Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gearless Mechanism in Right Angle: Atish Lahu Patil, Vinay Prabhakar Jadhav, Sagar Padmakar Patil, Roshan Suresh Shelar
Uploaded by
final projectOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gearless Mechanism in Right Angle: Atish Lahu Patil, Vinay Prabhakar Jadhav, Sagar Padmakar Patil, Roshan Suresh Shelar
Uploaded by
final projectCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication
Volume: 4 Issue: 4
ISSN: 2321-8169
145 - 149
______________________________________________________________________________________
Gearless Mechanism in Right Angle
Atish Lahu Patil1,Vinay Prabhakar Jadhav2, Sagar
Padmakar Patil3, Roshan Suresh Shelar4
1,2,3,4
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Vishwatmak Om Gurudev College of Engineering
Aghai-Kalyan, India
1
patilatish60@gmail.com
2
vinayj994@gmail.com
3
shelarroshan6@gmail.com
4
sagarp1610@gmail.com
Prof. Pavan Nikam
Assistant Professor. Department of Mechanical Engineering
Vishwatmak Om Gurudev College of Engineering
Aghai-Kalyan, India.
Abstract Todays world requires speed on each and every field. Hence rapidness and quick working is the most important. Now days for
achieving rapidness, various machines and equipments are manufactured by man. The engineer inconstantly conformed to the challenges of
bringing ideas and design in to reality. New machines and techniques are being developed continuously to manufacture various products at
cheaper rates and high quality. The project GEARLESS TRANSMISSION is being compact and portable equipment, which is skillful and is
having something precise in transmitting power at right angle without any gears being manufactured.
__________________________________________________*****_________________________________________________
I.
INTRODUCTION
What is Gearless Mechanism?
Gearless mechanism is an link mechanism of slider
and pair, which is also known as El-bow mechanism
The component is exceptionally valuable for
cornering or transmitting movements at right points.
However in certain mechanical application Gearless
Transmission at Right Angle can likewise work at
insensitive or exact edge plane can be contrasted with worm
and worm rigging or slant and pinion gear which are
constantly utilized as a part of the business for various
application. Similarly high proficiency between the info and
the yield power shafts as to the rigging efficiencies.
It has intricately examined in point of interest in the
whole books o designing that the apparatus drives have low
mechanical efficiencies. Since Factor identifying with under
frictional Forces between the mating gear teeth, the
unpredictable chasing of the riggings, the reaction between
the teeth can't be overcome and consequently the
proficiency can't be more than 55%of late apparatuses of
warm slant sort are being made in poly propqleneand epoxy
material where the Frictional Forces are similarly disposed
of. Despite the fact that such apparatuses are utilized for
moderately little applications the proficiency is not more
than 42%.The El-bow Mechanism transmits the I/P power
towards the O/P side such away that the rakish Forces
created in the slacks are essentially transmitted with the
assistance of connections which takes up the I/P power and
the right point drive is exchanged towards the O/P slack and
stick get together. Thus next to no grinding plays while the
force is being transmitted; the chasing and kickback one
missing. In this way, it is valued that proficiency as high as
90-92% are conceivable in apparatus less transmission
component.
II.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Skew Shaft :- The term shaft , used in this standards has a
wide meaning and serves for specifications of all outer
elements of the part , including those elements , which do
not have cylindrical shapes And skew means non-parallel
and non-intersecting so the shafts which are non-parallel and
non-intersecting are known as skew shafts.
Types of gears used for transmission of power at Right
Angle!
1. Helical Gear:
145
IJRITCC | April 2016, Available @ http://www.ijritcc.org
_______________________________________________________________________________________
International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication
Volume: 4 Issue: 4
ISSN: 2321-8169
145 - 149
______________________________________________________________________________________
4. Hypoid gears :-
The teeth on helical gears are cut at an angle to the
face of the gear. When two teeth on a helical gear system
engage, the contact starts at one end of the tooth and
gradually spreads as the gears rotate, until the two teeth are
in full engagement.This gradual engagement makes helical
gears operate much more smoothly and quietly than spur
gears.
2. Bevel & Pinion Gear:
Hypoid gears look like winding slope gears
with the exception of the pole tomahawks don't cross. The
pitch surfaces seem cone shaped yet, to make up for the
balance shaft, are truths being told hyperboloids of
insurgency. Hypoid riggings are quite often intended to
work with shafts at 90 degrees. The result that apparatus
proportions of 60:1 and higher are achievable utilizing a
solitary arrangement of hypoid apparatuses. This style of
apparatus is most regular in driving mechanical differentials,
which are typically straight cut incline gears, in engine
vehicle axles.
III.
Bevel gears are gears where the axes of the two
shafts intersect and the tooth-bearing faces of the gears
themselves are conically shaped. Bevel gears are most often
mounted on shafts that are 90 degrees apart, but can be
designed to work at other angles as well. The pitch surface
of bevel gears is a cone.
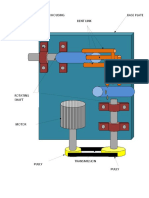
COMPONENTS OF THE MODEL AND
OPERATION
CONCEPT DRAWING OF MACHINE
3. Worm & Worm Gear:
Worm gears are used when large gear reductions are
needed. It is common for worm gears to have reductions of
20:1, and even up to 300:1 or greater. Many worm gears
have an interesting property that no other gear set has: the
worm can easily turn the gear, but the gear cannot turn the
worm. This is because the angle on the worm is so shallow
that when the gear tries to spin it, the friction between the
gear and the worm holds the worm in place. worm drive can
reduce rotational speed or allow higher torque to be
transmitted.
Construction
It consist of links or rods that are bend exactly at 90
degree (right angle).
The number of links required would be 3 to 8.
The more the links, the smoother will be the operation.
Links are made up of bright bars as the bright bar
material has good surface finish.
These links slides inside the through and through drilled
cylinder.
146
IJRITCC | April 2016, Available @ http://www.ijritcc.org
_______________________________________________________________________________________
International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication
Volume: 4 Issue: 4
ISSN: 2321-8169
145 - 149
______________________________________________________________________________________
Thus forming a sliding pair.
These cylinders are coupled to the input and output
shaft with help of key.
Power is supplied by electric motor.
located. If the holes drilled in the ends of the shafts have
blind or closed ends, there ought to be a small vent at the
bottom of each rod hole for the escape of air compressed by
the pumping action of the rods.
WORKING
The Gearless transmission or El-bow mechanism is a device
for transmitting Motions at any fixed angle between the
driving and driven shaft. The synthesis of this mechanism
would reveal that it comprises of a number of links would be
between 3 to 8 the more the links the smoother the operation. These
links slide inside hollow cylinders thus formatting a sliding
pair. Our mechanism has 3 such sliding pairs. These
cylinders are placed in a Hollow pipe and are fastened at
120* to each other. This whole assembly is mounted on
brackets wooden table. Power is supplied by an electric
motor.
These holes are useful for oiling to avoid blind holes shafts
may have enlarged port or shoulder. This transmission may
be provided centrally and in line with the axis of each shaft
and provided with a circular groove at each rod or a crosspin to permit rotation of the shaft about the rod simply
active as a retaining device for shipping and handling
purposed.
The working of the mechanism is understood by the
diagram. An unused form of transmission of power on shaft
located at an angle. Motion is transmitted from driving to
the driven shaft through the roads which are bent to conform
to the angles between the shafts. These roads are located at
in the holes equally spaced around a circle and they are free
to slide in & out as the shaft revolves. This type of drive is
especially suitable where quite operation at high speed is
essential but only recommended for high duty.
1) As a wood cutting machine The cutter is attached
on the output shaft
The operation of this transmission will be apparent by the
action of one rod during a revolution. If we assume that
driving shaft A is revolving as indicated by arrow the
driven shaft B will rotate counter clockwise. As shaft A
turns through half revolution C shown in the inner and most
effective driving position slides out of both shafts A & B.
The first half revolution and rod C then will be at the top
then during The remaining half this rod C slide in wards
until it again reaches to inner most position shown in Fig. in
the meanwhile the other roads have of course passed
through the same cycle of movements all rods are
successively sliding inwards and outwards. Although this
transmission is an old one many mechanics are skeptical
about its operation, however it is not only practicable but
has proved satisfactory for various applications when the
drive is for shafts which are permanently located at given
angle. Although this illustration shows a right angle
transmission this drive can be applied also to shafts located
at intermediate angle between 0* and 90*.In making this
transmission, it is essential to have the holes for a given rod located
accurately in the same holes must be equally spaced in
radial and circumferential directions, be parallel to each rod
should be bent to at angle atwhich the shaft are to be
As mentioned in first chapter that we are showing two
applications of
This mechanism at a time.
2) When motion is transmitted through mechanism to
output shaft the shaft will start to rotate at adjusted
speed. The speed is adjusted by means of pulley
(i.e.RPM). The cutters Will also start to rotate
along with the shaft the because of cutter is
250mm.the through slot introduces in the table for
free rotation of cutter edges in table. Now the feed
given to wooden rods or plywood to cut in desire
shape and size. The speed is adjusted by means of
pulley (i.e...RPM). The cutters will also start to
rotate along with the shaft the because of cutter is
250mm. the through slot is introduced in the table.
Now feed given to wooden rods or plywood to cut
in desired shape and size.
3) As a air compressor or air pump -> the compressor
or and pump also introduced in our project when
the links inside the drilled holes are reciprocates as
well as revolves along the axis of cylinder it gives
the compressor effect. Among the three links when
first pin goes at inner dead center it sucts the air
then it start to move at outer dead center by
revolving, it compresses the air against seal and
cylinder head discand does simultaneously by three
links and we can get continue discharge of air the
quantity.
4) Mechanical seal is defined as a devise which seals
by virtue of axial contact pressure between two
relatively flat surfaces in a plane right angle to the
axis of the shaft .The seal used in EL-BOW m/c
147
IJRITCC | April 2016, Available @ http://www.ijritcc.org
_______________________________________________________________________________________
International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication
Volume: 4 Issue: 4
ISSN: 2321-8169
145 - 149
______________________________________________________________________________________
compressor is stationary type. It is place between
cylinder and cylinder head.
IV.
POSSIBLE ARRANGEMENTS OF LINKS
View of the Shafts Below diagram shows a different view of
the shaft arrangement which are skew and angle between
them is 90 degrees, which helps us in the understanding of
the arrangement of shafts. In below figure
next 120 degrees and further for next 120 degrees and links
are exchanging the position in successive order as discussed
before.
V.
1.
2.
3.
.
Views of Setup Different views of the setups are shown in
Figure .These views show the arrangement of links and
shaft.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
High Efficiency between input and output power
shafts.
This coupling enables a variable parallel offset
between two shafts. They provide constant speed
velocity with extremely low backlash, and their
compact designs provide large floor space savings.
Easy manufacturing of links and links in
comparison of crossed helical and worm gear.
Very little friction.
Hunting & backlash is absent.
Backlash-free shaft securement and torque
transmission .
This is a very smooth-acting device, and the power
loss is minimum.
It can be run at nearly any speed, even at high
speed and is very quiet.
Time-saving installation due to simple and fast
shaftsecurement.
VI.
Analysis of Mechanism
From the above diagrams and views the setup is clearly
established in the mind, but as for convenience here we use
the front view of the setup for analysing the mechanism of
setup.
ADVANTAGES
APPLICATIONS
1.
Driving for all kinds four faced tower clocks. The
elbow mechanism was first use in the year 1685
for the famous London tower clock named bigben.
2.
The mechanism is invariable used for multiple
spindle drilling operation called the gang drilling.
Used for angular drilling between 0 to 90 degree
position.
Lubrication pump for C.N.C. lathe machines.
The mechanism is very useful for a reaching a
drive at a clumsy location.
Air blower for electronic and computer machine.
The mechanism has found a very usefully use in
electronic and computer technology for multiple.
The elbow mechanism is used for movement of
periscope in submarines, the year 1685 for the
famous London tower clock.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Figure Setup
Let at the starting instant shaft 1 starts rotation with 3 links
in anticlockwise direction and a reaction force developed at
the pin surface which in contact with the shaft and this force
transferred to the other end of the pin which is in the shaft
and applying on the shaft 2 due to which shaft 2 starts
rotating in the same direction as shaft 1, after 120 degree
rotation pin 1 comes at the place of pin 2 & pin 2 comes at
the place of pin 3 & pin 3 comes at the place of pin 1 by
sliding in shaft and self adjusting. This motion repeated for
VII. CONCLUSIONS
During working on experimental setup and after
a long discussion it is observed that proposed arrangement
used for any set of diameters with any profile of shafts for
skew shafts of any angle but the shafts must be having the
rotational motion about his own axis, transmission of motion
is very smooth and desirable and used only for the equal
R.P.M. of driving shaft and driven shaft by employing links
or given type of links for appropriate joints for revolute pair.
148
IJRITCC | April 2016, Available @ http://www.ijritcc.org
_______________________________________________________________________________________
International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication
Volume: 4 Issue: 4
ISSN: 2321-8169
145 - 149
______________________________________________________________________________________
Some successful mechanical devices function
smoothly however poor fly they are made while other does
this only by virtue of a accurate construction & fitting of their
moving parts. This projects which looks very simple & easy to
construct was actually very difficult to conceive & imagine
without seeing an actual one in practice. Motions demands
to be studied first & we have done that very thing. We find that
while acceptable analysis for existing mechanism can often
be Made quite easily we cannot without insight &
imagination make effective synthesis of new mechanism
hence we are mould to present this our project gear less
transmission at 90*(El-bow mechanism) which we have
managed to successfully device after long & hard input in
conceiving its working principle.
REFERENCES
[1] Book s. s. rattan Mc Graw Hill Education ( India )
private limited, new delhi.
[2] A. Kumar and S. Das, An arrangement for power
transmission between co-axial shafts of different
diameter, International journal of engineering
research and technology .
[3] Gear less power transmission: parallel offset shaft
coupling, Journal
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= School of
Mechanical and Building Sciences.
Books
[1] Strength of Materials by RS Khurmi & Gupta.
[2] Design Data Hand Book by Mahadevan.
[3] Machine Design by Bhandari.
149
IJRITCC | April 2016, Available @ http://www.ijritcc.org
_______________________________________________________________________________________
You might also like
- Title: Design and Analysis of Gearless Transmission SystemDocument6 pagesTitle: Design and Analysis of Gearless Transmission SystemLokeshNo ratings yet
- Gearless TransmissionDocument51 pagesGearless TransmissionRoyalAryansNo ratings yet
- Gearless TransmissionDocument48 pagesGearless TransmissionIpaseta Dhara88% (8)
- Gearless Mechanism at Right AngleDocument13 pagesGearless Mechanism at Right AngleAkshay Tatkare100% (1)
- Gearless Transmission: College of Engineering &technology Ghatikia, Bhubaneswar, Odisha - 751003, IndiaDocument32 pagesGearless Transmission: College of Engineering &technology Ghatikia, Bhubaneswar, Odisha - 751003, IndiahiteshNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Bent Link Bearing Pin HousingDocument21 pagesBase Plate Bent Link Bearing Pin HousingAjay NishadNo ratings yet
- Development of Gearless-04052022-3Document5 pagesDevelopment of Gearless-04052022-3madhanreddy953No ratings yet
- Gearless Transmission Project ReportDocument32 pagesGearless Transmission Project ReportHarish Kumar73% (22)
- Gearless Power-Transmission-Project Report 4Document2 pagesGearless Power-Transmission-Project Report 4A-2011 AKASH DUTTANo ratings yet
- Project Report: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument59 pagesProject Report: Department of Mechanical Engineeringpradeep9982100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Multi Nut Removing Tool: EngineeringDocument4 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Multi Nut Removing Tool: Engineeringsreejith2786No ratings yet
- Problem DefinitionDocument3 pagesProblem DefinitionGaurav PawarNo ratings yet
- Gearless Transmission Using Elbow MechanismDocument32 pagesGearless Transmission Using Elbow Mechanismsanoop joseNo ratings yet
- Four Speed Gear Box DesignDocument5 pagesFour Speed Gear Box DesignAtthuru ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Review On Bore Well Pipe Lifting and Transportation Machine Ijariie8295Document4 pagesReview On Bore Well Pipe Lifting and Transportation Machine Ijariie8295KADIRIPURAM ARJUNNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document34 pagesChapter - 1Yuva RajNo ratings yet
- Gearless TransmissionDocument51 pagesGearless TransmissionSid Max83% (6)
- GEARLESS TRANSMISSION Project File ORIGIONAL Send GeetDocument67 pagesGEARLESS TRANSMISSION Project File ORIGIONAL Send GeetGeeta VermaNo ratings yet
- Ball Traction Drive - FinalDocument46 pagesBall Traction Drive - FinalTejas Shete0% (1)
- Punjab Aircraft Maintenance Engineering College, Patiala Procedure Sheet: Module 6 (6.5 To 6.10)Document4 pagesPunjab Aircraft Maintenance Engineering College, Patiala Procedure Sheet: Module 6 (6.5 To 6.10)Arjun SharmaNo ratings yet
- ST1503 020Document7 pagesST1503 020MainãNo ratings yet
- Core Cutting Machine Ijariie12718Document5 pagesCore Cutting Machine Ijariie12718Habteyes AbateNo ratings yet
- Manual Operated Flore CleanerDocument5 pagesManual Operated Flore CleanerchetanmithanNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Oil Skimmer RobotDocument59 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Oil Skimmer RobotSathiya Udumalpet0% (1)
- Welding Slag CLEANING MachineDocument5 pagesWelding Slag CLEANING MachineSuganthan IasNo ratings yet
- gearless-power-transmission-projectreport-200113070417Document37 pagesgearless-power-transmission-projectreport-200113070417Abhay AwariNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document8 pagesLab 1Mansoob BukhariNo ratings yet
- Bme - Part 2Document44 pagesBme - Part 2Sumanth ChallaNo ratings yet
- Gearless Power Transmission Project ReportDocument37 pagesGearless Power Transmission Project ReportErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pulley and WinchesDocument62 pagesFundamentals of Pulley and WinchesvikasgahlyanNo ratings yet
- Gearless Power Transmission For Skew Shafts (A SRRS Mechanism)Document12 pagesGearless Power Transmission For Skew Shafts (A SRRS Mechanism)चन्दनप्रसादNo ratings yet
- KSRTC Final ReportDocument47 pagesKSRTC Final ReportBoby Thomas100% (1)
- Shu TrsDocument4 pagesShu Trsshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Aadesh Pathare Tom Micro ProjectDocument18 pagesAadesh Pathare Tom Micro ProjectAKASH THORATNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Chain Drive Power Transmission From Stationary To Oscillating DevicesDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Chain Drive Power Transmission From Stationary To Oscillating DevicesManoj Karthik KingNo ratings yet
- POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEMSDocument16 pagesPOWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEMSVasudev Gupta100% (1)
- MSBTE Summer 2015 Model AnswersDocument19 pagesMSBTE Summer 2015 Model AnswersDiyaNegiNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis of Steering Mechanism of A CarDocument12 pagesForce Analysis of Steering Mechanism of A Caranon_56220393533% (3)
- Fabrication of Tube Bending MachineDocument8 pagesFabrication of Tube Bending MachineSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing simple differential locking systemDocument8 pagesManufacturing simple differential locking systemKirtiPadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Design and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemDocument6 pagesDesign and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemShashank VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Project Report on Rack and Pinion Gear DesignDocument15 pagesProject Report on Rack and Pinion Gear DesignWaqasNo ratings yet
- IJRMCER vehicle wheel nuts removerDocument6 pagesIJRMCER vehicle wheel nuts removerAnonymous Clyy9N100% (1)
- Study and Design of Constant Velocity Universal Joints: Mini Project Report On TitleDocument21 pagesStudy and Design of Constant Velocity Universal Joints: Mini Project Report On TitleAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Machining Report Gear CuttingDocument15 pagesMachining Report Gear Cuttingمحمد طهNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Battery Operated Vehicle Using Joystick Control For Physically ChallengedDocument6 pagesLow Cost Battery Operated Vehicle Using Joystick Control For Physically Challengederode els erodeNo ratings yet
- Efficient gearless transmission design using elbow mechanismDocument6 pagesEfficient gearless transmission design using elbow mechanismsageetha756No ratings yet
- Gear Train PDFDocument10 pagesGear Train PDFABHIJITNo ratings yet
- Design Transmission Systems CourseDocument23 pagesDesign Transmission Systems CourseSuresh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of a Knuckle Joint Using FEMDocument7 pagesModeling and Analysis of a Knuckle Joint Using FEMVignesan MechNo ratings yet
- Lucky KatiyarDocument49 pagesLucky Katiyardabangg Siddharth mishraNo ratings yet
- Fesfsd DSFSD FdsDocument6 pagesFesfsd DSFSD Fdssscbemech90.backup01No ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of Spur Gear by Using Different Materials: A ReviewDocument9 pagesStress Analysis of Spur Gear by Using Different Materials: A Reviewafaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument58 pagesGearsapi-238832008100% (3)
- IJRPR23502Document4 pagesIJRPR23502Dharmaraj kisan KharpadeNo ratings yet
- Gearless Transmission SeminarDocument21 pagesGearless Transmission Seminarutkarsh67% (3)
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Performance-Based Gear Metrology: Kinematic - Transmission - Error Computation and DiagnosisFrom EverandPerformance-Based Gear Metrology: Kinematic - Transmission - Error Computation and DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Wood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingFrom EverandWood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingNo ratings yet
- Alignment Cooling Water Pump 4A: Halaman: 1 Dari 1 HalamanDocument3 pagesAlignment Cooling Water Pump 4A: Halaman: 1 Dari 1 Halamanpemeliharaan.turbin03No ratings yet
- The 7 Cs of CommunicationDocument10 pagesThe 7 Cs of CommunicationNauman Mashwani100% (1)
- Revision Question 2023.11.21Document5 pagesRevision Question 2023.11.21rbaambaNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10Document30 pagesSpecifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10ashrafNo ratings yet
- Components in Action Script 2.0 UNIT 3Document4 pagesComponents in Action Script 2.0 UNIT 3k.nagendraNo ratings yet
- CAT Álogo de Peças de Reposi ÇÃO: Trator 6125JDocument636 pagesCAT Álogo de Peças de Reposi ÇÃO: Trator 6125Jmussi oficinaNo ratings yet
- Noam Chomsky Propaganda Modela Critical EvaluationDocument24 pagesNoam Chomsky Propaganda Modela Critical Evaluationsatyanarayana vuyyapuNo ratings yet
- @airbus: Component Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Part ListDocument458 pages@airbus: Component Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Part Listjoker hotNo ratings yet
- PSK Lab ManualDocument4 pagesPSK Lab ManualSakshi DewadeNo ratings yet
- Bosley Declaration - FTC VemmaDocument69 pagesBosley Declaration - FTC VemmaThompson BurtonNo ratings yet
- Cereal Partners World Wide (Case Presentation)Document42 pagesCereal Partners World Wide (Case Presentation)Misbah JamilNo ratings yet
- Bank AlfalahDocument62 pagesBank AlfalahMuhammed Siddiq KhanNo ratings yet
- BS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Document46 pagesBS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Shaiful ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document2 pagesModule 7prof_ktNo ratings yet
- Agency Certificate of Compliance: IGHRS Update As of June 30, 2022Document2 pagesAgency Certificate of Compliance: IGHRS Update As of June 30, 2022Dacanay RexNo ratings yet
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540No ratings yet
- Service Level ManagementDocument8 pagesService Level Managementrashmib1980No ratings yet
- The Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13Document20 pagesThe Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13Yến Ngô HoàngNo ratings yet
- Remedy Shortcut Keys: Home Solutions & Services Products Partners Support Education ConnectDocument2 pagesRemedy Shortcut Keys: Home Solutions & Services Products Partners Support Education Connectaert5683No ratings yet
- PT Jayatama 1Document4 pagesPT Jayatama 1afriza zuniaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Design of Ring Footing For Oil Storage Steel TankDocument6 pagesA Case Study On Design of Ring Footing For Oil Storage Steel Tankknight1729No ratings yet
- Project Report On PepsiDocument87 pagesProject Report On PepsiPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Brushed Axial Fans: VA85-A101-96A Performance DiagramDocument3 pagesBrushed Axial Fans: VA85-A101-96A Performance DiagramJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Only PandasDocument8 pagesOnly PandasJyotirmay SahuNo ratings yet
- Jabra Evolve 40: More Than Headsets, A Workplace EvolutionDocument1 pageJabra Evolve 40: More Than Headsets, A Workplace EvolutionSloba87No ratings yet
- Basics of Directional-Control ValvesDocument11 pagesBasics of Directional-Control ValvesJosh LeBlancNo ratings yet
- Marie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th GradeDocument50 pagesMarie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th Gradeluiz carvalhoNo ratings yet
- 18mba0044 SCM Da2Document4 pages18mba0044 SCM Da2Prabhu ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- SMB GistDocument7 pagesSMB GistN. R. BhartiNo ratings yet
- Why Delegate Authority and Empower EmployeesDocument5 pagesWhy Delegate Authority and Empower EmployeesHarold MaribojocNo ratings yet