Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Naya Raipur Development Plan Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031 2031 2031 2031
Uploaded by
Jyotpreet SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Naya Raipur Development Plan Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031 2031 2031 2031
Uploaded by
Jyotpreet SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Naya Raipur Development Plan
2031
Naya Raipur Development Authority
Development Plan of Naya Raipur City
2031
Annex
Naya Raipur Development Authority
NAYA RAIPUR DEVELOPMENT PLAN-2031
PLANNING TEAM
NAYA RAIPUR DEVELOPMENT AUTHORITY
Shri P. Joy Oommen (I.A.S.)
Chairman
Shri S.S. Bajaj (I.F.S.)
Chief Executive Officer & Director T & CP
Shri A.K. Dubey , General Manager (Finance)
Shri P.C. Jain, Manager (Finance)
Shri S.K. Shrivastava , General Manager (PWD)
Shri. S.K.Nag, Manager (PWD)
Shri K.P. Bajpai , Building Officer & Town Planner
Shri. G.C.Nath, Deputy Manager ( Land)
Shri J.C. Singhal , Dy. G.M. (Public Relation)
Shri.V.R. Meshram, Asst. Manager (Land)
Shri J.P. Sharma ,Manager (Env) & Dy.M.(R)
OFFICERS ASSOCIATED WITH NRDA (EARLIER CADA) AND DIRECTORATE TOWN AND COUNTRY PLANNING
,RAIPUR, IN EARLY STAGES OF PLAN
Shri.Vivek Dhand, I.A.S, Chairman
Shri.M.K.Gupta, Dy.G.M.(Planning)
Shri. Sanjay Shukla, I.F.S, Chief Executive Officer
Shri.P.Nihalani, Nazul Officer & D.M (Land)
Shri. B.K.Sinha, I.F.S. Chief Executive Officer & Director T & CP
Shri. Alok Tiwari, Manager (Environnent)
Shri. K.C.Yadav, I.F.S. Chief Executive Officer
Shri. Akhilesh Shukla, Data Entry Director
Shri. Anil Tuteja, Chief Executive Officer
Shri. Rajkumar Mudliyar, T & CP
Shri. Vineet Nair, T & CP
OTHER OFFICIAL ASSOCIATED WITH NRDA
Shri.G.P.Sharma
Shri.N.L.Sahu
Shri.K.K.Singaur
Shri.Manoj Joshi
Shri.Pradeep Thambi
Shri.P.D.Yoshen
Shri.S.L. Dhruwanshi
Shri.B.L.Nishad
Shri.Mani Ram Dhruv
Shri.Navneet Kotwaliwale
CITY AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (CIDCO), NAVI MUMBAI
Shri N. Ramarao, Vice Chairman & Managing Director
Shri S. Sinha , Addl. Chief Transport Engineer
Shri Deepak Kapur, Joint Managing Director
Shri D.V. Shekdar, Addl. Chief Planner
Shri D.P. Samant ,Chief Architect and Planner
Smt. Aparna Vedula, Senior Planner
Shri C.S. Sanghavi, Chief Engineer & G.M. ( Technical)
Shri R.N. Dengle , Senior Planner
CONSULTING ENGINEERING SERVICES (I) PVT LTD, NEW DELHI
Shri S.S. Chakarborty
Project Coordinator and Managing Director
Urban Planning Team
Mrs Alpana Bose
Power and Telecommunication
Shri J.C. Gambhir, Team Leader
Shri Anoop Singh
Shri S.K. Chakarborty
Shri Virendra Kumar , Deputy Team Leader
Traffic and Transport Experts
Shri Suryakant Kejariwal
Miss Swati Khanna
Shri N. Ranganathan
Environment and Ecology Expert
Shri Neeraj Kumar Singh
Shri Jayashankar Thota
Shri Subhajit Maitra
Shri Harbhajan Singh
Environment & Infrastructure Expert
Site Representative
Miss Anwesha Chakarborty
Shri R.D. Panandhikar
Shri Haseen Zaidi
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
The Planner's Dilemma - A Foreword to the Development Plan
of Naya Raipur
"What human beings need is not utopia ('no place') but entopia ('in place') a
real city which they can build, a place which satisfies the dreamer and is acceptable
to the scientist, a place where the artist and the builder merge"
Constantinos A. Doxiadis
Most cities and towns of today are the products of an evolutionary process in
which some of the larger villages or a cluster of villages have grown and diversified at
a faster pace than others. While census definitions of urban areas have usually
emphasized the size and diversified occupational structure of the population,
settlements too have grown in geographical size and often diversified in terms of their
functions as market places, administrative capitals, industrial centres or tourist towns.
No doubt, the growth and diversification of human settlements into towns and
cities have been aided by human interventions of many kinds of which the efforts to
plan their physical features or lend them a distinctive architectural character have been
of special interest to town planners, architects and historians. India takes pride in the
archeological evidence of planned cities as early as in 3000 B.C., though none of the
cities of Indus Valley Civilization period appear to have survived long enough to
influence the building of similar planned settlements, in later times. We also know of
Indraprastha and Pataliputra as planned cities of olden times but with no surviving
architectural features, they are remembered as little more than old names of todays
Delhi and Patna. Kurukshetra has become more of a metaphor for a battleground for
just causes than the name of a planned ancient city. A long history of invasions and
internecine wars among kings, regional chieftains and other war lords have left us
with only a few forts, temples and palaces of ancient or medieval India. There are not
many cities of even 17th or 18th centuries except perhaps Jaipur, Udaipur and few
others that have been able to preserve their special architectural or planning features
up to the present day. Elsewhere, especially in Europe, some of the ancient as well as
medieval cities have survived the onslaught of time or marauders and retained much
i
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
of their charm and physical features. The Roman towns in many parts of Europe are
living examples of the efforts of human beings to shape their habitations scientifically
and aesthetically.
In modern times, the end of the colonial era led to the emergence of new
nations as also the redrawing of national boundaries and of provinces within those
nations.
This in turn necessitated creation of new cities or towns to serve as
administrative capitals of new nation states or their provinces. There are no doubt
some examples of new towns and cities developed by colonial governments too
essentially for administrative reasons like the creation of summer capitals in hill
stations or cantonment towns. There have also been more seriously planned cities of
colonial times like New Delhi and Canberra. Brasilia, Islamabad, Abuja and Putrajaya
are some of the new administrative capitals planned and developed in the postcolonial era. Another set of planned townships that have come up in many parts of the
modern world are those developed by large industrial corporations especially the steel
and automobile makers.
In India, Tata Iron and Steel Company developed the
planned township of Jamshedpur which later inspired building of similar large
integrated townships especially by public sector undertakings. Bhilai, Rourkela and
Bokaro are large greenfield townships which have grown and spilled over to their
neighbourhoods to become some of the most cosmopolitan cities of India. The first
major effort after independence to develop a wholesome planned city in the country
culminated in the building of Chandigarh. Planned with painstaking details by a team
of architects and planners led by the redoubtable French architect Corbusier,
Chandigarh inspired the building of two more planned capital cities Bhubaneshwar
and Gandhinagar.
Perhaps, the success of Chandigarh should have inspired the
building of many more planned green field towns and cities all across the country.
Though, this did not happen, preparation of master plans for existing cities and towns
and planned development of new city centres or satellite townships have indeed
become a serious preoccupation of many State Governments in the country.
Planning or building new cities have perhaps not been easy decisions for
governments or city authorities. More than the problems of mobilising the required
ii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
financial or skilled human resources, perhaps, what has truly deterred them is the fear
of criticism of the location of the new cities, scope of the plans, the consultative
process involved and the administrative arrangements for management of the cities
once they are built.
Planners and developers of new cities have to face many
dilemmas and deal with many imponderables. These include issues like how much of
history, heritage and culture of the region should or can be captured in the design of a
new city which is being built for future generations or may be how to balance
aesthetics and functionality. How much of the land could be set apart as open spaces
or for recreation without compromising the financial viability of the plans? How to
ensure that the plans promote social cohesion and also prevent the formation of illegal
or squatter settlements? Or say, how to devise a safe, reliable and energy efficient
transportation system for the city? Planning a robust management structure for the
planned city after it is built is another area of challenge. How does one build in
provisions against willful violations of planning norms by builders or the arbitrariness
of the city authorities themselves?
When the new state of Chhattisgarh was born on 1st of November 2000,
Raipur, the largest city of the state was named its capital. Raipur has for many
decades been a vibrant market place in central India. Yet, with an already burdened
civic infrastructure, it was ill-equipped to take on its newfound role as the
administrative capital of a rapidly growing state. There was a prolonged debate on the
need for a new city, its location and the mode of financing its development. It is
indeed a remarkable achievement that the people of Chhattisgarh and its political
leaders could arrive at a consensus on the building of a large green field city close to
Raipur. The new city which has been named Naya Raipur would at once serve as
the administrative capital of the State and also cater to the infrastructural needs of
industry and trade in the region. Many surveys and studies were undertaken before
deciding on the precise location of the city. Planners have taken into account the
existence of a number of human habitations, water bodies and wooded areas in the
proposed location and woven those features in to the physical plan of the city. The
development plan covers a total area of 237.42 sq.kms, out of which the core area
iii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
alone would be spread over 95.22 sq.kms. Development would be undertaken in
phases and the target population for the city in 2031 is 5.6 lacs.
The Urban Design of Naya Raipur is a blend of the traditional with the
futuristic, lending elegance to its major physical features and providing a soothing
ambience to its inhabitants. Fast and convenient connectivity to Raipur and other
large cities of Chhattisgarh would receive utmost attention while finalizing the
transportation plan of the new city. Building an access controlled expressway from
National Highway No. 6 and a short railway line to the new city from the Raipur
Titlagarh Vizagapatnam railway line and integrating the two with an intra-city Bus
Rapid Transport System (BRT) would form the core of a mass transportation plan for
Naya Raipur. Dedicated bus lanes, cycling tracks and safe pedestrian walkways
would complement the BRT and help the development of an energy efficient and
environmentally sustainable city. The road sections and junctions would be designed
to be friendly for children and persons with physical disabilities.
Planning for housing of the citizens would be another major challenge. Here,
the emphasis would be on appropriate land allocation policies to ensure affordable
housing with acceptable quality levels for all sections of the population. The existing
villages in the planning area would be upgraded with modern civic amenities to
integrate them with the rest of the city. The Development Plan has set apart large
open spaces as well as areas for sports, recreation and entertainment. It would help
people of all walks of life to come together may be to watch a game of cricket at a
stadium, a boat ride with the children in a lake or may be just for a brisk walk in one
of the many parks.
The city is also expected to generate new employment opportunities for the
citizens. Government offices, the proposed business district, educational institutions
and entertainment complexes would generate most of the fresh employment. The plan
also provides for Industrial Parks for Information Technology, Gems and Jewellery,
Apparels, Handicrafts and other light
non-polluting industries. Naya Raipur with
its high quality infrastructure should emerge as a major educational and cultural hub
iv
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
for the entire state and all efforts would have to be made to achieve this potential. The
Institutional Area should be able to accommodate many national as well as state level
educational and training institutions, laboratories and research centers. Museums,
libraries, exhibition halls and theatres for live performances will also have to come up,
to enliven and enrich the city's cultural life.
Naya Raipur Development Authority which has prepared this development
plan with the help of a number of competent city planners and after a series of
consultations with professional organizations and special interest groups as well as
elected representatives of people realizes that it will have to live with another dilemma
for some more time. Being a green field city, Naya Raipur of today does not have a
body populace or a constituency of citizens of its own, who would dream about its
future, continuously, provide ideas and suggestions for its development, keep watch
over implementation schedules and jealously guard against unsavory interferences
with its plans. The city will fill up only slowly and it would be some more years
before it acquires a critical mass of vigilant citizens with a sense of belonging to a
planned, modern and eco-friendly city. We surely are not without friends till then and
are conscious that a large number of well wishers within and outside Chhattisgarh
would lend all support and encouragement to make Naya Raipur a model and a source
of inspiration for city planners, architects, builders and policy makers anywhere in the
world.
Raipur,
Dated : 17th June, 2008
(P.Joy Oommen)
Chairman
Naya Raipur Development Authority
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Forward
Naya Raipur Development Plan Planning Team
Table of Contents
List of Tables
List of Maps
List of Abbreviations
Executive Summary
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
NAYA RAIPUR - OBJECTIVES & APPROACH ................................................................... 1
THE OBJECTIVES OF NAYA RAIPUR ..................................................................................... 1
THE METHODOLOGY ADOPTED IN PLAN-MAKING .......................................................... 1
PHYSICAL PLAN, FEASIBILITY & IMPLEMENTATION ...................................................... 2
PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT OF THE CITY ................................................................... 2
2
SITE SELECTION ...................................................................................................................... 4
2.1 INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................................... 4
2.2 METHODOLOGY FOR SITE SELECTION ................................................................................ 4
2.2.1 Transport and Infrastructure ................................................................................................ 6
2.2.2 Availability of Water Resources ......................................................................................... 7
2.2.3 Land Availability & Suitability ........................................................................................... 8
2.2.4 Environmental Considerations .......................................................................................... 10
2.2.5 Presence of Airport ............................................................................................................ 11
2.2.6 Quadrant Analysis ............................................................................................................. 11
2.2.7 Proposed Site ..................................................................................................................... 12
3
SITE PROFILE .......................................................................................................................... 13
3.1 DEFINING THE AREAS ............................................................................................................ 13
3.2 SPATIAL EXTENT OF THE PROPOSED NAYA RAIPUR INCLUDING 500 METER WIDE
GREEN BELT (LAYER I) ................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.1 Linkages and Surroundings ............................................................................................... 13
3.3 SPATIAL EXTENT OF THE NAYA RAIPUR PERIPHERAL REGION (LAYER II) ............ 14
3.4 AIRPORT ZONE (LAYER III) ................................................................................................... 14
3.5 NRDA PLANNING AREA ......................................................................................................... 14
3.5.1 Physiography of the NRDA area ....................................................................................... 14
4
EXISTING LAND USE NRDA PLANNING AREA ........................................................... 17
5
THE VISION AND CONCEPT ................................................................................................ 18
5.1 VISION AND CONCEPT FOR NAYA RAIPUR....................................................................... 18
5.1.1 The Vision ......................................................................................................................... 18
5.1.2 Precincts ............................................................................................................................ 18
5.1.3 The Form ........................................................................................................................... 19
5.1.4 The Peripheral Region ....................................................................................................... 20
6
DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE .................................................................................................... 21
6.1 POPULATION ............................................................................................................................. 21
6.1.1 Chhattisgarh: Population Growth Trends .......................................................................... 21
6.1.2 Population of Naya Raipur ................................................................................................ 21
6.1.3 Rural Urban Composition of the Projected Population of the Region ........................... 22
6.1.4 Population Projection of Urban Areas in the Region ........................................................ 22
6.1.5 Population Component of Naya Raipur ............................................................................ 23
vi
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
6.1.6 Age-Sex Composition ....................................................................................................... 23
6.1.7 Sex Ratio ........................................................................................................................... 24
6.2 POPULATION DISTRIBUTION IN NAYA RAIPUR............................................................... 24
7
ECONOMIC BASE, EMPLOYMENT AND WORK AREAS .............................................. 26
7.1 ECONOMIC BASE ..................................................................................................................... 26
7.1.1 Workforce Participation Rate ............................................................................................ 26
7.2 OCCUPATIONAL PATTERN .................................................................................................... 26
7.3 EMPLOYMENT GENERATION ............................................................................................... 28
7.4 WORK AREAS ........................................................................................................................... 29
7.4.1 Government Functions ...................................................................................................... 29
7.4.2 Wholesale Trade ................................................................................................................ 29
7.4.3 Retail Trade ....................................................................................................................... 30
7.4.4 Proposed Hierarchy of trade and commerce areas ............................................................ 30
7.4.5 Provision of Housing Area Centres/ Neighbourhood Shopping Centres and Community
Centres ............................................................................................................................... 30
7.4.6 City Centre / Central Business District ............................................................................. 30
7.4.7 Light & Service Industries ................................................................................................ 31
7.4.8 Composite Use Zone ......................................................................................................... 31
7.4.9 Special Industry Zone (Software Technology Park) ......................................................... 31
7.4.10 Informal Sector .................................................................................................................. 32
7.4.11 Weekly markets and Haats ................................................................................................ 32
8
HOUSING ................................................................................................................................... 33
8.1 HOUSING FOR NAYA RAIPUR ............................................................................................... 33
8.2 HOUSING REQUIREMENT ...................................................................................................... 33
8.2.1 Changing Socio-economic Profile and Housing the Indian context............................... 33
8.2.2 Household size .................................................................................................................. 34
8.2.3 Distribution of Households based on number of dwelling rooms ..................................... 35
8.2.4 Housing Density ................................................................................................................ 36
8.3 PLANNING APPROACH ........................................................................................................... 36
8.4 HOUSING IN RESIDENTIAL SECTORS (RESIDENTIAL USE) ........................................... 36
8.4.1 Typical Sector.................................................................................................................... 36
8.4.2 Land utilization pattern within each neighbourhood / sector ............................................ 37
8.4.3 Pedestrian friendly neighbourhoods .................................................................................. 38
8.4.4 Design Brief for Sector Development ............................................................................... 39
8.4.5 Urban Poor ........................................................................................................................ 40
8.4.6 Informal sector .................................................................................................................. 40
8.4.7 Housing typologies ............................................................................................................ 40
8.5 HOUSING IN OTHER AREAS .................................................................................................. 41
8.5.1 Housing for Private Employees ......................................................................................... 41
8.5.2 Housing in Commercial Areas .......................................................................................... 42
8.5.3 VIP Housing ...................................................................................................................... 42
8.5.4 Institutional Housing ......................................................................................................... 42
8.5.5 Existing Abadi Areas / Urban Villages ............................................................................. 42
8.6 DEVELOPMENT MODELS ....................................................................................................... 43
8.6.1 Housing by Co-operative Group Housing Societies ......................................................... 43
8.6.2 Public Private Partnership in housing................................................................................ 43
9
9.1
9.2
9.3
TRANSPORT ............................................................................................................................. 46
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................ 46
TRAVEL DEMAND ASSESSMENT ......................................................................................... 46
TRANSPORT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT POLICY FOR NAYA RAIPUR ........................... 47
9.3.1 Regional Transport System ............................................................................................... 47
9.3.2 Sub-Regional (NRDA area) Transport System ................................................................. 49
vii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
9.3.3 Naya Raipur City Transport System.................................................................................. 49
9.4 PUBLIC MASS TRANSPORT SYSTEM ................................................................................... 52
9.5 PHASING AND COST ESTIMATION ...................................................................................... 56
9.5.1 Phasing of Transport System Development ...................................................................... 56
10 PHYSICAL INFRASTRUCTURE ........................................................................................... 58
10.1 WATER SUPPLY ........................................................................................................................ 58
10.1.1 Water Supply Norms Prescribed By CPHEEO ................................................................. 58
10.1.2 Population Forecast ........................................................................................................... 59
10.1.3 Water Demand................................................................................................................... 59
10.1.4 Water resources and availability ....................................................................................... 59
10.1.5 Water Treatment Plant....................................................................................................... 59
10.1.6 Water transmission, Storage Reservoirs, and Distribution ................................................ 60
10.2 SEWERAGE SYSTEM ............................................................................................................... 61
10.2.1 Sewage Generation ............................................................................................................ 61
10.2.2 Sewage Pumping Stations ................................................................................................. 62
10.2.3 Sewage Treatment ............................................................................................................. 62
10.2.4 Disposal Options ............................................................................................................... 62
10.3 STORM WATER DRAINAGE ................................................................................................... 63
10.3.1 Storm Water Drainage For New Capital City ................................................................... 64
10.3.2 Rain-Water Harvesting ...................................................................................................... 65
10.4 SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................. 65
10.4.1 Estimated Solid Waste Generation in Naya Raipur........................................................... 65
10.4.2 Methods of Disposal .......................................................................................................... 66
10.4.3 Solid Waste Mamagement System For Naya Raipur City ................................................ 66
10.4.4 Solid Waste Collection System ......................................................................................... 66
10.4.5 Other Management Measures ............................................................................................ 67
10.5 POWER .................................................................................................................................... 68
10.5.1 Development of Power Supply in Phase-I......................................................................... 68
10.5.2 Development of Power Supply in Phase-II ....................................................................... 68
10.5.3 Development of Power Supply in Phase-III ...................................................................... 68
10.5.4 Proposed Power Requirement and Estimated Number of Grid/Substations for New
Capital City .................................................................................................................................. 69
10.5.5 General Recommendations for setting up modern Electrical Power Transmission and
Distribution system ...................................................................................................................... 69
10.6 TELECOMMUNICATIONS ....................................................................................................... 70
11
11.1
11.2
11.3
11.4
SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE ................................................................................................ 71
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................ 71
CITY STRUCTURE FOR THE PROVISION OF SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE ................... 71
HEALTH .................................................................................................................................... 71
EDUCATION .............................................................................................................................. 72
11.4.1 Primary Education ............................................................................................................. 72
11.4.2 Higher Education ............................................................................................................... 73
11.4.3 Vocational Education ........................................................................................................ 73
11.5 POLICE .................................................................................................................................... 73
11.6 FIRE
.................................................................................................................................... 74
11.7 DISASTER MANAGEMENT CENTRE .................................................................................... 74
11.8 COMMUNICATION ................................................................................................................... 75
11.8.1 Postal Facility .................................................................................................................... 75
11.8.2 Telephones ........................................................................................................................ 75
11.9 SOCIO CULTURAL FACILITIES .......................................................................................... 75
11.10 DISTRIBUTIVE SERVICES ..................................................................................................... 76
11.10.1 Provision of Distributive Facilities for the City .......................................................... 76
11.11 OTHER FACILITIES ................................................................................................................. 76
viii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
11.11.1 Cremation / Burial Ground .............................................................................................. 77
11.11.2 Grouping of Social Infrastructure at the Community Level ............................................ 77
12
12.1
12.2
12.3
12.4
12.5
12.6
RECREATION ........................................................................................................................... 79
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................ 79
PARKS AND PLAY AREAS (AS PART OF RESIDENTIAL USE ZONE) ............................. 79
PARKS AND PLAY AREAS (AT COMMUNITY LEVEL AND ABOVE) ............................. 79
PROVISION OF RECREATIONAL SPACES AT THE CITY-LEVEL .................................... 80
SPORTS FACILITIES ................................................................................................................. 80
GREEN BELT ............................................................................................................................. 80
13 ENVIRONMENT ....................................................................................................................... 81
13.1 INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................ 81
13.2 WATER .................................................................................................................................... 81
13.2.1 Surface water ..................................................................................................................... 81
13.2.2 Ground water ..................................................................................................................... 81
13.3 SEWERAGE ................................................................................................................................ 81
13.4 DRAINAGE ................................................................................................................................. 82
13.5 SOLID WASTE ........................................................................................................................... 82
13.6 AIR POLLUTION........................................................................................................................ 82
13.7 NOISE
.................................................................................................................................... 83
13.8 ENERGY CONSERVATION...................................................................................................... 83
13.9 ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY AND LEGAL ISSUES .............................................................. 83
14
14.1
14.2
14.3
14.4
14.5
14.6
14.7
PERIPHERAL AREA ............................................................................................................... 84
GENERAL INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................... 84
POPULATION ............................................................................................................................. 84
PLANNING APPROACH ........................................................................................................... 84
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION ................................................................................................ 86
HOUSING .................................................................................................................................... 86
CONNECTIVITY ........................................................................................................................ 87
PHYSICAL INFRASTRUCTURE .............................................................................................. 87
14.7.1 Water Supply ..................................................................................................................... 87
14.7.2 Rural Sanitation ................................................................................................................. 87
14.7.3 Solid Waste Management .................................................................................................. 87
14.8 SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE ................................................................................................... 88
14.8.1 Health Facilities................................................................................................................. 89
14.8.2 Educational Facilities ........................................................................................................ 89
14.9 OTHER FACILITIES .................................................................................................................. 90
15
AIRPORT ZONE ....................................................................................................................... 92
16 LAND USE ZONING PLAN - 2031 ......................................................................................... 93
16.1 LANDUSE 2031- NRDA PLANNING AREA ........................................................................... 93
16.1.1 Planning Layer I Naya Raipur City including green belt area ....................................... 93
16.1.2 Planning Layer II Peripheral Rural Zone ....................................................................... 95
16.1.3 Planning Layer III Airport Zone..................................................................................... 95
17
17.1
17.2
17.3
17.4
17.5
DEVELOPMENT PHASING AND INVESTMENT COST ESTIMATES .......................... 96
PLANNING HORIZON .............................................................................................................. 96
LAND DEVELOPMENT PHASING .......................................................................................... 96
POPULATION PHASING .......................................................................................................... 97
INVESTMENT COST ESTIMATES .......................................................................................... 97
INVESTMENT FOR TRANSPORT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT ............................................ 97
17.5.1 Unit Costs .......................................................................................................................... 98
ix
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
17.6 PRIVATE SECTOR PARTICIPATION...................................................................................... 98
18
18.1
18.2
18.3
18.4
18.5
18.6
DEVELOPMENT CODE .......................................................................................................... 99
SCOPE .................................................................................................................................... 99
DEFINITIONS ............................................................................................................................. 99
PLANNING LAYERS IN NRDA AREA.................................................................................... 99
CLASSIFICATION OF LAND USE ZONES ............................................................................. 99
LAND USE PERMISSIBILITY ................................................................................................ 100
DEVELOPMENT CONTROL REGULATIONS...................................................................... 104
18.6.1 Sub-division Regulations ................................................................................................ 104
18.6.2 Development Controls for integrated developments and individual buildings ............... 107
18.7 BASIC DEVELOPMENT REGULATIONS FOR PLANNING LAYERS II & III ................. 110
18.7.1 Regulations for Layer II .................................................................................................. 110
18.7.2 Layer III: Airport area including its expansion area....................................................... 111
18.8 OTHER REGULATIONS.......................................................................................................... 111
18.9 URBAN DESIGN CONTROL .................................................................................................. 112
19. SPECIAL REHABILITATION SCHEME FOR "NAYA RAIPUR'' PROJECT ............. 113
19.1. INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................................... 113
19.2. PLANNING AREA VILLAGES ............................................................................................... 113
19.3. SPECIAL REHABILITATION SCHEME OF NAYA RAIPUR DEVELOPMENT
AUTHORITY ............................................................................................................................ 113
19.3.1 Project Affected Person ................................................................................................... 113
19.3.2 Compensation for house and land related constructions ................................................. 114
19.3.3 State committee for deciding rates in the Project Affected Area. ................................... 114
19.3.4 Compensation to Project Affected Persons ..................................................................... 114
19.4 ELIGIBILITY FOR ALLOTMENT OF PLOTS/KIOSKS/SHOPS. ......................................... 115
19.5 VILLAGE REHABILITATION SCHEME ............................................................................... 117
19.6 SPECIAL BENEFITS TO PROJECT AFFECTED LANDLESS LABOURERS..................... 117
19.7 GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL MECHANISM............................................................................ 117
20.
20.1
20.2
20.3
20.4
20.5
20.6
20.7
INSTITUTIONAL MECHANISM ......................................................................................... 118
INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................................... 118
LOOKING BACK...................................................................................................................... 118
NAYA RAIPUR......................................................................................................................... 119
PROBABLE SET UP ................................................................................................................. 119
COORDINATION ..................................................................................................................... 119
PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP ........................................................................................ 120
SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT...................................................................................................... 120
Annex
Annexe I
Annexe II
Annexe III
Annexe IV
Annexe V
Annexe VI
Cumulative Facility Index (CFI) For Peripheral Region
Classification of Industries
Fire Protection and Fire Safety Requirements
Norms to provide facilitates in the Public Buildings excluding Domestic Buildings for
Disabled Persons
Formation of Naya Raipur Development Authority
Notice for the publication of draft development plan of Naya Raipur
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1
Table 3.1
Table 3.2
Table 3.3
Table 3.4
Table 3.5
Table 3. 6
Table 3.7
Table 6.1
Table 6.2
Table 6.3
Table 6.4
Table 6.5
Table 6.6
Table 6.7
Table 6.8
Table 6.9
Table 6.10
Table 6.11
Table 6.12
Table 7.1
Table 7.2
Table 7.3
Table 7.4
Table 7.5
Table 7.6
Table 7.7
Table 7.8
Table 7.9
Table 7.10
Table 7.11
Table 8.1
Table 8.2
Table 8.3
Table 8.4
Table 8.5
Table 8.6
Table 8.7
Table 8.9
Wind Data for site selection region in Chhattisgarh
Delineation of Planning Layers of the Naya Raipur & its Peripheral Region
Villages fully incorporated within Naya Raipur
Villages partly and marginally incorporated within the Naya Raipur
Villages fully included within the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region
Villages partly included within the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region
Hydro-geological information of the NRDA Area
Mean monthly maximum and minimum Temperature in the area
Population growth in India and Chhattisgarh
Future Population of the Region
Rural Urban Population Composition of the Region
Urban Population Composition of the Region
The Population Projection of Urban Areas
Population Projection of Naya Raipur
Age Structure of Chandigarh and Raipur, 1991
Sex ratio in Chandigarh
Sex ratio for Chhattisgarh and Raipur
Population distribution in Residential Sectors
Population distribution in Abadi Areas
Total Population in Naya Raipur
Work Participation Ratio of Chandigarh and Raipur
Comparative Analysis of Occupational Pattern: Chandigarh and Raipur, 1991
Occupational Classification of Raipur as per census 2001.
Proposed Occupational Structure for Naya Raipur
Employment generated by various activities
Suggested Broad Land-Use Break-up for an Integrated Freight Complex
Four-tier System adopted for Trade and Commercial Areas
Area break-up for the City Centre/CBD
Land utilization pattern for the Mixed-use zone
Broad Land use Distribution
Area reserved for informal sector
Average Household size of Raipur city
Average Household size of Chandigarh
Distribution of Households by Size and Number of Dwelling Rooms for
Raipur City, 1981 and 2001
Emerging trend showing number of rooms occupied in Chandigarh, 19812001
Emerging trend showing number of rooms occupied in Raipur, 1981-2031 by
CAGR method
Suggested (indicative) percentage of dwelling unit size based on number of
rooms
Suggested land utilization pattern at sector level
Hierarchy of Facilities at Neighbourhood level
xi
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
Table 8.10
Table 8.11
Table 8.12
Table 8.13
Table 8.14
Table 8.15
Table 8.16
Table 9.1
Table 9.2
Table 9.3
Table 10.1
Table 10.2
Table 10.3
Table 10.4
Table 10.5
Table 10. 6
Table 10.7
Table 10.8
Table 10.9
Table 10.10
Table 11.1
Table 11.2
Table 11.3
Table 11.4
Table 11.5
Table 11.6
Table 11.7
Table 11.8
Table 11.9
Table 11.10
Table 11.11
Table 11.12
Table 11.13
Table 11.14
Table 11.15
Table 12.1
Table 12.2
Table 12.3
Table 14.1
Table 14.2
Table 14.3
Table 14.4
Table 14.5
Table 14.6
Standards for travelling distance to social facilities
Distribution of Plotted and Apartment Housing
Suggested plot sizes and development control guidelines
Indicative dwelling unit sizes
Development Guidelines for Group Housing
Composition of Employees based on skill and annual income
Contribution by various housing sub-systems to the total housing stock of
Naya Raipur in comparison with Chandigarh
Travel Demand in Naya Raipur
Parking Standards
Phasing of Development of Transport System
Norms for Water Supply by CHPEEO
Population Projection
Phase wise demand of water supply
Phase Wise Additional Modules Of WTP
Capacities of Under Ground Reservoirs and Booster Pumping Stations
Sewage Generation in Naya Raipur
Capacities of Sewage Pumping Station required for Sewerage system
Capacity of STP at different phases of development
Length of storm water roadside drains for New Capital City, Chhattisgarh
Projected Phase-wise Solid Waste Generation in Naya Raipur
Proposed City structure
Provision For health facility
Norms for provision of Educational facility
Norms for provision of Higher education facilities
Provision of Higher and Vocational/Training Education
Prescribed norms for police service
Norms for Fire Station
Planning Norms for provision of Postal Facilities
Prescribed norms for Telecommunication Infrastructure
Norms for Socio-Cultural Facilities in Naya Raipur
Norms for Public Distribution System
Provision for Distributive Infrastructure in the New Capital City
Norms for the Petrol pumps
Norms for provision of other community facilities
Community level grouping of Social Infrastructure
Hierarchy of Open Spaces as part of residential use zone
Areas for Recreational Areas at city level
Adopted norms for the provision of Sports Facilities
Overall Population of Naya Raipur Peripheral Area
Hierarchy of Villages based on CFI
Proposed clustering & zoning of the villages
Cluster-wise projected population for Peripheral region.
Housing requirement for Peripheral Area
Zone wise Solid waste generation
xii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
Table 14.7
Table 14.8
Table 14.9
Table 14.10
Table 14.11
Table 15.1
Table 15.2
Table 16.1
Table 16.2.
Table 17.1
Table 17.2
Table 17.3
Table 17.4
Table 18.1
Table 18.2
Table 18.3
Table 18.4
Table 18.5
Landfill area requirement for Peripheral area
Norms adopted for Health Infrastructure
Proposed Health Infrastructure in peripheral area
Norms adopted for provision of Educational facilities
Proposed Educational facilities in Peripheral area
Height Restrictions with respect to Funnel.
Height Restrictions with respect to Transitional area.
Land Use Distribution in Naya Raipur City
Broad Land Use Distribution in Naya Raipur City
Suggested Land development phasing, Naya Raipur
Investment Cost Estimates for Plan Implementation
Phase wise Investment for Transport System Development (in Crores)
Unit Costs for Transport System
Land Use Permissibility in different Use Zones
Standards for facilities in a residential sub-division
List of facilities to be essentially provided in Industrial Areas
Setback Regulations for different plot sizes
Parking Standards for different uses
xiii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
LIST OF FIGURES
Fig 2.1
Fig 2.2
Fig 2.3
Fig 2.4
Fig 2.5
Fig 2.6
Fig 2.7
Fig 2.8
Fig 2.9
Fig 2.10
Fig 2.11
Fig. 5.1
Fig 6.1
Fig 6.2
Fig 7.1
Fig 8.1
Fig 8.2
Fig 8.3
Fig 8.4
Fig 9.1
Fig 9.2
Fig 9.3
Fig 9.4
Fig 10.1
Fig 10.2
Fig 10.3
Fig 14.1
Fig 14.2
Methodology for Site Selection
Delineation of the Site Selection Region and the Quadrants
NH 6 Connecting Mumbai via Nagpur, Durg, Bhilai and Raipur
NH 200 Connecting Raipur and Bilaspur
NH 43 Connecting Raipur and Visakhapatnam
Mahanadi River - Perennial Source Of Water
Kharun River At NH-6 Crossing (Seasonal)
Sheonath River At NH-6 Crossing (Seasonal)
The Rivers within the Site Selection Region
Availability of Government Land within the Site Selection Region
Average monthly rainfall for Raipur District
Conceptual location of the Precincts
Composition of Population in the Region w.r.t. Chhattisgarh
Age Sex Pyramid of Raipur City, 1991
Comparative Analysis of Occupational Pattern: Raipur and Chandigarh
Distribution of Households by Household income 1989-90 to 2009-10 (200102 prices) for Urban population of India
Conceptual plan of a typical sector
Incremental Housing
Development by Government as against Private sector/Co-operatives
Expressway Cross Section Details
Road Cross Section Details ( Phase I)
Schematic Location of Intra-city bus terminals
Typical Conceptual Plan For Bus Bay/Recess
Rainfall intensity Vs Time of Concentration Curve for the New Capital City
of Chhattisgarh (Based on IMD Data)
Methods of Rain Water Harvesting
Flow diagram for solid waste management system for Naya Raipur
Conceptual Hierarchy of Settlements
Proposed Facilities for Peripheral Region
xiv
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
LIST OF MAPS
Map No.
2.1
2.2
2.3
3.1
3.2
4.1
7.1
9.1
9.2
9.3
9.4
9.5
10.1
10.2
Title
Regional Connectivity
Existing Settlements in the Region
Drainage Pattern of the Region
Proposed Planning Layers NRDA Planning Area
Distribution of Government Land, Naya Raipur
Existing Land Use NRDA Planning Area
Major Work Areas - Naya Raipur
Proposed Expressway
Proposed Road Hierarchy for Naya Raipur
Road link Identification, Naya Raipur
Pedestrian Corridor
Proposed Light Rail Transit System
Water Supply System Naya Raipur
Sewerage System Naya Raipur
10.3
10.4
11.1
11.2
11.3
11.4
11.5
12.1
13.2
14.1
14.2
14.3
15.1
16.1
16.2
16.3
17.1
17.2
Drainage System Naya Raipur
Solid Waste Management Sites
Major City level facilities Naya Raipur
Identification of Planning Units
Master Plan Fire Stations
Master Plan Petrol Pumps
Central Facility Corridor, Naya Raipur
Distribution of Recreational Areas
Existing water bodies and plantations
Zoning and Clustering of settlements, Peripheral Area
Existing Health and Educational facilities, Peripheral Area
Proposed Health and Educational facilities, Peripheral Area
Airport Zone-Air Funnel and Height Restrictions
Land Use Zoning Plan for Naya Raipur
Proposed Land Use Zones NRDA Planning Area
Planning Zones - Naya Raipur City
Land Development Phasing
Road Network Development Phasing
xv
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
C.A.G.R.
C.B.D.
E.C.S.
F.A.R.
Ha
H.C.V.
I.F.C.
I.P.T.
L.C.V.
L.P.C.D.
L.R.T.S.
M.A.V.
M.L.D.
M.S.L.
N.R.D.A.
N.U.T.P
P.C.U
P.M.T.S.
P.U.
R.O.W
R.S.U.
S.E.Z.
S.T.P.
T.S.M.
W.F.P.R
W.T.P.
: Compounded Annual Growth Rate
: Central Business District
: Equivalent Car Space
: Floor Area Ratio
: Hectare
: Heavy Commercial Vehicle
: Integrated Freight Complex
: Intermediate Public Transport
: Light Commercial Vehicle
: Litres Per Capita per Day
: Light Rail Transit System
: Multi Axle Vehicle
: Million Litres per Day
: Mean Sea Level
: Naya Raipur Development Authority
: National Urban Transport Policy
: Passenger Car Unit
: Public Mass Transport System
: Planning Unit
: Right of Way
: Remote Subscriber Unit
: Special Economic Zone
: Sewage Treatment Plant
: Traffic Systems Management
: Work Force Participation Rate
: Water Treatment Plant
xvi
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
1
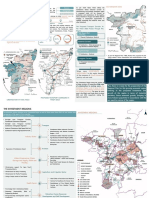
The Government of Chhattisgarh has envisaged the creation of a new city by the name of Naya
Raipur with state level administration functions. After various considerations a site in the south
east of Raipur, dotted with natural water bodies has been selected. The site is in the west of River
Mahanadi, a perennial source of water, in the middle of Naya Raipur Development Authority
(NRDA) Planning area.
The NRDA area is divided into 3 layers delineating the Naya Raipur, the peripheral and the
airport zone, as following:
Delineation of Planning Layers of the Naya Raipur & its Peripheral Region
SL. No. Layer
Area Included
1
Layer-I The Proposed Naya Raipur (Area-80.13 sq.km.)
Including 500 meter wide green belt (Area-95.22 sq. km.)
2
Layer-II Naya Raipur Peripheral Region (NRPR) (Area-130.28 sq.km.)
Layer-III Airport Zone (Area-11.92 sq.km.)
Within the Naya Raipur Planning Area, 130.28 sq. km is identified as peripheral area to act as
buffer zone between the proposed Naya Raipur City and the existing Raipur. This will continue to
be agricultural / rural area but to be provided with adequate social facilities for the existing
population.
The airport zone is defined in the 11.92 sq. km area. Within the zone the airport could be extended
ultimately from present 1950 m to 3810 m runway.
Naya Raipur would be a planned and designed city of the 21st century to focus on socio-economic
and cultural life of Chhattisgarh having its role and recognition at national and international
levels. The New city is set in salubrious natural surroundings accessed by an express way. It is
envisaged as lively and vibrant city equipped with state of art physical, social and economic
infrastructure.
The new city is envisaged to be developed in phases for an estimated population of 5.6 lakh by the
year 2031. The first phase population by 2011 is estimated as 1.5 lakh.
The main economic base of Naya Raipur would be Government / State Capital functions.
However diversification of economic activities would be attained by providing (a) software
technology park (b) gems & jewellery and other similar industries (c) business offices (d) health
education and research services and (e) regional recreational activities like Golf Course, Safari
Park, and Botanical Garden. The capital complex and the business complex i.e. the CBD would be
the two busiest areas in the city.
The new city would be provided with housing for quality living with comfortable well designed
xvii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
houses with required essential facilities for education, health, recreational, day-to-day shopping.
All section of the society to avail these essential community facilities. The new city would have
above one lakh twenty thousand dwelling units to be provided in partly plotted and partly flatted
developments divided within subsystem as following:
Contribution by various housing sub-systems to the proposed total housing stock of Naya
Raipur in comparison with Chandigarh
S. No. Housing Sub-system
1
2
Private Housing
Co-operative group housing societies
3
4
5
6
Housing for Government Employees
VIP Housing
Private Employee Housing
Institutional Housing
Others (CBD, Composite use, Facility
corridor)
Urban Villages
Total
7
8
74,602
14,430
6,315
Percentage of
Housing stock
(Naya Raipur)
60.23
11.65
5.1
2,666
2,220
7,780
9,287
2.15
1.79
6.28
7.5
6,560
123,860
5.3
100
Number of
Dwelling Units
Percentage of
Housing stock
(Chandigarh)
33
5
11
15
28
(CHB)
8
100
The Transport plan is proposed with the objective of high mobility for all and providing mass
transport system which is equitable and safe. The regional and city level transport is integrated
linking the city with regional rail, highway and airport. The envisaged hierarchy of roads by right
of way is:
City Arterial Road (100 m)
Sector peripheral (60 m)
Intra Sector Roads (24 m / 18m / 12m)
Parking standards for various activities area given to provide sufficient parking both in public and
private parking areas.
10 The city would be provided with high quality physical infrastructure. Mahanadi River has
perennial flow and is a dependable source of water. Based on norms to provide high quality
infrastructure, total water demand of 221 mld shall be supplied through this source. Water would
also be conserved through rainwater harvesting. Sewerage treatment plant with a total capacity of
150 mld, one for north and one for south is provided. The city would have two sanitary landfill
sites. It would be provided with 565 MVA power supply to nearly reach the standards of a
developed country and with high quality communication system.
11 Social infrastructure i.e. infrastructure for health, education, security, communication, sociocultural facilities has been proposed according to norms which are arguably the highest in the
country. Adequate provision of land has been made in the plan to provide an elaborate system of
social facilities at three levels of urban life, i.e. city level (for 5-6 lakh population), community
level (level 1-1.5 lakh population), and neighbourhood level (15-20,000 population).
12 The new city is developed in an area with a number of water bodies and plantations. The attempt
in the plan is to conserve all the existing water bodies and plantations. Energy conservation shall
xviii
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
be encouraged through community and site planning, designing and use of energy efficient
materials and through landscaping.
13 The image of Naya Raipur will be a wide band of green running through the city interlaced with
lakes, intertwined in a central spine carrying the social facilities and utilities for each level of
urban community life. Apart from an intricate system of intra-city green spaces, Naya Raipur
proposes major open spaces at the city level and regional level larger than the greens in the major
world cities. The green band is reflected through sizeable area allocated for open spaces.
Areas for Recreational Areas at city level
Open Spaces
Film city
Parks and Play Areas
Stadium & Sports Complex
Nature Resort/Theme Park
City Park
Reserved Forest
Botanical Park, Jungle Safari & Golf Course
Water body
Plantation (located within uses other than recreational)
Total Area
Area (Ha)
46.49
366.07
45.16
258.48
467.55
216.01
389.95
233.71
113.93
2137.36
Besides the above parks, playground areas are provided at neighbourhood level within the residential
sector.
14 Land Use Distribution in Naya Raipur City
S.No.
1
Land Use
Area (ha)
Percentage
Residential
2113.39
26.37
Commercial - Retail
146.67
1.81
Commercial - Wholesale
130.67
1.63
Industrial
196.13
2.42
Special Industry
263.05
3.28
Public & Semi Public
1846.38
23.04
Recreational
2137.44
26.67
Transport
1005.77
12.55
Composite Use
Total
177.6
8013.1
2.22
100
15 The new city would be developed in 3 phases:
Suggested Land development phasing, Naya Raipur
Phase
Horizon Year
Cumulative Population
Phase I
2011
150,000
Phase 11
2021
365,000
Phase III
2031
560,000
Total developed Area at the end of phase III
xix
Area (Ha)
3057.46
3733.56
1222.16
8013.1
Naya Raipur Development Plan 2031
16 The development code has been prepared for permitting land development and building activity in
Naya Raipur providing:
Landuse classification
Landuse permissibility
Development control regulations
Subdivision regulations
Set backs
Parking standard
Ground Coverage, FAR, Height and other controls.
The objective of the Development Control Regulations is to provide for high quality physical and
social environment.
xx
Naya Raipur Development Plan - 2031
Naya Raipur - Objectives and Approach
1.1 Objectives of Naya Raipur
A satellite city to Raipur holding Capital function is the primary identity of Naya Raipur. It will be
modern in the use of technology, uphold worthy traditions and core values, and conserve the
prevailing man- nature symbiotic culture as well as abundant natural & cultural assets in the region.
The citizens will be offered a wide range of living options with equity and dignity. The city will strive
to make an impact in the following role:
An agent of economic change and social transformation in the state.
An efficient engine of growth and prosperity.
A servicing hub not only in manufacturing of goods but also in Information Technology and BioTechnology sectors.
A financial centre of the region.
Hub of trade and hospitality sectors in Naya Raipur
Hub of cultural services which would supplement local economy.
Hub of affordable and high quality medical services.
Hub of quality educational facilities and strive to develop as a knowledge base.
However, the vision of the city in physical terms, i.e. its form and function in two as well as three
dimensional terms is delineated in a subsequent section.
For all the lofty or mundane purposes bestowed on this city, a comprehensive exercise was
undertaken to find a perfect location for it. An imaginary circle of 50 km radius was drawn around
Raipur and this massive area was divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant was analyzed in context
of regional development, existing development, climatic factors, flora and fauna, water resources,
transport network etc and the efforts yielded the present site southeast of Raipur at about 15 km
distance, close to Mana Airport. The site selection methodology and site profile are detailed out in
following chapters.
1.2 Methodology Adopted in Plan-Making
While venturing to prepare the Development Plan for Naya Raipur, basic studies were made in the
form of a secondary survey of data on Chandigarh (the first state capital of independent India) and
Raipur, the elder sister and the most important "organic" metropolis in the region.
Primary studies related to existing village population, site conditions, those related to water source/
water table etc were also carried out.
On the selected site, a thorough analysis was made of the given assets and constraints. From this
emerged a four-focus city structure, cruciform in shape. The foci are major work-centres, namely the
capital complex in the east, the freight complex/light industries in the north, the software hub in the
west and the institutional/tourist hub in the south. The activity corridors emerging from the four foci
Naya Raipur Development Plan - 2031
intersect at the CBD/cultural complex/city park at the geographical centre of the city.
The space quantum against each activity/work-centre was then ascertained going by accepted thumbrule of the concerned industry/trade/activity, to case of capital complex, and government jobs exact
figures were taken into consideration. The resultant space quantum was then allocated on twodimension on the structure plan and final quantum, shape, location, was defined by exact
boundaries/roads on the plan. With iterations, the allocated spaces were again translated in terms of
number of jobs and the total number of jobs in the city arrived at. With a population of 5.6 lakhs, the
Naya Raipur City is expected to generate approximately 2.2 lakh jobs, with an assumed workforce
participation rate of 40%. The high standards of physical and social infrastructure adopted for the city
will be able to cope with the maximum capacity of the city.
1.3 Physical Plan, Feasibility and Implementation
The present Development Plan, published hereby, is essentially a physical plan, depicting policy
choices in all physical aspects of city, i.e uses of land, housing, work activities, leisure, transportation
and communication, physical and social infrastructure etc. A rudimentary feasibility check has been
done to understand the necessary fund sources and flow, how and from where the city will start and
grow therefrom, the sources of revenue etc. This is a supporting exercise to assure that the policy
choices and the basic land use allocation is feasible and over time and in the planned manner the city
will be able to reach its goals.
It is envisaged that the NRDA will prepare detail plans within the prescribed zones of Development
Plan. Various sizes of plots shall be carved out and allotted after assigning plot level land use as
permissible within the given zone.
For certain areas, the NRDA may dispose land in bulk, e.g. one whole residential sector of 64 ha, for
which design brief shall be a pre-condition for allotment. Similar design brief may be prepared for
projects like IT Park, Golf Course etc.
A detailed feasibility study has been separately carried out, which charts out definite path for funds,
phasing, revenues, and city management. This study corroborates the same basic assurance offered by
the rudimentary study. However, only the rudimentary feasibility study and not the details have been
made part of the Development Plan.
1.4 Planning and Management of the City
Under the Chhattisgarh Nagar Tatha Gram Vikas Adhiniyam land development rules 1973, the Naya
Raipur Development Authority has been formed as a Special Area Development Authority to plan,
implement and administer Naya Raipur. The NRDA is already working out the future tasks, which
will be added on to its kitty especially in light of the 74th Constitutional Amendment.
At present an area of 237.42 sq. km is delineated fully under the control of NRDA, detailed as under:
Naya Raipur City with green belt (Planning Layer I) 95.22 sq km- (Proposed as City Proper
to be acquired in bulk with a 500 m green belt around)
Naya Raipur Development Plan - 2031
Tasks-Complete control in plan making, implementation and administration
Peripheral Zone (Layer II ) 130.10 sq.km. - (Proposed as predominantly rural area with
ancillary facilities and suitable uses, not to be acquired in bulk)
Tasks- Plan making, basic infrastructure provision, development permission, administration
Airport Zone (Layer III) 11.92 sq km- ( land to be acquired in bulk and handed over to
Airport Authority of India for implementation according to their plan after concurrence by
NRDA)
The NRDA is expected to be corroborated by the following agencies among others, in executing its
mammoth responsibilities.
Chhattisgarh State Housing and Environment Department
Chhattisgarh Housing Board - Building model housing colony for a cross section of
government employees and officers in the state.
Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board
Chhattisgarh State Water Supply and Irrigation department - Water supply and lake linking
project for the city.
Chhattisgarh State Rural Development Department - Rehabilitation and funds for rural
development
Chhattisgarh State Public Works Department
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Site Selection
2.1 Introduction
The state of Chhattisgarh was constituted on 1st November 2000, thereby opening up new
opportunities for development in the region. The state of Chhattisgarh envisions itself as a modern
state to provide its people with improved quality of life. It was in conformity with this broad vision
that the Government of Chhattisgarh envisaged the creation of a new Capital City by the name of
Naya Raipur for the State that would not only establish the States identity, but also depict the hopes
and aspirations of the people of Chhattisgarh.
2.2 Methodology for Site Selection
Raipur, the present day State capital has an immense potential to develop into a metropolis on account
of its location and its growing importance as a major node in the trade network of Central India.
Considering this latent value of the present day capital Raipur, it was decided to locate Naya Raipur
the proposed new city in close proximity to Raipur. Accordingly, a region of 50 km radius around
Raipur was demarcated for selecting a site for the Naya Raipur city. The final site was selected after a
detailed analysis based on the site suitability criteria with respect to several parameters (Refer fig.
2.1).
COLLECTION SECONDARY DATA
RELATED TO INFLUENCING FACTORS
STUDY & ANALYSIS OF SECONDARY
DATA RELATED TO INFLUENCING
FACTORS
1. Transport & Infrastructure
2. Land Availability & suitability
3. Environmental Considerations
4. Economic catalysts & Relation
to Raipur
5. Other Parameters
RECONNAISSANCE
SURVEY FOR SITE
SELECTION
QUADRANT ANALYSIS
DISTANCE CRITERIA
1. Raipur City
2. Airport
SURVEY OF PROBABLE SITE
SITE SELECTION FOR NAYA
RAIPUR
Figure 2.1: Methodology for Site Selection
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
The entire region for site selection was divided into three main zones based on the relative distance
from the present day State Capital as also into four different quadrants for location analysis. (Refer
fig. 2.2)
The analysis of the different quadrants has been carried out on the basis of certain select parameters as
discussed below:
i.
Transport and Infrastructure Related
Criteria
ii.
N-E
Quadrant
1
S-W
Quadrant
S-E
Quadrant
Availability of Government land
Land otherwise unsuitable for
agriculture, mining and quarrying
Figure 2.2: Delineation of the Site Selection Region
Land with development friendly and the Quadrants
contours and other physical
features
Land with less number of existing human settlements
Land with minimum forest cover and wildlife
Land with a gentle slope to facilitate easy drainage and discharge of effluents
Soil conditions with good bearing capacity for structural stability.
Environment friendly location
Favourable climatic conditions
Economic Catalysts
v.
N-W
Quadrant
Environmental considerations
iv.
Linkage to existing transport
network
and
easy
future
connectivity
Linkage to existing infrastructure
network including water, power
and telecommunications
Availability of water sources
Land Availability & Suitabilty
iii.
50
Existing industries, mining resources, reserve forests, wildlife sanctuaries and other
tourist attractions act as economic catalysts
Airport, Software Technology Park to act as anticipated economic catalysts
Proximity to the Raipur City
Other Parameters
Land Value in the region
Existing Airport Implications
Local Landscape Features
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
2.2.1
Transport and Infrastructure
The existing transport and other physical infrastructure with potential for augmentation to fulfil the
new citys demand is an important determinant for deciding the location of the proposed city. Good
connectivity by road and rail is an important decisive factor to decide the success of the project. (Refer
map 2.1)
2.2.1.1
Roadways
There are four major roads within the site selection region viz., three National Highways, namely;
NH-6, NH-200 and NH-43 and one State Highway i.e. SH-5.
Fig 2.3: NH 6 Connecting Mumbai via
Nagpur, Durg, Bhilai and Raipur
Fig 2.4: NH 200 Connecting Raipur
and Bilaspur
NH-6: On the west it connects the region with Nagpur as
also Nasik and Mumbai through NH-2 after Dhule. On the
east it connects Sambalpur and leads to Kolkata. While the
stretch of NH-6 between the city of Raipur and Durg
handles major volume of traffic because of the tremendous
interdependence and interaction of the industrial towns of
Bhilai, Durg, Borai industrial growth centre and the capital
city of Raipur, the stretch beyond Raipur towards
Sambalpur handles relatively less volume of traffic and
thus has the potential of handling higher volume of traffic
in future.
NH 200: It connects Raipur with Bilaspur. The stretch of
NH-200 lying within the concerned region has potential
mining belts on both the sides, cement plants and two
industrial growth centers of Orla and Siltara in its vicinity
thus making it highly prone to present and future heavy
traffic volume.
NH-43: This road connects Raipur with Koraput and
Bheemunipatnam on the south-east and further to
Vishakhapatnam through NH-5. This road links the
concerned region with the port city of Vishakhapatnam.
Thus this is a major road handling goods traffic to and from
Bhilai and Raipur to Vishakhapatnam.
Fig 2.5: NH 43 Connecting Raipur and
Visakhapatnam
SH-5 links Raipur with Dhamtari where it connects with
NH-43 and has the potential to act as a major reliever to
NH-43 in handling goods and passenger traffic, within the
concerned region.
The other important road is the one connecting Raipur to Baloda Bazar passing through the
prospective mining area and with the potential of handling high traffic volume while putting this area
under intensive economic use.
Thus the potential roads for future linkages to the capital city are the stretches of NH-6 from Raipur
towards Sambalpur and the NH-43 stretch from Raipur to Abhanpur.
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
2.2.1.2
Railways
The region enjoys very good railway connectivity. The railway lines run almost parallel to the
National and State Highways. The main Mumbai Howrah railway line passes through Raipur
dividing the region into two halves, namely the Northern and the Southern halves. The other railway
lines are from Raipur to Bilaspur and Raipur to Visakhapatnam. The existing railway stations within
the delineated region are as listed below:
1.
2.
3.
4.
2.2.1.3
Towards
Mumbai/Nagpur
Towards Dhamtari
Towards
Vishakhapatnam
Towards Bilaspur
Raipur, Sarona, Kumhari, Bhilai, Durg and Rasmaidan
Raipur City, Mana, Bhatgaon, Kendri, Abhanpur, Karvel
The line to Rajim has two Railway Station, Manikchaari and
Nawapara
Mandir Hasuad, Lakholi, Arang, Belonda
Urkura, Mandhar, Siliari, Baiknath, Tilda, Hatbandh
Airways
There are three airports in the sub-region. Two of the three existing airports near Tilda and Jamul
are private while the one at Mana is public. The Mana airport is about 13 km away from the city of
Raipur towards the South East. This
airport
presently
has
limited
facilities.
2.2.2
Availability
Resources
of
Water
The region delineated for location of
the proposed new city is dotted with
water bodies in the form of lakes,
ponds, rivers and irrigation canals.
Water from the three lakes Kumhari, Pirdaon and Kurud can be
tapped for supplying water to the
Naya Raipur. The ground water is
available at a depth of around 250 ft.
to 400 ft. Three rivers cross the
delineated region River Mahanandi
is a perennial river while the other
two viz., Seonath and Kharun are
seasonal rivers (Refer fig. 2.9).
Fig 2.6: Mahanadi River - Perennial Source Of Water
Fig 2.7: Kharun River at NH6 Crossing (Seasonal)
Fig 2.8: Sheonath River at NH-6
Crossing (Seasonal)
River Mahanandi being perennial in nature is also reinforced with water from Pairi and Sukha and has
the capacity to discharge the requisite amount of water for the proposed Naya Raipur.
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Fig 2.9: The Rivers within the Site Selection Region
2.2.3
2.2.3.1
Land Availability & Suitability
Availability of Government Land
The availability of Government land has an important bearing on the site selection process as cost and
time spent for land acquisition can be reduced substantially with the utilization of Government land.
Refer figure 2.10 for the availability of government land in the different Tehsils of Durg, Dhamda,
Patan, Abhanpur, Tilda and Raipur. High concentration of huge chunks of Government owned land is
present along the river Mahanadi near Arang & Abhanpur and between the Baloda Bazar Road and
Kharun River.
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Figure 2.10 : Availability of Government Land within the site selection region
2.2.3.2
Land otherwise unsuitable for Agriculture, Mining and Quarrying
The region is well irrigated with a double cropping pattern being practised in the Raipur district.
Therefore it would be prudent to locate the site for the capital city so that it has least effect on
agricultural land. Abhanpur Tehsil on the south-eastern quadrant has some upland / marginal land,
which is unsuitable for agriculture. Moreover, this land does not contain the mining areas.
2.2.3.3
Land with development-friendly Contours and other physical features
In general, the land in the site selection region gently slopes towards the west. The highest contour
level as indicated on the topo-sheet is 320 m above the sea level. The region has various physical
features in the form of lakes the largest being located near Bhilai, uplands, dispersed forest covers,
etc. The region surrounding Mandir Hasaud also has a number of big water bodies.
2.2.3.4
Land with few existing Human Settlements
The abadi areas are uniformly distributed over the fertile rice cultivated plain of the Mahanadi. Thus,
the uplands/marginal lands will be favourable for the location of Naya Raipur (Refer map 2.2).
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
2.2.3.5
Land with minimum Forest Cover and Wildlife
The site selection region does not have a widespread forest cover except for some protected forests
near Tilda, Mohrenga, Kendri and around the confluence of Mahanadi and Sukha river.
2.2.4
Environmental Considerations
The mining areas are mostly located to the north of the region stretching from northwest to northeast.
The cement plant at Siltara is in the northern part of the region and the Bhilai Steel Plant, Borai
Industrial growth centre and ACC cement plant are located on the western side of the region along the
NH-6. These are the air polluting zones as huge quantities of dust and smoke emanate from the
various industrial and mining activities in the region.
The predominant wind flow is from the southwest direction. However, in the post-monsoon and
winter months the predominant wind direction is from the northeast. The trend starts varying from the
month of March and by April the wind direction is from west and southwest. The wind speed in
general ranges between 2.9 km. per hr. to 8.69 km. per hr.
Table 2.1: Wind Data for site selection region in Chhattisgarh
WIND DIRECTION
Morning
Evening
C/NE
C/NE
SW/W
C/W
SW/W
W/SW
C/NE
C/NE
MONTH
JAN
MAY
AUG
NOV
Mean monthly wind speed
2.9
8.21
8.69
3.22
It is quite evident that the dust and pollution laden air zone stretches from south-west to north-east as
these zones contain the mining and the industrial belt. Thus, environmentally the southeastern part of
the site selection region is the non-polluting zone and is suitable for the location of the Naya Raipur.
2.2.4.1
Land conducive to Drainage and Effluent Discharge
In general, the region delineated for site selection has good drainage and irrigation network (Refer
map 2.3). However, the effluent will need to be treated before disposal and this must happen in the
downstream area, i.e. towards the northern side. It appears that the S-E Quadrant has the potential for
a well-planned drainage and effluent discharge system and is, therefore, suitable for locating the city .
2.2.4.2
Economic Catalysts
The presence of industrial growth centers (industrial, economic activity centre) on the northern and
the western side of the delineated region would acts as an economic catalyst for the overall
development of the new Capital City Region (Refer fig 4.11). The following industries in the vicinity
are bound to play a role in the progress of the Region and the State as a whole.
Cement plants (such as ACC and Century) on the northern and western side of Raipur city.
The Bhilai steel plant on the western side.
The mining site on the northern side of NH-6
10
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
TILDA
CENTURY
BAIKUNTH
MATRA
SEMARI
A
River Sheonath
PAUNI
L&T
HIRMI
CEMENT
MOHRENG
URLA
CCI MANDHAR
BORAI
Bhilai ACC JAMUL
Raipur
New
Capital
City
River Kharaun
River
Mahanadi
Important Urban Centres
Industrial Growth Centres
Existing Cement Plants
Proposed Cement Plants
Fig 2.11: Proposed Location of Naya Raipur City in the Region
2.2.5
Presence of Airport
An airport acts as an engine of economic growth. The
setting of the Naya Raipur with respect to the location of
the airport is thus an important factor where the
proximity to the airport gives the added benefit of
improved connectivity.
2.2.6
Quadrant Analysis
After an analysis of the different quadrants based on the
various parameters discussed in the foregoing sections,
the southeast quadrant was found to be most suitable for
the locating the proposed new Capital City (Refer fig
2.12).
Fig 2.12: South-Eastern Quadrant
Suitable Site for Naya Raipur
11
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Strengths of the southeast quadrant:
Availability of water due to proximity to Mahanadi River and Mahanadi Canal.
Absence of mining area
Availability of barren/non-agricultural land
Abundant availability of government owned land
Proximity to Raipur City
Proximity to NH-6 and NH-43
Conducive traffic condition on NH-43 and NH-6 for providing accessibility to the new City
Proximity to the Raipur-Vizainagaram and Mumbai-Kolkata Railway Line
Presence of natural features like water bodies for creation of recreational spots in the city
Proximity to the Airport, but availability of land outside the restricted Air Funnel zone.
Zone free from pollution due to industrial centres.
The other important factors that have been taken into consideration for deciding the spatial location of
the Naya Raipur is
i.
The New Capital City should not be so close to the present day capital city of Raipur that both
the old and the new cities merge together due to agglomerating effect and the befitting image
of the New Capital City is put to jeopardy.
ii. The site should not be so distant that Naya Raipur has a completely independent existence and
the existing Raipur City becomes irrelevant.
2.2.7
Proposed Site
Based on a detailed analysis of the region delineated for the location of Naya Raipur, a site has been
selected about 15 km away to the southeast of the existing Raipur. The site enjoys the advantage of
the presence of the Mahanadi Canal on the southeastern side and the NH-43 on the southwestern side.
The existing airport is situated between Raipur city and Naya Raipur.
Fig 2.13: Location of Naya Raipur, Chhattisgarh
12
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Site Profile
3.1 Defining the Areas
The NRDA Planning area has been divided into three Planning layers namely Layer-I, Layer-II and
Layer-III (Refer map 3.1)
Table 3.1: Delineation of Planning Layers of the Naya Raipur & its Peripheral Region
Sl. No.
Layer
Area Included
The Proposed Naya Raipur (Area 80.13 sq.km.) Including 500-meter wide
1
Layer-I
green belt (Area 95.22 sq.km.)
2
Layer-II
Naya Raipur Peripheral Region (NRPR) Area 130.28 sq.km.
3
Layer III
Airport Zone Area 11.92 sq.km.
3.2 Spatial extent of the proposed Naya Raipur including 500 meter
wide green belt (Layer I)
Naya Raipur along with the green belt is spread over a total area of 95.22 sq. Km. It covers ten
villages fully and twenty three villages partly (Refer table 3.2 and 3.3).
Table 3.2: Villages fully incorporated within proposed Naya Raipur City
S. No.
Villages
S.No.
Villages
1
Kayabandha
6
Uparwara
2
Chicha
7
Khapri-2 (Khapri)
3
Rakhi-1 (Rakhi)
8
Kotrabhata
4
Jhanj
9
Sendh
5
Tuta
10
Nawagaon south
Table 3.3: Villages partly and marginally incorporated within the proposed Naya Raipur City
Sr. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Villages
Chhatouna (Chhatouna)
Parsada
Paloud
Kotni
Kuhera
Tenduwa
Riko
Mandir Hasaud
Pacheda
Jhanki
Khuteri
Sr. No.
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Villages
Nawagaon north
Khandwa
Kendri
Bendri
Parasatti
Barauda
Mudpar
Nimora
Kurru
Mana
However, of all the above-mentioned villages only the following 13 abadis viz. Chhatauna, Nawagaon
(north), Sendh, Reiko, Chicha, Kotrabhata, Rakhi, Kayabandha, Jhang, Tuta, Uparwara, Khapri and
Nawagaon (south) are actually included within the Naya Raipur boundary.
3.2.1
Linkages and Surroundings
The site selected for Naya Raipur is bound by NH-6 connecting Mumbai-Kolkata on the north and
13
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
NH 43 connecting the city to Visakhapatnam on the west. The site also has good railway connectivity
on account of the Mumbai-Howrah line in close proximity.
3.3 Spatial Extent of the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region (Layer II)
The Naya Raipur Peripheral Region (referred as NRP hereafter) covers a total area of 130.28 sq. Km.
Villages, which are fully included in the NRP Region are as stated in table 3.4.
Table 3.4: Villages fully included within the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region
Sl. No.
Village Name
1
Cheriya
Banjari
Temri
Banarsi-2 (Banarsi)
Dharampura
Nakati
Tandul
Pauta
Serikhedi
Apart from the nine villages mentioned above there are 19 villages, which are partly included within
Naya Raipur peripheral region (refer table 3.5).
Table 3.5: Villages partly included within the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region
Sl. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Villages
Sl. No.
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Parsada
Paloud
Kotni
Kuhera
Tenduwa
Khandwa
Pacheda
Mudpar
Jhanki
Kendri
Villages
Bendri
Parasatti
Nimora
Mana
Baroda
Mandir Hasaud
Kurru
Ramchandi
Umariya
3.4 Airport Zone (Layer III)
Layer III fully includes two villages Ramchandi & Baroda and partially includes Mana extending
over an area of 11.92 sq.km.
3.5 NRDA Planning Area
The layers I, II and III together constitute the NRDA Planning area (23742.63 Ha or 237.42 sq.km.).
3.5.1
3.5.1.1
Physiography of the NRDA area
Topography
The site has a gentle topography with its slope ranging from 0% to 5%. The flat terrain with natural
14
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
drains flowing towards Northeast direction allows unhindered flexibility for an efficient transportation
system.
3.5.1.2
Drainage Pattern
The NRDA area is dotted with water bodies in the form of lakes, ponds, nallas and irrigation canals.
The area falls in the irrigation command of Left Main Canal System, on the eastern side.
3.5.1.3
Geology
The Naya Raipur and its Peripheral Region fall under three stages of geological formation viz., Raipur
Stage (Chandi Formation), Charmuria Stage and Gundardehi. As per IS:1984, Criteria for
Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures, the Naya Raipur Site including the Raipur city falls under
Seismic Zone I which is considered fairly stable against seismic forces.
3.5.1.4
Hydrogeology / Ground Water Availability
The study carried out in the Project report by Watson Solutions for Government of Chhattisgarh found
that a thick band offers conditions favourable for the occurrence of ground water. The average depth
of water level in open wells ranges from 6 to 10m below ground level.
Table 3.6: Hydro-geological information of the NRDA Area
Annual
Net
Annual
Ground
Utilisable
Annual
Repressible
Water
Ground
Ground
Tehsil
Ground
Balance
Water
Water
Water
(MCM)
Resource
(MCM)
(MCM)
(MCM)
Raipur/
111.39
94.68
18.88
15.82
Dharsiwa
Irrigation
Potential
from Ground
Water
Resource
(Ha)
236.70 ha
Arang
138.25
117.51
12.24
105.32
29.78
Abhanpur
111.82
95.05
10.18
84.87
237.63
Remarks
Area suitable for
Dug well
Area suitable for
Dug well
Most of the area of
the
tehsil
is
suitable for dug
well and partly
along
Mahanadi
River is suitable
for tube well.
Source: Project Report on Geology &Hydrogeology of Raipur District by Watson Solution to Govt. of Chhattisgarh
3.5.1.5
Soil
The main soil types found on the site are Yellow soil, Red soil and Alluvial and Sandy loamy soil,
which are suitable for construction.
3.5.1.6
Climate
In general the region is characterised by dry and warm climate. Summers are very hot, and last from
March to middle of June. Winter is between October and February. Monsoon commences in the 2nd
week of June and lasts till end of September.
15
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
A. Temperature
Table 3.7: Mean monthly maximum and minimum Temperature in the area
Mean highest
Mean monthly max.
Mean monthly
of the month
Period
Temp (C)
min. temp. (C)
(C)
JAN
27.5
13.2
30.9
MAY
41.8
27.8
44.8
AUG
29.9
23.8
33.8
NOV
28.7
15.9
31.5
Mean lowest of
the month (C)
9.2
22.8
21.9
11.2
Source: Planning Brief for Stage-II Competition, Capital Project Administration, Govt. of Chhattisgarh
B. Relative Humidity
Table 3.8: Relative Humidity in the area
Months
Morning
Evening
JAN
MAY
AUG
65
36
89
37
21
82
NOV
68
49
Source: Planning Brief for Stage-II Competition, Capital Project Administration, Govt. of Chhattisgarh
C. Rainfall
The average annual rainfall in the area is generally around 1400 mm. Rains are predominant during
July & August. On an average there are 61 rainy days in a year. The Raipur District receives 87.1% of
the total rainfall from the southwest monsoon during June to September. The winter rainfall
accounts for 9% of the total rainfall. During the Monsoon the maximum rainfall occurs during the
month of August where mean monthly rainfall was recorded at 363.7 mm. In monsoon season, the
mean annual rainfall is 1332 mm.
389.6
July
Aug
300
227.6
242.6
400
17.1
2.8
51.6
19.6
Feb
15
Jan
10.9
100
21.3
200
12.7
Rainfall in mm
500
393.5
Fig 3.1
Average Monthly Rainfall for Raipur District
Nov
Dec
0
Mar April May
June
Sep
Oct
Months
Source: CPA, Govt. of Chhattisgarh
D. Wind Direction
The predominant wind direction is south-western. In the post monsoon and winter months (December
to March) the wind direction is from the northeast.
16
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Existing Land Use NRDA Planning Area
The NRDA planning area consists of 41 villages covering a total of 23742.63 Ha. The Existing Land
Use Plan of these 41 villages was adopted under the provisions of section 69(B) read with section 15
(3) of the Chhattisgarh Nagar Tatha Gram Nivesh Adhiniyam 1973 (no. 23 of 1973) by the Housing
and Environment Department, Government of Chhattisgarh vide notification ref. no. 37, dated
20.06.2002.
The following table shows the existing land use distribution in the NRDA Planning Area (Refer Map
4.1).
Table 4.1: Land Use Distribution in the NRDA Planning Area
S.No.
Land Use
1
Residential
2
Commercial
3
Industrial
4
Public & Semi Public (Public amenities and facilities)
5
Transportation - Roads and Streets
6
Recreational
7
Water Body
8
Agriculture
Total
Area ( in Ha)
257.48
26.61
65.34
302.65
1131.44
107.73
1846.70
20004.68
23742.63
Percentage
1.08
0.11
0.28
1.27
4.77
0.45
7.78
84.26
100
Post- publication period of the existing land use plan for NRDA Planning Area has seen many new
developments coming up like the Muktanagana Open Air Museum, FCI Godowns, Shradhani Durbar,
and a number of facilities and utilities like schools, petrol pumps etc.
17
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
The Vision and Concept
5.1 Vision and Concept for Naya Raipur
5.1.1
The Vision
Naya Raipur would be a planned and designed new city of the 21st century to be a focus of socioeconomic and cultural life of the state of Chhattisgarh having its role and recognition at national and
international levels. The new city would be eco-friendly integrated in its inspiring existing landscape;
efficient, healthy; modern, but caring for its traditional values.
The new city of Naya Raipur would be:
5.1.2
Set in its natural surroundings thus conserving its existing landscape to include major city
park, botanical park, jungle safari, theme parks, integrated sports complex and a golf course.
Accessed by an eight-lane expressway, shall be equipped with modern mass transit system
coupled with a city wide pedestrian corridor linking all major urban activities.
Lively and vibrant in character with shopping malls, multiplexes, food courts, restaurants and
other intensive urban activities and recreational areas.
An intelligent city with full use of information and communication technology.
A visually pleasing cityscape in tune with the aesthetic principles of urban design and
landscaping
Equipped with state of the art physical, social and economic infrastructure providing the
city with high degree of urban convenience & cleanliness and thus with investor friendly
environment.
Precincts
The city is designed for a population of 5.6 lakh. The city has two prominent gateways that mark
entry to the Naya Raipur City one to the north and the other to the west. Naya Raipur has the
following precincts:
i. Government Complex to include Secretariat, Assembly, Government offices, and Police Headquarters area.
ii. Cultural Heart to include Museum, Art Gallery, Library, Theatres, Convention centre and
International Centre.
iii. City Centre to include city level shopping malls, commercial offices, restaurants, multiplexes
and other areas of recreation.
iv. University including research and institutional complexes.
v. Software Technology, Exhibition and Business centers
vi. Central City Park around an existing vast water body as one of the biggest city parks in the
country. Park and Sports Centre in the North end to include urban forest, theme park and sports
complex. City Park South to include Theme Park, Jungle Safari, Golf Course and Film City.
vii. Transport and integrated freight complex to service the city and its industrial area.
viii. Living areas with medium density development for the creation of a peaceful environment
envisaged for the city.
18
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Fig. 5.1: Conceptual location of the Precincts
These precincts will be interlinked by:
i. An efficient and smooth Mass Rapid Transit System running linearly along the North-South axis
of the city.
ii. City level pedestrian corridor, and
iii. A continuous green and open-space spine running centrally along the city spine and containing
sub-city level facilities.
5.1.3
The Form
The physical form of the Naya Raipur has been developed in conformity with the overall vision of a
Smart and eco-friendly city.
The physical form of the transport network system is a blend of three forms:
Linear
Cruciform and
Transport Hub
Grid
Software Technology
Park
Capital
Complex
CBD
cum
Central Park
Recreational
Green
1. Linear
2. Cruciform
3. Grid
19
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
The linear form is enabled by the proposed rail based, medium capacity system supported by the main
north-south activity green corridor.
The two axial road corridors provide the cruciform. The longer axial corridor runs along the activity
green corridor. The minor axial corridor runs orthogonal to the longer axial at about its mid length.
At the termini of the above corridors are located the major activities like the Capitol Complex, the
Software Technology Park, the University and Education & Research Complex, the Transport and
Logistics Hub and the Integrated Freight Complex.
Along the two axial corridors, at their mid sectors are the Central Business District, the government
offices, the City Centre Park and other Social & Cultural Institutions.
A grid of residential sectors is superimposed on these two forms, providing the necessary flexibility
and integrating people with activities. The minor axial corridor provides the grand vista.
A grid of 800 m x 800 m forms the typical minor residential sector housing a population of 16,000.
Four such grids together form the major grid.
The concept establishes a hierarchical system of urban development in terms of physical and social
infrastructure, transportation network, institutional, commercial, and recreational and other activities.
The central zone of proposed development becomes the heart of the city and is framed by green belts
that serve as an interface between the city centre and the planning units and neighbourhoods
5.1.4
The Peripheral Region
A peripheral region includes 28 surrounding villages referred to as the Naya Raipur Peripheral Region
(NRPR) to act as a buffer between the proposed Naya Raipur City and Raipur with an idea to control
and regulate development in the region. A balanced Settlement Development Strategy for this area is
evolved by providing access to infrastructure through a well-defined Settlement Pattern.
20
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Demographic Profile
6.1 Population
6.1.1
Chhattisgarh: Population Growth Trends
As per 2001 Census, the total population of Chhattisgarh is 20.83 million. The state of Chhattisgarh
has registered a population growth rate of 15.5% during 1991-2001, as compared to the average all
India growth rate of 21.54 % during the same period (Refer table 6.1).
Table 6.1: Population growth in India and Chhattisgarh
Year
India
(in Million)
Chhattisgarh
(in Million)
Growth Rate (%)
Growth Rate (%)
1901
238.3
4.18
1911
252.09
5.80
5.19
24.2
1921
251.32
-0.30
5.26
1.3
1931
278.97
11.00
6.02
14.4
1941
318.66
14.20
6.81
13.1
1951
361.08
13.30
7.45
9.4
1961
1971
439.23
548.15
21.60
24.80
9.15
11.63
22.8
27.1
1981
1991
683.32
846.30
24.70
23.90
14.01
17.61
20.5
25.7
2001
1028.61
21.54
20.83
15.5
Source: Census of India, 2001- Chhattisgarh; Provisional Population Totals Paper 1 of 2001
6.1.2
Population of Naya Raipur
Naya Raipur city is planned for a population of about 5.6 lakh in 2031. This new city would attract
population from Raipur, the adjoining region and to some extent other parts of India. An exercise in
this respect has been conducted with respect to the broad region, which is 50 km radius around
Raipur.
Table 6.2 Future Population of the Region
Year
1991
2001
2011
2021
2031
Percentage of Regions Population
to Total Population of the State
12.97
14.69
16.90
20.08
23.75
Population of the Region
2,285,044
3,060,485
4,099,076
5,490,117
7,353,216
Source: Census of India and Consultants Projection
The percentage share of the regions population to the total population of the state is likely to increase
from 12.97 % in 1991 to 23.75 % in 2031.
21
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
Fig 6.1: Composition of Population in the Region w.r.t. Chhattisgarh
COM POSITION OF POPULATION IN THE REGION WRT
CHHATTISGARH
350.00
309.62
300.00
273.37
Population in Lakhs
250.00
242.58
208.34
200.00
176.15
150.00
100.00
73.53
54.90
50.00
40.99
30.69
22.85
1991
2001
2011
Years
6.1.3
2021
Chattisgarh
2031
Region Population
Rural Urban Composition of the Projected Population of the Region
The rural urban population for the region has been given in Table 6.3. This has been worked out
considering the rural population increasing at the present growth rate up to the year 2031.
Table 6.3 Rural Urban Population Composition of the Region
Year
Rural
Urban
Urban Percentage
1991
1,137,007
1,148,037
50.24
2001
1,281,814
1,778,671
58.12
2011
1,445,063
2,654,013
64.75
2021
1,629,104
3,861,013
70.33
2031
1,836,583
5,516,633
75.02
Source: Census of India and Consultants Projection
6.1.4
Population Projection of Urban Areas in the Region
The urban population has been divided into three sections: Raipur Urban Agglomeration, Durg
Bhilai Urban Agglomeration and other urban areas in region. As per 2001 census the population in
these categories are as follows:
Table 6.4 Urban Population Composition of the Region
Urban Areas
2001
Percentage to the Total Population
Raipur UA
22.85
699,264
Durg Bhilai UA
30.18
923,559
Other Urban Areas
TOTAL
5.09
58.12
164,425
1,787,248
Source: Census of India, 2001
It is proposed to maintain the present balance in the urban components of the region through keeping
the same proportion by a balanced regional development. Thus, the projected population of the three
components is worked out as follows. Total urban population of region in 2031 will be 55.16 lakhs.
Table 6.5 Population Projection of Urban Areas
Urban Areas
Raipur UA
Durg Bhilai UA
Other Urban Areas
TOTAL
2001
2011
2021
2031
699,264
1,043,395
1,517,913
2,168,801
923,559
164,425
1,787,248
1,378,073
232,546
2,654,013
2,004,796
338,304
3,861,013
2,864,462
483,370
5,516,633
Source: Census of India and Consultants Projection
22
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
6.1.5
Population Component of Naya Raipur
Naya Raipur would be taking functions from the Raipur city and also would have impact in the
region. Being a special intensive activity in the new town it may also attract population from other
parts of Chhattisgarh and also from other states of India. The population of Naya Raipur would affect
the population projection in Raipur and Durg Bhilai Urban Agglomeration. The population of Naya
Raipur is planned as 150,000 in 2011 to 560,000 in 2031 (Refer Table 6.6).
Table 6.6 Population Projection of Naya Raipur
Sr.
Total Population
No.
1
2
3
4
5
2011
150,000
Additional Population
Natural Growth of the Existing
Population
Additional Population deducting Natural Growth
Population from Raipur UA (40%)
Population from Durg- Bhilai UA (30%)
Population from Other Areas of State (20 %)
Other Parts of India (10 %)
60,000
45,000
30,000
15,000
2021
365,000
215,000
2031
560,000
195,000
22,400
192,600
77,040
57,780
38,520
19,260
40,800
154,200
61,680
46,260
30,840
15,420
Source: Census of India and Consultants Projection
The population estimates for Naya Raipur are related to and dependent on the development of various
economic activities and other socio-economic and physical conditions. These may be reviewed after
the decadal census.
6.1.6
Age-Sex Composition
A study of the Age Sex Structure of new city of Chandigarh and the present day State capital of
Raipur reveals that the age category 15-59 i.e., the working age group is higher as mostly the
population is attracted for jobs to the new city. The age-sex pyramid of Raipur gives an idea of the
age-sex structure of Raipur in 1991.
Table 6.7 Age Structure of Chandigarh and Raipur, 1991
Chandigarh
Age
0 ~ 14
31.87
15 ~ 59
63.79
60+
4.34
Raipur
35.54%
58.86%
5.60%
Fig 4.1: Age Sex Pyramid of Raipur City, 1991
Fem ale (% age)
10 0 +
90-94
M ale (% age)
80-84
70-74
60-64
50-54
40-44
30-34
20-24
10 - 14
0-4
1 5 .0 0
1 0 .0 0
Source Census 1991
5 .0 0
0 .0 0
5 .0 0
% a g e o f P o pu l a ti o n
23
1 0 .0 0
1 5 .0 0
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
6.1.7 Sex Ratio
The migration to new cities is usually male biased as single men move in to take up jobs (refer table
6.8).
Table 6.8: Sex ratio in Chandigarh
Year
Chandigarh
1961
652
1971
749
1981
769
1991
790
2001
773
Punjab
854
865
879
882
874
Haryana
868
867
870
865
861
Source Census of India
Table 6.9: Sex ratio for Chhattisgarh and Raipur
Year
Chhattisgarh
1971
998
1981
996
1991
985
2001
989
Raipur
958
927
Since, Naya Raipur has a similar function as that of Chandigarh, Naya Raipur may have a low sex
ratio as compared to that of Chhattisgarh or the present day State Capital of Raipur. To deal with such
a situation and to work for better balance of sex ratio, it is important that housing and other social
infrastructure such as schools and health facilities be provided ahead of or simultaneous with job
creation.
6.2 Population Distribution in Naya Raipur
The population distribution in Naya Raipur city in 2031 is as follows
Table 6.10: Population distribution in Residential Sectors
Sector Number
Gross Sector
Area (Ha)
Net Residential Area
(Excl. of waterbody, plantation & abadi) (Ha)
Sector Population
(Exclusive of abadi population)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Total
141
114.63
61.16
63.55
84.4
94.08
136.56
64.5
65.8
97.75
80.66
97.17
62.59
58.82
61.1
60
60.31
60.29
267.39
88.35
91.74
1911.85
117.49
109.71
58.86
63.15
84.4
94.08
121.69
64.5
65.45
84.03
79.97
96.11
62.59
58.82
61.1
52.56
50.65
56.92
206.56
88.35
91.74
1768.73
29,373
27,428
14,715
15,788
21,100
23,520
30,423
16,125
16,363
21,008
11,996
24,028
15,648
14,705
15,275
13,140
12,663
14,230
51,641
22,088
22,935
434,192
24
Naya Raipur Development Plan -2031
As regards village population, abadi area of village Rakhi shall be acquired and the population
relocated to sector adjacent to the capitol complex. The population of Khandwa abadi falling under
the golf course shall be relocated in the peripheral area only.
Table 6.11: Population distribution in Abadi Areas
Sr.No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Abadi
Area (Ha)
Tuta
Uparwara
Nawagaon-1 (Nawagaon south)
Chhatouna (Chhatouna)
Riko
Chicha
Kayabandha
Khapri-2 (Khapri)
Nawagaon (north)
Kotrabhata
Sendh
Jhanj
Total Population in Abadi Areas
*57% growth rate has been adopted over the next 30 years
42.34
53.13
18.88
8.65
18.54
8.54
8.45
6.34
7.2
11.75
9.45
3.54
3455
4900
1525
2150
1950
1650
1160
274
1500
9060
1300
600
196.81
29,524
Table 6.12: Total Population in Naya Raipur
Sl. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Use Zone
CBD
Composite Use Zone
Special Industry Area (Software Park, Gems and
Jewellary Park)
Facility Corridor
Institutional housing
Residential Sectors
Abadi Areas
Cantonment/Police Academy and NCC
Total Population
25
Population*
Population
20,000
2,250
10,000
19,000
35,000
434,192
29,524
7,406
557,372
You might also like
- HMDA Draft Metro Development Plan Public NoticeDocument4 pagesHMDA Draft Metro Development Plan Public NoticeShaik Zayed100% (1)
- Analysing Chowk As An Urban Public Space A Case of LucknowDocument29 pagesAnalysing Chowk As An Urban Public Space A Case of LucknowAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Urban Design ReportDocument23 pagesUrban Design ReportLakshwanth ArchieNo ratings yet
- UDPFI GuidelinesDocument48 pagesUDPFI GuidelinesVineeta HariharanNo ratings yet
- Urban Design Studio Report - 2019Document96 pagesUrban Design Studio Report - 2019n22No ratings yet
- Development of Urban Villages in Delhi - 2013Document148 pagesDevelopment of Urban Villages in Delhi - 2013kmithilesh2736No ratings yet
- CDPDocument115 pagesCDPAr Kunal PatilNo ratings yet
- Planned City of ChandigarhDocument29 pagesPlanned City of Chandigarhnirmal pariharNo ratings yet
- Housing For Urban Poor: Scenario and Solutions For IndiaDocument25 pagesHousing For Urban Poor: Scenario and Solutions For IndiaShubhamNo ratings yet
- Indore City Development PlanDocument8 pagesIndore City Development Planpunitg_2No ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument23 pagesSynopsisMuthu ChellappanNo ratings yet
- Socio Economic Profile of AurangabadDocument72 pagesSocio Economic Profile of AurangabadShrinath DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Pedestrian Oriented Cities in India Shreeparna SahooDocument11 pagesPedestrian Oriented Cities in India Shreeparna SahooShreeparna SahooNo ratings yet
- Sabarmati River FrontDocument25 pagesSabarmati River Frontramyadwarapureddi0% (1)
- Coimbatore Mono Rail ProjectDocument40 pagesCoimbatore Mono Rail ProjectSathishNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Case StudyDocument4 pagesGujarat Case Studysketch up0% (1)
- Social InfrastructureDocument26 pagesSocial InfrastructureTulika GalaniNo ratings yet
- Prachi Di's Thesis ReportDocument63 pagesPrachi Di's Thesis Reportswatisinha989100% (4)
- Understanding The Need For Street Design GuidelinesDocument43 pagesUnderstanding The Need For Street Design GuidelinesITDP IndiaNo ratings yet
- Intro Scope and ObjectivesDocument15 pagesIntro Scope and ObjectivesAli Kemal ArkunNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Group 5 Arpan Jain Asim Babbar Kapil Kaushik Pramod Malik Raj Kamal Maurya Rajat Chopra Taruna Arora Yatharth ChoudharyDocument51 pagesPresented By:-Group 5 Arpan Jain Asim Babbar Kapil Kaushik Pramod Malik Raj Kamal Maurya Rajat Chopra Taruna Arora Yatharth ChoudharyAaditya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Working Paper - Tracing Modern Heritage in Panjim Landmarks - ChinmaySomanDocument14 pagesWorking Paper - Tracing Modern Heritage in Panjim Landmarks - ChinmaySomanChinmay SomanNo ratings yet
- Emerging SpecializationDocument4 pagesEmerging SpecializationVarshini AshwanthNo ratings yet
- Musi Riverfront Development in HyderabadDocument100 pagesMusi Riverfront Development in HyderabadyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Coimbatore - DCRDocument59 pagesCoimbatore - DCRHananeel SandhiNo ratings yet
- Elective Iv - Urban Design: Identification and Analysis of Urban Issues and Their SolutionDocument9 pagesElective Iv - Urban Design: Identification and Analysis of Urban Issues and Their SolutionDivyansha JainNo ratings yet
- YT Urban Design Case StudiesDocument59 pagesYT Urban Design Case StudiesSonsyNo ratings yet
- DDDDDDocument99 pagesDDDDDOtterino ZiosNo ratings yet
- 05 Final Shahjahanabad November 2017 156pp - LDocument160 pages05 Final Shahjahanabad November 2017 156pp - LRimjhim SwamiNo ratings yet
- Dissertation PPT PreliminaryDocument35 pagesDissertation PPT PreliminaryAnkush BhartiNo ratings yet
- FINAL REPORT ON WALKABILITY Edit Final Nov 1Document37 pagesFINAL REPORT ON WALKABILITY Edit Final Nov 1chandrakant dhawaleNo ratings yet
- Ozone Urbana - Investment Opportunity PDFDocument25 pagesOzone Urbana - Investment Opportunity PDFramanan_nNo ratings yet
- Occupancy UrbanismDocument11 pagesOccupancy UrbanismTapanshu KulNo ratings yet
- Urban Amenity PDFDocument1 pageUrban Amenity PDFParnika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Coimbatore Regional Plan Vision for Sustainable GrowthDocument30 pagesCoimbatore Regional Plan Vision for Sustainable GrowthvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Urban Design Lec01 090912Document26 pagesUrban Design Lec01 090912whatever530No ratings yet
- Need For The Regional PlanDocument2 pagesNeed For The Regional Planmanjusha manchalaNo ratings yet
- Redevelopment of Kotwali BazarDocument8 pagesRedevelopment of Kotwali BazarmanishNo ratings yet
- Paolo SoleriDocument13 pagesPaolo SoleriNandha Kumar GurusamyNo ratings yet
- Urban Artisans NeighborhoodDocument22 pagesUrban Artisans NeighborhoodIshuBabbarNo ratings yet
- Human Settlements and Town PlanningDocument18 pagesHuman Settlements and Town Planningsketch upNo ratings yet
- Redevelopment of Core AreasDocument12 pagesRedevelopment of Core Areassanghviriddhi100% (2)
- Integrated Township Final 26 Oct 2015.top 5 PagesDocument14 pagesIntegrated Township Final 26 Oct 2015.top 5 PagesLexus Mini Smart CitiesNo ratings yet
- Technique of Solid Waste Management in DharaviDocument13 pagesTechnique of Solid Waste Management in DharaviAli WarsiNo ratings yet
- Hriday Reflections - 02Document170 pagesHriday Reflections - 02Ar Afreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- GATE Architecture & PlanningDocument2 pagesGATE Architecture & PlanningAkanksha VermaNo ratings yet
- Urban IssuesDocument147 pagesUrban IssuesAvantika100% (1)
- Open Spaces of ChandigarhDocument26 pagesOpen Spaces of ChandigarhAfaafalaviNo ratings yet
- Nagpur CDPDocument120 pagesNagpur CDPsridiptaaaaNo ratings yet
- Eco Tourism JharkhaliDocument6 pagesEco Tourism JharkhaliAmit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Master Plan ToolkitDocument42 pagesMaster Plan ToolkitAr Aayush GoelNo ratings yet
- LeeDocument26 pagesLeeSobiyaNo ratings yet
- São Paulo CASE STUDYDocument19 pagesSão Paulo CASE STUDYOussama KhallilNo ratings yet
- Final Dissertation - Urban Open Spaces PDFDocument63 pagesFinal Dissertation - Urban Open Spaces PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Urban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDocument7 pagesUrban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDavid DanielsNo ratings yet
- UD-4 Intro & Assignment NotesDocument55 pagesUD-4 Intro & Assignment NotesnehaNo ratings yet
- Improving Interchanges: Toward Better Multimodal Railway Hubs in the People's Republic of ChinaFrom EverandImproving Interchanges: Toward Better Multimodal Railway Hubs in the People's Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Singapore’s Business Park Real Estate: - Viability, Design & Planning of the Knowledge-Based Urban Development (Kbud)From EverandSingapore’s Business Park Real Estate: - Viability, Design & Planning of the Knowledge-Based Urban Development (Kbud)No ratings yet
- MORE WATER LESS LAND NEW ARCHITECTURE: SEA LEVEL RISE AND THE FUTURE OF COASTAL URBANISMFrom EverandMORE WATER LESS LAND NEW ARCHITECTURE: SEA LEVEL RISE AND THE FUTURE OF COASTAL URBANISMNo ratings yet
- Determination of Expansion Factors To Estimate Average Annual Daily Traffic For Arterials in AmmanDocument14 pagesDetermination of Expansion Factors To Estimate Average Annual Daily Traffic For Arterials in AmmanShivangi KumarNo ratings yet
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENT EvsDocument9 pagesACKNOWLEDGEMENT EvsShivam ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument19 pagesCompetitive AdvantageosaidNo ratings yet
- Traffic Analysis TechniquesDocument23 pagesTraffic Analysis TechniquesMary Claire Barcenas100% (1)
- Colflex ADocument2 pagesColflex AAQwa EutasserNo ratings yet
- LRE077ENG - Curriculum Training Suspension Systems - Air Suspension SystemsDocument207 pagesLRE077ENG - Curriculum Training Suspension Systems - Air Suspension SystemsHugo DelagarzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - EarthingDocument26 pagesUnit 6 - Earthinggautam100% (1)
- Training Manual DynaSpike Model SLDocument17 pagesTraining Manual DynaSpike Model SLcharles luisNo ratings yet
- Balancing The Capacity of Hauling UnitsDocument18 pagesBalancing The Capacity of Hauling UnitsajayNo ratings yet
- Narrative Essay National Geographic PDFDocument26 pagesNarrative Essay National Geographic PDFkimberleysalgado100% (1)
- Kalokal Barangay Highway HillsDocument35 pagesKalokal Barangay Highway HillsDixie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Charminar Pedestrianisation Project SummaryDocument2 pagesCharminar Pedestrianisation Project SummaryRENUKA UNo ratings yet
- Owner's-Manual-CT 100 - 110-BS-VIDocument48 pagesOwner's-Manual-CT 100 - 110-BS-VIrahulNo ratings yet
- Annex 14 TerjemahDocument408 pagesAnnex 14 Terjemahsolihin100% (5)
- 3D Model For Highway Alignment: Ananya Augustine, Sahimol EldhoseDocument5 pages3D Model For Highway Alignment: Ananya Augustine, Sahimol EldhoseSesay AlieuNo ratings yet
- Important Points From IRC Roads and Bridge Codes PDFDocument23 pagesImportant Points From IRC Roads and Bridge Codes PDFrajasekaran123No ratings yet
- Sight Distance Requirements for Safe TransportationDocument48 pagesSight Distance Requirements for Safe TransportationMian Rehan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pump CalibrationDocument13 pagesHydrostatic Pump CalibrationHenry Huayhua100% (1)
- Elecon Scraper ReclaimerDocument8 pagesElecon Scraper ReclaimerADITYA_PATHAK100% (1)
- ECT Power SwitchDocument7 pagesECT Power SwitchKyaw Wai Phyoe AungNo ratings yet
- Sika at Work: San Francisco - Oakland Bay BridgeDocument4 pagesSika at Work: San Francisco - Oakland Bay BridgeLynx101No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument65 pagesUntitledRapheal AmehNo ratings yet
- BRT Project DetailsDocument1 pageBRT Project Detailsabhi0912No ratings yet
- The Copperbelt University School of Engineering Civil and Construction DepartmentDocument12 pagesThe Copperbelt University School of Engineering Civil and Construction DepartmentchileNo ratings yet
- FORM F7 Drivers LicenceDocument2 pagesFORM F7 Drivers Licencedainsworth ChristianNo ratings yet
- JKR TNB SpecDocument26 pagesJKR TNB SpecShafiq Mustapa100% (1)
- ERACTS Complaints ListDocument253 pagesERACTS Complaints ListNambirajanNo ratings yet
- TM 9-767 40-Ton Tank Transporter Truck-Trailer M25 1944Document533 pagesTM 9-767 40-Ton Tank Transporter Truck-Trailer M25 1944John hostnNo ratings yet
- 8x8 Avenger Parts Manual 8X8AVG-2012 2012-01-03 From Serial No 32501Document24 pages8x8 Avenger Parts Manual 8X8AVG-2012 2012-01-03 From Serial No 32501Adrian GómezNo ratings yet
- BNSF Demolition GuidelineDocument14 pagesBNSF Demolition GuidelineReza HidayatNo ratings yet