Professional Documents
Culture Documents
852 Topper 21 116 1 4 7205 Moving Objects Up201507231544 1437646441 3319
Uploaded by
Mansi Kakani BurhadeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
852 Topper 21 116 1 4 7205 Moving Objects Up201507231544 1437646441 3319
Uploaded by
Mansi Kakani BurhadeCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS MOVING OBJECTS
Moving Objects
Motion of an object
If the position of an object does not change with respect to its surroundings as time passes, then it is
said to be at rest. If the position of an object changes as time passes, then it is said to be in motion.
An object can be at rest with respect to one thing and in motion with respect to another at the same
time. So, states of rest and motion are relative only.
Displacement and Velocity
The distance travelled by an object is the length of the actual path traversed by the object during
motion. It is a scalar quantity.
The displacement of an object in motion is the shortest distance between the initial position and final
position of the object. It is a vector quantity.
The distance travelled by an object in motion can never be zero or negative. The displacement of an
object can be positive, zero or negative. In no case, distance travelled can be less than the
displacement.
Both distance and displacement have the same units.
Speed of a body is defined as the distance travelled by the body in unit time. The SI unit of speed is
metre/second (m/s).
Speed
www.topperlearning.com
Distance travelled
Time taken
PHYSICS MOVING OBJECTS
Velocity of a body is defined as the distance travelled by the body in unit time in a given direction. The
SI unit of velocity is the same as that of speed, i.e. metre/second (m/s).
Displacement
Velocity
Time taken
Velocity and speed have the same unit.
Velocity of an object can be changed in the following ways as listed below:
o Changing the speed and keeping the direction same.
o Changing the direction and keeping speed constant.
o Changing the speed as well as the direction of motion.
Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion along Straight Line
An object is said to be in uniform motion if it travels equal distances in equal intervals of time,
howsoever small the intervals may be.
An object is said to have non-uniform motion if it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Acceleration
Acceleration of a body is defined as the rate of change of its velocity with time.
Change in velocity
Acceleration
Time taken
Final velocity - Initial velocity
Time taken
or,
v -u
t
A body is said to possess uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and its velocity increases
by equal amounts in equal intervals of time.
A body is said to possess non-uniform acceleration if its velocity changes by unequal amounts in
equal intervals of time.
www.topperlearning.com
PHYSICS MOVING OBJECTS
DistanceTime Graphs for Uniform and Uniformly Accelerated
Motion
The distancetime graph of a body in uniform motion is a straight line.
Speed of a body is given by the slope of the distancetime graph.
Distance travelled
Speed
Time taken
AB
v
OB
The distancetime graph of a body in non-uniform motion is a curved line with a variable slope
indicating variable speed.
www.topperlearning.com
PHYSICS MOVING OBJECTS
VelocityTime Graph for Uniform Motion
The velocitytime graph of a body moving with uniform velocity is a straight line parallel to the time
axis.
o The magnitude of displacement or distance travelled by the body is equal to the area
enclosed by the velocitytime graph and time axis.
Distance travelled = Speed Time taken
= OA OC
= Area of rectangle OABC
VelocityTime Graph for Uniformly Accelerated Motion
The velocitytime graph of a body moving with uniform acceleration is a straight line inclined to the
time axis.
www.topperlearning.com
PHYSICS MOVING OBJECTS
o The slope of the velocitytime graph represents the acceleration of the body.
i. Acceleration
Change in speed
Time taken
PQ
OQ
o The area enclosed by the velocitytime graph and time axis gives the distance travelled by
the body.
Distance travelled = Area of triangle OPQ
=
1
OQ PQ
2
Equations of Motion
The three equations of motion of a body moving along a straight line with uniform acceleration are
v u at
1 2
at
2
v 2 u2 2as
s ut
Where u is initial velocity of the object which moves with uniform acceleration a for time t, v is final
velocity and s is distance travelled by the body in time t.
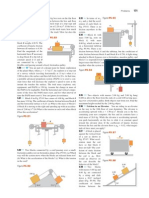
Uniform Circular Motion
When a body moves along a circular path with a uniform speed, its motion is called uniform circular
motion.
In uniform circular motion, although the speed remains constant, the direction of motion and velocity
change continuously. Thus, uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion.
The external force needed to make a body travel in a circular path is known as centripetal force.
The circumference of a circle of radius r is given by 2r. If a body takes t seconds to go once round the
circular path of radius r, then its speed v is given by
v
2r
t
www.topperlearning.com
You might also like
- Savitribai Phule Pune University UG Credit System RulesDocument11 pagesSavitribai Phule Pune University UG Credit System RulesMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- 823 Topper 21 116 1 1 7220 Life Simple and Complex Up201507231533 1437645790 7855Document13 pages823 Topper 21 116 1 1 7220 Life Simple and Complex Up201507231533 1437645790 7855Mansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment: A Guide to Primary, Secondary and Tertiary ProcessesDocument50 pagesWaste Water Treatment: A Guide to Primary, Secondary and Tertiary ProcessesMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Wastes Rules 2000 SummaryDocument31 pagesMunicipal Solid Wastes Rules 2000 SummarySarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Ehp 1307864 PDFDocument25 pagesEhp 1307864 PDFMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- 820 Topper 21 116 1 1 682 Cell The Unit of Life Up201507231524 1437645241 5531Document8 pages820 Topper 21 116 1 1 682 Cell The Unit of Life Up201507231524 1437645241 5531Mansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- CTC 450 Review: Guide to Stabilization Pond ProcessesDocument12 pagesCTC 450 Review: Guide to Stabilization Pond ProcessesMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- First Stage PresentationDocument23 pagesFirst Stage PresentationMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- T.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusDocument26 pagesT.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusHamidullah TotakhailNo ratings yet
- 853 Topper 21 116 1 4 7206 The Laws of Motion Up201507231545 1437646501 2479Document4 pages853 Topper 21 116 1 4 7206 The Laws of Motion Up201507231545 1437646501 2479Mansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- T.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusDocument26 pagesT.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusHamidullah TotakhailNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 Fluid Dynamics and Kinematics by Stephanie The Saylor MechanicDocument11 pagesUnit 02 Fluid Dynamics and Kinematics by Stephanie The Saylor MechanicMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- 851 Topper 21 116 1 4 7209 Energy The Driving Force Up201507231543 1437646395 3746Document5 pages851 Topper 21 116 1 4 7209 Energy The Driving Force Up201507231543 1437646395 3746Mansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- T.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusDocument26 pagesT.E.civil 2012 Course SyllabusHamidullah TotakhailNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering 27-5-13Document39 pagesCivil Engineering 27-5-13Mansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- 200 Questions and Answers On Practical Civil Engineering Works 2008Document84 pages200 Questions and Answers On Practical Civil Engineering Works 2008ramdj100% (4)
- MCQ 1 2 ExampleDocument1 pageMCQ 1 2 ExampleMusa Al-ShammaryNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 Finite and Differential Control Volume Analysis by TheDocument10 pagesUnit 03 Finite and Differential Control Volume Analysis by TheMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- Surveying Method Chosen Depends On:: - by The Purpose of The Survey E.G. Map MakingDocument27 pagesSurveying Method Chosen Depends On:: - by The Purpose of The Survey E.G. Map MakingAyaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- BUILDING MATERIALSDocument20 pagesBUILDING MATERIALSMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Introduction To Fluid Statics and Flow Phenomena by TheDocument16 pagesUnit 01 Introduction To Fluid Statics and Flow Phenomena by TheMansi Kakani BurhadeNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- General Physics ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerXyrell Claude Monta100% (1)
- Kinesiology MCQ PDFDocument6 pagesKinesiology MCQ PDFHasan Rahman79% (14)
- Eng Physics Notes 9thDocument22 pagesEng Physics Notes 9thNeelam ZahraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic FieldsAnonymous JnvCyu85No ratings yet
- Manual Balanza Ohaus NavigatorDocument104 pagesManual Balanza Ohaus NavigatorJuanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS REVIEWER 1st ACHIEVEMENT TESTDocument1 pagePHYSICS REVIEWER 1st ACHIEVEMENT TESTRhanessa Banacia NordanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field (12.02.14)Document21 pagesMagnetic Field (12.02.14)Rajaganapathi Rajappan100% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- E Sample Paper 5Document34 pagesE Sample Paper 5OscarNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 4 - Module 3: Momentum and Impulse Conservation of MomentumDocument15 pagesScience Quarter 4 - Module 3: Momentum and Impulse Conservation of MomentumAllison RoqueNo ratings yet
- Asae+s269 (2) 4+dec96 PDFDocument3 pagesAsae+s269 (2) 4+dec96 PDFMuhammad RochimNo ratings yet
- School Nutrition Report SummaryDocument27 pagesSchool Nutrition Report SummaryCecille AnnNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument74 pagesEngineering MechanicsNikki Lorraine DelenNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument13 pagesElectrostaticssjo0567% (3)
- Self-Test Exercises 1.1 Atoms & Molecules: 8 Relative No of IonsDocument2 pagesSelf-Test Exercises 1.1 Atoms & Molecules: 8 Relative No of IonsNor AfidahNo ratings yet
- ENGR 202 Evaluation and Presentation of Experimental Data II Beam Calibration and PerformanceDocument18 pagesENGR 202 Evaluation and Presentation of Experimental Data II Beam Calibration and PerformanceTom FoneNo ratings yet
- Water Bottle Flipping PhysicsDocument8 pagesWater Bottle Flipping Physicsanon_734398465No ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rectilinear MotionDocument20 pagesKinematics of Rectilinear Motionnithink100No ratings yet
- PHYSICS XI WORK, POWER & ENERGY CHAPTER REVIEWDocument1 pagePHYSICS XI WORK, POWER & ENERGY CHAPTER REVIEWraffia mahakNo ratings yet
- Stability of Floating BodiesDocument15 pagesStability of Floating BodiesKd CaisedoNo ratings yet
- Honors Physics Homework Solutions 5-3Document2 pagesHonors Physics Homework Solutions 5-3allison0kuftaNo ratings yet
- WPH04 01 Pef 20160817Document58 pagesWPH04 01 Pef 20160817Fuwad Abdul MuyeedNo ratings yet
- Test - 1: (Physics)Document56 pagesTest - 1: (Physics)Chandana InguvaNo ratings yet
- Physics 04-Statics, Torque, Rotational Motion (2016)Document46 pagesPhysics 04-Statics, Torque, Rotational Motion (2016)Yash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exampler CH 8 Motion QuestionsDocument8 pagesExampler CH 8 Motion QuestionsCrackneet SuratNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass and Linear MomentumDocument20 pagesCenter of Mass and Linear Momentumsojib yeasinNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeDocument831 pagesCivil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeJohn Carlo SabadoNo ratings yet
- HKPhO 2011 S4 Physics Olympiad SolutionsDocument10 pagesHKPhO 2011 S4 Physics Olympiad SolutionsHoàng ViệtNo ratings yet
- SciGen 8.1 Student PDFDocument23 pagesSciGen 8.1 Student PDFLeonida CabanigNo ratings yet
- 2006 Keiyo District Paper 1Document4 pages2006 Keiyo District Paper 1dkavitiNo ratings yet