Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypertension Treatment Steps For Hypertension
Uploaded by
AyaanTonseOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypertension Treatment Steps For Hypertension
Uploaded by
AyaanTonseCopyright:
Available Formats
Treatment steps for
hypertension
A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality
standards and materials to support implementation on a specific
topic area. The pathways are interactive and designed to be used
online. This pdf version gives you a single pathway diagram and
uses numbering to link the boxes in the diagram to the associated
recommendations.
To view the online version of this pathway visit:
http://pathways.nice.org.uk/pathways/hypertension
Pathway last updated: December 2015. To see details of any updates to this pathway since its
launch, visit: About this Pathway. For information on the NICE guidance used to create this path, see:
Sources.
Copyright NICE 2015. All rights reserved
NICEPathways
Pathways
Treatment steps for hypertension
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
NICE Pathways
Page 2 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Person aged under 55 with hypertension
No additional information
Step 1 ACE inhibitor or ARB
Offer people aged under 55 years step 1 antihypertensive treatment with an ACE inhibitor or a
low-cost ARB. If an ACE inhibitor is prescribed and is not tolerated (for example, because of
cough), offer a low-cost ARB.
Beta-blockers are not a preferred initial therapy for hypertension. However, beta-blockers may
be considered in younger people, particularly:
those with an intolerance or contraindication to ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor
antagonists or
women of child-bearing potential or
people with evidence of increased sympathetic drive.
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Person aged over 55 or black person of African or Caribbean family
origin of any age with hypertension
No additional information
Step 1 CCB
Offer step 1 antihypertensive treatment with a CCB to people aged over 55 years and to black
people of African or Caribbean family origin of any age. If a CCB is not suitable, for example
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 3 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
because of oedema or intolerance, or if there is evidence of heart failure or a high risk of heart
failure, offer a thiazide-like diuretic.
If diuretic treatment is to be initiated or changed, offer a thiazide like diuretic, such as
chlortalidone (12.525.0 mg once daily) or indapamide (1.5 mg modified-release once daily or
2.5 mg once daily) in preference to a conventional thiazide diuretic such as bendroflumethiazide
or hydrochlorothiazide.
For people who are already having treatment with bendroflumethiazide or hydrochlorothiazide
and whose blood pressure is stable and well controlled, continue treatment with the
bendroflumethiazide or hydrochlorothiazide.
NICE has produced a pathway on chronic heart failure.
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Step 2
If blood pressure is not controlled by step 1 treatment, offer step 2 treatment with a CCB in
combination with either an ACE inhibitor or an ARB 1.
If a CCB is not suitable for step 2 treatment, for example because of oedema or intolerance, or
if there is evidence of heart failure or a high risk of heart failure, offer a thiazide-like diuretic,
such as chlortalidone (12.525.0 mg once daily) or indapamide (1.5 mg modified-release once
daily or 2.5 mg once daily).
For black people of African or Caribbean family origin, consider an ARB in preference to an
ACE inhibitor, in combination with a CCB.
If therapy is initiated with a beta-blocker and a second drug is required, add a CCB rather than a
thiazide-like diuretic to reduce the person's risk of developing diabetes.
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 4 of 11
Choose a low-cost ARB.
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 5 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Before considering step 3 treatment, review medication to ensure step 2 treatment is at optimal
or best tolerated doses.
NICE has produced a pathway on chronic heart failure.
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Step 3
If treatment with three drugs is required, the combination of ACE inhibitor or ARB, CCB and
thiazide-like diuretic such as chlortalidone (12.525.0 mg once daily) or indapamide (1.5 mg
modified-release once daily or 2.5 mg once daily) should be used.
Regard clinic blood pressure that remains higher than 140/90 mmHg after treatment with the
optimal or best tolerated doses of an ACE inhibitor or an ARB plus a CCB plus a diuretic as
resistant hypertension, and consider adding a fourth antihypertensive drug and/or seeking
expert advice.
1
Quality standards
The following quality statement is relevant to this part of the pathway.
6.
Referral to a specialist for people with resistant hypertension
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Choose a low-cost ARB.
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 6 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Step 4 Resistant hypertension
For treatment of resistant hypertension at step 4:
Consider further diuretic therapy with low-dose spironolactone (25 mg once daily)1 if the
blood potassium level is 4.5 mmol/l or lower. Use particular caution in people with a
reduced eGFR because they have an increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Consider higher-dose thiazide-like diuretic treatment if the blood potassium level is higher
than 4.5 mmol/l.
When using further diuretic therapy for resistant hypertension at step 4, monitor blood sodium
and potassium and renal function within 1 month and repeat as required thereafter.
If further diuretic therapy for resistant hypertension at step 4 is not tolerated, or is
contraindicated or ineffective, consider an alpha- or beta-blocker.
If blood pressure remains uncontrolled with the optimal or maximum tolerated doses of four
drugs, seek expert advice if it has not yet been obtained.
Interventional procedures
NICE has published interventional procedures guidance on percutaneous transluminal
radiofrequency sympathetic denervation of the renal artery for resistant hypertension with
special arrangements for clinical governance, consent, and audit or research.
NICE has published interventional procedures guidance that implanting a baroreceptor
stimulation device for resistant hypertension should be used only in the context of research.
Quality standards
The following quality statement is relevant to this part of the pathway.
6.
Referral to a specialist for people with resistant hypertension
At the time of publication (August 2011), spironolactone did not have UK marketing authorisation for this
indication. Informed consent should be obtained and documented.
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 7 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Monitoring drug treatment
Use clinic blood pressure measurements to monitor the response to antihypertensive treatment
with lifestyle modifications or drugs.
For people identified as having a white-coat effect, consider ABPM or HBPM as an adjunct to
clinic blood pressure measurements to monitor the response to antihypertensive treatment with
lifestyle modification or drugs.
Resources
The following implementation tools are relevant to this part of the pathway.
Hypertension (drug treatment): audit support
Hypertension: (drug treatment): electronic audit tool
Hypertension: clinical case scenarios
Review annually
See Hypertension / Hypertension overview / Review annually
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 8 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Glossary
ACE inhibitor
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor
ARB
angiotensin II receptor blocker
CCB
calcium-channel blocker
ABPM
ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate
HBPM
home blood pressure monitoring
Severe hypertension
clinic systolic blood pressure is 180 mmHg or higher or clinic diastolic blood pressure is 110
mmHg or higher
Stage 1 hypertension
clinic blood pressure 140/90 mmHg or higher and subsequent ambulatory blood pressure
monitoring daytime average or home blood pressure monitoring average blood pressure 135/85
mmHg or higher
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 9 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
Stage 2 hypertension
clinic blood pressure 160/100 mmHg or higher and subsequent ambulatory blood pressure
monitoring daytime average or home blood pressure monitoring average blood pressure 150/95
mmHg or higher
White-coat effect
a discrepancy of more than 20/10 mmHg between clinic and average daytime ambulatory blood
pressure monitoring or average home blood pressure monitoring measurements at the time of
diagnosis
Sources
Hypertension (2011) NICE guideline CG127
Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension (2015) NICE
interventional procedure guidance 533
Percutaneous transluminal radiofrequency sympathetic denervation of the renal artery for
resistant hypertension (2012) NICE interventional procedure guidance 418
Your responsibility
The guidance in this pathway represents the view of NICE, which was arrived at after careful
consideration of the evidence available. Those working in the NHS, local authorities, the wider
public, voluntary and community sectors and the private sector should take it into account when
carrying out their professional, managerial or voluntary duties. Implementation of this guidance
is the responsibility of local commissioners and/or providers. Commissioners and providers are
reminded that it is their responsibility to implement the guidance, in their local context, in light of
their duties to avoid unlawful discrimination and to have regard to promoting equality of
opportunity. Nothing in this guidance should be interpreted in a way which would be inconsistent
with compliance with those duties.
Copyright
Copyright National Institute for Health and Care Excellence 2015. All rights reserved. NICE
copyright material can be downloaded for private research and study, and may be reproduced
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 10 of 11
Treatment steps for hypertension
NICE Pathways
for educational and not-for-profit purposes. No reproduction by or for commercial organisations,
or for commercial purposes, is allowed without the written permission of NICE.
Contact NICE
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
Level 1A, City Tower
Piccadilly Plaza
Manchester
M1 4BT
www.nice.org.uk
nice@nice.org.uk
0845 003 7781
Hypertension pathway
Copyright NICE 2015.
Page 11 of 11
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Taqwa - The Provision of BelieversDocument50 pagesTaqwa - The Provision of BelieversAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
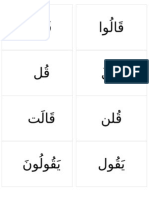
- Wordandsentencemodernstandardarabic 150702104648 Lva1 App6892Document18 pagesWordandsentencemodernstandardarabic 150702104648 Lva1 App6892AyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Scripts For Formulating Management PlanDocument3 pagesScripts For Formulating Management PlanAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocument21 pagesLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- SurvivalPhrases Arabic S1L03Document2 pagesSurvivalPhrases Arabic S1L03JohannCoxNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hamare NabiDocument22 pagesHamare NabiAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Taqwa - The Provision of BelieversDocument50 pagesTaqwa - The Provision of BelieversAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Quran UthmaniDocument105 pagesQuran UthmaniSameerNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Arabic Sight Words VerbsDocument11 pagesArabic Sight Words VerbsAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Arabic FlipbookDocument28 pagesArabic FlipbookAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocument21 pagesLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaNo ratings yet
- Essential Duas in The Life of A MuslimDocument84 pagesEssential Duas in The Life of A MuslimJawedsIslamicLibrary100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Selected Dua'sDocument33 pagesSelected Dua'seSisters UAE87% (39)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Un InstallDocument9 pagesUn InstallAyaanTonseNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Antipsychotics Mechanisms Indications SideEffectsDocument4 pagesAntipsychotics Mechanisms Indications SideEffectsRana MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Reseach ProposalDocument16 pagesReseach ProposalUmmul Khair Alam50% (4)
- Lab Practical UrinalysisDocument7 pagesLab Practical UrinalysisHeatherIz AwwsomeNo ratings yet
- Referat EndocarditisDocument25 pagesReferat EndocarditisNadya Hasna Rasyida DANo ratings yet
- Focused Clinical Case Study AssessmentDocument32 pagesFocused Clinical Case Study AssessmentAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Cell SaverDocument8 pagesCell SaverFrank QuitianNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Unit-VII Professional Autonomy and EthicsDocument13 pagesUnit-VII Professional Autonomy and Ethicsofficialgaming655No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Peran Perawat Dalam Penangan Kegawatn Jantung - ERWIN (Autosaved)Document64 pagesPeran Perawat Dalam Penangan Kegawatn Jantung - ERWIN (Autosaved)Adrianus AdrianusNo ratings yet
- Supra Ventricular Tachycardia in PregnancyDocument2 pagesSupra Ventricular Tachycardia in PregnancylulzimkamberiNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument4 pagesAngina PectorisAnn CunananNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Farmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Document84 pagesFarmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Alex FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Sports Injury Assessment PDFDocument43 pagesSports Injury Assessment PDFPatricia Andrea Acevedo ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document2 pagesModule 9ahsie1No ratings yet
- SimuzazuDocument3 pagesSimuzazuhelenjamelamulengaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Practice TestDocument6 pagesPractice TestJulie May SuganobNo ratings yet
- H&P and Dictation Template - Right Handed (6!4!15)Document1 pageH&P and Dictation Template - Right Handed (6!4!15)Solomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Full Avanto BrochureDocument30 pagesFull Avanto BrochureMas NoNo ratings yet
- Chiropractic Intake FormDocument4 pagesChiropractic Intake FormtmontagNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cleaning Toys Games and Play Equipment On The Paediatric WardDocument8 pagesPaediatric Cleaning Toys Games and Play Equipment On The Paediatric WarddidikNo ratings yet
- NTSB LIRR ReportDocument26 pagesNTSB LIRR ReportNewsdayNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 - Concept of EBP PDFDocument24 pagesModule 2.2 - Concept of EBP PDFvincyNo ratings yet
- The Roth RxDocument64 pagesThe Roth Rxvelangni0% (1)
- SBI Medical PolicyDocument80 pagesSBI Medical PolicyRajNo ratings yet
- Casting ProformaDocument2 pagesCasting ProformaPhillip CullenNo ratings yet
- Nux VomicaDocument2 pagesNux VomicaRashid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Tamsulosin Hydro ChlorideDocument2 pagesTamsulosin Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (3)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Type 2 Diabetes Final DraftDocument14 pagesType 2 Diabetes Final DraftAbbie HillsNo ratings yet
- Eportfolio New CmaDocument2 pagesEportfolio New Cmaapi-318874763No ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pediatric Anxiety DisordersDocument19 pagesAssessing and Treating Pediatric Anxiety Disordersayub01No ratings yet
- Jurnal Placenta PreviaDocument9 pagesJurnal Placenta Previasheva25No ratings yet