Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 17 Notes - The Special Senses
Uploaded by
Nick MaliziaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 17 Notes - The Special Senses
Uploaded by
Nick MaliziaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
Lobes of Cerebrum
Lobe
Sense
Parietal
Gustatory & Tactile
Temporal
Olfactory & Hearing
Occipital
Vision
Frontal
NONE
Gustation: Sense of Taste
o Tongue Taste
Sweet - Saliva
Salty - Saliva
Bitter - Saliva
Sour Circumvallate
o Papillae of Tongue
1. Filiform increase surface area; most abundant; NO taste
buds; used to detect temperature and texture
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
2. Fungiform taste buds on top; sweet, salty, sour
3. Circumvallate (9) large; bitter; taste buds underneath
4. Foliate involved in the sensations of taste and have taste
buds embedded in their surfaces; clustered into two groups
positioned on each side of the tongue
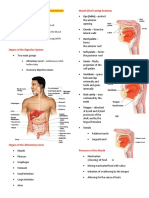
Olfaction: The Sense of Smell
o Smell 20,000x stronger than taste
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
Sense of Hearing
o Anatomy of Ear
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
Ceruminus gland produces cerumen, also known as ear wax.
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear chamber to the
nasopharynx.
Otitis Media - An infection from throat to ear.
Part
Function
Organ
Semicircular canals
Dynamic Equilibrium
Crista Ampularis
Vestibule
Static Equilibrium
Macula
Cochlea
Hearing
Organ of Conti
o Organs are always found on the inner surface of the membranous
labyrinth
Crista Ampullaris
o Dynamic equilibrium your body sensing the fact that your body is in
motion
o Endolymph in semicircular canal; moves, triggering crista ampullaris
o Mechanical energy electrical energy
Movement of cilia electrical energy
Cupula = gelatinous membrane
Macula same as crista ampullaris except the cupula is called the otolithic
membrane
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
o Otoliths present bob through membrane, hit the cilia and detect
gravitational pull
Organ of Corti same as the crista ampullaris except the gelatinous
membrane is called the tectorial membrane
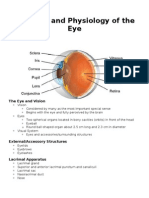
Vision
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
o Anatomy of the eye
3 layers:
o Sclera Outer layer: made of dense connective tissue [very tough] aka
the white of eyes.
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
Cornea
Canal of Schelmm
o Choroid - Middle layer: Melanocytes
Ciliary body smooth muscle
Iris smooth muscle
Consensual reflex stimulate one pupil and the other will be
stimulated as well
Suspensory ligaments
o Retina Inner layer: Neurons
Macula lutea
Fovea centralis
Rods black and white; side of eye (retina)
o Rhodopsin (usual purple) need light to be broken down into scotopsin
and retinine
o Scotopsin and retinine transferred into occipital lobe
Cones - color; back of eye (retina)
o Iodopsin broken down into 26 products
o Energy transferred to occipital lobe
Anterior Cavity: Cornea lens
o Anterior Chamber Cornea iris
o Posterior Chamber iris lens
o Aqueous humor fluid made daily in ciliary body
Gives pressure, has glucose (feeds cells)
Drains into Canal of Schlemm
Posterior Cavity: Lens retina
o Vitreous humor holds the retina in place and up against the choroid
layer
o Occipital lobe translates sight and turns it right side up (lens views
things upside-down)
o Lens is made of collagen
Diseases of the eye:
o Myopia nearsightedness; born with eye too long
Concave lens needed to correct
Chapter 17 The Special Senses
Less bending and refraction of light
o Hypermetropia farsightedness; born with eye too short
Convex lens needed to correct
o Presbyopia elderly sight
Lens loses elasticity and can no longer accommodate
o Glaucoma buildup of aqueous humor made by an over production in
the ciliary body.
o Cataracts disease of the lens
o Astigmatism irregularity of the cornea
Cylindrical (tauric) lens needed to correct
o Vitamin A used to make retinine
Betacarotine
You might also like
- Special SensesDocument9 pagesSpecial SensesTobhyNo ratings yet
- 13 Special SensesDocument77 pages13 Special SensesDarwin Mangabat100% (3)
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial SensesmasorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Study GuideNic Alcala100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnonymous 2k0o6az6lNo ratings yet
- The CerebrumDocument27 pagesThe Cerebrumapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Compilation Medsurg PrelimsDocument29 pagesCompilation Medsurg PrelimsEunice CuñadaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment IntroductionDocument50 pagesHealth Assessment IntroductionEdna Uneta RoblesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ExplainedDocument59 pagesNervous System ExplainedJeremiah Nayosan0% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary SystemJushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemCristinNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuScar Shadow100% (1)
- Central Nervous System PDFDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System PDFbilal officalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumanDocument20 pagesDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183No ratings yet
- The Human Organism ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Human Organism ReviewerAliyah and IomiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBryan Espanol100% (1)
- Framework For Professional PracticeDocument26 pagesFramework For Professional PracticeAdvait GulatiNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2Document4 pagesNCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2christyl necesitoNo ratings yet
- EE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLDocument29 pagesEE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLtmkiran100% (1)
- Quiz Urinary Reproductive 20Document5 pagesQuiz Urinary Reproductive 20estherNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Document13 pagesLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 - Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesChapter 2.1 - Nervous SystemHaizmeer BonzieNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Cellular Basis of Life: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Part 1: CellsDocument26 pagesOverview of The Cellular Basis of Life: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Part 1: CellsHans De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Document36 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Occupational TherapyDocument47 pagesDiploma in Occupational TherapyAzmi Plus100% (2)
- A-P Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument19 pagesA-P Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemMONIQUE VELASCO100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesReproductive SystemAileen Grace Delima100% (1)
- 04 Tissue, Glands and MembranesDocument52 pages04 Tissue, Glands and MembranesBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Course GuideDocument21 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Course GuideMary Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- Assessing Musculoskeletal (MSK) SystemDocument8 pagesAssessing Musculoskeletal (MSK) SystemKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ExplainedDocument4 pagesLymphatic System ExplainedJherhan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - (Skin) Integumentary System Laboratory ExerciseDocument7 pagesAnatomy - (Skin) Integumentary System Laboratory ExerciseTristan Babaylan100% (1)
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocument46 pagesReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- Erman Fandialan M.D. Department of Clinical Neurosciences UermmmcDocument48 pagesErman Fandialan M.D. Department of Clinical Neurosciences Uermmmclovelots1234100% (1)
- Parts and functions of the human respiratory systemDocument43 pagesParts and functions of the human respiratory systemBuuvee BeNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument3 pagesSpecial Senses NotesChelsa LeyritanaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Final 2Document23 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Final 2Exequiel Macalisang Ramientos Jr.No ratings yet
- Group QuestionsDocument7 pagesGroup QuestionsSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Health AssessmentDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Health AssessmentMa. Lou Danielle VallanoNo ratings yet
- Brain Lobes Functions GuideDocument12 pagesBrain Lobes Functions GuideLoccos SienaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument68 pagesTissues, Glands and MembranesMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Overview of The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesLab 6 - Overview of The Skeletal Systemsidro123No ratings yet
- Impulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseDocument9 pagesImpulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseCellina De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Principles and Practices in RehabilitationDocument32 pagesChapter 11 Principles and Practices in RehabilitationPearl DiBerardino100% (1)
- UNIT - 9 Digestive SystemDocument187 pagesUNIT - 9 Digestive SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Quiz 01 - Attempt ReviewDocument13 pagesMuscular System Quiz 01 - Attempt ReviewPsalm Jirehmae SantosNo ratings yet
- CHD 121 Anatomy and Physiology Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCHD 121 Anatomy and Physiology Course Outlinemalenya1No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Part BDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine System: Part BKaly RieNo ratings yet
- Essential Functions of the Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesEssential Functions of the Respiratory SystemEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Nervous System 2011Document33 pagesHistology of The Nervous System 2011Ng Bing JueNo ratings yet
- 06 TestBank TBDocument1,105 pages06 TestBank TBFrozanS17% (6)
- Anatomy Ch. 9 The Senses NotesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Ch. 9 The Senses Notesprincepalestine100% (1)
- Urinary System QuizDocument5 pagesUrinary System QuizCésar AntonioNo ratings yet
- Normal NewbornAssessmentDocument53 pagesNormal NewbornAssessmentMidori SanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves SummaryDocument4 pagesCranial Nerves Summarysahana2791No ratings yet
- Frog DissectionDocument7 pagesFrog DissectionKhairin KhairudinNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY: AN OVERVIEWDocument50 pagesMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY: AN OVERVIEWJoyce Adjei-boateng100% (1)
- General Physiology: First YearDocument67 pagesGeneral Physiology: First YearGo HellNo ratings yet
- The Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesDocument31 pagesThe Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesSarmila Sathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Skenario 2 Saraf & PerilakuDocument30 pagesSkenario 2 Saraf & PerilakuPrima Eriawan PutraNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentDocument35 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- DR Anu Arasu How Trauma Affects Your HormonesDocument14 pagesDR Anu Arasu How Trauma Affects Your HormonesShalu SaharanNo ratings yet
- HXX N3ur0anat0myyDocument29 pagesHXX N3ur0anat0myyLINDSLEY GONo ratings yet
- Peripheral Testosterone MetabolismDocument8 pagesPeripheral Testosterone MetabolismAgung SentosaNo ratings yet
- Brain Herniation SyndromeDocument28 pagesBrain Herniation SyndromeSarahScandy100% (4)
- 3B Arm Model - M11Document28 pages3B Arm Model - M11rswongym449No ratings yet
- TRX Force Tactical Kit - Essential Protein for Cellular ReactionsDocument11 pagesTRX Force Tactical Kit - Essential Protein for Cellular ReactionsRafael FilhoNo ratings yet
- 5096 w09 Ms 2Document7 pages5096 w09 Ms 2Asiff MohammedNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development TheoriesDocument7 pagesGrowth and Development TheoriesMabes100% (1)
- NPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentDocument5 pagesNPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentSnehaNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate HomeostasisDocument2 pagesHeart Rate Homeostasisapi-332478778No ratings yet
- The Tongue of Leopard Gecko (Eublepharis Macularius) LMDocument9 pagesThe Tongue of Leopard Gecko (Eublepharis Macularius) LMSandra Clavero ClopèsNo ratings yet
- ELECTROPHRESISDocument66 pagesELECTROPHRESISM.PRASAD NAIDU100% (1)
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument5 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life CycleGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Standard and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing HandoutDocument17 pagesStandard and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing HandoutDarcyNo ratings yet
- Throwing RehabDocument16 pagesThrowing RehabSean GlynnNo ratings yet
- How Sleep Deprivation Affects Students' Academic PerformanceDocument50 pagesHow Sleep Deprivation Affects Students' Academic PerformanceAstrophile0% (2)
- Neuropathic Painn PDFDocument20 pagesNeuropathic Painn PDFkaktusNo ratings yet
- Journey Through DigestionDocument4 pagesJourney Through DigestionJoy JonesNo ratings yet
- Pedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Document73 pagesPedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Medisina101No ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPbabycheska08No ratings yet
- Sarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemDocument4 pagesSarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemAdvancemicronics MedicalsystemsNo ratings yet
- StomachDocument16 pagesStomachnevelle4667No ratings yet
- Organic Molecules: Chapter 2-3Document33 pagesOrganic Molecules: Chapter 2-3Gissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of FishesDocument18 pagesSkeletal System of FishesYousaf AnwarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Chapter 11: The Pediatric Patient in The Adult Critical Care UnitDocument8 pagesTest Bank Chapter 11: The Pediatric Patient in The Adult Critical Care UnitAnonymous ZzjzIcmNo ratings yet
- Gastric Funcn TestDocument18 pagesGastric Funcn TestArshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Yellow Belt Level 01 - Solution - 0Document2 pagesYellow Belt Level 01 - Solution - 0Jo Marie LeeNo ratings yet