Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause Analysis
Uploaded by
Pedro ViegasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause Analysis
Uploaded by
Pedro ViegasCopyright:
Available Formats
AMCA 201-02 (R2007)
TYPE
BACKWARDINCLINED
BACKWARDCURVED
HOUSING DESIGN
Scroll-type design for efficient conversion of velocity
pressure to static pressure.
Maximum efficiency requires close clearance and
alignment between wheel and inlet
Efficiency only slightly less than airfoil fan.
Ten to 16 single-thickness blades curved or inclined
away from direction of rotation
Efficient for same reasons as airfoil fan.
Uses same housing configuration as airfoil design.
Higher pressure characteristics than airfoil,
backward-curved, and backward-inclined fans.
Curve may have a break to left of peak pressure
R
and fan should not be operated in this area.
Power rises continually to free delivery.
RADIAL
CENTRIFUGAL FANS
AIRFOIL
IMPELLER DESIGN
Highest efficiency of all centrifugal fan designs.
Ten to 16 blades of airfoil contour curved away from
direction of rotation. Deep blades allow for efficient
expansion within blade passages
Air leaves impeller at velocity less than tip speed.
For given duty, has highest speed of centrifugal
fan designs
Scroll. Usually narrowest of all centrifugal designs.
Because wheel design is less efficient, housing
dimensions are not as critical as for airfoil and
backward-inclined fans.
CENTRIFUGAL
CENTRIFUGAL
AXIAL
POWER ROOF VENTILATORS
SPECIAL DESIGNS
TUBULAR
VANEAXIAL
TUBEAXIAL
AXIAL FANS
PROPELLER
FORWARDCURVED
Flatter pressure curve and lower efficiency than the
airfoil, backward-curved, and backward-inclined.
Do not rate fan in the pressure curve dip to the left
of peak pressure.
Power rises continually toward free delivery. Motor
selection must take this into account.
Scroll similar to and often identical to other centrifugal
fan designs.
Fit between wheel and inlet not as critical as for airfoil
and backward-inclined fans.
Low efficiency.
Limited to low-pressure applications.
Usually low cost impellers have two or more blades of
single thickness attached to relatively small hub.
Primary energy transfer by velocity pressure.
Simple circular ring, orifice plate, or venturi.
Optimum design is close to blade tips and forms
smooth airfoil into wheel.
Somewhat more efficient and capable of developing
more useful static pressure than propeller fan.
Usually has 4 to 8 blades with airfoil or singlethickness cross section.
Hub usually less than transfer by velocity pressure.
Cylindrical tube with close clearance to blade tips.
Good blade design gives medium- to high-pressure
capability at good efficiency.
Most efficient of these fans have airfoil blades.
Blades may have fixed, adjustable, or controllable
pitch.
Hub is usually greater than half fan tip diameter.
Cylindrical tube with close clearance to blade tips.
Guide vanes upstream or downstream from impeller
increase pressure capability and efficiency.
Performance similar to backward-curved fan except
capacity and pressure are lower.
Lower efficiency than backward-curved fan.
Performance curve may have a dip to the left of
peak pressure.
Cylindrical tube similar to vaneaxial fan, except
clearance to wheel is not as close.
Air discharges radially from wheel and turns 90 to
flow through guide vanes.
Low-pressure exhaust systems such as general
factory, kitchen, warehouse, and some commercial
installations.
Provides positive exhaust ventilation, which is an
advantage over gravity-type exhaust units.
Centrifugal units are slightly quieter than
axial units.
Normal housing not used, since air discharges from
impeller in full circle.
Usually does not include configuration to recover
velocity pressure component.
Low-pressure exhaust systems such as general
factory, kitchen, warehouse, and some commercial
installations.
Provides positive exhaust ventilation, which is an
advantage over gravity-type exhaust units.
Essentially a propeller fan mounted in a supporting
structure
Hood protects fan from weather and acts as safety
guard.
Air discharges from annular space at bottom of
weather hood.
Figure 4.2 - Types of Fans
Adapted with permission from 1996 ASHRAE Systems and Equipment Handbook (SI)
11
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Alignment CourseDocument167 pagesAlignment Coursedennis_packiaraj3063100% (20)
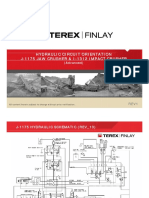
- HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT ORIENTATION J-1175 & I-1312 Advanced - REV1 - PPT (Read-Only)Document44 pagesHYDRAULIC CIRCUIT ORIENTATION J-1175 & I-1312 Advanced - REV1 - PPT (Read-Only)Stelian Crisan100% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 6 - Handling, Loading & Unloading of Loads Fall Hazards Work at Height - DraftDocument6 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 6 - Handling, Loading & Unloading of Loads Fall Hazards Work at Height - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- An Insider's Guide To CMMS Functions, Selection and ImplementationDocument26 pagesAn Insider's Guide To CMMS Functions, Selection and ImplementationPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- CMMS Failure CodesDocument9 pagesCMMS Failure CodesPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Price 2022-D - 1669879424Document19 pagesPrice 2022-D - 1669879424Moses SilvaNo ratings yet
- Defining Maintenance Routes - Oracle Enterprise Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesDefining Maintenance Routes - Oracle Enterprise Asset ManagementPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- The Golden Rules of SafetyDocument11 pagesThe Golden Rules of SafetyPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- GIW Slurry ManualDocument14 pagesGIW Slurry ManualMehrdad AminkazemiNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 4 - Machinery & Rotary Part Protection - DraftDocument7 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 4 - Machinery & Rotary Part Protection - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guide: Asset Family Centrifugal Process PumpsDocument1 pageTroubleshooting Guide: Asset Family Centrifugal Process PumpsPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 5 - LOTO & Work Permit - DraftDocument5 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 5 - LOTO & Work Permit - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Accumulators Selection and DesignDocument38 pagesAccumulators Selection and DesignVenkatesh Gangadhar0% (1)
- 21 Air Cond - New OriginalDocument318 pages21 Air Cond - New Originalcheemeng79No ratings yet
- 7000 Process Safety System T2Document150 pages7000 Process Safety System T2Gee Fung100% (2)
- NTPC 500 Power Plant Operation Pipe LineDocument84 pagesNTPC 500 Power Plant Operation Pipe LineJoselin Leo100% (1)
- (Name / Logo) : Internal Strengths Internal WeaknesssesDocument7 pages(Name / Logo) : Internal Strengths Internal WeaknesssesPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Expert User GuideDocument182 pagesPipe Flow Expert User Guidelilbie100% (1)
- Enova - Pedro Insigths 2023Document5 pagesEnova - Pedro Insigths 2023Pedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Dot Point Bar PowerPoint DiagramDocument1 pageDot Point Bar PowerPoint DiagramPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- IR Checks of Conveyor Idler RollersDocument5 pagesIR Checks of Conveyor Idler RollersPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 7 - Vehicles, Mobile Equipment & Workplace - DraftDocument11 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 7 - Vehicles, Mobile Equipment & Workplace - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Spiral Freezer Gearbox FailuresDocument7 pagesSpiral Freezer Gearbox FailuresPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Reasons To Do Laser AlignmentDocument8 pages7 Reasons To Do Laser AlignmentPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 2 - Body Protection - DraftDocument6 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 2 - Body Protection - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 1 - Safety Priority - DraftDocument4 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 1 - Safety Priority - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - List of RulesDocument1 page7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - List of RulesPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 3 - Safety Walks, Communication & Report - DraftDocument3 pages7 Global Golden Rules of Safety - Rule 3 - Safety Walks, Communication & Report - DraftPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 70 30 PhenomenonDocument2 pages70 30 PhenomenonPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Irregular English VerbsDocument1 pageIrregular English VerbsPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- 10 Ways To Reduce Reactive Maintenance: Ten Actions Worth ConsideringDocument4 pages10 Ways To Reduce Reactive Maintenance: Ten Actions Worth ConsideringPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Indicator MTBFDocument2 pagesIndicator MTBFPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Best Players FM2008Document2 pagesBest Players FM2008Pedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Backlog ManagementDocument3 pagesBacklog ManagementPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Signalling / Alarm and Interlock System Inspection RecordDocument1 pageSignalling / Alarm and Interlock System Inspection RecordPedro ViegasNo ratings yet
- Injector Specification: Nozzle Holder Assembly No. 34107Document2 pagesInjector Specification: Nozzle Holder Assembly No. 34107DIESEL MOTORSNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ReviewDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics Reviewvon_science08100% (1)
- 02-Problems On RayleighsDocument69 pages02-Problems On RayleighsRamu NagulaganiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics MCQ Questions & Answers - Chemical Engineering Page-10 Section-2Document1 pageFluid Mechanics MCQ Questions & Answers - Chemical Engineering Page-10 Section-2macky 2No ratings yet
- ch-3 Part-IDocument29 pagesch-3 Part-ILamiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel National Certificate/Diploma Principles and Applications of Fluid Mechanics Unit 13 NQF Level 3 Outcome 4 - Dynamic Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 - Model TestingDocument12 pagesEdexcel National Certificate/Diploma Principles and Applications of Fluid Mechanics Unit 13 NQF Level 3 Outcome 4 - Dynamic Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 - Model TestingrianrureNo ratings yet
- FiltersDocument3 pagesFiltersaliveNo ratings yet
- Nash Vectra XL BrochureDocument4 pagesNash Vectra XL BrochureTorus EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 Giacomini CatalogueDocument8 pagesChapter6 Giacomini CataloguecristyryeNo ratings yet
- Camless Engine: Working of Push Rod EngineDocument14 pagesCamless Engine: Working of Push Rod EngineAkshay Kumar pn AkshayNo ratings yet
- VDF6355 2 2 2 2 PDFDocument2 pagesVDF6355 2 2 2 2 PDFOnur Iseri0% (1)
- Types of PumpDocument7 pagesTypes of PumpRaya ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Cubal Cargo Manual Draft 2 November 2011Document384 pagesCubal Cargo Manual Draft 2 November 2011toma cristian100% (2)
- At TurbineDocument55 pagesAt TurbineDharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Distribution Manifolds FINALDocument8 pagesDistribution Manifolds FINALSrta IncognitaNo ratings yet
- NUTRON Forged Steel Floating Ball Valve Model T3 & B3 - XDocument32 pagesNUTRON Forged Steel Floating Ball Valve Model T3 & B3 - XElinton SarmientoNo ratings yet
- General Catalog: A New Vision For Quality PumpsDocument20 pagesGeneral Catalog: A New Vision For Quality PumpsDanialNo ratings yet
- S20-1 2001 Service Manuals DirectoryDocument2 pagesS20-1 2001 Service Manuals DirectorySean JonesNo ratings yet
- NEW Atlanta PPR - TRI FOLD - 2021Document2 pagesNEW Atlanta PPR - TRI FOLD - 2021Aldrex ValerosNo ratings yet
- دوسة ديناميكا الغازات د.نجدت نشأتDocument73 pagesدوسة ديناميكا الغازات د.نجدت نشأتMSeaiasNo ratings yet
- BOMBA WILDEN P1500 PlasticDocument24 pagesBOMBA WILDEN P1500 PlasticHiroaki HamadaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Ideal Rocket Theory Part 1Document13 pages2.1.3 Ideal Rocket Theory Part 1paulo gontranNo ratings yet