Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxation Principles Explained
Uploaded by
Clarisse Ann MirandaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxation Principles Explained
Uploaded by
Clarisse Ann MirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxation
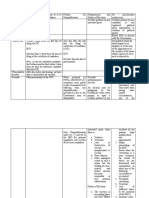
1.
2.
3.
4.
Local taxation barangay, municipal, city
National taxation
How do we impose tax?
General principles in local and national tax are
basically the same
5. What is taxation exercised by legislature for
purpose of raising revenue
6. From the definition, power of the state together
with power of einent domain and police power
these three are powers of legislature.
7. All tariff bills must originate from lower house
8. What does the legislature exercise? Ano ba ang
kanyang mga areas? SUBJECT MATTERS TO BE
TAXED, PURPOSE OF TAX, always presumed that
tax for public purpose sya. , some tariff bills
provides speicfiacally for purpose, without express
prov that it is for public purpose, public pa din sya
ang presumption
9. Magkano ba ang amount and rate of tax?
10.
Manner and ways of collection
11.
Remedies of tax payer in case of non
payment
12.
From definition, it is exercised by the
legislature
13.
Provides for the following : subject matter,
purpose, means and ends of collection
14.
When leg exercised manner of tax, g back to
two aspects of taxation act of levy, act of
collection
15.
If it is legislative in character, can legistlaute
deligate?
16.
yes. First is flexible tariff.
17.
Delegation in admin agencies bureau of
internal rev, dept of agri on tariff duties (only the
mechanical acts of collection )
18.
Delegation in favor of local government
units used to be treated as an exception to
delegability to tax power. Inherent power na lang
sya hindi na delegated.
19.
Exercised by legislature legislative in
character bills and laws
20.
What can legislature provides? Subject
matter, manner way, amount.
21.
Isnt is legislative in character, can it be
delegated? NO. exception : yung tatlo, president
bla bla.
22.
Exercised for purpose of raising revenues :
lahat ng taxes collected are forming part of public
funds. They forms part of national treasury.
23.
Every year the congress should approve the
general appropriation act24.
For purposes of raising revenue , walang
public funds, government walang funds to support
itself.
25.
1. Benefit theory ;necessity theory
26.
these are the justification why the
government should collect tax
27.
for promotion of general welfare. Di dapat
direct proportion lang.
28.
Purpose of taxation : reduction of
inequality. Bla bla
29.
What are the importance tariff- in order to
protect locally products
30.
For regulation din ito. The pp is exercised in
aid of taxing power, and sometimes other way
around.
31.
Non- rev purpose naachieve, when tax is
collected, when tax is imposed. Nag increase,
meron pa din priveleges and purposes.
32.
Progressive tayo. Higher income, higher tax
33.
Apportion the burden
34.
Tax payable in money. Payable in legal
tender. Generally payable in money payable in
cash or legally tender. Exception : if law provides :
tax credit certificate
35.
At the time of imposition and at the time of
disposition taxes dapat for public purpose in
exercise of taxing power
36.
Imposed on personos, prop, excises, priv,
rights within territorial taxing jurisidcition.
37.
Fiscal adequacy fiscal pera , adequacy
sakto.
38.
Fiscal adequacy- tax system dapat enough
to support itself.
39.
How to distinguish and compare tax sa
ibang klase ng terminologies.
40.
Tax and licensee
41.
There are instances that an imposition both
regulation and raising of revenue are achieved,
how will we determine? If tax or licensee. Primary
purpose is raise revenue even if incidental to
regulate TAX ; if purpose is to regulate : licensee.
Doesnt change its color dahil lang sa presence ng
other purpose
42.
How to distinguish tax from toll.
43.
Tax and special assessment
44.
Tax payer are not debtors and creditors of
each other
45.
Does not arise from contract and tax kaya di
pwede subject to compensation (indebtedness
and tax)
46.
Inherent limitation :
change
You might also like
- GEE 103 Module 8Document25 pagesGEE 103 Module 8Jay ar PatraNo ratings yet
- Public Procurement Rules 2004Document21 pagesPublic Procurement Rules 2004sajidNo ratings yet
- Market Failure: Externalities, Monopoly, Asymmetric Information, and Public GoodsDocument45 pagesMarket Failure: Externalities, Monopoly, Asymmetric Information, and Public Goodssumit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Speech Outlines and Source Materials: Group 3: SymposiumDocument7 pagesSpeech Outlines and Source Materials: Group 3: Symposiumtacki16No ratings yet
- Special Penal Laws Ticman 2015Document26 pagesSpecial Penal Laws Ticman 2015Siobhan RobinNo ratings yet
- Public SectorDocument3 pagesPublic SectorAdebowaleIsmailGaniyuNo ratings yet
- Ethics 1 Reading #5Document8 pagesEthics 1 Reading #5Angela Rain GolenNo ratings yet
- 3-Public Sector MGMNT ReformDocument9 pages3-Public Sector MGMNT ReformekorahayuNo ratings yet
- Area 7 LibraryDocument4 pagesArea 7 LibraryHelen GabrielNo ratings yet
- TOC PeschkeDocument10 pagesTOC Peschkeorj78No ratings yet
- Project IdentificationDocument7 pagesProject Identificationsimmi33No ratings yet
- Explain and Illustrate The Roles Played by Profit in Allocating Scarce ResoDocument4 pagesExplain and Illustrate The Roles Played by Profit in Allocating Scarce ResoFirdaus RaaiNo ratings yet
- Popular CultureDocument3 pagesPopular CulturekatiemhsNo ratings yet
- FullLaborRelationTSN2017 18 PDFDocument107 pagesFullLaborRelationTSN2017 18 PDFTindusNiobetoNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - MA - Budgetary ControlDocument20 pagesPart 2 - MA - Budgetary ControlatikahNo ratings yet
- Public Administration Unit-72 EvolutionDocument12 pagesPublic Administration Unit-72 EvolutionDeepika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Deregulation, Liberalization and LPG Presentation - Ladio (Final)Document34 pagesDeregulation, Liberalization and LPG Presentation - Ladio (Final)Khemberly Randing LadioNo ratings yet
- 001 Rff-Ugandan School Design GuideDocument48 pages001 Rff-Ugandan School Design GuideTaurai ChiwanzaNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 33-Southeast AsiaDocument3 pagesGeography Chapter 33-Southeast AsiaTheGeekSquadNo ratings yet
- PENADAAN BARANG DAN JASADocument54 pagesPENADAAN BARANG DAN JASASalsa HusnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document32 pagesChapter 4Nokulunga ManyangaNo ratings yet
- From Narrative of ColonialismDocument6 pagesFrom Narrative of ColonialismdrbhoopalNo ratings yet
- Challenges affecting public procurement performance in KenyaDocument11 pagesChallenges affecting public procurement performance in KenyaFelixNo ratings yet
- Niyati Jigyasu: Disaster Management For Buildings-I (AR-530)Document24 pagesNiyati Jigyasu: Disaster Management For Buildings-I (AR-530)Ekta MittalNo ratings yet
- Practices of Poverty Measurement and Poverty Profile of NepalDocument41 pagesPractices of Poverty Measurement and Poverty Profile of NepalAsian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Market FailureDocument8 pagesMarket FailuresassinemichelNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document10 pagesLiterature Review 1FahimAnwar100% (1)
- Applying Protracted Social Conflict Theory to Contemporary ConflictsDocument8 pagesApplying Protracted Social Conflict Theory to Contemporary ConflictsevitamouawadNo ratings yet
- Canons of Taxation ExplainedDocument3 pagesCanons of Taxation ExplainedVanlalruata PautuNo ratings yet
- Public Good: Rival. This Means It Is Not Possible To Exclude Individuals From The Good's ConsumptionDocument9 pagesPublic Good: Rival. This Means It Is Not Possible To Exclude Individuals From The Good's Consumptionsamik489No ratings yet
- Tariff Notes - Atty CabanDocument14 pagesTariff Notes - Atty CabancH3RrY1007No ratings yet
- Review Materials LinkDocument2 pagesReview Materials Linkgladys manaliliNo ratings yet
- Civil Society Organizations in Social Development: Archana Satya Priya Shaiju ChackoDocument19 pagesCivil Society Organizations in Social Development: Archana Satya Priya Shaiju Chackoschacko77No ratings yet
- Administrative History As A Core Dimension of Public AdministrationDocument32 pagesAdministrative History As A Core Dimension of Public AdministrationfamastarNo ratings yet
- Construction Project Planning and Management IntroductionDocument22 pagesConstruction Project Planning and Management IntroductionAztec MayanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial BehaviourDocument16 pagesEntrepreneurial Behaviournonalyn tomboconNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Tax Policy Design and DevelopmentDocument33 pagesIntroduction to Tax Policy Design and DevelopmentDiana Jane PajulasNo ratings yet
- The 3 sides of a spinning coin: Understanding the Social Amelioration ProgramDocument1 pageThe 3 sides of a spinning coin: Understanding the Social Amelioration Programgago kaNo ratings yet
- Public FinanceDocument2 pagesPublic Financemohamed sheikh yuusufNo ratings yet
- Public GoodsDocument85 pagesPublic GoodsMahamed sh abdullahiNo ratings yet
- Market Failure & Role of RegulationDocument38 pagesMarket Failure & Role of Regulationanand agrawalNo ratings yet
- Roman Origins and Modern Benefits of CorporationsDocument46 pagesRoman Origins and Modern Benefits of CorporationslibernardoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Economic DevelopmentDocument17 pagesWeek 5 - Economic DevelopmentAbraham ZeusNo ratings yet
- Public Procurement Reform in Developing Countries - The Uganda Experience PDFDocument19 pagesPublic Procurement Reform in Developing Countries - The Uganda Experience PDFByaruhanga EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Basic Legal Ethics IIDocument99 pagesBasic Legal Ethics IIJohn Patrick IsraelNo ratings yet
- Public PolicyDocument19 pagesPublic PolicyRubi BeegumNo ratings yet
- Tax PolicyDocument392 pagesTax PolicyNguyen Hai HaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policy in PhilippinesDocument6 pagesIndustrial Policy in PhilippinesSharon Rose GalopeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Laws and RegulationsDocument50 pagesEnvironmental Laws and RegulationsPaul Santos NonatNo ratings yet
- Traffic Solutions For Metro Manila A Realistic ApproachDocument10 pagesTraffic Solutions For Metro Manila A Realistic ApproachDoms Dominguez100% (1)
- 1 Government Intervention and PricingDocument74 pages1 Government Intervention and PricingKintan DNo ratings yet
- A Short History of Procurement PDFDocument16 pagesA Short History of Procurement PDFIbrahim PašalićNo ratings yet
- Methodological Guide On Impact of Public PoliciesDocument81 pagesMethodological Guide On Impact of Public PoliciesaghamcNo ratings yet
- Converting Base NumbersDocument2 pagesConverting Base Numbersartmaker43No ratings yet
- Approaches to Defining "DevelopmentDocument30 pagesApproaches to Defining "DevelopmentHealth Planning Unit CHD-MMNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Models of Public PolicymakingDocument3 pagesTheoretical Models of Public Policymakingmaheshkrishna1100% (1)
- National Tax Policy Draft Updated)Document59 pagesNational Tax Policy Draft Updated)Adesina Adedayo100% (3)
- Chapter 1 5 Income Tax MCDocument14 pagesChapter 1 5 Income Tax MCeddie mar jagunapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5 Income Tax MCDocument14 pagesChapter 1 5 Income Tax MCEysyel ZeyNo ratings yet
- Miranda Notes - RemDocument35 pagesMiranda Notes - RemClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Case DoctrinesDocument6 pagesCase DoctrinesClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Remedies and JurisdictionDocument4 pagesRemedies and JurisdictionClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Pagcor Vs BirDocument5 pagesPagcor Vs BirClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Grounds Marriage TableDocument3 pagesGrounds Marriage TableClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFDocument17 pages2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFDocument17 pages2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Miranda Notes - Crim ProDocument50 pagesMiranda Notes - Crim ProClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- DigestsDocument14 pagesDigestsClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFDocument17 pages2004 Sonza - v. - ABS CBN - Broadcasting - Corp.20180413 1159 1giwl7b PDFClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- POLITICAL LAW 1-8Document142 pagesPOLITICAL LAW 1-8schating2No ratings yet
- Rule 13 TableDocument3 pagesRule 13 TableClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- FAQs 2003-2007Document5 pagesFAQs 2003-2007Clarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cases For LIPDocument2 pagesCases For LIPClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cases For LIPDocument2 pagesCases For LIPClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Recit RemDocument3 pagesLecture - Recit RemClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Insurance SummaryDocument16 pagesInsurance SummaryClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Jurado ReviewerDocument3 pagesJurado ReviewerClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Insurance SummaryDocument6 pagesInsurance SummaryClarisse Ann Miranda100% (1)
- Contracts of InsuranceDocument3 pagesContracts of InsuranceClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Liability of Insurer On Death of Insured CHARTDocument2 pagesLiability of Insurer On Death of Insured CHARTClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rem Rev Crim Pro NotesDocument8 pagesRem Rev Crim Pro NotesClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument1 pageGraphClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Insurance SummaryDocument8 pagesInsurance SummaryClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Liability of Insurer On Death of Insured CHARTDocument2 pagesLiability of Insurer On Death of Insured CHARTClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Insurance Contract PartiesDocument6 pagesInsurance Contract PartiesClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Vs China REPORTDocument21 pagesPhilippines Vs China REPORTClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- List of Cases For WednesdayDocument3 pagesList of Cases For WednesdayClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic Validity Case DigestsDocument10 pagesExtrinsic Validity Case DigestsClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Casedigestswills MirandaDocument16 pagesCasedigestswills MirandaClarisse Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Economy & CostingDocument84 pagesAdvanced Engineering Economy & Costingduraiprakash83No ratings yet
- Partnership Dissolution and Liquidation ProcessDocument3 pagesPartnership Dissolution and Liquidation Processattiva jadeNo ratings yet
- IAS 33 EPS Calculation and PresentationDocument3 pagesIAS 33 EPS Calculation and Presentationismat jahanNo ratings yet
- Canara Bank Seminar HistoryDocument9 pagesCanara Bank Seminar Historydhanrajkumar947No ratings yet
- Monitoring Local Plans of SK Form PNR SiteDocument2 pagesMonitoring Local Plans of SK Form PNR SiteLYDO San CarlosNo ratings yet
- Aviation EconomicsDocument23 pagesAviation EconomicsAniruddh Mukherjee100% (1)
- 8 Sources of Funds For Nonprofits PDFDocument2 pages8 Sources of Funds For Nonprofits PDFskydawnNo ratings yet
- Cover NoteDocument1 pageCover NoteSheera IsmawiNo ratings yet
- India Inc's Baby Steps On Long Road To Normalcy: HE Conomic ImesDocument12 pagesIndia Inc's Baby Steps On Long Road To Normalcy: HE Conomic ImesShobhashree PandaNo ratings yet
- Jia Chen - Development of Chinese Small and Medium-Sized EnterprisesDocument8 pagesJia Chen - Development of Chinese Small and Medium-Sized EnterprisesAzwinNo ratings yet
- Customer Master Data Views in CMDDocument22 pagesCustomer Master Data Views in CMDVasand SundarrajanNo ratings yet
- OpTransactionHistoryTpr09 04 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesOpTransactionHistoryTpr09 04 2019 PDFSAMEER AHMADNo ratings yet
- Tax InvoiceDocument1 pageTax Invoicepiyush1809No ratings yet
- MBA Strategic Management Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesMBA Strategic Management Midterm Exammaksoud_ahmed100% (1)
- CH 07 Hull Fundamentals 8 The DDocument47 pagesCH 07 Hull Fundamentals 8 The DjlosamNo ratings yet
- Arjun ReportDocument61 pagesArjun ReportVijay KbNo ratings yet
- LA Metro - 625-626Document4 pagesLA Metro - 625-626cartographicaNo ratings yet
- Contem ReviewerDocument9 pagesContem ReviewerKenNo ratings yet
- Dissertation NikhilDocument43 pagesDissertation NikhilSourabh BansalNo ratings yet
- BY Sr. Norjariah Arif Fakulti Pengurusan Teknologi Dan Perniagaan, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 December 2013Document31 pagesBY Sr. Norjariah Arif Fakulti Pengurusan Teknologi Dan Perniagaan, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 December 2013Ili SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Upstox ApplicationDocument40 pagesUpstox ApplicationMilan K VachhaniNo ratings yet
- CH North&south PDFDocument24 pagesCH North&south PDFNelson Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Exam A2 JHWVLDocument3 pagesPublic Finance Exam A2 JHWVLKhalid El SikhilyNo ratings yet
- Hotel Industry - Portfolia AnalysisDocument26 pagesHotel Industry - Portfolia Analysisroguemba87% (15)
- Navi Mumbai MidcDocument132 pagesNavi Mumbai MidcKedar Parab67% (15)
- DaewooDocument18 pagesDaewooapoorva498No ratings yet
- Mxkufðuð: Elðumx (UlxmkDocument8 pagesMxkufðuð: Elðumx (UlxmkDharmesh MistryNo ratings yet
- The Role of Government in The Housing Market. The Eexperiences From AsiaDocument109 pagesThe Role of Government in The Housing Market. The Eexperiences From AsiaPUSTAKA Virtual Tata Ruang dan Pertanahan (Pusvir TRP)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroeconomics: Unit 1Document178 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics: Unit 1Navraj BhandariNo ratings yet
- Manual Book Vibro Ca 25Document6 pagesManual Book Vibro Ca 25Muhammad feri HamdaniNo ratings yet