Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Ob
Uploaded by
ednariaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Ob
Uploaded by
ednariaCopyright:
Available Formats
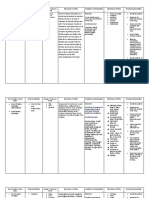
DRUG STUDY
Name of patient: Mrs. M. S .
Age: 48 yrs. old Sex:Female
Diagnosis: Uterine prolapse
Attending Physician: Dr. Kaguyatan
Date Ordered: February 19, 2010
Dose,
Side Effects &
Name of Classificati frequen Mechanism
Indication Contraindication Adverse Nursing Consideration
Drug on cy & of Action
Reaction
route
Generic Nonsteroid 30 mg q Unknown. It is indicated • Contraindicated in CNS: dizziness, • Correct hypovolemia
Name: al anti- 6 hours, produces anti- for short- patient drowsiness, before giving ketorolac.
Ketorolac inflammat IV inflammatory, term hypersensitive to sedation, • Don’t give drug
ory drug analgesic, and treatment of drug and in those epidurally or
headache
antipyretic moderately with active peptic intrathecally because of
Brand effects, severe, acute ulcer disease, GI: nausea, alcohol content.
Name: possibly by pain for recent GI bleeding • Carefully observe
vomiting,
Toradol inhibiting single- dose on p[perforation, patients with
prostaglandin and multiple- advanced renal diarrhea, coagulopathies and
synthesis dose impairment, dyspepsia, GI those taking
treatment cerebrovascular pain, peptic anticoagulants. Drug
bleeding, ulceration, inhibits platelet
hemorrhagic constipation, aggregation and can
diathesis, or flatulence, prolong bleeding time.
incomplete this effect disappears
stomatitis
hemostasis, and within 48 hours of
those at risk for stopping drug and
Hematologic:
renal impairment doesn’t alter platelet
decreased
from volume count, INR, PTT, or PT
platelet,adhesion,
depletion or at risk • NSAIDS may mask
purpura,
of bleeding. signs and symptoms of
prolonged
• Contraindicated as infection because of
bleeding time
Dose,
Side Effects &
Name of Classificati frequen Mechanism
Indication Contraindication Adverse Nursing Consideration
Drug on cy & of Action
Reaction
route
prophylactic their antipyretic and
analgesic before CV: edema, HPN, anti-inflammatory
major surgery or palpitations, actions.
intraopreatively arrhythmias • Serious GI toxicity,
when hemostasis is including peptic ulcers
critical; and in and bleeding, can occur
patients currently in p;atiet taking
receiving aspirin, NSAIDs, despite lack of
an NSAID, or symptoms
probenecid .
DRUG STUDY
Name of patient: Mrs. M. S.
Age: 48 yrs. Old Sex:Female
Diagnosis: Uterine prolapse
Attending Physician: Dr. Kaguyatan
Ordered: February 19, 2010
Dose,
Name of Classifica Mechanism of Contraindicati Side Effects &
frequency Indication Nursing Consideration
Drug tion Action on Adverse Reaction
& route
Generic
Name: Opioid 10mg, IV Unknown. binds Indicated for Contraindicate CNS: headache, • Drugs acts as an
Nalbuphine anlgesic with opiate patient with d in patient sedation, dizziness, opiod antagonist:
receptors in the moderate to hypersensitive vertigo, may cause
CNS, altering severe pain, to this drug. nervousness, withdrawal
Brand
Name: depression,
both perception adjunct to syndrome. For
Nubain restlessness, crying,
of and emotional balance patients who have
confusions,
response to pain anesthesia. hallucinations, received opiates
speech disorders. long term, give 25%
of the usual dose
CV: HPN, initially. Watch for
hypotension, signs of withdrawal.
tachycardia,
• ALERT: drug causes
bradycardia
respiratory
EENT: blurred vision, depression, which at
dry mouth 10 mg is equal to
respiratory
GI: cramps,
depression produced
dyspepsia, bitter
taste, nausea, by 10 mg of
vomiting, morphine.
constipation • PATIENT TEACHING
-Caution ambulatory
GU: urinary urgency patient about getting
Respiratory: out of bed or
respiratory walking.
depression. dyspnea, -Teach patient how
asthma, pulmonary to manage
edema troublesome adverse
Skin: pruritus, effects such as
burning, urticaria, constipation.
diaphoresis .
LABORATORY EXAMINATION
Name of Patient: Mrs. M.S.
Attending Physician: Dr. Kaguyatan
Age: 48y/o
DATE LABORATORY RESULT NORMAL IINTERPRETATIO SIGNIFICANCE
EXAMINATION VALUES N
February 12, CBC
2010
Hemoglobin 113g/ L 135-180g/l Normal To determine the
amount of blood-
carrying oxygen to
tissues and find out
presence of
hemorrhage, in any
form.
Hematocrit 0.36g/l 0.37-0.47g/l Normal
To determine the
presence of
erythrocytosis of any
cause, and in
dehydration or
hemoconcentration
associated with shock.
RBC 4.74X 10g/l 4.0-5.5x10g/l Normal
WBC 9.0x109/L 5.0-10.0x109/L . To determine the
presence of infection or
Normal
inflammation.
Neutrophils 61.1% 50-70% Normal
To determine variation
in the WBC’s
differential count that
may signifies infection
or suppress immune
response.
Lymphocytes 24% 25-40% 25-40%
To determine the
body’s immunologic
response.
Blood type A No normal values ---------------------- For possible transfusion
You might also like
- Methyldopa nursing management for hypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa nursing management for hypertensionRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Obat ObgynDocument8 pagesObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNo ratings yet
- Manage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginDocument2 pagesManage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityKimm Charmaine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPSaira SucgangNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study on CelecoxibDocument11 pagesDrug Study on CelecoxibPrincess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsRebecca JolieNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument2 pagesVitamin KMuvs RazonNo ratings yet
- Calcium AcetateDocument3 pagesCalcium AcetateKIM NAMJOON'S PEACHES & CREAM100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsDocument14 pagesKetorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On METHERGINEDocument4 pagesDrug Study On METHERGINEshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesVii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Managing dextrose therapyDocument2 pagesManaging dextrose therapySanket TelangNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Drug MonographDocument1 pageWarfarin Drug Monographekram100% (1)
- SDL4Document2 pagesSDL4Juviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- Simethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDocument1 pageSimethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Burn - Daily Physical AssessmentDocument8 pagesBurn - Daily Physical AssessmentkrishcelNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocument1 pageFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Biogesic Analgesic AntipyreticDocument8 pagesParacetamol Biogesic Analgesic AntipyreticGian Era100% (1)
- Indications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnDocument1 pageIndications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnTel SisonNo ratings yet
- GanciclovirDocument3 pagesGanciclovirRosher Deliman JanoyanNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreDocument14 pagesAssess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Setraline Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSetraline Drug StudyOtaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Postpartum MothersDocument5 pagesDrug Study For Postpartum MothersnnicakoNo ratings yet
- Albendazol PDFDocument8 pagesAlbendazol PDFDANIBATANo ratings yet
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- PHINMA Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPHINMA Nursing Drug StudyArianne NicoleNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 22Document8 pagesDisaster Nursing SAS Session 22ZiaNo ratings yet
- Medication for Postpartum HemorrhageDocument1 pageMedication for Postpartum HemorrhageclarimerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument14 pagesTB DrugsLexy CadigalNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Delivery: A Reading OnDocument4 pagesCesarean Delivery: A Reading OnAnge MinguitoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyJP2001No ratings yet
- CaffeineDocument2 pagesCaffeineSaini Malkeet100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Essential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careDocument11 pagesEssential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careAngelina Janiya NicoleNo ratings yet
- Module2 Day2 MetaparadigmDocument39 pagesModule2 Day2 MetaparadigmRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsDocument2 pagesKetorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsRona PieNo ratings yet
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- W1inse6220 PDFDocument11 pagesW1inse6220 PDFpicalaNo ratings yet
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemsDocument51 pagesFlexible AC Transmission SystemsPriyanka VedulaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Malik's Farms BrochureDocument18 pagesDr. Malik's Farms BrochureNeil AgshikarNo ratings yet
- StsDocument10 pagesStsSamonte, KimNo ratings yet
- R4 User GuideDocument48 pagesR4 User GuideAaron SmithNo ratings yet
- 99 181471 - Sailor System 6000b 150w Gmdss MFHF - Ec Type Examination Module B - Uk TuvsudDocument6 pages99 181471 - Sailor System 6000b 150w Gmdss MFHF - Ec Type Examination Module B - Uk TuvsudPavankumar PuvvalaNo ratings yet
- Eudragit ReviewDocument16 pagesEudragit ReviewlichenresearchNo ratings yet
- Joyful Living: (Based On Chapter 13: Advaitananda Prakaranam of Panchadashi of Sri Vidyaranya Swami)Document11 pagesJoyful Living: (Based On Chapter 13: Advaitananda Prakaranam of Panchadashi of Sri Vidyaranya Swami)Raja Subramaniyan100% (1)
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument8 pagesAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPearl AdamosNo ratings yet
- EMMS SpecificationsDocument18 pagesEMMS SpecificationsAnonymous dJtVwACc100% (2)
- Universal Robina Co. & Bdo Unibank Inc.: Research PaperDocument25 pagesUniversal Robina Co. & Bdo Unibank Inc.: Research PaperSariephine Grace ArasNo ratings yet
- Main Hoon Na - WikipediaDocument8 pagesMain Hoon Na - WikipediaHusain ChandNo ratings yet
- Overview for Report Designers in 40 CharactersDocument21 pagesOverview for Report Designers in 40 CharacterskashishNo ratings yet
- MVJUSTINIANI - BAFACR16 - INTERIM ASSESSMENT 1 - 3T - AY2022 23 With Answer KeysDocument4 pagesMVJUSTINIANI - BAFACR16 - INTERIM ASSESSMENT 1 - 3T - AY2022 23 With Answer KeysDe Gala ShailynNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument62 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsTeds TV89% (84)
- VNC Function Operation InstructionDocument11 pagesVNC Function Operation InstructionArnaldo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- LLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety TrendsDocument23 pagesLLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety Trendssuvabrata_das01100% (1)
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)Document3 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutenDocument14 pagesElectrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutensecucaNo ratings yet
- Exam Ref AZ 305 Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Sol 2023Document285 pagesExam Ref AZ 305 Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Sol 2023maniNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus: Performance TaskDocument6 pagesBasic Calculus: Performance TasksammyNo ratings yet
- SQL 1: Basic Statements: Yufei TaoDocument24 pagesSQL 1: Basic Statements: Yufei TaoHui Ka HoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Attainment.Document6 pagesLevels of Attainment.rajeshbarasaraNo ratings yet
- EE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument23 pagesEE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherMirza Azhar HaseebNo ratings yet
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- VARCDocument52 pagesVARCCharlie GoyalNo ratings yet
- Conserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyDocument4 pagesConserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyErden SizgekNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportHugsNo ratings yet
- Using Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysDocument12 pagesUsing Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysVo TinhNo ratings yet
- Learning Online: Veletsianos, GeorgeDocument11 pagesLearning Online: Veletsianos, GeorgePsico XavierNo ratings yet