Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atm
Uploaded by
Jegan RichardCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atm
Uploaded by
Jegan RichardCopyright:
Available Formats
On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card
with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a uniqu
e card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (
CVV). Authentication is provided by the customer entering a personal identificat
ion number (PIN).
Using an ATM, customers can access their bank deposit or credit accounts in orde
r to make a variety of transactions such as cash withdrawals, check balances, or
credit mobile phones. If the currency being withdrawn from the ATM is different
from that in which the bank account is denominated the money will be converted
at an official exchange rate.
TYPICAL ATM
HARDWARE: An ATM is typically made up of the following devices
CPU (to control the user interface and transaction devices)
Magnetic or chip card reader (to identify the customer)
PIN pad EEP4 (similar in layout to a touch tone or calculator keypad), manufactu
red as part of a secure enclosure
Secure cryptoprocessor, generally within a secure enclosure
Display (used by the customer for performing the transaction)
Function key buttons (usually close to the display) or a touchscreen (used to se
lect the various aspects of the transaction)
Record printer (to provide the customer with a record of the transaction)
Vault (to store the parts of the machinery requiring restricted access)
Housing (for aesthetics and to attach signage to)
Sensors and indicators
SOFTWARE
Today the vast majority of ATMs worldwide use a Microsoft Windows operating syst
em, LINUX primarily Windows XP Professional or Windows XP Embedded.
A small number of deployments may still be running older versions of Windows OS
such as Windows NT, Windows CE, or Windows 2000.
There is a computer industry security view that general public desktop operating
systems(os) have greater risks as operating systems for cash dispensing machine
s than other types of operating systems like (secure) real-time operating system
s (RTOS).
RISKS Digest has many articles about cash machine operating system vulnerabiliti
es.
TYPES & Various kinds of ATM
1.Handheld ATMS Used in remote areas-DENA bank introduced in GUJRAT
2.Mini ATMs POS enabled service with CASH-IN CASH -OUT through IMPS used for pensi
ons , govt schemes , PDS public distributed system
3.MICRO ATMs Used by Bussiness coresspondants ,BC handle physically
4.BIO-METRIC ATMs Rural areas , Used by govt of india
fer), MNREGA scheme
for DBT (direct benefit trans
5.On site ATM -within the premises of bank
6.Off site ATM
Outside the bank premises
7.White Label ATM
Provided by NBFC
8.Green Label ATM
Provided for Agricultural Transaction
9.Orange Label ATM
10.Yellow Label ATM
Provided for Share Transactions
provided for E-commerce
11.PINK label ATM women banking
12.BROWN label ATM ATM are those Automated Teller Machines where hardware and the
lease of the ATM machine is owned by a service provider but cash management and c
onnectivity to banking networks is provided by a sponsor bank .
USES
Although ATMs were originally developed as just cash dispensers, they have evolv
ed to include many other bank-related functions_
Paying routine bills, fees, and taxes (utilities, phone bills, social security,
legal fees, taxes, etc.)
Printing bank statements
Updating passbooks
Cash advances
Cheque Processing Module
Paying (in full or partially) the credit balance on a card linked to a specific
current account.
Transferring money between linked accounts (such as transferring between checkin
g and savings accounts)
Deposit currency recognition, acceptance, and recycling
You might also like
- The Smart Card ReportFrom EverandThe Smart Card ReportWendy AtkinsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- 01 - AtmDocument29 pages01 - AtmKarthiga JanarthananNo ratings yet
- Automated Teller Machine (ATM)Document31 pagesAutomated Teller Machine (ATM)pinkranger-4100% (1)
- ATM Security With RFID and One Time PasswordDocument6 pagesATM Security With RFID and One Time PasswordGR Techno SolutionsNo ratings yet
- ASA 019-23-0001 Potential Remote Code Execution On Opteva TerminalsDocument2 pagesASA 019-23-0001 Potential Remote Code Execution On Opteva TerminalsCatalin Cimpanu [ZDNet]No ratings yet
- NCR ATM Cash Loading Instructions Add - Reset No Rear Counts1Document2 pagesNCR ATM Cash Loading Instructions Add - Reset No Rear Counts1shaukat74No ratings yet
- RFID Payment Card Vulnerabilities Technical ReportDocument6 pagesRFID Payment Card Vulnerabilities Technical Reportgargy2512No ratings yet
- The ATM SystemDocument7 pagesThe ATM Systemmanoum2No ratings yet
- Passwords Stored Using Reversible Encryption - How It Works (Part 1)Document2 pagesPasswords Stored Using Reversible Encryption - How It Works (Part 1)clu5t3rNo ratings yet
- 93.ATM SecurityDocument3 pages93.ATM SecurityAjith manjuNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Atm: BY, Soumya Ranjan Pallai REGD - NO:0701218400 7 SemesterDocument22 pagesSeminar On Atm: BY, Soumya Ranjan Pallai REGD - NO:0701218400 7 SemesterMukesh BholNo ratings yet
- MB1500 Operator ManualDocument172 pagesMB1500 Operator Manualinkpusher4uNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Document21 pagesSeminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Vinod Kumar100% (1)
- Smart CardDocument14 pagesSmart CardPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 3-5-Emv L2Document6 pages3-5-Emv L2Rafael Perez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dispenser Operator GuidDocument24 pagesDispenser Operator GuidbeakalNo ratings yet
- Emv PresentationDocument8 pagesEmv PresentationTarget2009No ratings yet
- Chimene Hamilton Onyeri IndictmentDocument27 pagesChimene Hamilton Onyeri IndictmentkxanwebteamNo ratings yet
- XAC Countertop and Mobile EFTPOS User ManualDocument82 pagesXAC Countertop and Mobile EFTPOS User ManualAaronMulvihillNo ratings yet
- OWASPLondon 20180125leigh Anne Galloway TYunusov Buy Hack ATMDocument57 pagesOWASPLondon 20180125leigh Anne Galloway TYunusov Buy Hack ATMBoby JosephNo ratings yet
- Project Book of AtmDocument35 pagesProject Book of Atmpavan puppalaNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Techniques of Banking Security and ATMsDocument6 pagesStrategies and Techniques of Banking Security and ATMsVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- An Atm With An Eye2Document18 pagesAn Atm With An Eye2Hacker4a4No ratings yet
- ATM Top Tips: Supervisor Mode and Logical Cash OutsDocument2 pagesATM Top Tips: Supervisor Mode and Logical Cash OutsSrinivas Borra100% (1)
- PPT18Document27 pagesPPT18Dev KumarNo ratings yet
- Smart Card ReaderDocument122 pagesSmart Card ReaderLuiz Gustavo100% (1)
- Securing Atm by Image Processing - Facial Recognition AuthenticationDocument4 pagesSecuring Atm by Image Processing - Facial Recognition AuthenticationijsretNo ratings yet
- NCR Atms With Scalable Deposit ModuleDocument9 pagesNCR Atms With Scalable Deposit ModuleAnand Kumar100% (1)
- GSM GuideDocument34 pagesGSM GuideRachelAnneNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 Approved Prepared by Vignesh V Skcet 02.08.2016Document9 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 Approved Prepared by Vignesh V Skcet 02.08.2016vigneshNo ratings yet
- Emv 2011Document43 pagesEmv 2011testdumps12No ratings yet
- Error CodesDocument76 pagesError CodesVenkatesh Ravipati0% (2)
- ATM Malware - A Brief Description PDFDocument2 pagesATM Malware - A Brief Description PDFnishma bhandary100% (1)
- Tap On Phone Implementation Guide Oct2021Document16 pagesTap On Phone Implementation Guide Oct2021Raian DuqueNo ratings yet
- Security Awareness: The Dangers of Using ATM How To Protect Yourself?Document61 pagesSecurity Awareness: The Dangers of Using ATM How To Protect Yourself?chandru_aspNo ratings yet
- 17fin8653 e NCR Selfserv 38 DsDocument2 pages17fin8653 e NCR Selfserv 38 DsAntonio SolisNo ratings yet
- ATM Case Study, Part 1: Object-Oriented Design With The UMLDocument46 pagesATM Case Study, Part 1: Object-Oriented Design With The UMLVaidehiBaporikarNo ratings yet
- Use of Biometrics To Tackle ATM Fraud: Lawan Ahmed MohammedDocument5 pagesUse of Biometrics To Tackle ATM Fraud: Lawan Ahmed MohammedalamsboyNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Smart Information System For Lost ATM CardsDocument3 pagesGSM Based Smart Information System For Lost ATM Cardsadzri_azahariNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument23 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentHitesh BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Currency Printing CriteriaDocument4 pagesCurrency Printing CriteriaeconomistNo ratings yet
- TMD Security Deep Insert Skimming and CPP Overview June 2016Document14 pagesTMD Security Deep Insert Skimming and CPP Overview June 2016rdfv rNo ratings yet
- Immune-Inspired Adaptable Error Detection For Automated Teller MachinesDocument15 pagesImmune-Inspired Adaptable Error Detection For Automated Teller Machinespearllover007No ratings yet
- DU D Unit Question Bank 2018-19Document4 pagesDU D Unit Question Bank 2018-19Rajin Mahmud KhanNo ratings yet
- Pos Machine Security TestingDocument6 pagesPos Machine Security TestingAnkit DNo ratings yet
- Cash Dispenser Device Class Interface - Programmer's ReferenceDocument125 pagesCash Dispenser Device Class Interface - Programmer's ReferenceОлександр СтаровєровNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar On Automatic Teller Machine by Using BiometricsDocument23 pagesTechnical Seminar On Automatic Teller Machine by Using BiometricsNAGMA SULTANANo ratings yet
- Nautilus Hyosung MS500 DownloadDocument3 pagesNautilus Hyosung MS500 DownloadGilbert KamanziNo ratings yet
- EMV v4.1 Book 1 ICC To Terminal InterfaceDocument201 pagesEMV v4.1 Book 1 ICC To Terminal InterfaceLokesh100% (1)
- Basic Model ATM AlarmDocument3 pagesBasic Model ATM AlarmRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Atm EyeDocument9 pagesAtm EyeBirjesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Data Capture:: Bar Code TechnologyDocument22 pagesAutomatic Data Capture:: Bar Code TechnologyVinoth HariNo ratings yet
- Glory RZ 100 Currency RecyclerDocument2 pagesGlory RZ 100 Currency RecyclerAgustin Alonso LasenNo ratings yet
- Use Case Template and ATM ExampleDocument13 pagesUse Case Template and ATM Exampleadil054No ratings yet
- M3000 Mobile POS Terminal. User Guide PDFDocument18 pagesM3000 Mobile POS Terminal. User Guide PDFProgramación VolátilNo ratings yet
- ATM Alarm PanelDocument1 pageATM Alarm PanelgbcsmartNo ratings yet
- Brochure Desgin NCR ATMsDocument2 pagesBrochure Desgin NCR ATMskrishgopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- DisksDocument1 pageDisksJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- Computer ClassificationDocument2 pagesComputer ClassificationJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- Computer ClassificationDocument2 pagesComputer ClassificationJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument2 pagesBudgetJegan RichardNo ratings yet
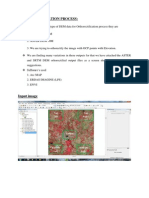
- Orthorectification Process:: Input ImageDocument6 pagesOrthorectification Process:: Input ImageJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- OSDocument2 pagesOSJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- World UTM MapDocument1 pageWorld UTM MapAgustinus Nugroho KarangNo ratings yet
- GIS - Convertin Google Earth KLM To ArcMap SHPDocument4 pagesGIS - Convertin Google Earth KLM To ArcMap SHPJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- Coastal DataDocument133 pagesCoastal DataJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- Timer Based Automatic Power Cutoff For Industrial Sealing Packaging MachinesDocument2 pagesTimer Based Automatic Power Cutoff For Industrial Sealing Packaging Machinesieee4mybusinessonlyNo ratings yet
- Spruhj 1 CDocument482 pagesSpruhj 1 CthietdaucongNo ratings yet
- ps1 1031c 1730 Bom PDFDocument41 pagesps1 1031c 1730 Bom PDFPinopinillo PinoNo ratings yet
- XPS-10 E02 WDocument48 pagesXPS-10 E02 WJaviera EraNo ratings yet
- 8dio Borosilicate Bells Read MeDocument8 pages8dio Borosilicate Bells Read MebizzysgsNo ratings yet
- CVT Pressure TestsDocument18 pagesCVT Pressure TestsاحمدميدوNo ratings yet
- Industrial TrainingDocument34 pagesIndustrial TrainingafiqNo ratings yet
- CNIT 125: Information Security Professional (Cissp Preparation)Document124 pagesCNIT 125: Information Security Professional (Cissp Preparation)subas khanalNo ratings yet
- Real Time KernelsDocument39 pagesReal Time KernelsHamdan Mahat0% (1)
- LH300 SERIES MANUAL EN R2 Web PDFDocument130 pagesLH300 SERIES MANUAL EN R2 Web PDFBaZi Arta Decodificarii DestinuluiNo ratings yet
- B.Suresh Mobile No: +91 9052794134: ExperienceDocument2 pagesB.Suresh Mobile No: +91 9052794134: ExperiencemaniNo ratings yet
- fmd-3200 3300Document10 pagesfmd-3200 3300Jose Julius Paloma Jr.No ratings yet
- Scad500l ManualDocument35 pagesScad500l ManualcsmanienNo ratings yet
- Network and System AdministrationDocument79 pagesNetwork and System AdministrationTsedia TgstuNo ratings yet
- Apple Lesson of The Day - Inventory Is EvilDocument3 pagesApple Lesson of The Day - Inventory Is EvilJennifer JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Tubestand: Operator'S ManualDocument35 pagesTubestand: Operator'S ManualVremedSoluCionesNo ratings yet
- Vortex Pok3r User Manual v1.5Document4 pagesVortex Pok3r User Manual v1.5derelayNo ratings yet
- Eurotherm 620 Vector Series Drive PDFDocument2 pagesEurotherm 620 Vector Series Drive PDFMarkNo ratings yet
- EMC Symmetrix Vmax 10K: Accelerate Transformation To The Hybrid Cloud Download This SlideDocument54 pagesEMC Symmetrix Vmax 10K: Accelerate Transformation To The Hybrid Cloud Download This SlideKaveh VatankhahNo ratings yet
- Manual de Utilização FBs IDocument380 pagesManual de Utilização FBs IstgpereiraNo ratings yet
- Install Mikrotik On GNS3Document11 pagesInstall Mikrotik On GNS3Oscar Andres PeñaNo ratings yet
- Floppy Disk Emulator For Windows User's Manual: ERC, MRC, and XRC ControllerDocument68 pagesFloppy Disk Emulator For Windows User's Manual: ERC, MRC, and XRC ControllerRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Repair Instructions - Off Vehicle Aveo 1.6Document32 pagesRepair Instructions - Off Vehicle Aveo 1.6rectificamos100% (1)
- Dell Inspiron 15 5567 BAL20 LA-D801P Rev 1.0 (A00) SchematicsDocument61 pagesDell Inspiron 15 5567 BAL20 LA-D801P Rev 1.0 (A00) SchematicsFreddy CachumbaNo ratings yet
- CSS10 - Q1 - Module2 - Ronald A. RiguaDocument26 pagesCSS10 - Q1 - Module2 - Ronald A. Riguajoe mark d. manalangNo ratings yet
- FCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1Document38 pagesFCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1cuonglunNo ratings yet
- AECC Basic Computer SkillsDocument118 pagesAECC Basic Computer SkillsAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Jimmy George - Electrical Engineer-ResumeDocument2 pagesJimmy George - Electrical Engineer-ResumeJimmy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocessor For ScientistDocument21 pages8086 Microprocessor For ScientistRam Kishore RoyNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta Bizhub 654e PDFDocument4 pagesKonica Minolta Bizhub 654e PDFanbvn99No ratings yet
- Ben & Jerry's Double-Dip Capitalism: Lead With Your Values and Make Money TooFrom EverandBen & Jerry's Double-Dip Capitalism: Lead With Your Values and Make Money TooRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Getting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorFrom EverandGetting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (63)
- Wall Street Money Machine: New and Incredible Strategies for Cash Flow and Wealth EnhancementFrom EverandWall Street Money Machine: New and Incredible Strategies for Cash Flow and Wealth EnhancementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- How to Win a Merchant Dispute or Fraudulent Chargeback CaseFrom EverandHow to Win a Merchant Dispute or Fraudulent Chargeback CaseNo ratings yet
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- Buffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorFrom EverandBuffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- IFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SASFrom EverandIFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SASRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Introduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsFrom EverandIntroduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- The Startup Visa: U.S. Immigration Visa Guide for Startups and FoundersFrom EverandThe Startup Visa: U.S. Immigration Visa Guide for Startups and FoundersNo ratings yet
- AI For Lawyers: How Artificial Intelligence is Adding Value, Amplifying Expertise, and Transforming CareersFrom EverandAI For Lawyers: How Artificial Intelligence is Adding Value, Amplifying Expertise, and Transforming CareersNo ratings yet
- The Financial Planning Puzzle: Fitting Your Pieces Together to Create Financial FreedomFrom EverandThe Financial Planning Puzzle: Fitting Your Pieces Together to Create Financial FreedomRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Disloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpFrom EverandDisloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (214)
- The Chickenshit Club: Why the Justice Department Fails to Prosecute ExecutivesFrom EverandThe Chickenshit Club: Why the Justice Department Fails to Prosecute ExecutivesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsFrom EverandA Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Contract Law in America: A Social and Economic Case StudyFrom EverandContract Law in America: A Social and Economic Case StudyNo ratings yet
- California Employment Law: An Employer's Guide: Revised and Updated for 2024From EverandCalifornia Employment Law: An Employer's Guide: Revised and Updated for 2024No ratings yet
- Law of Leverage: The Key to Exponential WealthFrom EverandLaw of Leverage: The Key to Exponential WealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- International Trade and FDI: An Advanced Introduction to Regulation and FacilitationFrom EverandInternational Trade and FDI: An Advanced Introduction to Regulation and FacilitationNo ratings yet
- The Real Estate Investing Diet: Harnessing Health Strategies to Build Wealth in Ninety DaysFrom EverandThe Real Estate Investing Diet: Harnessing Health Strategies to Build Wealth in Ninety DaysNo ratings yet