Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation: Course Offered by
Uploaded by
emiliaroslan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesThis document provides an overview of four geometric transformations: translation, reflection, dilation, and rotation. It defines each transformation, provides examples of how to perform each one, and includes example problems applying the different transformations to geometric shapes. The document is from an online math course on geometric transformations taught by the e-learning company Winpossible.
Original Description:
TRANSLATION
Original Title
Translation Reflectiondilation 100305195532 Phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of four geometric transformations: translation, reflection, dilation, and rotation. It defines each transformation, provides examples of how to perform each one, and includes example problems applying the different transformations to geometric shapes. The document is from an online math course on geometric transformations taught by the e-learning company Winpossible.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesTranslation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation: Course Offered by
Uploaded by
emiliaroslanThis document provides an overview of four geometric transformations: translation, reflection, dilation, and rotation. It defines each transformation, provides examples of how to perform each one, and includes example problems applying the different transformations to geometric shapes. The document is from an online math course on geometric transformations taught by the e-learning company Winpossible.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation
course offered by
www.winpossible.com
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation
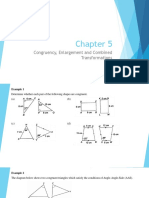
Translation
A transformation in which a geometric figure is moved to another location without
any change in size or orientation. Every translated figure, called the image of the
original figure, is congruent to original figure.
Example:
before translation
after translation
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
In the translation means ABC to ABC,
A
B
Point A has moved to A
Point B has moved to B
Point C has moved to C
A
AA = BB = CC and AA || BB || CC
ABC ABC
C
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
A translation has a horizontal component and a vertical component. If movement
with respect to the x-axis is l units and movement with respected to the y-axis is m
units, then for any point A(x, y), its coordinates become A(x + l, y + m).
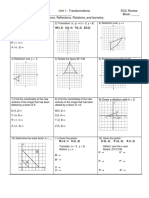
Example: Translate ABC, 6 units left and 6 units down.
5
y
A (3, 4)
B
(5, 3)
3
2
1
-5 -4
-3 -2 -1
A (-3, -2)
(-5, -5)
C
C (1, 1)
1 2
-1
-2
-3
B (-1, -3)
-4
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
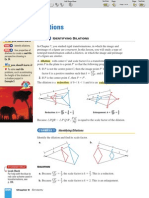
Reflection
A transformation in which a geometric figure is reflected across a line, creating a
mirror image. The line is called the line of reflection.
Example:
Axis of reflection
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
B
A A
C
k
A is fixed point on line of reflection.
B is reflection of B in line k(B
B)
C is reflection of C in line k(C
C)
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Reflection in a vertical line:
Reflection in a horizontal line:
Reflection in a diagonal line:
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Reflection in the x axis
The x coordinates are the same and the y coordinates are the opposite.
5
4
y
A (1, 3)
3
C(3, 2)
2
1
-5
-4
-3
-2 -1
-1
-2
-3
-4
B (1, 1)
1
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Reflection in the y axis
The y coordinates are the same and the x coordinates are the opposite.
y
4
A (-1, 3)
3
1
B (-1, 1)
-4
C(5, 2)
C (-5, -2)
-5
A (1, 3)
-3
-2 -1
-1
-2
-3
-4
B (1, 1)
1
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Dilation
A transformation in which a figure is enlarged or reduced with respect to a point
called the center of dilation.
Dilation of a Geometric Figure
A transformation in which all dimensions are lengthened or shortened by a common
scale factor.
C
The smaller figure above is dilated with a scale factor of 2 and a center of dilation C
to produce the larger figure.
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Rotation
A transformation in which a figure is rotated around a given point called the center
of rotation by a specified degree measure in a specified direction.
Example:
before rotation
angle of rotation = 90 clockwise
after rotation
center
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
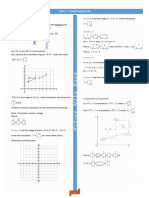
Example:
Translate the triangle 4 units left and 5 units down.
5 y
A (2, 4)
4
C(5, 5)
3
2
1
-5 -4
-3
-2 -1
-1
-2
-3
-4
B (3, 1)
1
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
If the image of point C(0, -12) under a translation is C'(-5, -9), find the coordinates
of the image of point E(7, -8) under the same translation.
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
Find the images of points A(2, 3), B(-5, 2) and C(-1, 4) after a reflection in the
x-axis.
y
(-1, 4) C
4
A(2, 3)
3
B(-5, 2)
2
1
-5 -4
-3 -2 -1
-1
-2
-3
-4
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
Triangle ABC has coordinates A(-2, 0), B(6, 0), and C(4, 0). Find the coordinates of
the images of the vertices of the triangle after a reflection in the y-axis.
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
After a reflection in the x-axis, (10, -3) is the image of point E. What is the
original location of point E?
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
After a dilation, (45, 0) are the coordinates of the image of a point with
coordinates (5, 0). What are the coordinates of the image of (10, 25) after the
same dilation?
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
Translate the triangle 1 unit right and 3 units up, then rotate the image 180
clockwise about the origin.
y
8
6
4
2
-10 -8
-6 -4 -2
-2
-4
-6
-8
10 x
Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation (continued)
Example:
Rotate the triangle in the figure 90 clockwise about the origin.
y
8
6
4
2
-10 -8
-6 -4 -2
-2
-4
-6
-8
10 x
Winpossible is a rapidly growing e-learning company based in California and New
York. Winpossible's math courses employ its patented ChalkTalk method or unique
ChalkTalkTM technology for presenting clear explanations on solving hundreds of
problems of varying levels of difficulty. Our methodology helps accurately diagnose
students performance levels, and allows them to focus content that is most relevant
to them. For more info, lots of free content, access to free math-homework help
and lots more on high-school math, please visit: www.winpossible.com
You might also like
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Unit2 5.2.1 and 5.2.2Document44 pagesUnit2 5.2.1 and 5.2.2Mrs. LaraNo ratings yet
- Transformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementDocument23 pagesTransformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementmangimanNo ratings yet
- Transformations Cont.Document17 pagesTransformations Cont.mfaganNo ratings yet
- MCQ CAD Unit 1Document9 pagesMCQ CAD Unit 1kapil bhoi100% (1)
- Chapter 5 TransformationsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 TransformationsDalia Al-dairyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Transformations of The Euclidean PlaneDocument14 pagesChapter 5 Transformations of The Euclidean PlaneLitoy ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document30 pagesUnit 4api-525019368No ratings yet
- Composite TransformationsDocument11 pagesComposite TransformationsPushpender AttalNo ratings yet
- Transformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217Document17 pagesTransformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217WaniAimiNo ratings yet
- Matrix TransformDocument8 pagesMatrix TransformJ Christopher ClementNo ratings yet
- Rotation & DilationDocument29 pagesRotation & DilationMuhammad Ribhi MurobbiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes On Transformation-1Document40 pagesTeaching Notes On Transformation-1kaykampamba9No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - TransformationDocument19 pagesWorksheet 2 - TransformationShnia RodneyNo ratings yet
- Transformation NotesDocument20 pagesTransformation NotesbiancaNo ratings yet
- Composition of TransformationsDocument4 pagesComposition of TransformationsSherlyn Amado-RosasNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Transformations in The Coordinate PlaneDocument23 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Transformations in The Coordinate PlanehNo ratings yet
- Transformations in Geometry: By: Mathryn Obligado and Reshel Ladio BSED - Mathematics 2Document59 pagesTransformations in Geometry: By: Mathryn Obligado and Reshel Ladio BSED - Mathematics 2Reshel LadioNo ratings yet
- CG MCQDocument38 pagesCG MCQsuraj rautNo ratings yet
- Geometry-HS-V2-Workbook GéometrieDocument79 pagesGeometry-HS-V2-Workbook GéometrieJulie Bergeron-AllardNo ratings yet
- TransformationDocument1 pageTransformationpop0008No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Transformations "Translations"Document139 pagesUnit 1: Transformations "Translations"ARNOLD NOVEMRINo ratings yet
- Isometries, Orientation, and Other Properties:: Vocabulary To MemorizeDocument2 pagesIsometries, Orientation, and Other Properties:: Vocabulary To MemorizeScent CemoNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics 2D TranslationDocument6 pagesComputer Graphics 2D TranslationSample UseNo ratings yet
- 2345unit11geometrynotes TransformationalgeometryDocument24 pages2345unit11geometrynotes Transformationalgeometryapi-326933003No ratings yet
- Cad MCQ 2Document138 pagesCad MCQ 2Taha Bin ZubairNo ratings yet
- Cim 23.6Document81 pagesCim 23.6RajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Geometry CGT.5.G.7cDocument3 pagesGeometry CGT.5.G.7cJames BorNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Question BankDocument4 pagesComputer Graphics Question BankEr Sachin ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry 12-2Document21 pagesGeometry 12-2yaneth calderonNo ratings yet
- 9-4 Compositions of TransformationsDocument59 pages9-4 Compositions of Transformationsakbarali khanNo ratings yet
- Transformations Study GuideDocument3 pagesTransformations Study GuidecrystalMorgan123No ratings yet
- Subject:-Computer Graphics Objective Type Questions Unit-IIIDocument18 pagesSubject:-Computer Graphics Objective Type Questions Unit-IIISE 18 Ganesh pawarNo ratings yet
- Transformations - Practice Problems For CADDocument6 pagesTransformations - Practice Problems For CADbinduNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1pankaj12345katreNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 - Aim 12 10HDocument7 pagesMod 1 - Aim 12 10HShubham TelrandheNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous TransformDocument10 pagesHomogeneous TransformAaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Final Transfomation NotesDocument36 pagesFinal Transfomation Notesnontobekosibanda62No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document51 pagesChapter 3Teze TadeNo ratings yet
- CG 3Document10 pagesCG 3sefefe hunegnawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 II Transformations III (1) ENRICHDocument16 pagesChapter 12 II Transformations III (1) ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- 7.5glide Reflections CompositionsDocument10 pages7.5glide Reflections CompositionsŽygimantas GriciusNo ratings yet
- Transformations I & II: Institut Perguruan Persekutuan Pulau Pinang (I4P)Document40 pagesTransformations I & II: Institut Perguruan Persekutuan Pulau Pinang (I4P)mkijamilNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - 2D Transformations - 1Document91 pagesModule 3 - 2D Transformations - 1Rajeswari RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 解析几何(AMC10)Document18 pagesChapter 2 解析几何(AMC10)Xuemei zhangNo ratings yet
- ???2-D, 3-D Transformations and ProjectionsDocument44 pages???2-D, 3-D Transformations and ProjectionsROHAN PATILNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GraphicsDocument37 pagesChapter Five GraphicswalelegneNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument34 pagesReflectionSalsabila FitriNo ratings yet
- LinearTransformations PDFDocument8 pagesLinearTransformations PDFCorneliusNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Part - IDocument55 pagesUnit 2 - Part - IVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Part - IDocument55 pagesUnit 2 - Part - IVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CG Exp5 C28Document24 pagesCG Exp5 C28Prathmesh GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four 4. TransformationsDocument14 pagesChapter Four 4. TransformationsmazengiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Transformations Eoc Review 2018Document3 pagesUnit 1 Transformations Eoc Review 2018clara.hyun.baeNo ratings yet
- GR 12 l10 Transformation1Document11 pagesGR 12 l10 Transformation1Njabulo DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Transformations IDocument19 pagesThree Dimensional Transformations IروابيNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Solutions: D. Transformations (25 Points)Document2 pagesMidterm Exam: Solutions: D. Transformations (25 Points)masyuki2002No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument20 pagesVectorsMuhammad ShamoeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 4 PDFirusha100% (1)
- Formulae: Mathematics Form 2 Standardised Test 1: Circles Duration: 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesFormulae: Mathematics Form 2 Standardised Test 1: Circles Duration: 30 MinutesemiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Index and LogDocument5 pagesIndex and LogemiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- (A) State Whether Each of The Following Statement Is True or False. (I) 7 X 7 X 7 X 7 X 7 X 7Document7 pages(A) State Whether Each of The Following Statement Is True or False. (I) 7 X 7 X 7 X 7 X 7 X 7emiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Directed Numbers: Emilia Roslan 1Document17 pagesDirected Numbers: Emilia Roslan 1emiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Airil AhmadDocument97 pagesAiril AhmademiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Thursday, August 25, 2016: Airil AhmadDocument64 pagesThursday, August 25, 2016: Airil AhmademiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: MRSM Lenggong Class: NameDocument9 pagesPaper 1: MRSM Lenggong Class: NameemiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- IT6501 Notes PDFDocument109 pagesIT6501 Notes PDFsowrishalNo ratings yet
- Lab - Manual - CG FinalDocument60 pagesLab - Manual - CG FinalShreyas ChateNo ratings yet
- Cim 23.6Document81 pagesCim 23.6RajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Geometric Transformation-2D UpdatedDocument57 pagesGeometric Transformation-2D Updatedzain javaidNo ratings yet
- Transformation - 2DDocument93 pagesTransformation - 2DKashika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument81 pagesIntroduction To CAD/CAMTafesse100% (6)
- 2D Transformation: Prepared By-Deep Tank (160110116052) Kishan Thakur (160110116054) Harshal Dankhara (160110116064)Document17 pages2D Transformation: Prepared By-Deep Tank (160110116052) Kishan Thakur (160110116054) Harshal Dankhara (160110116064)Lak HinsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 2d TransformationDocument18 pagesChapter 2 - 2d TransformationShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 SIGNAL TRANSFORMATION UsmanDocument16 pagesLab 3 SIGNAL TRANSFORMATION UsmanUsman jadoonNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question of Computational GeometryDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Question of Computational GeometryShriya ChalkeNo ratings yet
- 2023-05 Grade BoundariesDocument7 pages2023-05 Grade Boundariessaldoseri939No ratings yet
- 2D - TransformationDocument95 pages2D - TransformationShubhamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 2D and 3D TransformationsDocument35 pagesLecture 6 - 2D and 3D TransformationsFatiNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area After A DilationDocument3 pagesPerimeter and Area After A DilationMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 3Document89 pagesMMW Module 3GersonNo ratings yet
- Geometric TransformationsDocument40 pagesGeometric TransformationsidheivyaNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Geometric TransformationsDocument41 pagesTwo-Dimensional Geometric Transformationsreem goNo ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 06 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 06 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- 2D Transformation PDFDocument11 pages2D Transformation PDFbassam lateefNo ratings yet
- Lectures 9-10: Imaging Geometry and Camera Model: Dr. V MasilamaniDocument37 pagesLectures 9-10: Imaging Geometry and Camera Model: Dr. V MasilamaniPrateek Agrawal100% (1)
- ML Geometry 8-7 DilationsDocument8 pagesML Geometry 8-7 Dilationsashish663No ratings yet
- 2.image GeometryDocument31 pages2.image GeometrySrikanth Goud NagelliNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 2 NotesDocument144 pagesMaths Form 2 NotesHila KipsNo ratings yet
- Math Active Notebook Grade 11 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONDocument12 pagesMath Active Notebook Grade 11 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONahmad athallahNo ratings yet
- How To Resize or Rescale An Autocad Drawing: IssueDocument3 pagesHow To Resize or Rescale An Autocad Drawing: IssueDiether Uera MiclaNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Math - Chapter 5Document21 pagesForm 5 Math - Chapter 5surya vishnuNo ratings yet
- Geometry Flashcards PDFDocument59 pagesGeometry Flashcards PDFsekharsamyNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Question BankDocument4 pagesComputer Graphics Question BankEr Sachin ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides For Signals and Systems-2016-01-25Document896 pagesLecture Slides For Signals and Systems-2016-01-25gantayatNo ratings yet
- Computer-Graphics U3 PDFDocument10 pagesComputer-Graphics U3 PDFMehak KawatraNo ratings yet