Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fmea 101
Uploaded by
SukanthOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fmea 101
Uploaded by
SukanthCopyright:
Available Formats
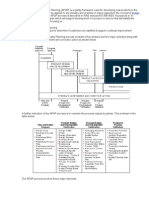
FMEA FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS
An analytical methodology to ensure potential problems are considered and
addressed throughout the product and process (APQP) development stages
Timing of FMEA is critical Before the event action is what is needed and not
After the event of failure
Design FMEA should be done during project initialization phase and process
FMEA before tooling or manufacturing equipments are developed / purchased
Cross functional expert inputs remain mandatory
Risk assessment product & process design phase is vital
Basic cases for FMEA application that remains mandatory;
o New design, new technology, new process
o Modification of existing design or process
o Use of an existing design or process in a new environment, location,
application or usage profile(duty cycle, regulatory requirements etc)
FOCUS OF FMEA
o Plan and define program
o Product design and development
o Process design and development
o Product and process validation
o Feedback, assessment and corrective action
Clear statements, concise terminology and focus on actual effects are the key to
effective identification and mitigation of risk issues.
FMEA is a living document effective communication to all affected
activities/functional is ultimately necessary to give life to a proper effective
thorough, thought-out FMEA.
o Review designs, processes and related records to ensure recommended
o
actions have been implemented
Confirmation of incorporation of changes to
design/assembly/manufacturing documents
o Review design/process FMEAs, special applications and control plans
COMMON APPROACH
o Potential product/process failure modes need to be identified
Different ways or manner by which a product/process could fail
o
o
Potential
Potential
to meet the design intent or process requirements
consequences need to be discussed upon
Effects of the failure as perceived by the customer/end user
causes for each mode need to be identified
Indication of how the failure might occur
Direct proportionality to failure modes, if the risk causing factor
occurs, the probability of failure mode happening is very high
Control plans need to be drafted for each of the failure causes
Application of current control plan needs to be verified
Prevention or identification of failure or failure modes
It is important to understand what is causing the failure, why
Level of
and how to prevent the recurrence
Controls focused on prevention will provide greatest returns
risk should be analyzed
Severity effect on the customer
Occurrence how often the cause may occur
Detection how well the control plan detects the cause of failure
mode
Reduction of risk is the key
Recommended actions for each of the failure mode is important
Ensuring design requirements including reliability are achieved
Reviewing engineering drawings and specifications
Confirming incorporation in process
Reviewing related FMEAs, control plans and operation
instructions
Responsibility and time plan to complete recommended actions
should be recorded
At closure of every action, rating for severity, occurrence and
detection should be recorded
FMEA REQUIREMENTS
o Functions, requirements and deliverables of product/process being
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
analyzed
Failure modes when functional are not met
Effects and consequences of failure modes
Action plan and control plan to address each failure modes
Preventive action plan to control recurrence of failure mode
General purpose of the product
Safety
Government regulations
Reliability life of the function
NVH limitations
Fluid retentions
Ergonomics
Appearance
Packaging and shipping
Service
o Design for assembly
o Design for manufacturability
Scope of FMEA should be very clear to the CFT before drafting the FMEA what
is to be excluded is as important as what is to be included in discussion
o System FMEA
o Subsystem FMEA
o Component FMEA
BLOCK DIAGRAM
o Block diagram shows physical and logical relationships between
o
components of the product
It indicates interaction of components and subsystems within the scope of
design
o Flow of information, energy, fore or fluid
PARAMETER (P) DIAGRAM
o A structured tool to help understand the physics related to the functions of
o
design
Potential failure modes are clearly listed
You might also like
- Hydraulic TrainingDocument132 pagesHydraulic TrainingJose Luis Rodriguez100% (3)
- FMEADocument12 pagesFMEARADHIKA CHANDAKNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and EffectsDocument23 pagesFailure Modes and Effectsdm mNo ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- Design FMEADocument77 pagesDesign FMEAAnil DwivediNo ratings yet
- THE BASICS OF FAILURE MODE AND EFFECT ANALYSIS (FMEADocument32 pagesTHE BASICS OF FAILURE MODE AND EFFECT ANALYSIS (FMEApsrajjNo ratings yet
- Project Execution ModelDocument99 pagesProject Execution ModelEdha Ali100% (3)
- FMEA analysis of quality management processesDocument17 pagesFMEA analysis of quality management processesGowtham D'Night FoxNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGNo ratings yet
- Electrical Protection Relay IntroductionDocument200 pagesElectrical Protection Relay IntroductionmlutfimaNo ratings yet
- Avr Conversion Instructions: FITTING KIT 45-0054 FOR USE WITH SX440 AVR Part No. E000-24030Document2 pagesAvr Conversion Instructions: FITTING KIT 45-0054 FOR USE WITH SX440 AVR Part No. E000-24030Jose Pirulli100% (1)
- The 5 Core Quality Tools ExplainedDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core Quality Tools ExplainedRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument42 pagesFMEAibal_machine100% (1)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (Design) : Importance in NPD ProcessDocument12 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (Design) : Importance in NPD Processsushant3240No ratings yet
- FMEA and CharacteristicsDocument47 pagesFMEA and Characteristicsmalbarnes100% (4)
- FMEA Guide to Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument4 pagesFMEA Guide to Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument91 pagesFMEAscorpionarnoldNo ratings yet
- Fmea TrainingDocument54 pagesFmea Trainingazadsingh10% (1)
- EFB User GuideDocument322 pagesEFB User GuideChrisL100% (3)
- Failure Modes And: Step-By-Step FailuresDocument31 pagesFailure Modes And: Step-By-Step FailuresVimala Selvaraj VimalaNo ratings yet
- PFMEADocument13 pagesPFMEASarigameNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14Document13 pagesTQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14mechatronicsmkNo ratings yet
- Hazop-Hazid, Sil StudyDocument15 pagesHazop-Hazid, Sil Studydesign electricalNo ratings yet
- Quality Core Tools APQP FMEA MSA SPC PPAPDocument14 pagesQuality Core Tools APQP FMEA MSA SPC PPAPالعاب الاطفال- jeux enfantsNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document9 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)yashar2500No ratings yet
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariNo ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Document5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningAbraham GuerraNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument29 pagesFMEAKarthik Kr100% (1)
- The Basics of FMEA: Understanding Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument30 pagesThe Basics of FMEA: Understanding Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisClaudia MarquesNo ratings yet
- Analyze Product Failures with FMEADocument7 pagesAnalyze Product Failures with FMEAAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- PPAPDocument7 pagesPPAPsunnysunsationNo ratings yet
- GS-0002D, Design FMEADocument26 pagesGS-0002D, Design FMEAmesa142100% (1)
- CQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Document54 pagesCQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Gabryel BogdanNo ratings yet
- VPLEX Administration Student GuideDocument261 pagesVPLEX Administration Student GuideLuis SandersNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Analysis Guide - FMEA Process OverviewDocument19 pagesFailure Mode Analysis Guide - FMEA Process OverviewpatnaikpsNo ratings yet
- (English) The World in 2050 (The Real Future of Earth) - BBC & Nat Geo DocumentariesDocument30 pages(English) The World in 2050 (The Real Future of Earth) - BBC & Nat Geo Documentariesnagendrasteer100% (2)
- Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects AnalysisBoBo KyawNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Document22 pagesSeminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Atharva SanglikarNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)Document2 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)RathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Management of Highly Hazardous & Explosive ChemicalsDocument49 pagesProcess Safety Management of Highly Hazardous & Explosive ChemicalsSardar PerdawoodNo ratings yet
- APQP Process GuideDocument35 pagesAPQP Process GuideThuận HoàngNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument9 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysisameliaNo ratings yet
- Hazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Document14 pagesHazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Ihadz CleverleyNo ratings yet
- Function:: Yield Fatigue Material Instability Creep Wear Corrosion Cracked Deformed LeakingDocument16 pagesFunction:: Yield Fatigue Material Instability Creep Wear Corrosion Cracked Deformed LeakingAnita SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 PSM Process Hazard Analysis2Document49 pages3 PSM Process Hazard Analysis2muvin236No ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesBryan Gregory DucusinNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument21 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysisAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- R.Hariharan, Lect / EeeDocument31 pagesR.Hariharan, Lect / EeeJinto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Are The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapDocument4 pagesAre The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapSergio Cristobal Bonilla CegadorNo ratings yet
- Reaction PlanDocument14 pagesReaction PlanMariaNilaZaragozaPalacioNo ratings yet
- Design, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxDocument32 pagesDesign, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Innovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind RamuDocument34 pagesInnovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind Ramukskr_44No ratings yet
- Highlight Points: Fmea - 4 EditionDocument14 pagesHighlight Points: Fmea - 4 EditionSelvaraj SNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis 2Document15 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis 2Oyebanji SurajNo ratings yet
- Identification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects AnalysisDocument8 pagesIdentification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects Analysisashishmechengg31No ratings yet
- Clause Wise Tutorials-7.1.4 Change Control ExplanationDocument2 pagesClause Wise Tutorials-7.1.4 Change Control ExplanationBharathNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 MEMDocument11 pagesExperiment No 7 MEMImdad JalaliNo ratings yet
- Core Tools PDFDocument3 pagesCore Tools PDFR.BalasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Long IFTPS 2015Document38 pagesLong IFTPS 2015Mohamed Ali BoumarafNo ratings yet
- Sudhan Ppap (Sem)Document15 pagesSudhan Ppap (Sem)sudhans029No ratings yet
- Quality Management AnswersDocument42 pagesQuality Management AnswersVrushali Nayak100% (1)
- Manlapaz Final Done V2Document66 pagesManlapaz Final Done V2Herobrine CosmoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ethics, Fraud and Internal ControlDocument44 pagesChapter 3 Ethics, Fraud and Internal ControlFarah ByunNo ratings yet
- Case Study PotipotDocument11 pagesCase Study PotipotCyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Stub Loss Correction Table For Coated ElectrodesDocument1 pageStub Loss Correction Table For Coated ElectrodesTAMILNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Grid Connected Single PhaseDocument78 pagesModelling of Grid Connected Single PhaseMurat KarabacakNo ratings yet
- SNT Notes 2022Document7 pagesSNT Notes 2022OrlinNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology - Unit - 3 - NotesDocument10 pagesResearch Methodology - Unit - 3 - Notessatya prakashNo ratings yet
- Coins Pro APIDocument74 pagesCoins Pro APIwarren madayagNo ratings yet
- MSP430F123Document44 pagesMSP430F123NagyNo ratings yet
- CS6K-265 - 270 - 275 - 280 P: Key Features Linear Power Output WarrantyDocument2 pagesCS6K-265 - 270 - 275 - 280 P: Key Features Linear Power Output Warrantyadolfo escobarNo ratings yet
- Low Filter Order Digital Equalization for Mobile Device EarphonesDocument12 pagesLow Filter Order Digital Equalization for Mobile Device EarphonesJuan Sebastian RicoNo ratings yet
- Installing The TCD To FID Series Connector: 4890, 5890, 6890 Gas Chromatographs Accessory 19232CDocument10 pagesInstalling The TCD To FID Series Connector: 4890, 5890, 6890 Gas Chromatographs Accessory 19232C신지훈No ratings yet
- Magnomatics BrochureDocument4 pagesMagnomatics BrochureVijay17101972No ratings yet
- Multimedia ComputingDocument29 pagesMultimedia ComputingVikky GourNo ratings yet
- Effect If Bolt Torque and Contact Resistance On Performance of ElctrolyserDocument11 pagesEffect If Bolt Torque and Contact Resistance On Performance of ElctrolyserAravind ShankarNo ratings yet
- PIO and Interrupt StudentsDocument12 pagesPIO and Interrupt StudentsLê Đình TiếnNo ratings yet
- Service Parts Manual: Series 51-1: 60 CC, 80 CC, and 110 CC Variable Displacement MotorsDocument68 pagesService Parts Manual: Series 51-1: 60 CC, 80 CC, and 110 CC Variable Displacement Motorscarlos farfanNo ratings yet
- MEC85 - Matlab S2023Document3 pagesMEC85 - Matlab S2023Aidan McNabbNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1Document37 pagesData Mining: Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1Jay ShahNo ratings yet
- This Document Has Been Prepared by Sunder Kidambi With The Blessings ofDocument4 pagesThis Document Has Been Prepared by Sunder Kidambi With The Blessings ofJohn DaveNo ratings yet
- Aparna GupatDocument24 pagesAparna GupatAkshat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Sound Reinforcement Equipment Rack LayoutDocument1 pageSound Reinforcement Equipment Rack LayoutJeghiNo ratings yet
- DG Sets (Stationary Engines)Document7 pagesDG Sets (Stationary Engines)Vijayabu Akula100% (1)
- XpathDocument3 pagesXpathLena Dutf0% (1)