Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Band Theory For Solids
Uploaded by
Karthiik88100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
132 views6 pageselectrical engineering materials-band theory of solids
Original Title
Band Theory for Solids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentelectrical engineering materials-band theory of solids
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
132 views6 pagesBand Theory For Solids
Uploaded by
Karthiik88electrical engineering materials-band theory of solids
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Band Theory for Solids
Band Theory of Solids
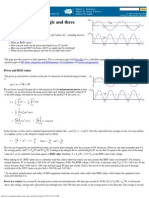
A useful way to visualize the difference between conductors,
insulators and semiconductors is to plot the available energies for
electrons in the materials. Instead of having discrete energies as in the
case of free atoms, the available energy states form bands. Crucial to
the conduction process is whether or not there are electrons in the
conduction band. In insulators the electrons in the valence band are
separated by a large gap from the conduction band, in conductors like
metals the valence band overlaps the conduction band, and in
Index
semiconductors there is a small enough gap between the valence and
conduction bands that thermal or other excitations can bridge the gap. Semiconductor
With such a small gap, the presence of a small percentage of a doping
concepts
material can increase conductivity dramatically.
Semiconductors
An important parameter in the band theory is the Fermi level, the top for electronics
of the available electron energy levels at low temperatures. The
position of the Fermi level with the relation to the conduction band is
a crucial factor in determining electrical properties.
Closer look at bands Band gap dependence on interatomic spacing
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
R
Nave
Go Back
Energy Bands for Solids
Index
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
Band Theory for Solids
Click on any part of the illustration for further information.
Band theory More details on diagram
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
R
Nave
Go Back
Energy Bands Comments
Index
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
Band gap dependence on interatomic spacing
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
R
Nave
Go Back
Band Theory for Solids
Insulator Energy Bands
Most solid substances are insulators, and in terms
of the band theory of solids this implies that there
is a large forbidden gap between the energies of
the valence electrons and the energy at which the
electrons can move freely through the material
(the conduction band).
Glass is an insulating material which may be
transparent to visible light for reasons closely
correlated with its nature as an electrical insulator.
The visible light photons do not have enough
Index
quantum energy to bridge the band gap and get
the electrons up to an available energy level in the Semiconductor
conduction band. The visible properties of glass
concepts
can also give some insight into the effects of
"doping" on the properties of solids. A very small Semiconductors
percentage of impurity atoms in the glass can give for electronics
it color by providing specific available energy
levels which absorb certain colors of visible light.
The ruby mineral (corundum) is aluminum oxide
with a small amount (about 0.05%) of chromium
which gives it its characteristic pink or red color
by absorbing green and blue light.
While the doping of insulators can dramatically
change their optical properties, it is not enough to
overcome the large band gap to make them good
conductors of electricity. However, the doping of
semiconductors has a much more dramatic effect
on their electrical conductivity and is the basis for
solid state electronics.
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
R
Nave
Semiconductor Energy Bands
For intrinsic semiconductors like silicon
and germanium, the Fermi level is
essentially halfway between the valence
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
Go Back
Band Theory for Solids
and conduction bands. Although no
conduction occurs at 0 K, at higher
temperatures a finite number of electrons
can reach the conduction band and
provide some current. In doped
semiconductors, extra energy levels are
added.
Index
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
The increase in conductivity with
temperature can be modeled in terms of
the Fermi function, which allows one to
calculate the population of the conduction
band.
Band theory of solids
Show the effect of
impurities
Silicon energy
bands
Germanium energy
bands
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
R
Nave
Go Back
Conductor Energy Bands
Index
In terms of the band theory of solids,
metals are unique as good conductors of
electricity. This can be seen to be a result
of their valence electrons being
essentially free. In the band theory, this
is depicted as an overlap of the valence
band and the conduction band so that at
least a fraction of the valence electrons
can move through the material.
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
R
Nave
Go Back
Band Theory for Solids
Silicon Energy Bands
At finite temperatures, the number of electrons which reach the conduction
band and contribute to current can be modeled by the Fermi function. That
current is small compared to that in doped semiconductors under the same
conditions.
Index
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
Compare to germanium
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
R
Nave
Go Back
Germanium Energy Bands
At finite temperatures, the number of electrons which reach the conduction
band and contribute to current can be modeled by the Fermi function. That
current is small compared to that in doped semiconductors under the same
conditions.
Index
Semiconductor
concepts
Semiconductors
for electronics
Compare to silicon
HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
Go Back
Band Theory for Solids
Nave
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/band.html[20-Nov-15 4:10:15 PM]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Module 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TDocument2 pagesModule 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TKarthiik88No ratings yet
- RRB 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesRRB 2015 PDFKarthiik88No ratings yet
- C Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-We m1Document7 pagesC Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-We m1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- Syllabus CWCDocument5 pagesSyllabus CWCDowlath BashaNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Worked Out Problems:) / Sinh / Sinh (. Sin 1) 1 (2), (Document10 pagesModule 4: Worked Out Problems:) / Sinh / Sinh (. Sin 1) 1 (2), (Karthiik88No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument16 pagesSyllabusapi-297121029No ratings yet
- AC Power, RMS and 3-Phase CircuitsDocument3 pagesAC Power, RMS and 3-Phase CircuitsKarthiik88No ratings yet
- Book CatalogueDocument16 pagesBook CatalogueAnusha GayathriNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering SyllabusDocument49 pagesEnergy Engineering SyllabusKarthiik88No ratings yet
- EDC Notes PDFDocument377 pagesEDC Notes PDFramyadspNo ratings yet
- Notification - TNPSC 2014Document22 pagesNotification - TNPSC 2014Sivamurugan PerumalNo ratings yet
- M 1 Teacher SlidesDocument15 pagesM 1 Teacher SlidesMidhun DavisNo ratings yet
- Anna University R2013 EEE SyllabusDocument108 pagesAnna University R2013 EEE SyllabusMuruga RajNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument12 pagesElectric Motors and GeneratorsKarthiik88No ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion (AP, May2008) R2004Document4 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion (AP, May2008) R2004Karthiik88No ratings yet
- 2A Maintenance OrganizationDocument38 pages2A Maintenance OrganizationKarthiik88No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- Indian Railway Station Code IndexDocument3 pagesIndian Railway Station Code IndexmayurshahNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0038092X11004609 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0038092X11004609 MainKarthiik88No ratings yet
- IEEE Outline FormatDocument3 pagesIEEE Outline FormatAlex HerrmannNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermo Dynamics (AP, May2008)Document4 pagesApplied Thermo Dynamics (AP, May2008)Karthiik88No ratings yet
- Indian Railway Station Code IndexDocument3 pagesIndian Railway Station Code IndexmayurshahNo ratings yet
- IEEE Outline FormatDocument3 pagesIEEE Outline FormatAlex HerrmannNo ratings yet
- Interview TipsDocument3 pagesInterview TipsKarthiik88No ratings yet
- C Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Qb m1Document1 pageC Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Qb m1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- C Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-We m1Document7 pagesC Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-We m1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- C Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Qb m1Document1 pageC Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Qb m1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- 1Document84 pages1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- C Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Lo m1-1Document1 pageC Docume 1 Tempcm 1.007 Locals 1 Temp Plugtmp Plugin-Lo m1-1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MagneticMaterials1Document603 pagesMagneticMaterials1Adinda Van Den BergNo ratings yet
- FYSMENA4111 Computer Lab 5 SurfacesDocument5 pagesFYSMENA4111 Computer Lab 5 Surfaceswer809No ratings yet
- Energy Band DiagramDocument6 pagesEnergy Band DiagramAlyssa GuiyabNo ratings yet
- Energy Band Theory in SolidsDocument3 pagesEnergy Band Theory in Solidsashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Kulite Pressure Transducer HandbookDocument76 pagesKulite Pressure Transducer Handbookpmud123No ratings yet
- Insulators, Conductors and Semiconductors (With Band Diagram) - StudyElectrical - Online Electrical Engineering Study Site PDFDocument3 pagesInsulators, Conductors and Semiconductors (With Band Diagram) - StudyElectrical - Online Electrical Engineering Study Site PDFGoutham DevisettyNo ratings yet
- Irjmets JournalDocument10 pagesIrjmets JournalIRJMETS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Band GapDocument19 pagesBand Gapilham ditamaNo ratings yet
- E.P. Wohlfarth Volume 1 Handbook of Magnetic Materials, Volume 1986Document603 pagesE.P. Wohlfarth Volume 1 Handbook of Magnetic Materials, Volume 1986Luka KelharNo ratings yet
- Vitalii Dugaev, Vladimir Litvinov - Modern Semiconductor Physics and Device Applications-CRC Press (2021)Document399 pagesVitalii Dugaev, Vladimir Litvinov - Modern Semiconductor Physics and Device Applications-CRC Press (2021)Angel Carrasco0% (1)
- Infrared Light-Driven CO Overall Splitting at Room TemperatureDocument14 pagesInfrared Light-Driven CO Overall Splitting at Room TemperatureRuchi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Band TheoryDocument3 pagesBand TheoryGauri Deshmukh KaranjgaokarNo ratings yet
- Band StructureDocument85 pagesBand StructureJorge Andres Hernandez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Tyuiop PDFDocument4 pagesTyuiop PDFDikshit GautamNo ratings yet
- What Is Electronic Band StructureDocument10 pagesWhat Is Electronic Band StructureHoang Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- Band Parameters For III-V Compound Semiconductors and Their AlloysDocument61 pagesBand Parameters For III-V Compound Semiconductors and Their AlloysErika GiangrisostomiNo ratings yet
- NCERT SemiconductorNCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2Document91 pagesNCERT SemiconductorNCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2Ranjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Toolbox DFTDocument20 pagesToolbox DFTAshok Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- (2017 - JPCS - Frazão) - 3R and 2H Polytypes of MoS2 DFT and DFPT Calculations of Structural...Document9 pages(2017 - JPCS - Frazão) - 3R and 2H Polytypes of MoS2 DFT and DFPT Calculations of Structural...niltonfrazaoNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of NanomaterialsDocument23 pagesPhysical Properties of NanomaterialsNaveed UR RehmanNo ratings yet
- 2009-10 T.Y.B.SC. ElectronicsDocument26 pages2009-10 T.Y.B.SC. Electronicshys0671No ratings yet
- Z Unger 1998Document9 pagesZ Unger 1998PaulGutiérrezGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Theory and Devices 11.1 - 11.2Document35 pagesSemiconductor Theory and Devices 11.1 - 11.2jamalur.lNo ratings yet
- Gresch-Soluyanov2018 Chapter CalculatingTopologicalInvarianDocument30 pagesGresch-Soluyanov2018 Chapter CalculatingTopologicalInvarianYizhi HuNo ratings yet
- Cse R20 1-1Document21 pagesCse R20 1-1Viswanadh JvsNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument12 pagesBand Theory of SolidsFitrianiNo ratings yet
- DFT First Principle LDA, PBE, PBEsol ZnO With Hubbard (2022)Document18 pagesDFT First Principle LDA, PBE, PBEsol ZnO With Hubbard (2022)Febriman ZendratoNo ratings yet
- Physics Presentation Topic: Submitted To Monika Mishra MamDocument23 pagesPhysics Presentation Topic: Submitted To Monika Mishra MamSatyam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Journal of Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesJournal of Solid State ChemistrySikander AzamNo ratings yet