Professional Documents
Culture Documents
African Ginger
Uploaded by
SNCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
African Ginger
Uploaded by
SNCopyright:
Available Formats
11/7/2016
AfricanGinger
The Leaders in Natural Traditional
African Medicines
Home
AFRICAN GINGER
AboutUs
ContactUs
Siphonochilus aethiopicus
Products
HerbalFacts
IdentifyAilment
Common names:
Wildegemmer (Afrikaans); Natal ginger,
Wild ginger (English); indungulo,
isiphephetho (Shangaan, Sotho, Zulu).
Introduction:
African ginger is one of the Zulus top herbal medicines and widely used throughout its distribution area. This
plant is highly prized for its medicinal value and as a result has been over harvested from the wild to a point just
short of total extinction in South Africa.
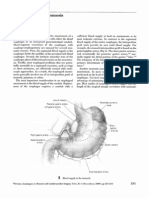
African ginger is a deciduous plant with large, hairless leaves, developing annually from a small, distinctive
coneshaped rhizome. The spectacular flowers appear at ground level in early summer.
The root or rhizome is the part used, and comes to market in jointed branches called races or hands. The smell
of the African ginger is aromatic and penetrating, the taste spicy, pungent, hot and biting.
Distribution:
http://www.herbalafrica.co.za/africanginger.html
1/4
11/7/2016
AfricanGinger
Distribution:
Wild African ginger has a restricted distribution in Mpumalanga, Northern Province and has become extinct in
KwaZulu Natal. The plant also occurs in Mozambique and Zimbabwe.
Medicinal Uses:
This plant has a long history in African traditional medicine for a range of conditions including arthritis, asthma,
candida, colds & flu, coughs, dysmenorrhoea, headaches, hysteria, influenza, menstrual cramps, mild asthma,
mood swings, premenstrual syndrome, sinusitis, throat infections, thrush and to clear nasal passages.
The African ginger has a stimulating effect on the heart and circulation, creating a feeling of warmth and well
being and restoring vitality, especially for those feeling the cold in winter.
Hot ginger tea promotes perspiration, brings down a fever and helps to clear catarrh. Ginger has a stimulating
and expectorant action in the lungs, expelling phlegm and relieving catarrhal coughs and chest infections.
African ginger is a wonderful aid to digestion. It invigorates the stomach and intestines, stimulating the
appetite and enhancing digestion by encouraging secretion of digestive enzymes. It moves stagnation of food and
subsequent accumulation of toxins, which has a farreaching effect throughout the body, increasing general
health, vitality and enhancing immunity.
African ginger is famous for relieving nausea and vomiting, from whatever cause. It settles the stomach,
soothes indigestion and calms wind. Its painrelieving and relaxing effects in the gut relieve colic and spasm,
abdominal pain, distension and flatulent indigestion and help to relieve griping caused by diarrhoea.
In the uterus it promotes menstruation, useful for delayed and scanty periods as well as clots. African ginger
relaxes spasm and relieves painful ovulation and periods, and is recommended to invigorate the reproductive
system. African ginger also inhibits clotting and thins the blood; it lowers blood pressure and cholesterol.
A preparation of this plant is administered to horses as prevention against horse sickness.
Europeans regard the African ginger as Africas best natural antiinflammatory remedy, besides its many other
uses.
Other beneficial uses:
http://www.herbalafrica.co.za/africanginger.html
2/4
11/7/2016
AfricanGinger
African ginger is an excellent remedy for digestive complaints (indigestion, nausea, gas, colic and
congestion).
African ginger 's antiseptic qualities make it highly beneficial for gastrointestinal infections.
Circulatory stimulant stimulates the circulation making it an important remedy for chilblains and poor
circulation. By improving the circulation, ginger helps reducing high blood pressure.
African ginger helps to "thin" the blood as well as to lower cholesterol.
African ginger is useful as a supplement for heartburn & halitosis (bad breath).
African ginger is known to relieve vomiting and to sooth the stomach and spleen in the process.
African ginger is a warm vascular stimulant and body cleanser. It encourages the removal of toxins
through the skin, and through increased kidney filtration.
African ginger relieves motion sickness and morning sickness.
Active Ingredients:
The conical rhizome and roots contain a high percentage of a characteristic sesquiterpenoid, which is a key
phytochemical active. Extracts of the rhizome have been demonstrated to be antiinflammatory
(prostaglandinsynthetase inhibition), bronchodilatory, smooth muscle relaxant, mildly sedative, and anti
candidal. The presence of antiseptic monoterpenoids contributes to the bioactivity
The African ginger also contains a volatile oil with terpinerol (a natural antiseptic) and various other
monoterpenoids.
The peculiar flavour of the root appears to depend on the volatile oil; its pungency is due to a yellowish liquid
called gingerol. This is a mixture of homologous phenols of the formula C16H26O3. (CH2O) no Zingerone,
C11H14O3, is crystalline and has a sweet odour and an extremely pungent taste; it is chemically related to vanillin,
and is formed when gingerol is treated with baryta water. The pungency of gingerol, in contrast to that of
capsicum, is destroyed by heating with alkaline hydroxides.
The volatile oil is yellow and consists largely of a mixture of terpenes, camphone, phellandrene and a new
sesquiterpene, which the discoverers, von Soden and Rojahn (Ph. Ztg., 1900, p. 414) call zingiberene. There is
also some citral, cineol and borneol in the oil.
Pharmacological Effects:
The African ginger has been studied for its antibacterial, antifungal, painrelieving, antiulcer, antitumour
and other properties.
The monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids in the oil are most likely responsible for the reported benefits in
colds and influenza. Volatile oils are generally used for their decongestant, antiseptic and diuretic effects.
http://www.herbalafrica.co.za/africanginger.html
3/4
11/7/2016
AfricanGinger
Research done at Cornell University Medical College has found that ginger may help prevent strokes and
hardening of the arteries. The active ingredient in ginger (gingerol) is proven effective in preventing recurrences
of socalled "little strokes". It is believed that this substance (gingerol) inhibits an enzyme that causes cells to
clot.
How it works in the body:
The phenolic compounds are the agents responsible for relaxing the muscles of the stomach, and this may also
explain their effect in easing travel or motion sickness. Fresh or dried, the root has been shown to minimize
vomiting. In addition, the phenolic ingredients act within the stomach as a sedative and painkiller, which helps
to reduce overactivity of the gut. In stomach infections, the oil acts as an antiseptic and an antiinflammatory.
The gingerols alone are thought to be responsible for ginger's action as a liver protective. In the cardiovascular
system, ginger is thought to also reduce cholesterol levels, while at the same time increasing a sluggish
circulation
Nutrient Content:
Ginger is rich in minerals and contains Vitamins B3 & B5.
Safety and Toxicity:
Contraindicated in pregnancy and while breastfeeding. Side effects of ginger are rare when used as
recommended. However, some people may be sensitive to the taste or may experience heartburn. Persons with a
history of gallstones should consult a nutritionally oriented doctor before using ginger. A doctor should be
informed if ginger is used before surgery to counteract possible post anaesthesia nausea. The German
therapeutic monograph on ginger warns patients with gall bladder disease to avoid it and also cautions against
exceeding the recommended dosage. Because of its heating properties, ginger is not recommended for those who
do not tolerate heat well or those with gastritis or peptic ulcers.
BACK TO HERBAL FACTS
Copyright Herbal Africa 2016 Designed by: Willem van Moerkerken
http://www.herbalafrica.co.za/africanginger.html
4/4
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Earth Science B SyllabusDocument3 pagesEarth Science B SyllabusSNNo ratings yet
- DIY Jerky Drier InstructionsDocument38 pagesDIY Jerky Drier InstructionsAhmet Altin100% (2)
- The Complete Guide to Growing and Selling MicrogreensDocument50 pagesThe Complete Guide to Growing and Selling Microgreensghonamy91% (34)
- Leaching Acorn - Riekes Nature AwarenessDocument5 pagesLeaching Acorn - Riekes Nature AwarenessSNNo ratings yet
- Earth PDFDocument6 pagesEarth PDFSNNo ratings yet
- AP GovernmentDocument12 pagesAP GovernmentSNNo ratings yet
- Cajete 1994 PDFDocument244 pagesCajete 1994 PDFSN100% (2)
- Earth Science ADocument16 pagesEarth Science ASNNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus CDocument16 pagesAP Calculus CSNNo ratings yet
- Handbook Robyn FrancisDocument139 pagesHandbook Robyn FrancisSNNo ratings yet
- Your Crap, Our Compost - Turning Human Feces Into Fertile Soil - AlternetDocument4 pagesYour Crap, Our Compost - Turning Human Feces Into Fertile Soil - AlternetSNNo ratings yet
- Art Foundations ABDocument13 pagesArt Foundations ABSNNo ratings yet
- Wild-Simulated Forest Farming For Ginseng ProductionDocument4 pagesWild-Simulated Forest Farming For Ginseng ProductionSNNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- AP Calculus CDocument16 pagesAP Calculus CSNNo ratings yet
- Handbook Robyn FrancisDocument139 pagesHandbook Robyn FrancisSNNo ratings yet
- Algebra Iab MXLDocument6 pagesAlgebra Iab MXLSNNo ratings yet
- Palm AshDocument5 pagesPalm AshSNNo ratings yet
- AP US History ADocument7 pagesAP US History ASNNo ratings yet
- Palm AshDocument5 pagesPalm AshSNNo ratings yet
- The Power of Consciousness - Magic, Magicians and SorcerersDocument16 pagesThe Power of Consciousness - Magic, Magicians and SorcerersSNNo ratings yet
- African Knowledges and SciencesDocument176 pagesAfrican Knowledges and SciencesSNNo ratings yet
- Some Physical Properties of Gbafilo ( - I - Chrysobalanus Icaco - I - ) Fruits and Kernels Preparatory To Primary ProcessingDocument11 pagesSome Physical Properties of Gbafilo ( - I - Chrysobalanus Icaco - I - ) Fruits and Kernels Preparatory To Primary ProcessingSNNo ratings yet
- Finger MilletDocument34 pagesFinger MilletSNNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Kaun Potash (Akanwu)Document11 pagesBenefits of Kaun Potash (Akanwu)SNNo ratings yet
- VIBRATIONAL JEWELLERY - Symbology of The Ages (Amulets & Talismans) - Page 3 - Alicja Centre of Well-BeingDocument4 pagesVIBRATIONAL JEWELLERY - Symbology of The Ages (Amulets & Talismans) - Page 3 - Alicja Centre of Well-BeingSNNo ratings yet
- From Diop To AsanteDocument23 pagesFrom Diop To AsanteSN100% (1)
- Sieber Hair in African ArtDocument18 pagesSieber Hair in African ArtSNNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Esophageal AnastomosisDocument11 pagesEsophageal Anastomosisndang01No ratings yet
- Imaging in Acute Abdomen: Dr. Wan Najwa Zaini Wan Mohamed Radiologist, Hospital Queen Elizabeth IiDocument70 pagesImaging in Acute Abdomen: Dr. Wan Najwa Zaini Wan Mohamed Radiologist, Hospital Queen Elizabeth IiYogi drNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in HorsesDocument14 pagesFluid Therapy in HorsesMarianaNo ratings yet
- Nat MurDocument19 pagesNat MurSun BNo ratings yet
- BIRLA KERALA VAIDYASALA PRODUCT GUIDEDocument42 pagesBIRLA KERALA VAIDYASALA PRODUCT GUIDEAndrey Golovinov100% (1)
- ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN PARACLINICAL FINDINGSDocument9 pagesACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN PARACLINICAL FINDINGSDona Teodor FCNo ratings yet
- Equine Anesthesia Course NotesDocument15 pagesEquine Anesthesia Course NotesSam Bot100% (1)
- Correctional Healthcare Management Oklahoma Class Action LawsuitDocument55 pagesCorrectional Healthcare Management Oklahoma Class Action LawsuitMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and treatment of metal poisoningDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and treatment of metal poisoningAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Adult With Abdominal Pain - UpToDateDocument13 pagesEvaluation of The Adult With Abdominal Pain - UpToDateAudricNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument44 pagesAbdominal PainAjo YayanNo ratings yet
- Estabilizacion de PotrillosDocument6 pagesEstabilizacion de PotrillosCarlos Pedro VillaNo ratings yet
- IM On Call (LANGE On Call) PDFDocument738 pagesIM On Call (LANGE On Call) PDFindia2puppy100% (8)
- Horse HerniaDocument2 pagesHorse HerniaHadi Putra RihansyahNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain History TakingDocument8 pagesAbdominal Pain History TakingParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Everything About DogsDocument292 pagesEverything About Dogstobiasaxo5653100% (1)
- History Taking in Medicine and Surgery: Third EditionDocument48 pagesHistory Taking in Medicine and Surgery: Third EditionSapreni agustinaNo ratings yet
- Urology Semiology Guide for Renal Colic & HematuriaDocument30 pagesUrology Semiology Guide for Renal Colic & HematuriaNikita KumariNo ratings yet
- Vademecum PDFDocument36 pagesVademecum PDFwalter0% (1)
- Abdominal Pain and Vomiting in ChildrenDocument18 pagesAbdominal Pain and Vomiting in ChildrenSimon Ganesya RahardjoNo ratings yet
- Thibault 2019Document8 pagesThibault 2019Mafe HerreraNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument11 pagesAbdominal PainSNo ratings yet
- Int Obs PDFDocument37 pagesInt Obs PDFsurgeon77No ratings yet
- Essence of Bowen PDFDocument36 pagesEssence of Bowen PDFsorodocelena100% (1)
- Management of A Patient With Acute Abdominal Pain - College of Surgeons of Sri Lanka 2007 PDFDocument30 pagesManagement of A Patient With Acute Abdominal Pain - College of Surgeons of Sri Lanka 2007 PDFRevalitha PutriNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen - Shaking Down The SuspectsDocument11 pagesAcute Abdomen - Shaking Down The SuspectsKeldon15100% (1)
- Horse I-Search PaperDocument5 pagesHorse I-Search Paperapi-317898511No ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Obliteration of The Nephrosplenic Space Using Polypropylene Mesh in Five HorsesDocument7 pagesLaparoscopic Obliteration of The Nephrosplenic Space Using Polypropylene Mesh in Five HorsesÜöGinaÖüConsueloNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Visions of America 3rd Edition by Jennifer D Keene PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Visions of America 3rd Edition by Jennifer D Keene PDFclarence.barcia711100% (31)
- MSN I 25.06 .2020 AN Unit IV. Small Intestinal Malabsorption & ObstructionDocument92 pagesMSN I 25.06 .2020 AN Unit IV. Small Intestinal Malabsorption & ObstructionYAMINIPRIYAN0% (1)