Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TMSTR Popov A Selection of General Condition Exercises
Uploaded by
marin0410Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TMSTR Popov A Selection of General Condition Exercises
Uploaded by
marin0410Copyright:
Available Formats
A SELECTION OF GENERAL
CONDITIONING EXERCISES
By V. Popov
General conditioning exercises play an important role in the development of
muscle elasticity, strength, mobility and coordination. The exercises also form a
foundation for specific conditioning exercises. The following selection of general
conditioningexer
ci
sesar
eext
r
ac
t
edf
r
om aser
i
esofar
t
i
cl
est
i
t
l
ed
1001
Exer
ci
sesf
orTr
ackandFi
el
dAt
hl
et
est
hatappear
edi
nLegkayaAt
l
et
i
ka,
Russia, No. 7 to 12, 1994. Re-printed with permission from Modern Athlete and
Coach.
The following text attempts to draw attention to a variety of general and specific
exercises and their execution procedures in order to provide athletes and
coaches a wider choice of appropriate exercises for a particular task.
GENERAL PRINCIPLES
It is important to understand that general preparation exercises have the task to
develop the cardiovascular system, improve work capacity, strengthen the
movement and support systems, improve coordination and form a sound base for
the performance of specific exercises. The following factors should be taken into
consideration in the execution of general preparation exercises:
Flexibility exercises should always be performed with the largest possible
movement range. The same exercises can also be performed at maximal
speed to assist the improvement of movement speed.
Exercises against external resistances are performed to develop muscular
strength capacities.
General endurance is developed by increasing the number of repetitions
and the intensity of an exercise. The exercises chosen to assist in the
development of general endurance should involve a large number of
muscle groups.
The development of local muscular endurance takes place when a select
small muscle group is involved in the performance of the exercise.
Exercises involving a large number of muscle groups under frequently
changing tensions and sequences help to improve coordination and
agility.
Most general preparation exercises are performed with a sufficient number
of repetitions to create slight fatigue.
Eight to ten continually changing exercises are incorporated in each
training session.
It is important to ease muscular tension between the exercises by using
relaxation techniques in standing, sitting and hanging from a bar. The
relaxing and shaking of the muscles should take place after creating a
short (4 to 10 sec) pretension phase.
Relaxation exercises should be performed in 3 to 4 repetitions of about 30
to 60 seconds.
GENERAL EXERCISES
Where necessary to draw attention to the performance of an exercise the
following signs are used in the illustrations:
= stressed change of direction
=doubl
edi
r
ect
i
onc
hange
= static performance
0=0 = suitable for the use of additional resistance (weight).
Shoulder and Arm Exercises
Shoulder and arm exercises are illustrated in Fig. 1. The selection includes
various arm circles, jumps into a front lean position, different push-ups, dips on
parallel bars, etc.
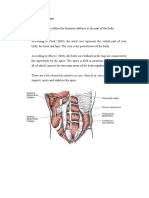
Trunk and Abdominal Exercises
Trunk and abdominal exercises are illustrated in Fig. 2. The selection includes
trunk and hip rotations, different trunk and leg lifts, sideways bends, various
exercises on wall ladders, etc.
Leg Exercises
Leg exercises are illustrated in Fig. 3. The selection includes different leg swings
and stretches, single leg squats, rebound jumps from height, bounding, upstairs
runs, upstairs jumps, repetition squats etc.
Other General Exercises
Among other general exercises are simple gymnastics exercises in Fig. 4. The
selection includes vaults over boxes, forward rolls, somersaults, wall bars
exercises, handstand movements etc.
PARTNER EXERCISES
There is a wide variety of partner exercises, including the following illustrated
examples:
Flexibility exercises in different positions, performed in 3 to 5 sets of 8 to
12 repetitions (Fig. 5).
Partner resisted strength development exercises for different muscle
groups, performed in not less than 3 sets of 12 to 18 repetitions (Fig. 6).
Partner resisted jumping exercises, performed in 4 to 6 sets with up to a
total of 50 to 60 jumps (Fig. 7).
Combined partner resisted flexibility and strength development exercises,
performed in 5-4 sets of 12 to 18 repetitions (Fig. 7).
MEDICINE BALL EXERCISES
A selection of medicine ball exercises is illustrated in Fig. 8. The exercises can
be performed in a variety of positions and include:
Medicine ball throws over the head forward, upward from between the
legs, from one hand to the other etc.
Jumps with a medicine ball in the hands or held by feet, a variety of
abdominal strength development exercises.
Medicine ball throws in standing, sitting and lying positions in different
directions.
In general, medicine ball exercises are performed in 4 to 5 sets with 10 to 12
repetitions, up to a total of 50 to 60.
You might also like
- SEAL Screener 5.0Document24 pagesSEAL Screener 5.0marin0410100% (3)
- Lexus GS300 Wiring DiagramDocument4 pagesLexus GS300 Wiring Diagramrenz100% (1)
- Tactical Training TemplateDocument9 pagesTactical Training Templatemarin0410100% (6)
- Charles PoliquinDocument1 pageCharles Poliquinmarin0410100% (1)
- Binder 50 Weight TrainingDocument3 pagesBinder 50 Weight TrainingmarkwsheppardNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Strength and Conditioning: A Trainer's Guide to Building Strength and StaminaFrom EverandAnatomy of Strength and Conditioning: A Trainer's Guide to Building Strength and StaminaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Natural Bodybuilding TemplateDocument3 pagesNatural Bodybuilding Templatemarin0410100% (1)
- Hospital and Clinical Pharmacist PDFDocument23 pagesHospital and Clinical Pharmacist PDFmajd67% (6)
- Behavior Neurobiology of Alcohol AddictionDocument722 pagesBehavior Neurobiology of Alcohol AddictionDassaev Fritz100% (1)
- Generalstrength - Boo SchexnayderDocument4 pagesGeneralstrength - Boo Schexnayderryan98710% (1)
- Programming Abdominal Training Part IIDocument4 pagesProgramming Abdominal Training Part IIHawk Eye100% (1)
- Individual PresentationDocument3 pagesIndividual PresentationCarl JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mass ExercisesDocument8 pagesMass ExercisesMANANNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Optimal Core Training Program Design: AuthorDocument5 pagesStrategies For Optimal Core Training Program Design: AuthorDanavir Sarria100% (1)
- Ped 025 - Lesson 2 (Stabilization)Document26 pagesPed 025 - Lesson 2 (Stabilization)Michael MarzonNo ratings yet
- Physicaleducationandhealthgrade11 190109130928 PDFDocument42 pagesPhysicaleducationandhealthgrade11 190109130928 PDFKelvin NoynayNo ratings yet
- Homenkova Dev of Strength in Physical ConditioningDocument6 pagesHomenkova Dev of Strength in Physical ConditioningHarcownik Rafał100% (1)
- Isometric Exercises For Static Strength TrainingDocument5 pagesIsometric Exercises For Static Strength TraininggashaglavaNo ratings yet
- 1 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Demo FinalDocument17 pages1 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Demo FinalKeith SajulgaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fitness Exercises Lesson 1Document18 pagesIntroduction To Fitness Exercises Lesson 1Maxine de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Fall 2013 Instructor: Melissa KellyDocument12 pagesFall 2013 Instructor: Melissa KellyJonathan RolfsenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 TherapeuticDocument26 pagesModule 1 TherapeuticMar Jersey MartinNo ratings yet
- Fitness ActivitiesDocument29 pagesFitness ActivitiesCydeizel Mercado100% (1)
- First Monthly Exam PehDocument4 pagesFirst Monthly Exam PehMara JNo ratings yet
- Strength and Conditioning For Triathletes: Bruce Day, BSC and Don Johnson, MD, Frcs CDocument6 pagesStrength and Conditioning For Triathletes: Bruce Day, BSC and Don Johnson, MD, Frcs CeducobainNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health: Core Subject DescriptionDocument40 pagesPhysical Education and Health: Core Subject DescriptionCin DyNo ratings yet
- Resistance Training: Arran, Keanoe, Daniel and ClovisDocument10 pagesResistance Training: Arran, Keanoe, Daniel and ClovismancollNo ratings yet
- Strength Size or Power PDFDocument5 pagesStrength Size or Power PDFSphinx Strong100% (2)
- TMSTR Ozolin Conditioning ExercisesDocument10 pagesTMSTR Ozolin Conditioning Exercisesmarin0410100% (1)
- PlyometricsDocument5 pagesPlyometricsAlethea TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Resistance Training For Judo Functional Strength.6Document10 pagesResistance Training For Judo Functional Strength.6AnonymNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Vs Unilateral BlogDocument5 pagesBilateral Vs Unilateral BlogPaulNo ratings yet
- Tabat Module 3Document20 pagesTabat Module 3Julan AlatanNo ratings yet
- Strength For EnduranceDocument2 pagesStrength For EndurancejohnNo ratings yet
- Increased Physical Attractiveness: Strength Training Involves The Performance of Physical Exercises Which Are Designed ToDocument3 pagesIncreased Physical Attractiveness: Strength Training Involves The Performance of Physical Exercises Which Are Designed ToVirgen Beatriz Pocená UrquíaNo ratings yet
- Sum Designing Resistance Steven Fleck, William Kraemer deDocument5 pagesSum Designing Resistance Steven Fleck, William Kraemer deIELTS Council100% (1)
- R PeDocument9 pagesR PeKwin KwinNo ratings yet
- The Crunchless Core Workout For Runners: 7 Comments Tweet Share ShareDocument5 pagesThe Crunchless Core Workout For Runners: 7 Comments Tweet Share ShareMailin RipauNo ratings yet
- 1ºterm 1Document3 pages1ºterm 1ANA ISABEL ALCAZARNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitationofinjuredathlete Copy 160704054530Document24 pagesRehabilitationofinjuredathlete Copy 160704054530مركز ريلاكس للعلاج الطبيعيNo ratings yet
- Document 8Document2 pagesDocument 8Anneshelley GarciaNo ratings yet
- Planning Process For Core TrainingDocument1 pagePlanning Process For Core TrainingMinecraft TutorialovskiNo ratings yet
- Training The CoreDocument15 pagesTraining The CoreAfizieNo ratings yet
- Exercitii ReabilitareDocument5 pagesExercitii ReabilitareGabriela Istrati-StanciugelNo ratings yet
- Strength TrainingDocument3 pagesStrength Trainingusaf_jamalNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Sports TrainingDocument19 pagesExercise and Sports TrainingJulianel GocotanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet HOPE 11Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet HOPE 11guyaoaudrey23No ratings yet
- G10-Strength Training Exercises - LMDocument46 pagesG10-Strength Training Exercises - LMAlessa100% (1)
- Hope 1 Lesson 3Document20 pagesHope 1 Lesson 3Cisca Noda RafusonNo ratings yet
- FITTDocument23 pagesFITTJem VenturaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Principles of Resistance Training andDocument12 pagesChapter 1: Basic Principles of Resistance Training andLuis Eduardo Barbosa Ortega100% (1)
- Eric Velayo PE102Document2 pagesEric Velayo PE102Noriel CodoyNo ratings yet
- Fitness For Life: English For Health Sciences Vocabulary For Activity 1 Unit 3Document10 pagesFitness For Life: English For Health Sciences Vocabulary For Activity 1 Unit 3macaomacNo ratings yet
- 24 Shoulder PDFDocument3 pages24 Shoulder PDFLouit LoïcNo ratings yet
- PE32 Unit-II 2022 PDFDocument34 pagesPE32 Unit-II 2022 PDFtrisNo ratings yet
- PathFit 1 (MOD 2)Document6 pagesPathFit 1 (MOD 2)HazzaNo ratings yet
- Increased Physical AttractivenessDocument22 pagesIncreased Physical AttractivenessNasir SaleemNo ratings yet
- Four Main Types of ExerciseDocument1 pageFour Main Types of ExerciseLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes Exercise PrescriptionDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Notes Exercise PrescriptionAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Module 9Document20 pagesPathfit 1 Module 9Katherine Lauren MaglayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document11 pagesChapter 10JohnNo ratings yet
- Mike Durand-Wiaa Organization of Strength Training ProgramsDocument40 pagesMike Durand-Wiaa Organization of Strength Training ProgramsNick100% (2)
- Core Stability ExercisesDocument5 pagesCore Stability ExercisesAfizie100% (1)
- Types of Body Conditioning Exercises: and Their BenefitsDocument32 pagesTypes of Body Conditioning Exercises: and Their Benefitscrizel in nameNo ratings yet
- How To Build Muscular Strength & Power - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Blueprint For Strength And Power GainsFrom EverandHow To Build Muscular Strength & Power - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Blueprint For Strength And Power GainsNo ratings yet
- Functional Training for Athletes at All Levels: Workouts for Agility, Speed and PowerFrom EverandFunctional Training for Athletes at All Levels: Workouts for Agility, Speed and PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- SWINGS 20 WorkoutsDocument6 pagesSWINGS 20 Workoutsmarin0410No ratings yet
- Combat Sports: Warm-Up For All WorkoutsDocument15 pagesCombat Sports: Warm-Up For All Workoutsmarin0410No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive 3-Month Plan For Beginner Group LessonsDocument10 pagesA Comprehensive 3-Month Plan For Beginner Group Lessonsmarin0410No ratings yet
- 30 Days Without Weights For Ultimate StrengthDocument9 pages30 Days Without Weights For Ultimate Strengthmarin0410No ratings yet
- Managing Group Training PDFDocument9 pagesManaging Group Training PDFmarin0410No ratings yet
- A New Perspective On Energy Systems Joel Jamieson CVASPS 2011Document70 pagesA New Perspective On Energy Systems Joel Jamieson CVASPS 2011andrewallen1986No ratings yet
- Lactate ThresholdDocument22 pagesLactate Thresholdmarin0410No ratings yet
- Station #1 (Perform in A Circuit Mode)Document2 pagesStation #1 (Perform in A Circuit Mode)marin0410No ratings yet
- Triple ThreatDocument1 pageTriple Threatmarin0410No ratings yet
- Protein Requirements For Athletes: TrainingDocument2 pagesProtein Requirements For Athletes: Trainingapi-58002895No ratings yet
- Glycemic Index and RecoveryDocument3 pagesGlycemic Index and Recoverymarin0410No ratings yet
- Every Day Nutritionvs Game Day NutritionDocument2 pagesEvery Day Nutritionvs Game Day Nutritionmarin0410No ratings yet
- Kettlebell 5 PillarsDocument4 pagesKettlebell 5 Pillarsmarin0410100% (1)
- 3 Day Per Week Strength Training With Work CapacityDocument3 pages3 Day Per Week Strength Training With Work Capacitymarin0410No ratings yet
- NHC Lunch and Learn (Peterson)Document54 pagesNHC Lunch and Learn (Peterson)marin0410No ratings yet
- Periodization For The Tactical AthleteDocument12 pagesPeriodization For The Tactical Athletemarin0410100% (8)
- Remedial PT ProgramDocument4 pagesRemedial PT Programmarin0410100% (1)
- Sample Static and Dynamic StretchesDocument32 pagesSample Static and Dynamic Stretchesmarin0410No ratings yet
- Discharge Plan FhayeDocument4 pagesDischarge Plan FhayeTin-Tin RutaquioNo ratings yet
- 1preface To Introduction To KayachikitsaDocument2 pages1preface To Introduction To KayachikitsadrbharatsharmagNo ratings yet
- Forensic Pharmacy & Forensic Pharmacist: Presented By: Ibrahim Shafqat Uzair Abid Fahad Wadood Shoiab ShakeelDocument16 pagesForensic Pharmacy & Forensic Pharmacist: Presented By: Ibrahim Shafqat Uzair Abid Fahad Wadood Shoiab ShakeelJaved IqbalNo ratings yet
- HACCP Carbonated Soft DrinksDocument9 pagesHACCP Carbonated Soft DrinksmubdiantiNo ratings yet
- Application For The Post of Assistant Professor in DentistryDocument5 pagesApplication For The Post of Assistant Professor in DentistryVenkata Ramana Murthy VasupilliNo ratings yet
- PREP & COGENT - 13th and 14th December 2014Document6 pagesPREP & COGENT - 13th and 14th December 2014FdghNo ratings yet
- Reading 9thDocument3 pagesReading 9thicemangdNo ratings yet
- Arixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionDocument26 pagesArixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- We Want The Airwaves - Star Amerasu PT 1Document9 pagesWe Want The Airwaves - Star Amerasu PT 1Nia KingNo ratings yet
- Hospital Network in IndiaDocument200 pagesHospital Network in IndiaAlex GiDeonNo ratings yet
- EncoperesisDocument6 pagesEncoperesisRishi SelvamNo ratings yet
- Sat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseDocument7 pagesSat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiNo ratings yet
- What Is Kombucha Tea?Document12 pagesWhat Is Kombucha Tea?starprideNo ratings yet
- Art Theraphy AutismDocument2 pagesArt Theraphy AutismMatheaFiliNo ratings yet
- Report CapsicumDocument105 pagesReport CapsicumRina WijayantiNo ratings yet
- The Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisDocument4 pagesThe Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisPatricia Avalos C.No ratings yet
- 5 After The Last Breath (Written in 1904 On The Death of Hardy's Mother, Jemima Hardy, 1813-1904) .PDDocument3 pages5 After The Last Breath (Written in 1904 On The Death of Hardy's Mother, Jemima Hardy, 1813-1904) .PDsylviaordoNo ratings yet
- Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factors-Lauяeиs© TolosaNo ratings yet
- Twin Block Appliance ThesisDocument6 pagesTwin Block Appliance Thesisjessicahillnewyork100% (2)
- DR - Harish DurejaDocument26 pagesDR - Harish Durejaarpita_949242356No ratings yet
- PRIME Appetite and Weight Reduction Daily Food Plan For The HCG Diet: Monday - ThursdayDocument1 pagePRIME Appetite and Weight Reduction Daily Food Plan For The HCG Diet: Monday - ThursdayskydivercoNo ratings yet
- Iraq Biotechnology Conference May 7 - 9 Agenda ENGLISHDocument6 pagesIraq Biotechnology Conference May 7 - 9 Agenda ENGLISHGavin Macgregor-SkinnerNo ratings yet
- Zantac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesZantac Drug StudyCee Kaye Gee0% (1)
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 pagesBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Cam4 6 1861Document10 pagesCam4 6 1861Ćatke TkećaNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen PoisoningDocument19 pagesAcetaminophen PoisoningMARIA TELLEZNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Pas BingDocument8 pagesContoh Soal Pas BingAnnisa AuliaNo ratings yet