Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Form
Uploaded by
api-337402609Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Form
Uploaded by
api-337402609Copyright:
Available Formats
Form
2
Comprehensive
Unit
Format,
Part
B
Design
of
Assessment:
Diagnostic
and
Summative
Assessment
Context
&
Overview:
This
integrated
science
unit
is
aligned
with
the
North
Carolina
fourth
grade
science
standards.
It
is
also
meant
to
be
taught
at
Altamahaw-Ossipee
Elementary
School
in
a
fourth
grade
class.
The
Unit
is
comprised
of
ten,
thirty-minute
lessons
that
will
be
taught
over
the
course
of
eight
school
days.
The
unit
has
a
focus
on
project-based
learning
and
student
centered
learning.
It
also
aims
to
incorporate
English
Language
Arts
and
Technology
standards.
Students
should
have
a
variety
of
opportunities
to
work
in
groups
as
well.
The
unit
will
start
with
a
diagnostic
assessment
comprised
of
twelve
vocabulary
words
that
the
students
are
expected
to
match
with
their
definition.
The
summative
assessment
will
be
the
same
task
in
order
to
best
understand
the
students
growth
in
terms
of
knowledge
of
basic
electricity.
The
students
will
also
be
working
on
a
project
to
apply
their
electrical
knowledge
to
a
real-life
circumstance
such
as
a
lighthouse
located
in
North
Carolina.
Formative
assessments
students
will
be
asked
to
write
about
what
life
would
be
like
without
electricity,
complete
a
word
match
puzzle,
make
a
light
bulb
light
using
materials,
complete
a
graphic
organizer
of
types
of
circuits,
and
discuss
progress
on
their
project.
Essential
Understanding
(big
idea
of
unit):
The
essential
understanding
of
this
unit
is
electricity
is
a
key
element
in
modern
lives
and
is
a
source
of
energy
caused
by
moving
electrons
from
one
atom
to
another.
Additionally,
there
are
two
major
types
of
electricity:
static
and
current
and
each
type
has
different
properties.
Exploration
and
understanding
of
the
basic
electrical
concepts
are
essential
for
future
understandings
of
more
complex
concepts
in
both
chemistry
and
physics.
Through
this
learning,
students
should
have
the
opportunity
to
apply
their
content
knowledge
to
real
life
scenarios.
Research
of
the
electric
wiring
of
lighthouses
will
not
st
only
integrate
21
Century
Skill
development,
but
also
English
Language
Arts
and
Technology
standards
as
well.
Students
will
be
asked
to
hypothesize
how
to
light
a
bulb
after
being
given
the
appropriate
materials
and
an
introduction
to
the
topic.
The
essential
understanding
helped
create
a
course
for
the
unit
plan.
Students
will
not
be
able
to
look
critically
at
more
advanced
forms
of
electrical
devices
and
use
their
vocabulary
knowledge
to
analyze
other
mechanisms.
Furthermore,
students
will
also
be
able
to
better
understand
any
future
electrical
problems
they
face.
The
overall
assessment
plan
focuses
on
vocabulary
knowledge
and
application
of
basic
concepts.
This
aligns
with
the
essential
understanding
because
without
the
vocabulary
students
would
not
be
able
to
understand
deeper
electrical
concepts
or
comprehend
electric
st
instructional
manuals.
Additionally,
in
order
to
create
21
Century
students,
they
must
be
able
to
apply
their
content
knowledge
to
real-life
scenarios.
Their
ability
to
do
this
in
alignment
with
the
essential
understanding
of
this
unit
will
be
evaluated
through
presentations
on
lighthouses
located
in
North
Carolina
on
which
students
conducted
independent
research.
Before
the
presentations,
students
were
given
a
rubric
that
provided
clear
expectations
for
their
presentation.
Assessment
System:
Model
1:
Diagnostic
and
Summative
Assessments
are
the
Same
Task
I
am
also
using
an
additional
summative
assessment
to
provide
additional
information
to
evaluate
student
mastery
Directions
for
Model
1:
Same
Task
1. Diagnostic
(Pre)
and
Summative
(Post)
Assessment
is
the
same
task.
Student
Mastery:
This
assessment
demonstrates
student
mastery
of
the
learning
outcomes
because
it
will
demonstrate
the
students
understanding
of
the
basic
concepts
of
electricity.
Many
of
the
learning
objectives
for
lessons
focus
on
vocabulary
and
therefore,
an
assessment
focused
on
vocabulary
knowledge
is
deeply
aligned
with
the
essential
understanding
of
the
unit.
This
assessment
will
show
student
mastery
of
these
concepts
if
students
successfully
identify
the
correct
definition
for
each
essential
vocabulary
word.
It
will
be
scored
on
a
scale
from
0-12,
with
each
correct
answer
being
worth
1
point.
Vocabulary
words
featured
on
the
assessment
will
be
chosen
from
the
text
given
to
students
as
well
as
key
words
from
experiments.
All
vocabulary
words
will
be
reviewed
and
discussed
in
detail.
2.
Instructional
Effectiveness:
Since
the
same
task
will
be
administered
prior
to
any
instructional
material
as
well
as
after
students
have
been
exposed
to
all
material,
this
will
give
a
clear
representation
of
what
students
have
learned
over
the
course
of
the
lessons.
The
growth
from
the
diagnostic
assessment
to
the
summative
assessment
will
be
closely
examined
in
order
to
determine
instructional
effectiveness.
Scoring
Guides:
Scores
will
be
determined
by
counting
the
correct
number
of
answers
a
student
achieves
according
to
the
answer
key.
There
is
a
maximum
number
of
12
points
for
this
assessment.
Scores
will
be
analyzed
based
on
the
growth
from
the
pre
to
post
assessment.
The
teacher
should
be
able
to
conclude
that
instruction
was
effective
if
the
average
growth
of
each
student
was
positive.
Avoiding
Bias:
Test
will
be
graded
blindly,
meaning
that
the
teacher
candidate
will
not
know
whose
paper
she
is
grading
while
she
is
grading
them.
Furthermore,
the
assessment
was
designed
to
only
assess
what
was
introduced
in
the
classroom
and
avoid
students
benefitting
previous
knowledge
and
experience.
This
plan
was
implemented
by
teaching
each
of
the
vocabulary
words
individually
and
providing
a
visual
aid
when
possible.
Furthermore,
the
assessment
itself
required
no
outside
knowledge.
Accommodations:
One
student,
who
receives
services
for
a
learning
disability
in
the
area
of
reading
took
both
the
diagnostic
and
summative
assessment
orally
in
order
to
prevent
a
decrease
in
score
due
to
his
learning
disability.
Taking
the
assessment
orally
allowed
for
testing
him
on
his
content
knowledge
opposed
to
his
reading
ability
and
therefore
supports
the
learner
in
the
best
way
possible
without
lowering
the
expectations.
The
teacher
will
be
able
to
assess
the
knowledge
of
the
student
on
the
content
rather
than
on
his
reading
disability
because
the
student
must
still
be
able
to
define
each
of
the
vocabulary
terms
on
the
assessment
in
order
to
receive
a
passing
score.
Although
this
initial
understanding
will
only
measure
the
basic
levels
of
Blooms
Taxonomy,
an
additional
assessment
has
been
added
to
understand
their
thorough
understanding.
Additional
Summative
Assessment
It
was
determined
that
in
order
to
have
a
deep
understanding
of
students
growth
throughout
the
unit,
an
additional
summative
assessment
would
be
necessary
in
order
to
access
deeper
levels
of
Blooms
Taxonomy
in
the
assessment
plan.
This
additional
assessment
will
be
comprised
of
a
group
research
project
and
presentation
based
on
an
assigned
lighthouse.
Students
will
be
placed
in
groups
of
5
or
6
students
and
assigned
a
role
within
that
group.
These
groups
were
strategically
designed
and
students
were
given
a
role
expected
to
bring
out
their
individual
strengths.
Roles
within
the
group
included:
Team
Captain,
Presentation
Creator,
Author,
Electrician,
and
Researcher.
In
groups
of
6,
there
were
two
researchers.
Team
Captains
were
expected
to
lead
the
group
in
completing
the
project
in
a
timely
manner
and
ensure
that
all
elements
were
completed.
Additionally,
they
were
responsible
for
all
materials
and
for
submitting
a
score
for
their
group
analyzing
how
well
they
met
all
the
requirements
on
the
rubric.
Presentation
Creators
were
responsible
for
putting
all
of
the
necessary
information
for
the
groups
presentation
in
a
PowerPoint
format.
Authors
were
asked
to
write
a
paragraph
about
the
lighthouses
history.
Electricians
were
responsible
for
wiring
the
lighthouse
using
the
materials
so
that
it
functioned
correctly.
Researchers
were
responsible
for
conducting
research
on
the
lighthouse
and
communicating
this
information
to
other
group
members.
All
group
partners
were
responsible
for
the
appearance
of
their
lighthouse
model
as
well
as
participating
in
the
presentation.
Products
submitted
for
grading
included:
a
paragraph
written
by
the
author
about
the
lighthouse
history,
a
lighthouse
model
that
lights,
a
PowerPoint
presentation,
a
worksheet
completed
by
the
electrician
describing
the
circuit
they
used,
a
worksheet
completed
by
the
author
that
served
as
prewriting,
a
worksheet
completed
by
the
researched
describing
what
sources
they
used,
a
model
of
the
lighthouse,
and
rubrics
completed
by
the
Team
Captain
evaluating
the
groups
work.
The
teacher
will
grade
all
of
these
products
and
the
presentation
based
off
a
rubric
given
to
the
Team
Captains
at
the
beginning
of
the
project
work
time.
Student
Mastery:
This
project
requires
students
to
apply
what
they
have
learned
to
a
real-life
situation
and
incorporate
other
content
areas
with
the
science
knowledge.
Successfully
completing
the
project
shows
mastery
of
the
concepts
because
students
must
understand
circuits,
conductors,
and
insulators
in
order
to
correctly
assemble
their
lighthouse
so
that
is
lights
up.
Avoiding
Bias:
This
project
was
designed
to
avoid
bias
by
giving
students
as
many
supports
as
possible
such
as:
resources,
examples,
and
rubrics.
This
way
they
knew
exactly
what
their
final
product
should
look
like
and
what
expectations
they
should
meet.
Furthermore,
the
assignment
was
implemented
in
a
way
that
all
students
could
receive
help
and
guidance
at
any
time.
Examples
of
the
projects
are
attached
at
the
end
of
this
unit.
Scoring
Guides:
Students
will
receive
two
scores
for
this
project:
one
for
the
presentation
and
one
for
the
products
they
submitted.
These
scores
will
be
determined
by
rubrics
given
to
students
at
the
beginning
of
the
project
experience.
The
teacher
will
use
the
same
rubric
to
determine
both
final
scores.
All
members
of
the
group
will
receive
the
same
score
unless
an
issue
is
brought
to
the
attention
of
the
teacher.
Students
understand
that
they
are
expected
to
share
the
work
of
the
project
equally
while
completing
their
role
assignments.
Students
will
be
expected
to
receive
a
score
of
14
or
higher
on
each
rubric
in
order
to
be
given
a
passing
grade.
Reliability
and
Validity:
Team
Captains
were
asked
to
grade
their
group
based
off
of
the
same
rubric
used
by
the
teacher
to
grade
the
final
project.
These
scores
and
comments
were
taken
into
consideration
when
grading.
Accommodations:
Accommodations
for
this
assessment
are
seen
through
the
differentiation
in
the
group
work.
The
three
students
who
are
on
Tier
II
in
the
area
of
reading
were
each
given
a
role
that
tested
their
content
knowledge
but
at
a
lower
reading
level.
Additionally,
students
were
all
in
teams
and
were
given
permission
to
consult
other
team
members
when
they
had
areas
of
concern.
This
allowed
the
teacher
to
make
inferences
on
student
mastery
of
the
skill
and
allowed
students
to
further
develop
both
their
strengths
and
areas
of
need
through
individual
and
group
work.
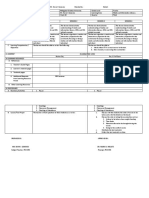
Comparing Diagnostic (Pre-) Assessment Scores with
Summative (Post-) Assessment Results
The following charts can be used to compare students diagnostic and summative assessments in order to evaluate the
effectiveness of my teaching.
Chart Comparing Individual Students Results
Assessment Design: Same Task
Same Task
Diagnostic (Pre-)
Summative
Growth (Post Pre
Assessment
(Post-)
Assessment Score)
score/rating
Assessment score/rating
(x/12)
(x/12)
Student
Charts Comparing Class Results
Assessment Design: Same Task/Different Task
Diagnostic (PRE)
Summative (POST)
Growth (Post Pre)
Mean score:
Mean score:
Mean
growth:
Additional
Task
Group
Students
Presentation
Score
Product
Score
Analysis of Student Learning Data
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- B.ed Syllabus 2017-18Document134 pagesB.ed Syllabus 2017-18Nidhi DedhiaNo ratings yet
- MAPEH6-Q3 Week 5 Music Straight Ma'am ZelDocument5 pagesMAPEH6-Q3 Week 5 Music Straight Ma'am Zeljodzmary86No ratings yet
- Math in Focus Components BrochureDocument5 pagesMath in Focus Components Brochureelgransultan50% (2)
- Active Learning An IntroductionDocument6 pagesActive Learning An IntroductionswarnaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Republic of The PhilippinesRomeo AvanceñaNo ratings yet
- Problem-Based Learning - Deck 5 - PBL AssessmentDocument44 pagesProblem-Based Learning - Deck 5 - PBL AssessmentKartyka NababanNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument6 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsZyra CabarleNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Information For WebsiteDocument2 pagesCurriculum Information For Websiteapi-263335251No ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I.Layunin (Objectives)Document2 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I.Layunin (Objectives)Arvin Dayag100% (1)
- SpeakingDocument16 pagesSpeakingjsayer622No ratings yet
- Ipcrf Verification FormDocument2 pagesIpcrf Verification FormMARCIAL ASADANo ratings yet
- Teacher Created Resources, Inc.: 12621 Western Avenue Garden Grove, CA 92841Document3 pagesTeacher Created Resources, Inc.: 12621 Western Avenue Garden Grove, CA 92841Boris FellguthNo ratings yet
- Why Cornell Notes in Science and at Kofa?Document14 pagesWhy Cornell Notes in Science and at Kofa?Sergio VinsennauNo ratings yet
- PMCFDocument2 pagesPMCFMaitem Stephanie GalosNo ratings yet
- Advance Educational Psychology - SME 629Document2 pagesAdvance Educational Psychology - SME 629bilal khanNo ratings yet
- Lipay Elementary School Weekly Learning Plan Classifies Objects by PropertiesDocument7 pagesLipay Elementary School Weekly Learning Plan Classifies Objects by PropertiesJennyAuroNo ratings yet
- Katrina Jornadal Bruners Constructivist TheoryDocument2 pagesKatrina Jornadal Bruners Constructivist TheoryKat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Position and Competency Profile: Rpms Tool For Teacher I-Iii (Proficient Teachers)Document3 pagesPosition and Competency Profile: Rpms Tool For Teacher I-Iii (Proficient Teachers)Chel GualbertoNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination First Quarter ExaminationDocument3 pagesFirst Quarter Examination First Quarter ExaminationErma JalemNo ratings yet
- Donna Teaching Resume For EportfolioDocument2 pagesDonna Teaching Resume For Eportfolioapi-302147846No ratings yet
- Greater or Less Than Lesson Plan WeeblyDocument4 pagesGreater or Less Than Lesson Plan Weeblyapi-490362164100% (1)
- Five Models of Staff DevelopmentDocument34 pagesFive Models of Staff DevelopmentZulaiha Abdul Rahman100% (3)
- EDEL453 Spring2014 RebeccaWaltz Unit Plan REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesEDEL453 Spring2014 RebeccaWaltz Unit Plan REFLECTIONBecci WaltzNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument2 pagesWorksheetRobert WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Grammar in ContextDocument20 pagesGrammar in ContextJaved IqbalNo ratings yet
- Writing A Letter Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWriting A Letter Lesson Planapi-505825348No ratings yet
- LAC Narrative 2019-2020Document6 pagesLAC Narrative 2019-2020mae santos100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1api-361854774No ratings yet
- Aet 562 wk6 Signature Assignment The Integrated Classroom and The Role of The EducatorDocument7 pagesAet 562 wk6 Signature Assignment The Integrated Classroom and The Role of The Educatorapi-557342105No ratings yet
- DLL For 3rd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesDLL For 3rd Quarter ExamDiana Leonidas64% (11)