Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JEE221 FM Assignment 3 2016
Uploaded by
Tom FallonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE221 FM Assignment 3 2016
Uploaded by
Tom FallonCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
2016
Pages: 5
Questions: 10
UNIVERSITY OF TASMANIA
[Australian Maritime College]
JEE221 Fluid Mechanics
Dr Rouzbeh Abbassi
Deadline: Wednesday 12/10/2016 (5 pm)
Instructions:
Total marks = 100 (10% of the final Mark)
Marks for each part are indicated
Answer ALL questions (10 in total)
State all assumptions and show all workings, including diagrams
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
Question 1. In Figure 1, there are 38.1 m of pipe with diameter of 0.051 m, 22.7 m of
pipe with diameter of 0.152 m, and 45.7 m of pipe with diameter of 0.076 m, all cast
iron. There are three 90 elbows and an open globe valve, all flanged. If the exit
elevation is zero, what horsepower is extracted by the turbine when the flow rate is
0.0045m3/s of water at 20C? Note: take = 1000 kg/m3 , = 10-3 kg/m.s and mean
roughness is = 0.26 mm.
(10 marks)
Elevation 30.5m
0.051 m
0.152 m
0.076 m
Figure 1. Piping and turbine system
Question 2. A blower delivers air at 3000 m3/h to the duct circuit in Figure 2. Each duct is
commercial steel and of square cross section, with side lengths a1 = a3 = 20 cm and a2 = a4 =
12 cm. Assuming sea-level air conditions ( = 1.2 kg/m3 , = 1.8 E-5 kg/m.s), estimate the
power required if the blower has an efficiency of 75%, mean roughness of the duct is = 0.046
mm . Neglect minor losses.
(10 marks)
Figure 2. Duct Circuit with Blower
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
Question 3. The showerhead in Figure 3 delivers water at 50C. An orifice-type flow reducer
is to be installed. What flow rate, in gal/min, results without the reducer? What reducer orifice
diameter would decrease the flow by 40 percent? Take = 988 kg/m3 , = 0.54E-3 kg/m.s
and the pressure in the head is p=400 kPa.
(10 marks)
Figure 3. Flow through Showerhead
Question 4. A wedge splits a sheet of 20C water, as shown in Figure 4. Both wedge
and sheet are very long into the paper. If the force required to hold the wedge
stationary is F = 124 N per meter of depth into the paper, what is the angle of the
wedge? Take = 998 kg/m3.
(10 marks)
Figure 4. Splitting Water Flow with a Wedge
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
Question 5. A 12-cm-diameter pipe, containing water flowing at 200 N/s, is capped by
an orifice plate, as shown in Figure 5. The exit jet is 25 mm in diameter. The pressure
in the pipe at section 1 is 800 kPa (gauge). Calculate the force F required to hold the
orifice plate. Take = 998 kg/m3.
(10 marks)
2.5 cm
7.6 cm
0.61 m
Figure 5. Orifice in a Pipe
Question 6. A horizontal air jet having a velocity of 50 m/s and a diameter of 20 mm
strikes the inside surface of a hollow hemisphere as indicated in Figure 6. How large
is the horizontal anchoring force (FA) to hold the hemisphere in place? Note: the
magnitude of velocity of air remains constant.
(10 marks)
Figure 6. Air jet striking a hollow hemisphere
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
Question 7. A pump is to be specified to transport oil of specific gravity 0.87
(kinematic viscosity: 1.9 mm2/s) from a holding tank to a service tank 8 metres above.
The proposed mild steel piping run is 37 metres long with an internal diameter of 40
mm and includes three 90o smooth bends, four gate valves and one strainer. (10 marks)
a) What is power required to be delivered to the oil by the pump in order to
achieve a maximum mass flow rate of 100 tonnes per day? (3 marks)
b) What is the NPSH required in order to avoid cavitation inside the pump
(assume that the pump is on the lower deck). (3 marks)
c) What type of pump would be the most suitable for this application and why?
(2 marks)
d) What is the mechanical power required to be supplied to the pump shaft in
order to achieve the desired flow rate? (2 marks)
Question 8. An ultralight airplane has a wing with an aspect ratio of 5 and with lift
and drag coefficient corresponding to the below figure. The planform area of the wing
is 18.58 m2. The total weight of the flying airplane is 1800 N. The airplane flies at 15.24
m/s in air with a density of 1.03 kg/m3.
(a): Find the angle of attack and the drag force on the wing? (4 marks)
(b): What is the stall speed? (4 marks)
(c): What is the angle of attack to take off at 65 km/h? (2 marks)
Figure 7. Coefficient of lift for various angle if attacks
(10 marks)
Fluid Mechanics
Assignment 3
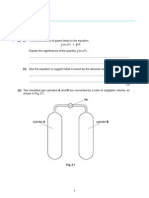
Question 9. A helium-filled balloon in Figure 8 is tethered at 20C and 1 atm with a
string of negligible weight and drag. The diameter is 50 cm and the balloon material
weighs 0.2 N, not including the helium. If the helium pressure is 120 kPa, estimatre
the tilt angle if the airstream velocity U is a) 5 m/s b) 10 m/s. Note that helium density
is helium = 0.197 kg/m3, air density is air = 1.23 kg/m3 and its viscosity is = 1.8E-5 kg/m.s)
(10 marks)
Figure 8. Helium-filled balloon subjected to air stream
Question 10. Estimate the wind velocity necessary to blow over the train car shown
in Figure 9, if the weight of the car is 250 kN and air density air = 1.23 kg/m3
(10
marks)
Figure 9. Train car subjected to cross wind
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 3.2 DeformationDocument8 pages3.2 DeformationSalmanNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty: Problems & Answers: CM CM CM CMDocument10 pagesUncertainty: Problems & Answers: CM CM CM CMarrowayNo ratings yet
- CFD Assignment 1Document4 pagesCFD Assignment 1Tom FallonNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Timber StructuresDocument60 pagesSeismic Design of Timber StructuresSairam Venkat100% (1)
- MATH2930 Prelim 1Document4 pagesMATH2930 Prelim 1cidermelonNo ratings yet
- Steel Design DraftDocument15 pagesSteel Design DraftTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab Design DraftDocument13 pagesConcrete Slab Design DraftTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Waves LoadtutDocument11 pagesWaves LoadtutTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Wave Assignment1Document3 pagesWave Assignment1Tom FallonNo ratings yet
- Wave Assignment1Document3 pagesWave Assignment1Tom FallonNo ratings yet
- Fastening Design: Longitudinal BendingDocument6 pagesFastening Design: Longitudinal BendingTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Project Meetings: Meeting Number Date Time AttendeesDocument1 pageProject Meetings: Meeting Number Date Time AttendeesTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainDocument1 pageDifferent Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainDocument1 pageDifferent Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and Again JhfvuhgvDocument1 pageDifferent Again and Again and Again and Again and Again and Again JhfvuhgvTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and Again and Again and AgainDocument1 pageDifferent Again and Again and Again and AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainDocument1 pageDifferent Again and Again and Again and Again and AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different AgainDocument1 pageDifferent AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- DifferentDocument1 pageDifferentTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different Again and AgainDocument1 pageDifferent Again and AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different AgainDocument1 pageDifferent AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Different AgainDocument1 pageDifferent AgainTom FallonNo ratings yet
- BlankblankDocument1 pageBlankblankTom FallonNo ratings yet
- Mitsuboshi Products ARPMDocument102 pagesMitsuboshi Products ARPMRizal Agus FiantoNo ratings yet
- CJC Prelim Paper 1 AnsDocument8 pagesCJC Prelim Paper 1 Ansnewtonian_physicsNo ratings yet
- Wellsteg eDocument14 pagesWellsteg eron_danyNo ratings yet
- Ocean Wave DerivationsDocument64 pagesOcean Wave DerivationsDanielNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument37 pagesIdeal GasesEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Stability and Control - Helmut F. BauerDocument43 pagesVehicle Stability and Control - Helmut F. BauerChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamic 3 PDFDocument50 pagesGas Dynamic 3 PDFMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Vertical Stress Increases in SoilDocument24 pagesVertical Stress Increases in SoilGerards ChinNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Mathematical Model For Special Relativity Guy Tsabary and Aviv CensorDocument17 pagesAn Alternative Mathematical Model For Special Relativity Guy Tsabary and Aviv CensorYotam KatzirNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document8 pagesHW 5Anonymous AjrDxGNo ratings yet
- Unified Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageUnified Mechanical Engineeringshalom_pklNo ratings yet
- Second Day January 21 Structural 1Document9 pagesSecond Day January 21 Structural 1BongA.SalinasNo ratings yet
- Connections Manual ErrataDocument31 pagesConnections Manual ErratalucianduNo ratings yet
- Almanac Data For IRNSSDocument2 pagesAlmanac Data For IRNSSBaka NuduNo ratings yet
- 1918 - On The Mechanical Theory of The Vibrations'of Bowed - RamanDocument34 pages1918 - On The Mechanical Theory of The Vibrations'of Bowed - RamanMarcus Vinicius Da Silva EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics PDFDocument2 pagesStructural Mechanics PDFJOHN MAKOTONo ratings yet
- Phys2 Ch3 Firstlawthermo NewDocument54 pagesPhys2 Ch3 Firstlawthermo NewQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Open Quantum Systems An IntroductionDocument100 pagesOpen Quantum Systems An IntroductionRachel Baltazar VitancolNo ratings yet
- Thermo Physical Properties of NanofluidDocument20 pagesThermo Physical Properties of Nanofluidvishnoi19No ratings yet
- FM-II CHP 13 CFDDocument41 pagesFM-II CHP 13 CFDMALIK MUHAMMAD HAMZA FAROOQ MALIK MUHAMMAD FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Linear Models and Calculation of Aeroelastic FlutterDocument10 pagesLinear Models and Calculation of Aeroelastic FluttercareerNo ratings yet
- Buckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Document5 pagesBuckling and Ultimate Strength Assessment For Offshore Structures APRIL 2004Flávio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 1995 - Numerical Simulation of Gas and Particle FlowDocument9 pages1995 - Numerical Simulation of Gas and Particle FlowSwati Lalit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Benchtop Learning Model: Robotized Manual Gearbox: User's Guide For MT-BVRDocument74 pagesBenchtop Learning Model: Robotized Manual Gearbox: User's Guide For MT-BVRKristiqn KolevNo ratings yet