Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S.E. 2012 (Mechanical Engg.) Engineering Metallurgy
Uploaded by
Tejas AdakOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S.E. 2012 (Mechanical Engg.) Engineering Metallurgy
Uploaded by
Tejas AdakCopyright:
Available Formats
Total No of Questions: [VIII]
SEAT NO. :
[Total No. of Pages : II] ]
S.E. 2012 (Mechanical Engg. )
Engineering metallurgy
(Semester - II)
Time: 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 50
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate answer books.
2) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Figures to the right side indicate full marks.
4) Use of Calculator is allowed.
5) Assume Suitable data if necessary
6) Answer Q1 or Q2, Q3 or Q4, Q5 or Q6 , Q7 or Q8
Q1)
a)
b)
c)
Q2)
Q3)
a)
b)
c)
d)
a)
b)
c)
d)
Q4)
a)
Q5)
b)
c)
d)
a)
What are the advantages of alloy steels over plain carbon steel
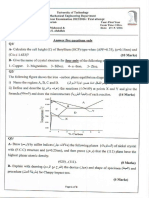
Draw an equilibrium diagram for Ag-Cu system which are partially soluble in the soli
state.The data is as follows:Melting temp. of Ag - 961C, Melting temp. of Cu 1083C, Eutectic composition28.1% Cu, Eutectic temp. - 780C, Solubility of Cu in Ag 8.8% Cu at 780C,
Solubility of Ag in Cu 92.1%Cu. The solubility in both decreases to 2% at room
temperature. Discuss slow cooling of alloy with 6% Cu from liquidus temperature.
Explain the weld decay in stainless steels
OR
Draw Iron carbon equilibrium diagram
Draw the microstructures of : 1) AISI 1020 steel
State the Hume Rotherys rules of solid solubility
What is coring ? Which alloys show cored structures ?
Explain secondary hardening
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Induction hardening over Flame
hardening
Explain how corrosion can be prevented by taking care in proper design
Explain what is anodic protection
OR
Draw self explanatory diagram for any one of the below 1] Ausforming 2]
Martempering
Write short notes on ( Any one ) : 1] Carbonitriding 2) nitriding
[04]
[06]
[03]
[04]
[02]
[04]
[03]
[02]
[04]
[3]
[3]
[02]
Explain min 4 types of corrosion .
What is cathodic inhabitors
What is chilled cast Iron ,how it is produced? Give its applications ?
[04]
[04]
[02]
[04]
b)
Draw microstructure : 1] Ferritic Speroidal gray cast iron, 2) 4.3 eutectic cast Iron
[04]
c)
Explain the cooling of 3.5 % carbon cast Iron from its melting temperature till
room temperature.
[04]
OR
Q6)
Q7)
a)
What is Equivalent carbon in cast Iron. Explain role of individual element present in
Equivalent carbon in cast iron .
[04]
b)
Compare S.G. iron and Malleable iron with respect to microstructure, production,
composition and one application each.
[04]
c)
What are the advantages of cast iron over steels?
[04]
a)
Give typical composition, property and application for the following ( any four) :
[12]
1] LM14 2]Invar 3]statuary bronze 4]cartridge brass 5) Gun metal
Q8)
b)
Ni is used in measuring equipment justify its property for this application .
a)
OR
Explain classification of Cu base alloys based on the percentage of Cu and Zn?
[1]
[04]
Explain role of Zn in brasses
b)
Write short note on 1) Dezincification 2)coring in Sn bronzes
[04]
c)
What are the requirements of bearing materials ? explain with suitable example
[05]
You might also like
- 33 Jigs and Fixtures For Machine ShopsDocument21 pages33 Jigs and Fixtures For Machine ShopsPRASAD326100% (10)
- 17-7 PH Data BulletinDocument16 pages17-7 PH Data Bulletinmeckup123No ratings yet
- (Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Document1 page(Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Ivan Briscoe100% (7)
- A109210306-Metallurgyandmaterialsscience - November 2010Document6 pagesA109210306-Metallurgyandmaterialsscience - November 2010venkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- Rao Minerals PDFDocument348 pagesRao Minerals PDFOppie ChelyNo ratings yet
- Carbon Equivalent (Ce) Composition Parameter (PCM)Document9 pagesCarbon Equivalent (Ce) Composition Parameter (PCM)Arif Budi JatmikoNo ratings yet
- Question Papers Metallurgy and Material Science Jntu Previous YearsDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers Metallurgy and Material Science Jntu Previous YearsAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- Question Papers - Heat TreatmentDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers - Heat TreatmentSrilakshmi Shunmugaraj100% (3)
- Orbu SPC 44 0 22Document98 pagesOrbu SPC 44 0 22geverett2765No ratings yet
- Lab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleDocument58 pagesLab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleSantosh Kumar75% (4)
- Practicereadingtests ComprehensionDocument16 pagesPracticereadingtests Comprehensionapi-369396594No ratings yet
- Fire Explosion Hazard SX-EWDocument104 pagesFire Explosion Hazard SX-EWGeorgi SavovNo ratings yet
- Semester 4 - 2017 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Document4 pagesSemester 4 - 2017 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNo ratings yet
- EIM212 16 EIM212Nov2013Document6 pagesEIM212 16 EIM212Nov2013Priviledge MuzotaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 02Document6 pagesTugas 02Andika Aldi IINo ratings yet
- MMS Nov08Document7 pagesMMS Nov08Kiran KancharlaNo ratings yet
- Semester 4 - 2017 - May - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Document4 pagesSemester 4 - 2017 - May - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNo ratings yet
- Semester 4 - 2018 - May - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Document3 pagesSemester 4 - 2018 - May - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Exam GuideDocument9 pagesEngineering Materials Exam GuideTamiranashe Tammie NyunguNo ratings yet
- PM PaperDocument4 pagesPM PaperSomya KabraNo ratings yet
- Regulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExamDocument4 pagesRegulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExambalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Himpunan Contoh Soalan Exam Soalan Ujian SN BHNDocument50 pagesHimpunan Contoh Soalan Exam Soalan Ujian SN BHNNur Atikah100% (1)
- MT Question Bank Unit 1Document1 pageMT Question Bank Unit 1Numesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Code No: 35041Document4 pagesCode No: 35041SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- r05311803 Heat Treatment TechnologyDocument8 pagesr05311803 Heat Treatment TechnologySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2013Document12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2013Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- QP HT April 2021Document2 pagesQP HT April 2021Kshitij NeekhraNo ratings yet
- r05311804 Iron MakingDocument6 pagesr05311804 Iron MakingSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTIONTECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesPRODUCTIONTECHNOLOGYSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Code No: 45043Document4 pagesCode No: 45043SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized title for Advance Welding exam paperDocument2 pagesSEO-Optimized title for Advance Welding exam paperchetan dixitNo ratings yet
- 1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09Document3 pages1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- MEM - Assignment MEDocument1 pageMEM - Assignment MEsandipdas20250No ratings yet
- 07a81803 SuperalloysDocument4 pages07a81803 SuperalloysSharanya ThirichinapalliNo ratings yet
- Semester 4 - 2019 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Document4 pagesSemester 4 - 2019 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Exam GuideDocument5 pagesEngineering Materials Exam Guidekundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- r05322003 Metal FormingDocument8 pagesr05322003 Metal FormingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Materials science document analysisDocument7 pagesMaterials science document analysisPuspendu Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.imamuddeenNo ratings yet
- MCL131 Minor-1 Exam Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesMCL131 Minor-1 Exam Questions and AnswersVishal kumar SawNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer Question One (40 Marks) and Any Other Two (60marks)Document4 pagesInstruction: Answer Question One (40 Marks) and Any Other Two (60marks)quickdannyNo ratings yet
- سنوات سابقة خواصDocument64 pagesسنوات سابقة خواصmechanical depNo ratings yet
- Class Test Question Paper MMP I SCHEMEDocument4 pagesClass Test Question Paper MMP I SCHEMErajendra20No ratings yet
- CCB 231 Supp ExamDocument6 pagesCCB 231 Supp ExamTumisang100% (1)
- G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankDocument12 pagesG. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- NAME - 2013-2014 (L-2, T-1)Document18 pagesNAME - 2013-2014 (L-2, T-1)partho RoyNo ratings yet
- PR8592 Welding Technology TT-IIIDocument1 pagePR8592 Welding Technology TT-IIIகணேஷ்No ratings yet
- Pre-Leaving Certiϐicate Examination, 2018 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2018Document12 pagesPre-Leaving Certiϐicate Examination, 2018 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2018Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- Pre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2016 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2016Document12 pagesPre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2016 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2016Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- B.Tech., End-Semester (Autumn) Examination, 2015 SUBJECT: Steel Making (MM-305)Document2 pagesB.Tech., End-Semester (Autumn) Examination, 2015 SUBJECT: Steel Making (MM-305)anon_945096555No ratings yet
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2019Document12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2019Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- July 2004Document6 pagesJuly 2004ffgfgfgffgNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW Examinations iearchiveexampapers2022LC027ALP000EV PDFDocument12 pagesHTTPSWWW Examinations iearchiveexampapers2022LC027ALP000EV PDFWeres DiwetNo ratings yet
- rr321803 Foundry TechnologyDocument6 pagesrr321803 Foundry TechnologySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2017Document12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination, 2017Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- Epp 201-3 - Manufacturing Technology I Nov 09.Document10 pagesEpp 201-3 - Manufacturing Technology I Nov 09.fatengzNo ratings yet
- Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2013 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2013Document12 pagesPre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2013 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2013Diaa SaberNo ratings yet
- Rr411802 Steel MakingDocument6 pagesRr411802 Steel MakingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Rr321803 Foundry TechnologyDocument5 pagesRr321803 Foundry TechnologySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- 131212-131904-Material Science and MetallurgyDocument1 page131212-131904-Material Science and Metallurgysameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodMohammad Khairul Azmi Mohd KassimNo ratings yet
- Semester 4 - 2018 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015Document3 pagesSemester 4 - 2018 - November - Engineering Metallurgy em Pattern 2015AYUSHNo ratings yet
- NIT Jamshedpur End Sem Exam Extractive Metallurgy Non-FerrousDocument15 pagesNIT Jamshedpur End Sem Exam Extractive Metallurgy Non-FerrousVishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Q. Papers ME2015 PDFDocument1,669 pagesQ. Papers ME2015 PDFKamleshNo ratings yet
- Main Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresFrom EverandMain Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresNo ratings yet
- Unusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandUnusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Hyrdogen Storage TechnologiesFrom EverandHyrdogen Storage TechnologiesMehmet SankirNo ratings yet
- Mechanical-Engineering Gate2016.InfoDocument3 pagesMechanical-Engineering Gate2016.InfoHenryNo ratings yet
- S.E. 2012 (Mechanical, Mechanical Sandwich, Automobile)Document2 pagesS.E. 2012 (Mechanical, Mechanical Sandwich, Automobile)Tejas AdakNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines AprilDocument7 pagesTheory of Machines AprilTejas AdakNo ratings yet
- 40 Non Conventional MachiningDocument20 pages40 Non Conventional MachiningPRASAD326100% (6)
- 9 Non Conventional MachiningDocument15 pages9 Non Conventional MachiningsohameyNo ratings yet
- 35 Non Conventional MachiningDocument13 pages35 Non Conventional MachiningPRASAD326100% (8)
- TOM1Document3 pagesTOM1Abhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDocument3 pagesS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakNo ratings yet
- ATDocument4 pagesATTejas AdakNo ratings yet
- Brrrochure GATE2017 PDFDocument63 pagesBrrrochure GATE2017 PDFKarthik NarayananNo ratings yet
- 940 601 Ball Transfer For Air CargoDocument2 pages940 601 Ball Transfer For Air CargoHyundianto AgNo ratings yet
- International Commodity MarketDocument47 pagesInternational Commodity MarketDibyesh DasNo ratings yet
- Tcsq11305r0 CmuDocument24 pagesTcsq11305r0 CmuAJEC IndiaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry QuestionDocument6 pagesSPM Chemistry QuestionSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- PS Chemical BondingDocument31 pagesPS Chemical BondingSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNo ratings yet
- A 470 - 03 Piezas ForjadasDocument8 pagesA 470 - 03 Piezas ForjadasWILLIAM ROMERONo ratings yet
- SET-2 Brazing - SolderingDocument8 pagesSET-2 Brazing - SolderingSyed TanveerNo ratings yet
- Tufftride - Qpq-Process: Technical InformationDocument19 pagesTufftride - Qpq-Process: Technical InformationSinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- WK 3 EARTHDocument23 pagesWK 3 EARTHClaire ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageChemistry Paper 1 Cheat SheetyinkaNo ratings yet
- Rusting of IronDocument15 pagesRusting of IronDeepanshu Arya100% (1)
- Underground Metal Mining TechnologyDocument2 pagesUnderground Metal Mining TechnologysrinuNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument105 pagesInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- 3 3 Euragglo Komarek Roller Presses Presentation Pascal Hervieu PDFDocument55 pages3 3 Euragglo Komarek Roller Presses Presentation Pascal Hervieu PDFssmith2007100% (1)
- Aqa CHM3W W QP Jun09Document18 pagesAqa CHM3W W QP Jun09aqa123aqaNo ratings yet
- Specification for Piping Materials Rev B3Document52 pagesSpecification for Piping Materials Rev B3shervinyNo ratings yet
- Sadsd PHYSSDocument37 pagesSadsd PHYSSnaseh__nNo ratings yet
- D11.2-89 R2006 PVDocument8 pagesD11.2-89 R2006 PVluisma1220No ratings yet
- Lead analysis in Group I and IIDocument15 pagesLead analysis in Group I and IIChristylle CosasNo ratings yet
- Sodium Borohydride Amides To AminesDocument4 pagesSodium Borohydride Amides To AminesalchymystNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Investigatory Project2xxDocument24 pagesMetallurgy Investigatory Project2xxSathyaNo ratings yet
- Info Ozone Compatible MaterialDocument2 pagesInfo Ozone Compatible MaterialsaracelyNo ratings yet