Professional Documents
Culture Documents
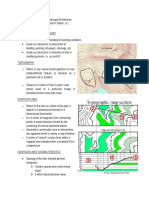
Surveying Topo
Uploaded by
Jelena Kilić-GrgićCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surveying Topo
Uploaded by
Jelena Kilić-GrgićCopyright:
Available Formats
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
1/6
Topographic Survey
Introduction
Introduction
] Topography - defined as the
shape or configuration or
relief or threedimensional
quality of a surface
] U.S. Geological Survey
(USGS) has developed
maps for a large part of
the US
] Napoleon Bonaparte
received his first promotion
because of ability to make
and use maps
] Topography maps are very
useful for engineers when
planning and locating a
structure
Topographic Survey
Typical USGS Topographic Map
Topographic Survey
Contours
] The most common method of representing the
topography of an area is to use contour lines
] A contour line is an
imaginary level line
that connects points
of equal elevation
USGS Topographic Map of Mt. Shasta, CA - 1883
Topographic Survey
Contours
There are several rules to note when viewing topographic maps:
] The rule of Vs: sharp-pointed V usually are in stream valleys,
with the drainage channel passing through the point of the V,
with the V pointing upstream.
Topographic Survey
Contours
] Contours that point
up hill can indicate a
valley or stream
] The rule of Os: closed loops are normally uphill on the inside and
downhill on the outside, and the innermost loop is the highest
area.
] Spacing of contours: close contours indicate a steep slope;
distant contours a shallow slope. Two or more contour lines
merging indicates a cliff.
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
Contours
2/6
Topographic Survey
Contours
] Imagine a hill that
has its top sliced off
with a really big knife
] When is the steepest
part of this terrain?
] The shallowest part?
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
] The selection of the contour is important
] The contour interval should be small enough to give
the desired topographic detail while remaining
economic
] Usually every fifth contour line is shown in a heavy,
wider line, this is called a index line
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
3/6
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
Topographic Survey
Contours
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
Contours
4/6
Topographic Survey
Characteristics of Contours
] Closely spaced contours indicate steep slopes
] Widely spaced contours indicate moderate slopes
] Contours should be labeled to the elevation value
] Contours are not shown going through buildings
] Contour line do not cross
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey
Characteristics of Contours
Construction of Contours
] Depression and hill look the same; note the contour
value to distinguish the terrain
] The first step in developing a contour map is measuring
the elevations of a group of points
] Important points can be further defined by including a
spot elevation
] It will be easier for us to establish a rectangular grid
of points (marked with flags) and measure the elevation
] Contour lines tend to parallel each other on uniform
slopes
] The location of the flag points can be established by
taping and checked by pacing or the odometer
Topographic Survey
Construction of Contours
] Once your contour grid is established, measure the
elevation of each grid point
C
Topographic Survey
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey
112
106
102
98
5/6
Construction of Contours
101
108
109
111
] The basic method for estimating contour is applied to
each grid cell individually
106
111
119
108
] Use linear interpolation to find the location of the
desired contour interval
112
112
106
] Let consider the cell in the upper lefthand corner remember the contour interval is 5 ft
A
108
] We want a contour map on 5 ft intervals
] The grid is rectangular, the dimensions of the sides are
80 ft (north) and 100 ft (east)
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey
] Lets look at the top edge of the grid cell
Construction of Contours
100
98
100
102
101
108
] First see if a contour
interval exist between
nodes of the grid cell; if
105 so, estimate where along
the side the contour
interval would be located
100
102
101
105
x =
4(100)
= 57ft
7
x =
108
2(100)
= 50ft
4
98
100
100
108 101
a = slope =
100
100 =
102
102 98
100
4
x + 98
100
F(x) = ax + b
a = slope =
101
x =
105
2(80)
= 53ft
3
101
100
98
x
100
b = intercept = 101
7
x + 101
100
] Lets look at the left edge of the grid cell
F(x) = ax + b
105 =
F(x) = ax + b
b = intercept = 98
108
108
105
101
102
100
98
Topographic Survey
] Lets look at the bottom edge of the grid cell
98
102
a = slope =
101
Topographic Survey
105
100
] Apply simple linear
interpolation to each side
to locate the contour
interval
105
100
98
108
101 98
80
b = intercept = 98
100 =
3
x + 98
80
CIVL 1101
Introduction to Topographic Surveying
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey
] Lets look at the right edge of the grid cell
100
98
102
105
105
100
105
101
x =
108
] Locate the contour intervals locations on the grid cell
108
105
102
100
98
F(x) = ax + b
108 102
a = slope =
80
105 =
102
b = intercept = 102
3(80)
= 40ft
6
6/6
105
100
101
105
108
] Next, simply connect
points of equal contour
intervals
] One grid cell down,
eight to go . . .
6
x + 102
80
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey
] Repeating the linear interpolation for each of the
remaining grid cell gives:
102
98
112
106
D
101
108
109
111
106
111
119
108
112
112
A
108
End of Topographic Surveying
106
You might also like
- Surveying 5 Topo Modeling PDFDocument8 pagesSurveying 5 Topo Modeling PDFanon_194491857No ratings yet
- Introduction LevellingDocument75 pagesIntroduction Levellingthuaiyaalhinai100% (1)
- 2021 Plane Survey 1Document13 pages2021 Plane Survey 1Marshall NhodzaNo ratings yet
- Plane Survey Notes 2021Document92 pagesPlane Survey Notes 2021Mike mikeNo ratings yet
- AR 303 6 Topography Site GradingDocument4 pagesAR 303 6 Topography Site GradingJoyce Rachelle VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Importance and uses of surveying for civil engineersDocument34 pagesImportance and uses of surveying for civil engineersSagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Weebly Skills RevisionDocument62 pagesWeebly Skills Revisionapi-253723056No ratings yet
- Topo MapDocument47 pagesTopo MapAbdul Moeed Kalson100% (2)
- Use of Surveying in Watershed ManagementDocument9 pagesUse of Surveying in Watershed ManagementPramod Garg100% (1)
- Engineering SurveyingDocument12 pagesEngineering SurveyingzelalemNo ratings yet
- Introduction and ScaleDocument18 pagesIntroduction and Scaleayushsuhagiya380No ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument34 pagesSurveyingSuraj DhondNo ratings yet
- Soil and Water Conservation Engg.: Surveying, Chain SurveyingDocument13 pagesSoil and Water Conservation Engg.: Surveying, Chain SurveyingMUKESH KUMAR ce100% (1)
- Contouring Map TechniquesDocument94 pagesContouring Map TechniquesSuraj DhondNo ratings yet
- Topographic Surveying and MappingDocument8 pagesTopographic Surveying and Mappingamanuel66958662No ratings yet
- Introduction SurveyingDocument17 pagesIntroduction SurveyingMuralee KrishnanNo ratings yet
- SPD - Unit 3Document89 pagesSPD - Unit 3Shif renNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CE 214 Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument7 pagesMODULE 1 CE 214 Fundamentals of SurveyingJake Ryan Belen BuanNo ratings yet
- LEVELS AND LEVELLING: DETERMINING ELEVATION DIFFERENCESDocument13 pagesLEVELS AND LEVELLING: DETERMINING ELEVATION DIFFERENCESNusrat Bintee KhaledNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Surveying and LevelingDocument8 pagesUnit - 1 Surveying and LevelingPavan G ReddyNo ratings yet
- Surveying and Leveling-1Document45 pagesSurveying and Leveling-1anas tariqNo ratings yet
- GE186-Lecture 3-CONTOURINGDocument70 pagesGE186-Lecture 3-CONTOURINGEdward Gabada JnrNo ratings yet
- Surveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1Document37 pagesSurveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1zain IshaqNo ratings yet
- Surveying: Unit-1: Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument11 pagesSurveying: Unit-1: Fundamentals of SurveyingShriya MadooriNo ratings yet
- 10 Civl235 Slope StakeDocument9 pages10 Civl235 Slope StakeOsamaa Eisa100% (1)
- Surveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1Document36 pagesSurveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1Mistr MaskNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Topographic Surveying: 2.1 IntroductiontopographyDocument13 pagesChapter Two Topographic Surveying: 2.1 IntroductiontopographyDawudamanAbduljelilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SurveyingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To SurveyingAlone TimeNo ratings yet
- Surveying Definition of SurveyingDocument6 pagesSurveying Definition of SurveyingPraveenkumar ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Mapwork, Photographic Interpretation, FieldworkDocument135 pagesMapwork, Photographic Interpretation, FieldworkTusiime86% (7)
- Topographic Map Contour Characteristics & Slope AnalysisDocument18 pagesTopographic Map Contour Characteristics & Slope AnalysisNiharika Sharma67% (6)
- UNIT-II SASTRA University Basic Civil EngineeringDocument26 pagesUNIT-II SASTRA University Basic Civil EngineeringstarNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 1Document23 pagesNotes Unit 1div300482No ratings yet
- Triangulation and Trilateration TechniquesDocument38 pagesTriangulation and Trilateration TechniquesMilind Gupta71% (7)
- Surviyung Chapter One Topo, MappingDocument62 pagesSurviyung Chapter One Topo, MappingNura GuyoNo ratings yet
- Surveying - IDocument36 pagesSurveying - IElsa KhanNo ratings yet
- Definition of SurveyingDocument7 pagesDefinition of SurveyingArun LalNo ratings yet
- Surveying & LevellingDocument113 pagesSurveying & Levellinggiribarch100% (3)
- V Rule MEthodeDocument27 pagesV Rule MEthodeR Okfariano WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- 319 - CE8351 Surveying - NotesDocument167 pages319 - CE8351 Surveying - NotesMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Route Surveying & ContouringDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Route Surveying & ContouringAllan DeGuzman Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Engineering SurveyDocument116 pagesModule 1-Engineering SurveySurekha Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- CE2204 Surveying I Lecture NotesDocument49 pagesCE2204 Surveying I Lecture NotesjananiNo ratings yet
- Topography and Topographic MapsDocument14 pagesTopography and Topographic MapsAbdul Jewad HayredinNo ratings yet
- Topo Survey GuideDocument30 pagesTopo Survey GuideHunter Bravo100% (1)
- 1 Surveying ConceptsDocument115 pages1 Surveying ConceptsMelliah Joy Garciano100% (1)
- Group 4 Soil MechanicsDocument43 pagesGroup 4 Soil MechanicsSid WorldNo ratings yet
- Mapping Surveys & GIS FundamentalsDocument44 pagesMapping Surveys & GIS FundamentalsdeemaNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture 2016 Sep 19Document30 pages02 Lecture 2016 Sep 19Asfahan PENo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document12 pagesLecture 15Syed Azmat Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Surveying FundamentalsDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Surveying FundamentalsAspirant MNo ratings yet
- Contouring: Fig. 1 Two Dimensional MapDocument16 pagesContouring: Fig. 1 Two Dimensional MapVinit ChavanNo ratings yet
- Triangulation and Trilateration: 1.1 GeneralDocument10 pagesTriangulation and Trilateration: 1.1 GeneralWahyu Teo ParmadiNo ratings yet
- Trvaerse CairoU Civil Publish TotalDocument43 pagesTrvaerse CairoU Civil Publish TotalMohamedNo ratings yet
- EGL ManualAzDOCUMENTS - In-26-54Document25 pagesEGL ManualAzDOCUMENTS - In-26-54reshmaNo ratings yet
- PME Mine Surveying Lec 1and 2Document48 pagesPME Mine Surveying Lec 1and 2Shakil Rahman AfidNo ratings yet
- Curve Ranging ProcedureDocument28 pagesCurve Ranging ProcedureF2009 LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Practical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemFrom EverandPractical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemNo ratings yet
- Hengl 2011Document163 pagesHengl 2011Jelena Kilić-GrgićNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Reallocation Criteria in Land Consolidation Studies Using The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)Document8 pagesEvaluation of Reallocation Criteria in Land Consolidation Studies Using The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)Jelena Kilić-GrgićNo ratings yet
- ZFV 2013 2 Demetriou PDFDocument13 pagesZFV 2013 2 Demetriou PDFJelena Kilić-GrgićNo ratings yet
- Up & GisDocument12 pagesUp & GisJamie FosterNo ratings yet
- Urban Surveyor BrochureDocument32 pagesUrban Surveyor BrochureJelena Kilić-GrgićNo ratings yet
- Army Aviation Digest - Apr 1985Document48 pagesArmy Aviation Digest - Apr 1985Aviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument24 pagesData Warehousingkishraj33No ratings yet
- User Guide: Rack Mount Power SupplyDocument7 pagesUser Guide: Rack Mount Power SupplyWilliam WankerNo ratings yet
- NT 7G Med 11 2021 GB JED1Xy9Document12 pagesNT 7G Med 11 2021 GB JED1Xy9Ricardo LangerNo ratings yet
- DB - NoiseDocument81 pagesDB - Noisehappy girl100% (1)
- Configure SNMPDocument14 pagesConfigure SNMPANGEL GuzmanNo ratings yet
- A.V AidsDocument19 pagesA.V AidsRohini RaiNo ratings yet
- ED6001 Project ReportDocument9 pagesED6001 Project Reportsaloni jainNo ratings yet
- EapDocument4 pagesEapDayhen Afable Bianes0% (1)
- Real-Time Monitoring and Performance Harvesting For Grid-Connected PV System - A Case in SharjahDocument5 pagesReal-Time Monitoring and Performance Harvesting For Grid-Connected PV System - A Case in SharjahNeethu Elizabeth MichaelNo ratings yet
- Michael Nasol (April)Document10 pagesMichael Nasol (April)Anonymous CuIeVjHNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide: Electronic PotentiometerDocument7 pagesReference Guide: Electronic PotentiometerBanyar AungNo ratings yet
- University Question Bank PDFDocument16 pagesUniversity Question Bank PDFlathavenkyNo ratings yet
- VR Ajp 18 To 20Document8 pagesVR Ajp 18 To 201213 Vaibhav KothareNo ratings yet
- Cabling Guide V1.0Document6 pagesCabling Guide V1.0nguyen vuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document32 pagesUnit 5Shashank RaghunathanNo ratings yet
- XL2576 DatasheetDocument14 pagesXL2576 DatasheetMo Hit MksNo ratings yet
- Making a Python list of namesDocument14 pagesMaking a Python list of namesSoniaNo ratings yet
- Disini Vs Secretry DigestDocument2 pagesDisini Vs Secretry DigestChristian John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Music) Grade 10Document9 pagesModule 2 (Music) Grade 10mary jane100% (1)
- ASP.NET Core MVC Web App with CRUD for Departments and SellersDocument11 pagesASP.NET Core MVC Web App with CRUD for Departments and SellersElder MoraisNo ratings yet
- Resonant Inverter OrCADDocument13 pagesResonant Inverter OrCADCh ChristianNo ratings yet
- TASM 5 Intel 8086 Turbo AssemblerDocument3 pagesTASM 5 Intel 8086 Turbo AssemblerKeating Lopez100% (1)
- The Different Types of Application Software Include The FollowingDocument18 pagesThe Different Types of Application Software Include The Followingtimothy pahaladNo ratings yet
- Solu of Assignment 9Document5 pagesSolu of Assignment 9dontstopmeNo ratings yet
- Apollo Training Guidance and Control 02-10-67Document176 pagesApollo Training Guidance and Control 02-10-67sn_crowley9661No ratings yet
- DVD Player Service Manual Ver. 1Document176 pagesDVD Player Service Manual Ver. 1peterb99No ratings yet
- 01 - Failure Analysis of A Special Vehicle Engine Connecting RodDocument12 pages01 - Failure Analysis of A Special Vehicle Engine Connecting RodBima SorayaNo ratings yet
- EE 577A Spring 2022 - VLSI System Design Homework 1: TH TH THDocument4 pagesEE 577A Spring 2022 - VLSI System Design Homework 1: TH TH THvedeshNo ratings yet
- Binsort Versatile BrochureDocument1 pageBinsort Versatile BrochureFercho GutierrezNo ratings yet