Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reported Speech 2016
Uploaded by
Alex PeraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reported Speech 2016
Uploaded by
Alex PeraCopyright:
Available Formats
A.
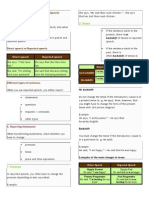
Reporting Statements
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
tense
place and time expression
1- Pronouns
In reported speech, you often have to change the pronoun depending on who says what.
Example:
She says, My dad likes roast chicken. She says that her dad likes roast chicken.
2- Tenses
If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported speech.
If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported speech.
Direct speech
Reported speech
(no backshift)
I write poems.
He says that he writes poems.
(backshift)
I write poems.
He said that he wrote poems.
No backshift
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause is in a present tense (e. g. He says). Note,
however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person
singular).
Example:
He says, I write poems. He says that he writes English.
Backshift
You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e. g. He said).
Example:
He said, I am happy. He said that he was happy.
Examples of the main changes in tense:
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Simple Present
Simple Past
He said: "I am happy"
He said that he was happy
Present Progressive
Past Progressive
He said: "I'm looking for my keys"
He said that he was looking for his keys
Simple Past
Past Perfect Simple
He said: "I visited New York last year"
He said that he had visited New York the
previous year.
Present Perfect
Past Perfect
He said: " I've lived here for a long time "
He said that he had lived there for a long time
Past Perfect
Past Perfect
He said: "They had finished the work when
He said that they had finished the work when
I arrived"
he had arrived"
Past Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I was playing football when the
He said that he had been playingfootball when
accident occurred"
the accident had occurred
Present Perfect Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
He said:"I have been playingfootball for two
He said that he had been playingfootball for two
hours."
hours
Past Perfect Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I had been reading a newspaper
He said that he had been reading a newspaper
when the lightwent off"
when the light had gone off
Future Simple (will+verb)
Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I will open the door."
He said that he would open the door.
Conditional (would+verb)
Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I would buy Mercedes if
He said that he would buyMercedes if he had
I were rich"
been rich"
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn't, ought to, used to do not normally
change.
Example:
He said, "She might be right." He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
Modal
can
Direct speech
"I can do it."
Reported speech
He said he could do it.
may
"May I go out?"
He wanted to know if he might go out.
must
"She must apply for the job."
He said that she must/had to apply for the job.
will
"They will call you."
He told her that they would call her.
3- Place, demonstratives and time expressions
Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement
(i.e. the location and/or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place; demonstratives and time
expressions.
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Time Expressions
today
that day
now
then
yesterday
the day before
days ago
days before
last week
the week before
next year
the following year
tomorrow
the next day / the following day
Place
here
there
Demonstratives
this
that
these
those
B. Reporting Questions
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
place and time expressions
tenses (backshift)
Also note that you have to:
transform the question into an indirect question
use the question word (where, when, what, how) or if / whether
Types of questions
With question word (what,
why, where, how...)
Direct speech
"Why" dont you speak He asked me why I didnt
English?
speak English.
Without question word (yes or Do you speak
no questions)
Reported speech
English?
He asked me whether / if I
spoke English.
C. Reporting requests / commands
When transforming requests and commands, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
place and time expressions
Direct speech
Reported speech
Nancy,do the exercise.
He told Nancy to do the exercise.
"Nancy, give me your pen, please."
He asked Nancy to give him her pen.
Tenses are not relevant for requests simply use to / not to + verb (infinitive without "to")
Example:
She said, Sit down." - She asked me to sit down.
She said, "don't be lazy" - She asked me not to be lazy
For affirmative use to + infinitive (without to)
For negative requests, use not to + infinitive (without to).
D. Other transformations
Expressions of advice with must, should and ought are usually reported
using advise /urge.
Example:
"You must read this book."
He advised / urged me to read that book.
The expression lets is usually reported using suggest. In this case, there are two
possibilities for reported speech: gerund or statement with should.
Example:
"Lets go to the cinema."
1. He suggested going to the cinema.
2. He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
Main clauses connected with and/but
If two complete main clauses are connected with and or but, put that after the conjunction.
Example:
He said,I saw her but she didn't see me. He said that he had seen her but thatshe hadn't
seen him.
If the subject is dropped in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do
not use that.
Example:
She said,I am a nurse and work in a hospital. He said that she was a nurse andworked in a
hospital.
You might also like
- Say What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.From EverandSay What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechDoris Ana-MariaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechJohn Alvin de LaraNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 pagesIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515No ratings yet
- Reported Speech in EnglishDocument6 pagesReported Speech in EnglishIoanaR2011No ratings yet
- Reported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesReported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechZaniShiraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument5 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsSofia AngelovaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive GuideDocument3 pagesDirect and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive GuideAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported Speechstanjack99No ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument12 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsOfelia MontielNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument4 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsZaniShira100% (1)
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (1)
- 2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument4 pages2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechAbdelhadi Ait AllalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ChartDocument4 pagesReported Speech ChartAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNo ratings yet
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech GuideDocument5 pagesReported Speech GuideKatita VieraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechYevit RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Reported speech rulesDocument6 pagesReported speech rulesaravindrnairNo ratings yet
- (GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)Document15 pages(GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)NamNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument14 pagesExercisesJoyCamilleReyesNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ProjectDocument21 pagesReported Speech ProjectS fu fu86% (7)
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document3 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Pili Lema BlancoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 0Document6 pagesReported Speech 0Eva VillamedianaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechWaleed Marouf A. NueiratNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechalwiNo ratings yet
- Mamllantino Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesMamllantino Reported SpeechMaría Angeles Martín Llantino0% (1)
- EnglishDocument11 pagesEnglishrastamanl9No ratings yet
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported SpeechLinda FatmasariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesLesson 5 - Indirect SpeechAkbarul AminNo ratings yet
- HS-001A L 4 Reported SpeechDocument39 pagesHS-001A L 4 Reported SpeechS KohliNo ratings yet
- Example: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishDocument4 pagesExample: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishRita QuispeNo ratings yet
- Statements in Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesStatements in Reported SpeechZenmetsu No AkaiNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech FinalDocument8 pagesDirect Speech FinalMahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument28 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechKaashvi AroraNo ratings yet
- 1 Reported Speech PDFDocument17 pages1 Reported Speech PDFdinu69inNo ratings yet
- Virtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationDocument6 pagesVirtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- 1 Reported SpeechDocument17 pages1 Reported SpeechIsrael SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDivya Rai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAdine RachmadinnaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNoa PahlićNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported Speechapi-241242931100% (1)
- Direct and indirect speech rulesDocument8 pagesDirect and indirect speech rulessarfarazNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect SpeechMahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechLisseth Andrea Ledesma GarriazoNo ratings yet
- 8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)Document6 pages8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)HangNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ExplainedDocument14 pagesReported Speech ExplainedДильназ КожахметоваNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechRondel Forjes100% (1)
- Direct Speech Vs Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect Speech Vs Reported SpeechMiguel MontoyaNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechMAGDALENA MELANIA GHERGHENo ratings yet
- MEETING 10 - 11 REPORTED SPEECH (New)Document25 pagesMEETING 10 - 11 REPORTED SPEECH (New)AiluNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: English Grammar RulesDocument4 pagesReported Speech: English Grammar RulesCidinha Pinto CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: StatementsDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: StatementsЛеся ЧабаненкоNo ratings yet
- Devina E.L.M. - Direct and IndirectDocument5 pagesDevina E.L.M. - Direct and IndirectDyah Ayu Arum WNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDeka FabNo ratings yet
- He Said, "I Have Lost My Umbrella.": Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesHe Said, "I Have Lost My Umbrella.": Indirect SpeechSRIFINo ratings yet
- Reported Speech NotesDocument5 pagesReported Speech NotesChipo MulundikaNo ratings yet
- A Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsDocument8 pagesA Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- How To Spend The Most Perfect Week in PortugalDocument6 pagesHow To Spend The Most Perfect Week in PortugalAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- The Top Portuguese Dishes You Need To TryDocument9 pagesThe Top Portuguese Dishes You Need To TryAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- A Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsDocument11 pagesA Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- How To Spend The Most Perfect Week in PortugalDocument6 pagesHow To Spend The Most Perfect Week in PortugalAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- 20 Must-Visit Attractions in LisbonDocument15 pages20 Must-Visit Attractions in LisbonAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- A Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsDocument8 pagesA Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- A Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsDocument11 pagesA Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- A Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsDocument11 pagesA Seasonal Guide To Portugal's Best AttractionsAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple InterrogativeDocument2 pagesPresent Simple InterrogativeAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Positive FeedbackDocument3 pagesActivity 1 Positive FeedbackAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- 14 Fascinating Facts About South KoreaDocument13 pages14 Fascinating Facts About South KoreaAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Business idioms explainedDocument10 pagesBusiness idioms explainedAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- HBR - Russia & InternetDocument1 pageHBR - Russia & InternetAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- English p4 6Document4 pagesEnglish p4 6Alex PeraNo ratings yet
- English p7 9Document3 pagesEnglish p7 9Alex PeraNo ratings yet
- English p1 3Document3 pagesEnglish p1 3Alex PeraNo ratings yet
- They Know My View On This SubjectDocument1 pageThey Know My View On This SubjectAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Negative WorksheetDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Negative WorksheetAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- We AcknowledgeDocument1 pageWe AcknowledgeAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- They KnowDocument1 pageThey KnowAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple or ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple or ContinuousAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- I Understand Your Point of ViewDocument1 pageI Understand Your Point of ViewAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Glossary - CEPI - CONFEDERATION OF EUROPEAN PAPER INDUSTRIES PDFDocument4 pagesGlossary - CEPI - CONFEDERATION OF EUROPEAN PAPER INDUSTRIES PDFAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- We AcknowledgeDocument1 pageWe AcknowledgeAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument1 pageHTTPAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Papermaking or Bookmaking TermsDocument25 pagesGlossary of Papermaking or Bookmaking TermsRichard PollardNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Grammar Errors (English)Document1 pageTop 10 Grammar Errors (English)Reddmar José Quevedo CarrasqueroNo ratings yet
- Subject IAM You Are HE She Is IT WE YOU TheyDocument1 pageSubject IAM You Are HE She Is IT WE YOU TheyAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- AgencyDocument1 pageAgencyAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Test Simple Past - Present Perfect - Present Perfect Continues - Will - Going ToDocument7 pagesTest Simple Past - Present Perfect - Present Perfect Continues - Will - Going Toliseth sandoval arangoNo ratings yet
- New Headway Int 4th Ed SBDocument162 pagesNew Headway Int 4th Ed SBاسراء الداعور100% (1)
- Special FinitesDocument2 pagesSpecial FiniteswalteremmNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech (FS)Document13 pagesPart of Speech (FS)mafma qlateNo ratings yet
- Stowaway's reckless flightDocument2 pagesStowaway's reckless flightMarcella FeliciaNo ratings yet
- Project 2 Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument12 pagesProject 2 Gerunds and InfinitivesValeria AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Basic Simple Present Tense 3Document99 pagesBasic Simple Present Tense 3Ahmad Abdul SyakurNo ratings yet
- Ease and Difficulty in Vocabulary Learning: Factors That Affect Word MemorizationDocument9 pagesEase and Difficulty in Vocabulary Learning: Factors That Affect Word MemorizationBaladika Al-HaririNo ratings yet
- 102 English Tips: Another Quick Guide To Avoiding "Slovenglish"Document70 pages102 English Tips: Another Quick Guide To Avoiding "Slovenglish"AronaNo ratings yet
- (CNA) Activity - Expansion 1Document3 pages(CNA) Activity - Expansion 1doug20521891No ratings yet
- Noun PhrasesDocument7 pagesNoun PhrasesSaya BaisultanovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22: Asking Questions in Korean: How, What, Which, How ManyDocument11 pagesLesson 22: Asking Questions in Korean: How, What, Which, How ManyAvicenna Zahara BungaNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Passive Voice Explainedعلي عامر احمد C1No ratings yet
- How OftenDocument16 pagesHow OftenHamed hamidiNo ratings yet
- BE Verb IntroductionDocument2 pagesBE Verb IntroductionmokifaNo ratings yet
- Future TestDocument3 pagesFuture TestDA MANo ratings yet
- Week 9-Book 1Document3 pagesWeek 9-Book 1Kiều Ny ĐườngNo ratings yet
- 003 Lista de Verbos Irregulares en Ingles PDFDocument6 pages003 Lista de Verbos Irregulares en Ingles PDFjya17No ratings yet
- SOF International English Olympiad 2017-18 Sample Paper Syllabus Class 2Document2 pagesSOF International English Olympiad 2017-18 Sample Paper Syllabus Class 2amp127983% (6)
- John Soars - Headway-Oxford University Press (1987) PDFDocument141 pagesJohn Soars - Headway-Oxford University Press (1987) PDFVNMedia100% (1)
- Word Meaning Past and Past Participle ListDocument6 pagesWord Meaning Past and Past Participle ListMay Mœnä GülNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesPassive VoiceRodrigoNo ratings yet
- New Proficiency - Use of English (Students' Book)Document267 pagesNew Proficiency - Use of English (Students' Book)Dominika Kalista100% (3)
- Spotting The Error Quiz: 60+ Preposition Questions Part IIDocument10 pagesSpotting The Error Quiz: 60+ Preposition Questions Part IInazmulNo ratings yet
- BasicwritingskillsDocument170 pagesBasicwritingskillsYonatan YirgaNo ratings yet
- Minggu ke-6 (19 APRIL 2021) BISPRO 1B Mata Kuliah Pendalaman Tata Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesMinggu ke-6 (19 APRIL 2021) BISPRO 1B Mata Kuliah Pendalaman Tata Bahasa InggrisMuh Imaduddin BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Irregular PluralDocument9 pagesIrregular PluralNOOR HARLINA ABDUL JALILNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense ChartDocument2 pagesVerb Tense ChartGloria LópezNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Contextual Meaning in Maherzain's Song LyricsDocument87 pagesAnalyzing Contextual Meaning in Maherzain's Song Lyricskeynatalia siahaanNo ratings yet