Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types Of Cam And Followers
Uploaded by
l8o8r8d8s8i8v8Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types Of Cam And Followers
Uploaded by
l8o8r8d8s8i8v8Copyright:
Available Formats
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
HOME
ABOUT ME
INTERVIEW GUIDE
MECHANICAL PROJECTS
SEMINAR TOPICS
BASIC CONCEPTS
GATE
GUEST POST
BreakingNews
ng System
BasicMech.Concepts
Adsby Google
DesignCam
Effects of Common Alloying Elements in Steel
CamToy
PDFPPT
CareerInMechanicalField
PaperPDF
TYPES OF CAM AND FOLLOWERS-BASIC OF THEORY
OF MACHINE
SachinThorat
Adsby Google
PPTPresentation
ProjectReport
Types Of Cam And Followers-Basic Of Theory
Of machine
A cam is a rotating machine element which gives reciprocating or oscillating motion to
another element known as follower. The cam and the follower have a line contact and
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
1/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
constitute a higher pair. The cams are usually rotated at uniform speed by a shaft, but
the follower motion is pre- determined and will be according to the shape of the cam.
The cam and follower is one of the simplest as well as one of the most important
mechanisms found in modern machinery today.
The cams are widely used for operating the inlet and exhaust valves of internal
combustion engines, automatic attachment of machinery, paper cutting machines,
spinning and weaving textile machinery, feed mechanism of automatic lathes etc.
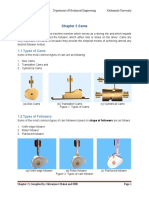
1. According to the surface in contact.
The followers, according to the surface in contact, are as follows:
(a) Knife edge follower.
When the contacting end of the follower has a sharp knife edge, it is called a knife edge
follower, as shown in Fig.. The sliding motion takes place between the contacting
surfaces (i.e. the
knife edge and the cam surface). It is seldom used in practice because the small area of
contacting surface results in excessive wear. In knife edge followers, a considerable side
thrust exists between the follower and the guide.
Like
Types Of Followers according to surface of contacts
(b) Roller follower.
When the contacting end of the follower is a roller, it is called a roller follower, as shown
in Fig. Since the rolling motion takes place between the contacting surfaces (i.e. the roller
and the
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
2/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
cam), therefore the rate of wear is greatly reduced. In roller followers also the side thrust
exists between the follower and the guide. The roller followers are extensively used
Share
where more space
is available such as in stationary gas and oil engines and aircraft engines.
(c) Flat faced or mushroom follower.
When the contacting end of the follower is a perfectly at face, it is called a at-faced
follower, as shown in Fig. It may be noted that the side thrust between the follower and
the guide is much reduced in case of at faced followers. The only side thrust is due to
friction between the contact surfaces of the follower and the cam. The relative motion
between these surfaces is largely of sliding nature but wear may be reduced by osetting the axis of the follower, as shown in Fig so that when the cam rotates, the
follower also rotates about its own axis. The at faced followers are generally used
where space is limited such as in cams which operate the valves of automobile engines.
(d) Spherical faced follower
When the contacting end of the follower is of spherical shape, it is called a spherical
faced follower, as shown in Fig. It may be noted that when a at-faced follower is used in
automobile engines, high surface stresses are produced. In order to minimize these
stresses, the at end of the follower is machined to a spherical shape.
2. According to the motion of the follower.
The followers, according to its motion, are of the following two types:
Like
a. oscillating Follower b. Reciprocating followers
(a) Reciprocating or translating follower.
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
3/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
When the follower reciprocates in guides as the cam rotates uniformly, it is known as
reciprocating or translating follower.
Share
(b) Oscillating or rotating follower.
When the uniform rotary motion of the cam is convertedinto predetermined oscillatory
motion of the follower, it is called oscillating or rotating follower. The follower, as shown
in Fig ., is an oscillating or rotating follower.
3. According to the path of motion of the follower.
The followers, according to its path of motion, are of the following two types:
a. Raidal b. O-set follower
(a) Radial follower.
When the motion of the follower is along an axis passing through the centre of the cam,
it is known as radial follower.
(b) O-set follower.
When the motion of the follower is along an axis away from the axis of the cam centre, it
Like
is called o-set follower,
CAMS :
Cams can be classied into the following three types based on their shapes.
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
4/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
Share
Types Of Cams
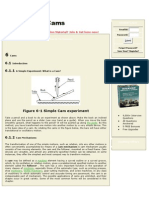
1.) Plate or disk cams:
Plate or disk cams are the simplest and most common type of cam. A plate cam is
illustrated in gure. This type of cam is formed on a disk or plate. The radial distance
from the center of the disk is varied throughout the circumference of the cam. Allowing
a follower to ride on this outer edge gives the follower a radial motion.
2) Cylindrical or drum cam:
A cylindrical or drum cam is illustrated in gure . This type of cam is formed on a
cylinder. A groove is cut into the cylinder, with a varying location along the axis of
rotation. Attaching a follower that rides in the groove gives the follower motion along
the axis of rotation.
Like
3) Linear cam:
A linear cam is illustrated in gure. This type of cam is formed on a translated block. A
groove is cut into the block with a distance that varies from the plane of translation.
Attaching a follower that rides in the groove gives the follower motion perpendicular to
the plane of translation.
Applications of cams
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
5/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
Cams are widely used in automation of machinery, gear cutting machines, screw
Share
machines, printing press, textile industries, automobile engine valves, tool changers of
machine centers, conveyors, pallet changers, sliding fork in wearhouses etc.
Cams are also used in I.C engines to operate the inlet valves and exhaust valves.The cam
shaft rotates by using prime moveres. It causes the rotation of cam. This rotation
produces translatory motion of tappet against the spring. This translatory motion is used
to open or close the valve.
NanotechnologyProducts
NanoParticles/Powders/DispersionsNanotubes,additives&NanoLubes
Gotomknano.com
Adsby Google
FinalYearProjects
CamMachines
Faceboo
k
Tumblr
NEXT
Important fuel specifications for Diesel Used
In IC Engine
Quiz 1: Basic of Thermodynamics Online
Objective Quiz
Like
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
6/7
10/15/2016 TypesOfCamAndFollowersBasicOfTheoryOfmachine|MechanicalEngineeringWorld|ProjectIdeas|SeminarTopics|Ebooks(Pdf)|NewTre
Share
Like
http://www.mechengg.net/2016/06/typesofcamandfollowers.html#more
7/7
You might also like
- Industrial Robotics PDFDocument39 pagesIndustrial Robotics PDFcemoksz71% (14)
- Your Benefit 250 SCALA: Control Center SystemDocument6 pagesYour Benefit 250 SCALA: Control Center SystemJennibabes AlgosoNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveijsretNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesCam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and Applicationsniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower MechanismDocument44 pagesCam and Follower MechanismAkshay100% (1)
- Cam Based Sand FilterDocument56 pagesCam Based Sand FilterANAND KRISHNAN100% (1)
- ME 7 - Activity 5Document5 pagesME 7 - Activity 5Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowersDocument18 pagesCam and Followersnandkishore_singh100% (1)
- Cams FollowersDocument31 pagesCams FollowersSeranicoustic BandNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis of Spring and Cam Follower Mechanism: June 2020Document5 pagesDesign Analysis of Spring and Cam Follower Mechanism: June 2020Abiola AjayiNo ratings yet
- 02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFDocument18 pages02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFadidas tempoNo ratings yet
- ME 3011 Kinematics & Dynamics Capstone ReportDocument20 pagesME 3011 Kinematics & Dynamics Capstone ReportMuhammad Hussain Bilal100% (1)
- Cam Shaft Design and Analysis for Multi-Cylinder EngineDocument52 pagesCam Shaft Design and Analysis for Multi-Cylinder EngineNationalinstituteDsnr67% (3)
- PillaVenkataRavi SKHidayatullaSharief 10Document10 pagesPillaVenkataRavi SKHidayatullaSharief 10Mario CeddiaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Prof K N Wakchaure: A Frame Which Supports The Cam and Guides The FollowerDocument11 pagesPrepared By: Prof K N Wakchaure: A Frame Which Supports The Cam and Guides The Followerkiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- DTS-Short Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDTS-Short Questions and AnswerAlfred Franklin V100% (1)
- Project Report on Rack and Pinion Gear DesignDocument15 pagesProject Report on Rack and Pinion Gear DesignWaqasNo ratings yet
- Jaw Crusher Kinematics Simulation and AnalysisDocument5 pagesJaw Crusher Kinematics Simulation and AnalysisInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and ScienceNo ratings yet
- CAMSHAFT (Machining) : A Project Report ONDocument21 pagesCAMSHAFT (Machining) : A Project Report ONDHRUV SINGHALNo ratings yet
- CAMSHAFT (Machining) : A Project Report ONDocument21 pagesCAMSHAFT (Machining) : A Project Report ONDHRUV SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab Procedure TheoryDocument10 pagesMachine Design Lab Procedure TheoryMuhammad Taufiq YusofNo ratings yet
- CamDocument30 pagesCamShangarab BeraNo ratings yet
- CamesDocument22 pagesCamesعبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- Cam DesignDocument3 pagesCam DesignJoe KenyonNo ratings yet
- Easychair Preprint: Siddharth Boon, R. C. Singh and Rajiv ChaudharyDocument8 pagesEasychair Preprint: Siddharth Boon, R. C. Singh and Rajiv ChaudharyayushNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument6 pagesCam and FollowerMUHAMMAD UMAR KAMRANNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument38 pagesCam and Follower1blank100% (4)
- Cam Design and ManufacDocument140 pagesCam Design and ManufacJoseph H Finigan100% (4)
- Lab Project Engineering Drawing & Graphics Second Semester: Submitted byDocument10 pagesLab Project Engineering Drawing & Graphics Second Semester: Submitted bysafi abdullahNo ratings yet
- CAM MechanismDocument15 pagesCAM MechanismAshrut AryalNo ratings yet
- BY Daniel .HDocument49 pagesBY Daniel .Hdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Cams: Cams With Different Follower MotionDocument76 pagesKinematics of Cams: Cams With Different Follower MotionMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower PDFDocument17 pagesCam and Follower PDFKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument17 pagesCam and Followerniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Design of Three-roll Bending Machine Tool and ReseDocument12 pagesDesign of Three-roll Bending Machine Tool and Resevarshithagowdasv2002No ratings yet
- Involute Gear Tooth Profile vs Cycloidal Gear Tooth ProfileDocument12 pagesInvolute Gear Tooth Profile vs Cycloidal Gear Tooth ProfileBalvinderNo ratings yet
- Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!: Introduction To MechanismsDocument14 pagesLooking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!: Introduction To MechanismsAkash SoniNo ratings yet
- EXP 03 - Kinematics of Cam MechanismsDocument9 pagesEXP 03 - Kinematics of Cam Mechanismsdtl.nnmNo ratings yet
- Automobile Transmission System Solved Papers PDFDocument52 pagesAutomobile Transmission System Solved Papers PDFSyedJavedAli100% (9)
- Duel Side Sapher PDFDocument9 pagesDuel Side Sapher PDFsageetha756No ratings yet
- Samuthra Projects PDFDocument9 pagesSamuthra Projects PDFsageetha756No ratings yet
- Kinematic Analysis of The Roller FolloweDocument2 pagesKinematic Analysis of The Roller Followedtl.nnmNo ratings yet
- Box Transport Mechanisum (Handle) ReportDocument48 pagesBox Transport Mechanisum (Handle) ReportMayugam InfotechNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument12 pagesCam and FollowerAjay HadaNo ratings yet
- Multi Operation Machine Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDocument65 pagesMulti Operation Machine Using Scotch Yoke MechanismCrispNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower Final NotesDocument18 pagesCam and Follower Final NotesSexy IdolNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsDocument51 pagesMechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsJustin IanNo ratings yet
- Applying Computer Aided Designing For Steam Turbine BladeDocument6 pagesApplying Computer Aided Designing For Steam Turbine Blademishranamit2211100% (1)
- Gear PumpDocument21 pagesGear PumpMudassir Hussain83% (6)
- Introduction To CAMS:: Definition of CamDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CAMS:: Definition of CamSultan FuryNo ratings yet
- 03 CHAPTER THREE CamsDocument15 pages03 CHAPTER THREE CamsJerome XaviorNo ratings yet
- Design of Electric Machines: Axial Flux MachinesDocument23 pagesDesign of Electric Machines: Axial Flux MachinesCh V S RajuNo ratings yet
- Gearless Power-Transmission-Project Report 4Document2 pagesGearless Power-Transmission-Project Report 4A-2011 AKASH DUTTANo ratings yet
- Fesfsd DSFSD FdsDocument6 pagesFesfsd DSFSD Fdssscbemech90.backup01No ratings yet
- Failure of CamshaftDocument3 pagesFailure of Camshaftsultanu89No ratings yet
- Gear Pump PDFDocument21 pagesGear Pump PDFAli HassanNo ratings yet
- CamsDocument22 pagesCamsFelagot SisayNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Quick Return MechanismDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Quick Return Mechanismlzpyreqhf100% (1)
- Cam and Follower - pptx-1Document24 pagesCam and Follower - pptx-1Syam Raju50% (2)
- Semi-Active Suspension Control Design for VehiclesFrom EverandSemi-Active Suspension Control Design for VehiclesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Ce6451 April - May - 2015 PDFDocument3 pagesCe6451 April - May - 2015 PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- 2mark With Answer UCM M.E 6004 PDFDocument22 pages2mark With Answer UCM M.E 6004 PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11th Chemistry Chapter 10 The S-Block ElementsDocument24 pagesCBSE Class 11th Chemistry Chapter 10 The S-Block Elementsl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- IE6605 Production Planning and ControlDocument8 pagesIE6605 Production Planning and Controll8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument3 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Cellular Manufacturing Systems An IntroductionDocument42 pagesCellular Manufacturing Systems An IntroductionNilesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFanjupal80% (5)
- Nov Dec 2016 ENGINEERING-MECHANICS PDFDocument4 pagesNov Dec 2016 ENGINEERING-MECHANICS PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Arihant AIEEE PhysicsDocument376 pagesArihant AIEEE PhysicskdsiddhantNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY PDFDocument12 pages2 Marks DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Me6402 MT II Ques Bank With AnswerDocument28 pagesMe6402 MT II Ques Bank With Answerl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Forces on inclined planes and pulleys problem setDocument2 pagesForces on inclined planes and pulleys problem setl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Advanced I C Engine Part I PDFDocument17 pagesLecture Notes On Advanced I C Engine Part I PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Unit 3 SNM Ma6452Document51 pagesUnit 3 SNM Ma6452l8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Heat Release in Engine Advanced Ic EnginesDocument45 pagesHeat Release in Engine Advanced Ic Enginesl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Iit Stratified Charge EnginesDocument20 pagesIit Stratified Charge Enginesa.mech2009100% (2)
- Value Analysis - Meaning Steps and AdvantagesDocument27 pagesValue Analysis - Meaning Steps and Advantagesl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- IE6605 Production Planning and ControlDocument8 pagesIE6605 Production Planning and Controll8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Sheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Document34 pagesSheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Advanced I.C Engines Slide Share Unit 1Document31 pagesAdvanced I.C Engines Slide Share Unit 1l8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- For More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IDocument4 pagesFor More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - Il8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Advanced I C Engine Part I PDFDocument17 pagesLecture Notes On Advanced I C Engine Part I PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Me6004 QBDocument39 pagesMe6004 QBl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- 2 Marks SOM RejinpaulDocument12 pages2 Marks SOM Rejinpaull8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- ME6016 Advanced I.C EnginesDocument10 pagesME6016 Advanced I.C Enginesl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Unit2 PDFDocument27 pagesUnit2 PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Arth MaticDocument7 pagesArth Maticl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- IE6605-Production Planning and ControlDocument11 pagesIE6605-Production Planning and Controll8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Quotation - Supply and Installation For Roller Shutter - SKBDocument2 pagesQuotation - Supply and Installation For Roller Shutter - SKBCC Cost AdvisoryNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business DevelopmentDocument46 pagesProject Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business Developmentayushi gargNo ratings yet
- Understanding Routing What Is Routing?Document17 pagesUnderstanding Routing What Is Routing?Sanjay Kumar MahanaNo ratings yet
- SDM Vol 1 2abcd 3abcdDocument4,778 pagesSDM Vol 1 2abcd 3abcdfliphellNo ratings yet
- InfoU+Manual EngDocument911 pagesInfoU+Manual EngChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- Pg153 Axi Quad SpiDocument120 pagesPg153 Axi Quad SpiIvan AlyaevNo ratings yet
- GDC Tech Bulletin Hard Drive Diagnostics v2Document5 pagesGDC Tech Bulletin Hard Drive Diagnostics v2guerreroNo ratings yet
- Revised Demolition Code SS 557:2010Document4 pagesRevised Demolition Code SS 557:2010Jianhua WuNo ratings yet
- TALKING ELECTRONCS 555 Page 2Document7 pagesTALKING ELECTRONCS 555 Page 2Eugene FlexNo ratings yet
- CAT-4003 MRI-M500 Series Intelligent Modules PDFDocument2 pagesCAT-4003 MRI-M500 Series Intelligent Modules PDFEddi Pelaez SalinasNo ratings yet
- ASRock ION 330HT RAID Installation GuideDocument15 pagesASRock ION 330HT RAID Installation GuidekenwNo ratings yet
- Computer Lab: How To Install WindowsDocument12 pagesComputer Lab: How To Install WindowsRashid GhafoorNo ratings yet
- 18CSC303J - (Database Management Systems) UNIT-2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pages18CSC303J - (Database Management Systems) UNIT-2 Multiple Choice QuestionsCh Rd ctdNo ratings yet
- Catalog of RBS Honda ListDocument35 pagesCatalog of RBS Honda Listcbaautoparts197No ratings yet
- Digital IC Lab Manual by A.DARWIN JOSE RAJU, M.E., SMIEEEDocument8 pagesDigital IC Lab Manual by A.DARWIN JOSE RAJU, M.E., SMIEEEA.Darwin Jose RajuNo ratings yet
- CompTIA+PenTest++ (PT0 002) +Study+NotesDocument234 pagesCompTIA+PenTest++ (PT0 002) +Study+NotesDaniel ProfantNo ratings yet
- CEH Module 06 Enumeration PDFDocument17 pagesCEH Module 06 Enumeration PDFAbdo ElmamounNo ratings yet
- 7UT613 63x Manual PIXIT A2 V046101 en PDFDocument130 pages7UT613 63x Manual PIXIT A2 V046101 en PDFMJNo ratings yet
- B04 Management, Law, Quality: Standard Number Standard Title Price ( )Document96 pagesB04 Management, Law, Quality: Standard Number Standard Title Price ( )Akbar ShaikNo ratings yet
- BMW E34 EtmDocument701 pagesBMW E34 EtmKoos Spindler50% (4)
- Brochure Wheel Balancers Hofmann enDocument21 pagesBrochure Wheel Balancers Hofmann enANDREA PALLOTTANo ratings yet
- ZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsDocument15 pagesZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsLi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255Document15 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255shivaniNo ratings yet
- More Control Flow Tools - Python 3.10.4 DocumentationDocument17 pagesMore Control Flow Tools - Python 3.10.4 DocumentationraviboggartNo ratings yet
- Upgrade Windows 7 To Windows 10Document5 pagesUpgrade Windows 7 To Windows 10Linda NababanNo ratings yet
- 808D 808D ADV Diagnostics Man 0117 en-USDocument602 pages808D 808D ADV Diagnostics Man 0117 en-USParlog DamianNo ratings yet
- Da 14 1862a1 PDFDocument169 pagesDa 14 1862a1 PDFManuel GuiracochaNo ratings yet
- KA7630/KA7631: Fixed Multi-Output RegulatorDocument6 pagesKA7630/KA7631: Fixed Multi-Output RegulatorTecnico GenioNo ratings yet
- 6-2 Short Paper Information AssuranceDocument4 pages6-2 Short Paper Information AssuranceJoe RodriguezNo ratings yet