Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Simplied Example of Littlefield Game 1
Uploaded by
David LeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Simplied Example of Littlefield Game 1
Uploaded by
David LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
WHITE
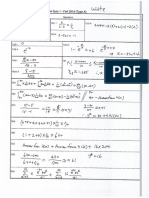
4. (25 points) Recall that the Littlefield game has three stations. Each job is processed in Station 1 and
proceeds to Station 2 for the 1st test. Then a job is processed in Station 3 and sent back to Station 2
for the final test. After the test is done, the job finally leaves the system. Each station has a waiting
area with infinite capacity in front of the service area. Jobs arrive with rate 10 jobs per day to Station
1. After simulating the system for 200 days, the following statistics were reported:
Station 1
Station 2
Station 3
average number of jobs waiting in queue
3
5
1.5
number of servers
3
2
4
utilization
0.5
0.9
0.8
(a) (5 points) Is this system stable? Why or why not? If you think we do not have sufficient
information to answer the question, then write need more information.
Yes, because at each station is less than 1 and `q at each station is finite.
(b) (5 points) What is the arrival rate of jobs to Station 2?
Station 2 has arrivals from Station 1 with rate 10/day and there are also jobs returning to Station
2 from Station 3 with rate 10/day. In total, the arrival rate of Station 2 is 20 jobs per day.
(c) (10 points) What is the average total number of jobs in the system? A numerical answer is
expected.
`total = 3 + 3(0.5) + 5 + 2(0.9) + 1.5 + 4(0.8) = 3 + 1.5 + 5 + 1.8 + 1.5 + 3.2 = 16 jobs.
(d) (5 points) What is the average total system time in days for a job (time from arrival to the system
until departure from the system)? A numerical answer is expected.
wtotal =
`total
16
=
= 1.6 days.
10
5. (3 points) The Goal explains how to manage bottlenecks. Which of the followings is not recommended
in the book to manage bottlenecks? (d)
(a) Perform quality inspection before the bottleneck to improve bottleneck yields.
(b) Maintain a buffer inventory in front of the bottleneck so that it is never starved.
(c) Reduce bottleneck setup time.
(d) Release jobs faster than the bottleneck throughput rate.
Turn to the next page for a bonus question.
You might also like
- Fall15Midterm1 Sol PDFDocument6 pagesFall15Midterm1 Sol PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Motivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDocument28 pagesMotivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Motivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDocument28 pagesMotivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Ztable PDFDocument1 pageZtable PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- TeamRegistrationb PDFDocument2 pagesTeamRegistrationb PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- 1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDocument23 pages1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide to R SimulationDocument4 pagesQuick Guide to R SimulationDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t2Fall2014A PDFDocument4 pagest2Fall2014A PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- T1spring2013key PDFDocument2 pagesT1spring2013key PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- T2fall2014b PDFDocument6 pagesT2fall2014b PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t1Fall2014A PDFDocument5 pagest1Fall2014A PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t1Spring2013A PDFDocument6 pagest1Spring2013A PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t2Fall2013A PDFDocument7 pagest2Fall2013A PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t1Fall2014Keys PDFDocument2 pagest1Fall2014Keys PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Spring15Midterm1 PDFDocument6 pagesSpring15Midterm1 PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t1Fall2014Keys PDFDocument2 pagest1Fall2014Keys PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- t1Fall2013A PDFDocument6 pagest1Fall2013A PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- ISYE 3232C Quiz 6 Production Line AnalysisDocument2 pagesISYE 3232C Quiz 6 Production Line AnalysisDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Spring15Midterm2 PDFDocument8 pagesSpring15Midterm2 PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Spring15Midterm1 Sol PDFDocument20 pagesSpring15Midterm1 Sol PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz3Solution PDFDocument1 pageQuiz3Solution PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- ISYE 3232C Spring 2015 Quiz 5 - Solutions: Fall 7Document3 pagesISYE 3232C Spring 2015 Quiz 5 - Solutions: Fall 7David LeeNo ratings yet
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 13Document1 pageISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 13David LeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz10Solution PDFDocument1 pageQuiz10Solution PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz11Solution PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz11Solution PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 9 Honor CodeDocument2 pagesISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 9 Honor CodeDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 2Document1 pageISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 2David LeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz5Solution PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz5Solution PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz2Solution PDFDocument1 pageQuiz2Solution PDFDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)