Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Trees
Uploaded by
SrivastavaAmol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views2 pagesThe documents discusses about decision models used in corporate finance.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe documents discusses about decision models used in corporate finance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views2 pagesDecision Trees
Uploaded by
SrivastavaAmolThe documents discusses about decision models used in corporate finance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Decision Trees
In a capital budgeting exercise, the decision-maker has to identify
and evaluate the various alternative courses of action leading to the
investment decision. A decision tree captures these alternatives in
form of a diagram and is useful for clarifying the range of alternative
course of action, assessing possible outcomes.
In a statistical sense, when a sequential series of conditional
decisions are required to be taken under conditions of uncertainty,
decision tree model comes in handy to visualize and evaluate all
possible options for action.
Consider this example. The purchase of an asset could lead to an
increase in sales. This increase can either be low, medium or high
with probabilities of 0.5, 0.3 and 0.2 respectively. Each of these could
be referred to as a branch and may yield differing contributions and
fixed costs, and in turn to differing profit levels giving rise to various
outcomes. Such possibilities are captured in decision tree.
There are two stages in preparing decision tree. The first step is
drawing the decision tree itself, in a manner that reflects all
outcomes and choices. The second step is to incorporate
probabilities, relevant values and derive expected monetary values.
Rules for drawing a decision tree diagram
Some basic rules in drawing the decision tree are:
Rule 1 : A decision tree begins with a decision point. A decision point
( also known as node) is represented by a rectangle. An outcome
point (also known as chance node) is denoted in circle.
Rule 2 : Decision alternatives (e.g. sales volume in the preceding
example) are shown by a straight line originating from decision node.
Rule 3 : A decision tree diagram is drawn from left to right. The
rectangles and circles are sequentially numbered.
Rule 4 : Values and probabilities for each branch are then
incorporated.
Evaluation and decision rules
A decision tree is analyzed and evaluated using toll-back method.
That is the value of each circle and each square is computed by
evaluating from right to left. This technique proceeds from last
decision in the sequence, wand works back to the first, for each of
the possible decisions. There are two rules in this evaluation.
Rule 1 : The expected monetary value at a chance node (branches
emanating from a circle) is aggregate of the expected values of the
various branches and emanate from the chance node.
Rule 2 : The expected value at a decision node (branches emanating
from a square) is the highest amongst the expected values of the
various branches that emanate from the decision node.
Problems on decision tree are usually part of corporate finance and
finance studies. It addresses the ways in which organizations take
decision of projects considering risk factor. It sometimes becomes
difficult for students to work their way around these problems. This is
where professional homework help websites can help you in
efficiently completing your corporate finance homework. Advantages
of using such website are :
Error free work Homework help websites have worked over a
number of years with multiple students. This helps them understand
the needs of each and every courses student in a unique way and
offer solutions according to that.
Completion of deadline College deadline can be very strict and
missing deadline on even a single assignment can adversely effect
your grade. This is where website like www.assignmentguys.com
specialize. In meeting the deadline 100% of time.
Varied topics These websites can help multiple topics on
corporate finance like capital budgeting, NPV analysis, simulation,
portfolio management and dividend discount models.
Read more at www.assignmentguys.com
You might also like
- Exercise 1-4 PDFDocument2 pagesExercise 1-4 PDFSrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Determinants of Interest Rates - Quiz 01Document4 pagesChapter 02 - Determinants of Interest Rates - Quiz 01SrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Introduction - Quiz 01Document7 pagesChapter 01 - Introduction - Quiz 01SrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Present Value and Future Value CalculatorDocument13 pagesPresent Value and Future Value CalculatorSrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Risk Adjusted Discount RateDocument2 pagesRisk Adjusted Discount RateSrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Cost Indifference PointDocument1 pageCost Indifference PointSrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- The Sources of BETADocument1 pageThe Sources of BETASrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- Certainity Equivalent FactorDocument2 pagesCertainity Equivalent FactorSrivastavaAmolNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 5 Steps To Negotiating PaymentDocument39 pages5 Steps To Negotiating PaymentThanh Loan100% (1)
- Civil CaseDocument2 pagesCivil CaseEl-babymike Paquibot PanaresNo ratings yet
- Transparency & Accountability in AaaDocument13 pagesTransparency & Accountability in AaaCordy IkeanyiNo ratings yet
- Benefits and ServicesDocument26 pagesBenefits and ServicesSushmit ShettyNo ratings yet
- Financial Behavior and Problems Among University Students: Need For Financial EducationDocument18 pagesFinancial Behavior and Problems Among University Students: Need For Financial EducationDarlene Mae HerrasNo ratings yet
- Keith Weiner The Swiss Franc Will CollapseDocument16 pagesKeith Weiner The Swiss Franc Will CollapseTREND_7425No ratings yet
- 2012-2013 PNHA Tables - 2Document9 pages2012-2013 PNHA Tables - 2Juan CarlosNo ratings yet
- 6 - Power of AttorneyDocument2 pages6 - Power of AttorneyJahi100% (4)
- 1 STND Cost Calculation CK11N and CK24 - PPC1 & ZPC2Document15 pages1 STND Cost Calculation CK11N and CK24 - PPC1 & ZPC2Mohammad Aarif100% (1)
- The Role of Public Sectors in Developing INDIADocument8 pagesThe Role of Public Sectors in Developing INDIAL. Lawliet.No ratings yet
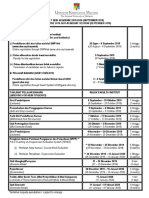
- Semester 1 of The 2019-2020 Academic Session (September 2019)Document3 pagesSemester 1 of The 2019-2020 Academic Session (September 2019)Ct HajarNo ratings yet
- Ability Abrogation Accent All Abject abrogation Accepted AccordionDocument12 pagesAbility Abrogation Accent All Abject abrogation Accepted AccordionMae Anthonette RamosNo ratings yet
- 14th Annual Book PDFDocument78 pages14th Annual Book PDFAbhayNo ratings yet
- Investment Principles and Checklists OrdwayDocument149 pagesInvestment Principles and Checklists Ordwayevolve_us100% (2)
- DOTgazette - Aug06 - July08.Document196 pagesDOTgazette - Aug06 - July08.M Munir Qureishi100% (1)
- Weekly Choice - Section B - April 05, 2012Document6 pagesWeekly Choice - Section B - April 05, 2012Baragrey DaveNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet of Union Bank of IndiaDocument2 pagesBalance Sheet of Union Bank of Indiajini02No ratings yet
- The Quiet Panic - Kyle Bass On Hong Kong's Looming Financial & Political Crisis - Zero HedgeDocument11 pagesThe Quiet Panic - Kyle Bass On Hong Kong's Looming Financial & Political Crisis - Zero HedgeLuizNo ratings yet
- Machuca V ChuidianDocument3 pagesMachuca V ChuidianMark Leo BejeminoNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document7 pagesChap 9GinanjarSaputra0% (1)
- Icwim PDFDocument2 pagesIcwim PDFWolfgangNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Books 2016Document3 pagesPrescribed Books 2016phillip muzhambiNo ratings yet
- 5 RCBC Savings V Odrada DigestDocument1 page5 RCBC Savings V Odrada DigestDamienNo ratings yet
- PBD Cluster 27Document48 pagesPBD Cluster 27Datu Puwa MamalacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document58 pagesChapter 2Aminul Islam AmuNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Barangay FormsDocument53 pagesPrescribed Barangay FormsSeth Cabrera100% (1)
- Multi Bintang Indonesia TBK.: Company Report: January 2017 As of 31 January 2017Document3 pagesMulti Bintang Indonesia TBK.: Company Report: January 2017 As of 31 January 2017Solihul HadiNo ratings yet
- Irrevocable Power of AttorneyDocument6 pagesIrrevocable Power of AttorneyAlpesh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Documentary Stampt Tax PDFDocument22 pagesModule 6 Documentary Stampt Tax PDFTitania ErzaNo ratings yet
- Bwa M 033116Document10 pagesBwa M 033116Chungsrobot Manufacturingcompany100% (1)