori rotary-motion valves.
Training on Valve Technology
23
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1.5 Klasifikasi Menurut Port Size
1. Full-Port Size
Valves with internal flow equal to the full area of the
inlet port.
Jenis ini utamanya digunakan sebagai on-off and
blocking service valves, dimana aliran harus distop
atau dialihkan.
Full-port valves memungkinkan penggunaan pig
dalam pipeline.
The pig is a self-driven (or flow-driven) mechanism
designed to clean the inside of the pipeline and to
remove any process buildup or scale.
Training on Valve Technology
12
24
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
2. Reduced-Port Size
Reduced-port valves are those whose closure
elements restrict the flow (area of closure element is
less then the area of the inside diameter of pipeline.)
Pembatasan aliran menyebabkan terjadinya pressure
drop saat aliran melewati closure element dan
sebagian tekanan dapat direcovery setelahnya.
The primary purpose of reduced-port valves is to
control the flow through reduced flow or throttling,
which is defined as regulating the closure element to
provide varying levels of flow at a certain opening of
the valve.
Training on Valve Technology
25
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
1.6 Common Piping Nomenclature
Valve and piping nomenclature has been heavily influenced
by imperial system (ANSI standards).
The psi is used to refer to pressure and NPS to refer to
valve and pipe size (in inches across the pipes inside
diameter.
In many countries, outside of the USA, valve and piping
nomenclature is based on the International System of Units
(metric system) from ISO.
Typically metric valve measurement are called out in
millimeter and pressure are noted in kilopascal (kPa) (or
bar).
ISO standards refer to pipe diameter as nominal diameter
(DN) and pressure rating as nominal pressure (PN).
Tables 1 and table 2 provide quick reference for both ANSI
and ISO standards.
Training on Valve Technology
13
26
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Table 1 NPS versus DN
NPS (in.)
DN (mm)
NPS (in.)
DN (mm)
0.25
8.0
200
0.5
15
10.0
250
0.75
20
12.0
300
1.0
25
14.0
350
1.25
32
16.0
400
1.5
40
18.0
450
2.0
50
20.0
500
2.5
65
24.0
600
3.0
80
36.0
900
4.0
100
42.0
1000
6.0
150
48.0
1200
Training on Valve Technology
27
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Table 2 ANSI Pressure Class vs. Nominal Pressure*)
ANSI Pressure Class
Nominal Pressure (PN)
(pounds of force per square
inch of surface area)
(allowable pressure in bar)
150
16
300
40
600
100
900
160
1500
250
2500
400
4500
700
Note:
PN is an approximation to the corresponding ANSI pressure class, and should
not be used as an exact correlation between two standards.
Training on Valve Technology
14
28
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
Reference
Skousen, P.L., Valve Handbook, McGraw-Hill, USA,
1998.
Fisher, Control Valve Handbook, Fisher Control
International, USA, 2001.
Training on Valve Technology
29
Training on Valve Technology
30
Ch. I Introduction to Valves
15
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- DllmeDocument1 pageDllmeBagus AgungNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Introduction To ValvesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To ValvesBagus AgungNo ratings yet
- ImjjDocument1 pageImjjBagus AgungNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Air Coolers Excerpt From Rules of Thumb For Chemical EngineersDocument3 pagesAir Coolers Excerpt From Rules of Thumb For Chemical Engineershalder_kalyan9216No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Belajar Menggambar 3d Dengan Autocad 2007Document200 pagesBelajar Menggambar 3d Dengan Autocad 2007Iswant MacanNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- FRD17Document3 pagesFRD17Raul FloresNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- California Plumbing CodeDocument7 pagesCalifornia Plumbing CodeMOHAMMAD ASIFNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- TCC15 Resistance of Retaining Members XLDocument8 pagesTCC15 Resistance of Retaining Members XLalexanderNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Secondary Composite ExampleDocument12 pagesSecondary Composite Examplef2662961No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Comparative Analysis of Green Building Rating Systems and Codes - 1Document46 pagesComparative Analysis of Green Building Rating Systems and Codes - 1Rohit TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Cost in House ConstructionDocument32 pagesCost in House ConstructionSj interiorNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Casting Fundamentals and Basics ConceptsDocument68 pagesCasting Fundamentals and Basics Conceptsquiron2010No ratings yet
- The History of Investment Foundry ProcessDocument11 pagesThe History of Investment Foundry ProcessVrinda NilotpalNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Zhao - Lee - Post Weld Heat Treatment For High Strength Steel Welded ConnectionsDocument11 pagesZhao - Lee - Post Weld Heat Treatment For High Strength Steel Welded Connectionsbob8c5No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- ADM Masonry M1Document26 pagesADM Masonry M1Ronel ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Subject: Redevelopment of The Society Buildings An UpdateDocument11 pagesSubject: Redevelopment of The Society Buildings An Updatekkundan52No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Lifting Lug CalculationDocument2 pagesLifting Lug Calculationrustamriyadi100% (2)
- Activity - 01&02 - Capitalizable Costs and Modes of Acquisition of PPEDocument2 pagesActivity - 01&02 - Capitalizable Costs and Modes of Acquisition of PPEFrankie AsidoNo ratings yet
- My Dream HouseDocument2 pagesMy Dream HouseDannish JayabalaNo ratings yet
- Selection and Application of Piping System Materials: Standard Practice ForDocument23 pagesSelection and Application of Piping System Materials: Standard Practice ForRoberto Omar Morante VillarrealNo ratings yet
- 2011 UK Waste WoodDocument31 pages2011 UK Waste WoodStuart JonesNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Engineering Interview QuestionDocument174 pagesEngineering Interview QuestionKharisma Jayatra100% (1)
- Case Study Structure Building Collapse - CompressDocument9 pagesCase Study Structure Building Collapse - CompressnaserNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Pubcatalog 2019winter PDFDocument16 pagesAshrae Pubcatalog 2019winter PDFkunkzNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Foundation Design For A High Bay Warehouse With A Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete SlabDocument13 pagesFoundation Design For A High Bay Warehouse With A Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete SlabEstetika chinta PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Interroll PDFDocument3 pagesCatalogo Interroll PDFIgorXavierNo ratings yet
- 2006 Navistar DT466 Engine Torque ValuesDocument5 pages2006 Navistar DT466 Engine Torque ValuesMeadows TruckNo ratings yet
- DIN Low Pressure Fittings and AccessoriesDocument184 pagesDIN Low Pressure Fittings and AccessoriesImtiaz NusratNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- 02 Bituseal e enDocument2 pages02 Bituseal e enYoussef ElgendyNo ratings yet
- Colosseum ResearchDocument3 pagesColosseum ResearchUnmasked kidNo ratings yet
- IABSE-JSCE Bridge Conference August 2015 Bridge Collapses - FinalDocument27 pagesIABSE-JSCE Bridge Conference August 2015 Bridge Collapses - FinalJamilur Reza ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- SPAN Part H - Particular Construction...Document8 pagesSPAN Part H - Particular Construction...ang.xicongNo ratings yet
- Registration CRDocument5 pagesRegistration CRnandha gopalNo ratings yet
- Hvac Boq - R0 - 2914Document46 pagesHvac Boq - R0 - 2914Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Plumbing & Fire Fighting Design & Construction - IPC & NFPA - Online Training CourseDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - Plumbing & Fire Fighting Design & Construction - IPC & NFPA - Online Training CourseShaik Bepari JakeerNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)