Professional Documents
Culture Documents
025 Ea 7 BD 0 CF 2 Ce 7 F 65 Dafadb
Uploaded by
Rahmad RamadhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
025 Ea 7 BD 0 CF 2 Ce 7 F 65 Dafadb
Uploaded by
Rahmad RamadhanCopyright:
Available Formats
World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 5 (5): 572-576, 2009
ISSN 1817-3047
IDOSI Publications, 2009
Analysis of Phytochemical Constituents and Antimicrobial Activities
of Aloe vera L. Against Clinical Pathogens
S. Arunkumar and M. Muthuselvam
Muthaiyah Research Foundation, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India-613 005
Abstract: The aim of the study was to investigate the Aloe vera phyto chemical compounds and antimicrobial
activity of different extracts. The phytochemical compound screened by qualitative and GC-MS method.
Qualitatively analyzed Tannin, Saponin, Flavonoids and Terpenoids gave positive results and phlobactanins
and Steriods and Steriods gave negative results. In the GC-MS analysis, 26 bioactive phytechemical compounds
were identified in the ethanolic extract of Aloe vera. Three different solvents such as aqueous, ethanol and
acetone were used to extract the bioactive compounds from the leaves of Aloe vera to screen the antimicrobial
activity selected human clinical pathogens by agar diffusion method. The maximum antibacterial activities were
observed in acetone extracts (120.45nm, 200.35nm, 200.57nm and 150.38nm) other then aqueous extracts
and ethanol extract. Antifungal activity of Aloe vera was analyzed gains Aspergillus flavus and
Aspergillus niger. The maximum antifungal activity was observed in acetone extracts (150.73nm and 80.37nm)
when compared other extracts. Aloe vera plant extract with acetone can be used as antimicrobial agents.
Key words: Aloe vera
Phyto chemical
Antibacterial
INTRODUCTION
Antifungal activity
alloeh meaning bitter because of bitter liquid found in
the leaves. It is also known as lily of the desert the plant
of immortatity and the medicine plant with qualities to
serve as alternate medicine.
Aloe vera is as old as civilization and throughout
history it has been used as a popular folk medicine. It is
present in the arid regions of India and is believed to be
effective in treating stomach ailments, gastrointestinal
problems, skin diseases, constipation for radiation injury,
for its anti-inflammatory effect, for wound healing and
burns, as an anti-ulcer and diabetes. Currently the plant is
widely used in skin care, cosmetics and as nutraceuticals
[5].In this present study Aloe vera phyto chemical
compounds analysis (Qualitative method (Screening) and
GC-MS Analysis), also analyzed antibacterial and
antifungal activity (extracts of Aqueous, Ethanol and
Acetone).
Plants have been an important source of medicine
for thousands of years. Even today, the World Health
Organization estimates that up to 80 percent of people still
rely mainly on traditional remedies such as herbs for their
medicines. Its civilization is very ancient and the country
as a whole has long been known for its rich resources of
medical plants.Today, Ayurvedic, Hoemoeo and Unani
physicians utilize numerous species of medicinal plants
that found their way a long time ago into the Hindu
Material Media [1]. Aloe vera has been used to treat
various skin conditions such as cuts, burns and eczema.It
is alleged that sap from Aloe vera eases pain and reduces
inflammation.Evidence on the effects of Aloe vera sap on
wound healing, however, is contradictory [2]. Screening
techniques of biologically active medicinal compounds
have been conducted on well-known species of plants
used in traditional medicines and most plants have shown
antibacterial activity [3]. Aloe vera is a member of liliaceae
family. Alove vera (L.) Burm. Fil (Synonym A. brobadensis
Miller) (Tamil- Southakathalai, Hindi- Gikanvar) is a cactus
like plant with green, dagger- shaped leaves that are
fleshy, tapering, spiny, marginated and filled with a clear
viscous gel [4]. The name was derived from the aeabic
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection of Plant Material: The plant of Aloe vera
(leaves) was collected from Herbal Garden of Ponnaiyah
Ramajayam College, Thanjavur.The plant part (leaves)
was identified by a taxonomist in the Department of
Botany, PRIST University, Thanjavur.
Corresponding Author: S. Arunkumar, Karisakkadu, Maramadakki (Po), Aranthangi (Tk), Pudukkottai (Dt), Tamilnadu, India
572
You might also like
- Pharmacology of Indian Medicinal PlantsFrom EverandPharmacology of Indian Medicinal PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activity of Aloe Vera LDocument3 pagesPhytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activity of Aloe Vera LdhyantiNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Activities of Aloe Vera (Aloe Barbadensis)Document12 pagesPhytochemicals and Antioxidant Activities of Aloe Vera (Aloe Barbadensis)Journal of Nutritional Science and Healthy DietNo ratings yet
- Azadirachta Indica Allium Cepa Aloe Vera: Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plants-A. Juss, L. and LDocument7 pagesAzadirachta Indica Allium Cepa Aloe Vera: Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plants-A. Juss, L. and LLeandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Use of Aloe Vera - A ReviewDocument17 pagesCosmetic Use of Aloe Vera - A ReviewAdnanNo ratings yet
- Achyranthes Aspera PDFDocument7 pagesAchyranthes Aspera PDFzenith492No ratings yet
- Published PaperDocument6 pagesPublished PaperDemoz AddisuNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Plants Used in Indian Herbal MedicineDocument7 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Plants Used in Indian Herbal Medicinetitik ismandariNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial properties of medicinal plantsDocument20 pagesAntimicrobial properties of medicinal plantsAvinash GajaNo ratings yet
- Neem 2Document5 pagesNeem 2Ram RajwadeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Phytochemical Constituents and AntimicDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Phytochemical Constituents and AntimicRussel AloceljaNo ratings yet
- Alavijeh2012 - A Study of Antimicrobial Activity of Few Medicinal HerbsDocument7 pagesAlavijeh2012 - A Study of Antimicrobial Activity of Few Medicinal HerbschemvgasuNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activities of Some Medicinal Plants of The Western Region of IndiaDocument6 pagesAntibacterial Activities of Some Medicinal Plants of The Western Region of IndiaZobia AzizNo ratings yet
- Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine: Maharjan H. Radha, Nampoothiri P. LaxmipriyaDocument6 pagesJournal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine: Maharjan H. Radha, Nampoothiri P. LaxmipriyaMuh. Idham RahmanNo ratings yet
- Kel 11 - PPT ANTIMIKROBIAL ACTIVITY OF FEW MEDICINAL HERBSDocument17 pagesKel 11 - PPT ANTIMIKROBIAL ACTIVITY OF FEW MEDICINAL HERBSSyafira IrtantiNo ratings yet
- Mentha Piperita (Mint) Against Various Strains Of: IJISRT23JUN1991Document10 pagesMentha Piperita (Mint) Against Various Strains Of: IJISRT23JUN1991International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of LiteratureShankarNo ratings yet
- 408Document4 pages408LinguumNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Activities of Artemesia Herba-Alba and Rosmarinus Officinalis Against Microbial Infection: A ReviewDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Activities of Artemesia Herba-Alba and Rosmarinus Officinalis Against Microbial Infection: A ReviewyoucefNo ratings yet
- 2 FcopyFulltext1 PDFDocument10 pages2 FcopyFulltext1 PDFLurensssNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Eclipta alba ExtractsDocument4 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Eclipta alba ExtractsElanghovan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Green Source: A Power of Nature To Cure CancerDocument6 pagesGreen Source: A Power of Nature To Cure Cancerxiuhtlaltzin100% (1)
- BBRC7 015 PDFDocument16 pagesBBRC7 015 PDFSayali JoshiNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Terminaliabellerica Leaf and Stem Collected From Twodifferent SitesDocument13 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Terminaliabellerica Leaf and Stem Collected From Twodifferent SitesDavid BriggsNo ratings yet
- Moringa Oleifera in Vitro in Vivo: Research ArticleDocument13 pagesMoringa Oleifera in Vitro in Vivo: Research Articlegoldenday_hdpNo ratings yet
- Research Project Proposal: Government College University FaisalabadDocument6 pagesResearch Project Proposal: Government College University FaisalabadIrsa ShaheenNo ratings yet
- To Study Antibacterial Activity of Allium Sativum, Zingiber: Officinale and Allium Cepa by Kirby-Bauer MethodDocument3 pagesTo Study Antibacterial Activity of Allium Sativum, Zingiber: Officinale and Allium Cepa by Kirby-Bauer MethodRiestaKierantiNo ratings yet
- A Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantDocument4 pagesA Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- FULLTHESISDocument40 pagesFULLTHESISCrazyGamer 14738No ratings yet
- Research-Nutrients On AloeDocument3 pagesResearch-Nutrients On Aloesisang98147No ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument40 pagesFull ThesisIskriblihahaNo ratings yet
- adubiaroDocument21 pagesadubiaroAdefila Sunday DadaNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument40 pagesFull ThesissamNo ratings yet
- Antitussive and Antibacterial Activity of Trompang Elepante (Heliotropium indicum LinnDocument5 pagesAntitussive and Antibacterial Activity of Trompang Elepante (Heliotropium indicum LinnNeust TrainingNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument40 pagesFull ThesisNareshNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Antibacterial Prospective of Crude Leaf Extracts of MeliDocument6 pagesIn Vitro Antibacterial Prospective of Crude Leaf Extracts of MeliMuhammad sherazNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument40 pagesFull ThesisPe SaswNo ratings yet
- PHYTOCHEMICAL ACTIVITYDocument7 pagesPHYTOCHEMICAL ACTIVITYPeter DindahNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Food: Boerhavia Diffusa Lonchocarpus SericeusDocument8 pagesMeasurement: Food: Boerhavia Diffusa Lonchocarpus SericeusCamilo FlorezNo ratings yet
- Antibactrial Activities and Phytochemical Properties of Aju Mbaise1414Document45 pagesAntibactrial Activities and Phytochemical Properties of Aju Mbaise1414JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Making Hand Sanitizier From Natural MaterialsDocument5 pagesMaking Hand Sanitizier From Natural MaterialsAyu SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Abbas AyDocument7 pagesAbbas AyIbrahim Abdulrazaq YahayaNo ratings yet
- Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Erythrina Variegata Leaves ExtractsDocument5 pagesAnalgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Erythrina Variegata Leaves Extractsfirlysuci mutiazNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Testing On Red GingerDocument48 pagesPhytochemical Testing On Red GingerIrvandar NurviandyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognostic and Phytochemical Properties of Aloe Vera LinnDocument5 pagesPharmacognostic and Phytochemical Properties of Aloe Vera LinnazaliaswNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review of Mentha Arvensis: January 2016Document7 pagesPhytochemical and Pharmacological Review of Mentha Arvensis: January 2016betriaNo ratings yet
- Journel H Isora PDFDocument6 pagesJournel H Isora PDFbastNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Anti-Acne Astringent of Methanolic Leaves Extract FROM KAMIAS (Averrhoa Balimbing Fam. Oxalidaceae) AGAINST Staphylococcus EpidermisDocument7 pagesFormulation of Anti-Acne Astringent of Methanolic Leaves Extract FROM KAMIAS (Averrhoa Balimbing Fam. Oxalidaceae) AGAINST Staphylococcus EpidermisMylz MendozaNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Bioactivity Screening of Six NigerianDocument8 pagesPhytochemical and Bioactivity Screening of Six NigerianOladipupo Adejumobi LawalNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of A Combination of Three Natural Plant Extracts and Development of A Herbal SoapDocument12 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of A Combination of Three Natural Plant Extracts and Development of A Herbal SoapLeandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Antimicrobial Activities of Aloe Extracts and Antibiotics Against Isolates From Skin InfectionsDocument6 pagesComparative Study of Antimicrobial Activities of Aloe Extracts and Antibiotics Against Isolates From Skin InfectionsJulie MayNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Physicochemical Analysis of The Leaves of Laportea Aestuans (Linn) Bchew and Laportea Ovalifolis (Schumack) Chew (Male and Female)Document8 pagesPhytochemical and Physicochemical Analysis of The Leaves of Laportea Aestuans (Linn) Bchew and Laportea Ovalifolis (Schumack) Chew (Male and Female)Celme JRNo ratings yet
- 2016 Corliss PHDDocument40 pages2016 Corliss PHDBad SleeperNo ratings yet
- Senna AlataDocument12 pagesSenna AlataRoberto Serrano VegaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Pharmacological Properties of Aloe VeraDocument7 pagesA Review On Pharmacological Properties of Aloe VeraDevi Dwi AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan IC50Document7 pagesPerbandingan IC50luluNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Activity of Pimenta Dioica L Merril AnDocument4 pagesAntifungal Activity of Pimenta Dioica L Merril AnNazir BsahaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Properties of Aloe Vera and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesMedicinal Properties of Aloe Vera and Their FunctionsKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF A HERBAL SOAP INCORPORATING Cassia senna(L) Roxb Leaves and Ageratum conyzoides Linn WHOLE PLANT POWDERS. O.R. Omobuwajo , A. Abdu , O. A. Igbeneghu, I.O. Agboola and G.O. AladeDocument10 pagesPRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF A HERBAL SOAP INCORPORATING Cassia senna(L) Roxb Leaves and Ageratum conyzoides Linn WHOLE PLANT POWDERS. O.R. Omobuwajo , A. Abdu , O. A. Igbeneghu, I.O. Agboola and G.O. AladeFrancis AbuludeNo ratings yet
- Fullthesis PDFDocument40 pagesFullthesis PDFJαmír TαpícNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Jaga Rsud Rokan Hulu Periode 11 Juni - 10 OktoberDocument5 pagesJadwal Jaga Rsud Rokan Hulu Periode 11 Juni - 10 OktoberRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- PENGOBATANDocument1 pagePENGOBATANRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
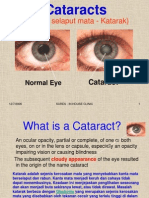
- Cataract and Eye Care DCaDocument26 pagesCataract and Eye Care DCaSamuil SumpalNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Rahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Indonesia. Jakarta: Perhimpunan Dokter Paru Indonesia: Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesIndonesia. Jakarta: Perhimpunan Dokter Paru Indonesia: Daftar PustakaRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Dasdad SDDocument1 pageDasdad SDRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Cover Fix JiwaDocument1 pageCover Fix JiwaRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- PENGOBATANDocument1 pagePENGOBATANRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Trans JurnalDocument4 pagesTrans JurnalRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Managing Acute Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument30 pagesManaging Acute Abnormal Uterine BleedingRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 1Document13 pages1Rahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- So SorryDocument1 pageSo SorryRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Typhoid Fever (WHO)Document48 pagesDiagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Typhoid Fever (WHO)Nina KharimaNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFDocument5 pages9 PDFRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Benito Et Al PDFDocument8 pages10 Benito Et Al PDFRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Video 3Document9 pagesVideo 3Rahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 1936 PDFDocument5 pages1936 PDFNurul Khairiyah IINo ratings yet
- Indonesian Country Report On Traditional MedicineDocument21 pagesIndonesian Country Report On Traditional MedicineRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 464 Ijar-2927Document16 pages464 Ijar-2927Rahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 044 KhurramDocument8 pages044 KhurramRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 2013 12 Pelvic ConsensusDocument8 pages2013 12 Pelvic ConsensusRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Benito Et Al PDFDocument8 pages10 Benito Et Al PDFRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- E Coli Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesE Coli Literature Reviewc5qvh6b4100% (1)
- French-American Hybrid Grape OriginsDocument6 pagesFrench-American Hybrid Grape OriginsWLD100% (1)
- PESTICIDES b-1Document51 pagesPESTICIDES b-1Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- Handout Elimination Diet PatientDocument6 pagesHandout Elimination Diet PatientSara NordNo ratings yet
- 2421-Article Text-7963-1-10-20191022Document9 pages2421-Article Text-7963-1-10-20191022Fikri HaikalNo ratings yet
- ALLEN - NCERT Based Objective - BiologyDocument131 pagesALLEN - NCERT Based Objective - BiologyTanish LatherNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Endosperm Culture and Seedling Growth of Mallotus Philippienesis (Lam.) M.ArgDocument6 pagesIn-Vitro Endosperm Culture and Seedling Growth of Mallotus Philippienesis (Lam.) M.ArgJeli SamadaraNo ratings yet
- 2018 Insect Pest of Coconut Lect PDFDocument139 pages2018 Insect Pest of Coconut Lect PDFJohn Drei100% (1)
- Agricultural Crop Production NC IDocument25 pagesAgricultural Crop Production NC IEJ Atsilab91% (11)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-1Document11 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-1Andre LauNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Berberine From Berberis VulgarisDocument6 pagesIsolation of Berberine From Berberis VulgarisArieNo ratings yet
- Field Crops 2Document164 pagesField Crops 2Gary Bhullar0% (2)
- DLL - Epp 6 - Q1 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Epp 6 - Q1 - W3Merlie Agtina Salamangkit-OlaloNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera-A Wonder Plant Its History, Cultivation and Medicinal Uses PDFDocument4 pagesAloe Vera-A Wonder Plant Its History, Cultivation and Medicinal Uses PDFveronyk28No ratings yet
- Biology: Unit: KBI0/4BI0 Paper: 2BDocument20 pagesBiology: Unit: KBI0/4BI0 Paper: 2BMohamedNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Thyroid With The Help of Coriander SeedDocument9 pagesTreatment of Thyroid With The Help of Coriander SeedNuhaRasheedNo ratings yet
- Reading NewDocument137 pagesReading NewSajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Phytopathogenic Fungi With Potential As Biocontrol Agents For Weeds of Importance in Crops of Antioquia, ColombiaDocument15 pagesPhytopathogenic Fungi With Potential As Biocontrol Agents For Weeds of Importance in Crops of Antioquia, ColombiaFabian GarzonNo ratings yet
- h1n1 Master TonicDocument2 pagesh1n1 Master TonicmmetaNo ratings yet
- BiopiracyDocument25 pagesBiopiracyapi-3706215100% (1)
- Vanda Mimi Palmer ThesisDocument217 pagesVanda Mimi Palmer ThesisMohd Hairul Ab Rahim100% (1)
- Mango Juice MakingDocument29 pagesMango Juice Makingsaiarvind0809No ratings yet
- Fungi Characteristics and ClassificationDocument2 pagesFungi Characteristics and ClassificationRia AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 18 FY12 CEAgricultural Science QPDocument13 pages18 FY12 CEAgricultural Science QPSelina VuninaiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Sciences: A Study On Synergestic Wound Healing Activity of Capsicum and Pigeon PeaDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Sciences: A Study On Synergestic Wound Healing Activity of Capsicum and Pigeon PeaBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Potato and Sweetpotato Seed Systems in AfricaDocument210 pagesPotato and Sweetpotato Seed Systems in Africamarianaivanovaprof100% (1)
- Exploring Science Textbook AnswerDocument96 pagesExploring Science Textbook AnswerNirshraya GajanNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Uses of Carrots: A ReviewDocument7 pagesTherapeutic Uses of Carrots: A ReviewReni WulansariNo ratings yet
- Botany Field Visit Report Class 12Document13 pagesBotany Field Visit Report Class 12Abhisek Adhikari50% (4)
- Alternative MedicineDocument306 pagesAlternative MedicineDamir Brankovic100% (3)