Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 6
Uploaded by
IndahPertiwiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 6
Uploaded by
IndahPertiwiCopyright:
Available Formats
JTP 505 2 SKS
VENTILASI TAMBANG
14 Oktober2014 Hendra Harisman, S.T., M.Eng.Sc.
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Calculation of airway resistance and frictional losses
based on:
Shape and length of the airway or duct
Roughness of the surface
Flow regime (turbulent or laminar)
Quantity of air, gas or fluid in the airway or duct.
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction loss:
pressure loss due to flow over rough surface
Discontinuity loss:
pressure loss when air flows through and around
discontinuities (e.g. bends).
Obstruction loss: Pressure loss due to objects
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Viscosity
When a fluid begin to move, individual molecules or
layers start to move over each other in an approximately
linear fashion with retardation dependent on internal
cohesion between molecules.
As the velocity of the fluid increases, molecules or layers
move in increasingly random fashion as the magnitude of
inertial forces increase and the flow become turbulent.
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
The degree of turbulence in a moving fluid depends on:
viscosity
velocity
Less viscous fluids moving faster and more turbulent than
more viscous fluids moving slower.
Turbulence is associated with energy or pressure loss.
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Turbulence is associated
with energy or pressure loss.
In laminar conditions
pressure loss is proportional
to velocity
In turbulent conditions
pressure loss is proportional
to velocity squared
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
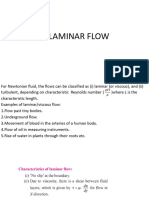
The limits of laminar and turbulent flow can be
determined from the dimensionless Reynolds number
Reynolds number:
= density(kg/m3)
L = characteristic dimension e.g. diameter(m)
V = Velocity(m/s)
= viscosity (kg/ms)
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
The limits of laminar and turbulent flow can be
determined from the dimensionless Reynolds number
Generally, the upper limit of laminar flow is between
Reynolds number of 2,000 and 3,000.
in other words:
Turbulent flow starts between Re 2,000 to 3,000
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Reynolds number:
L = characteristic dimension e.g. diameter(m)
In circular ducts or airways:
L = diameter
In non-circular ducts or airways
L = hydraulic diameter
A = Area
C = Circumference
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Contoh soal:
Hitung kecepatan (velocity) dan quantity udara yang
dapat menyebabkan turbulent flow (Re = 2500) di sebuah
terowongan development yang lebarnya 5 m dan
tingginya 3 m.
Assumsi:
density udara = 1.16 kg/m3
Viskositas udara = 18 x 10-6 kg/ms
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction Loss on Rough Surface
As gas or liquids flow over rough surfaces, there is loss of
pressure due to the interaction of the boundary layer
with the surface.
This loss results in a reduction of static pressure, and in
airways of constant cross sectional area, an equal
reduction of total pressure.
In most applications, flow is assumed to be turbulent
The frictional pressure loss is proportional to the square of
velocity.
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction Loss on Rough Surface
Frictional pressure loss represents a loss of energy to the
system
- it results in a loss of static pressure which is not reversible
- in turbulent regimes the loss is proportional to the
square of velocity
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction Loss on Rough Surface
Atkinsons equation is the mathematical representation
of the relationship between frictional pressure loss
occurring on rough surfaces and velocity.
Atkinsons equation in terms of Velocity
Atkinsons equation in terms of Quantity
Density is incorporated as
a ratio of actual fluid
density
to
standard
density of 1.2 kg/m3
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction Loss on Rough Surface
Atkinsons equation
k = roughness factor of the surface (Ns2/m4)
C = Circumference/perimeter (m)
L = Length(m)
A = Area (m2)
= density of the fluid/gas(kg/m3)
V = Velocity (m/s)
Q = Quantity (m3/s)
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Friction Loss on Rough Surface
Airway resistance (R)
K factors can be obtained
from text books but should be
checked by survey
K are range from 0.003 for
smooth ducts to 0.015 for
rough walls
FRICTION, DISCONTINUITY & OBSTRUCTION
Contoh soal:
Friction factor (k) suatu terowongan dengan tinggi 3 m dan
lebar 5 m adalah 0.012 Ns2/m4. Apabila densitas udara di
terowongan tersebut adalah 1.17 kg/m3, berapakah
resistance (R) dari terowongan tersebut per 100 m
panjangnya?
THE END
INERTIA
a property of matter by which it continues in its existing state of rest or uniform motion in a
straight line, unless that state is changed by an external force.
Inertia is a word we use when we talk about matter and movement. Basically, our idea of
inertia goes back to Sir Isaac Newton's first two laws of physics:
1. An object at rest tends to stay at rest.
2. An object in motion tends to stay in motion.
Inertia is the quality in matter (matter is anything you can touch) that lets it stay still if it is still,
or keeps it moving if it is moving.
If you want to overcome inertia, you have to apply a force. A force will make something that
is still start to move, like flicking a wad of paper with a pencil will make it move. Also force,
due to resistance, will slow or stop something that is already moving. The wad of paper will
be slowed by resistance made by rubbing up against the air it is passing through.
You might also like
- 7 - Airflow Through Mine Opening and Ducts IDocument24 pages7 - Airflow Through Mine Opening and Ducts ISude Yağmur ÇalışırNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Seacom Skills UniversityDocument40 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Seacom Skills UniversitykadamsnNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Laws of Fluid Friction and Flow Through PipesDocument94 pagesFluid Mechanics - Laws of Fluid Friction and Flow Through Pipessrutii100% (1)
- Airway ResistanceDocument23 pagesAirway ResistanceRitik BerwaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Seacom Skills UniversityDocument40 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Seacom Skills UniversityShubham MahajanNo ratings yet
- Ventilasi - Week 7Document20 pagesVentilasi - Week 7Rifky FarhanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Boundary Layer Theory GuideDocument32 pagesFluid Mechanics Boundary Layer Theory GuideSubhasish MitraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Boundary Layer Theory GuideDocument32 pagesFluid Mechanics Boundary Layer Theory GuideDharigra AlcitaNo ratings yet
- CHE131 - Module6 Fluid Flow Phenomena (Part 2)Document43 pagesCHE131 - Module6 Fluid Flow Phenomena (Part 2)Jason PacilNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Boundary LayerDocument110 pagesUnit 5 - Boundary LayerSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- Unit 5 With QP-1Document31 pagesUnit 5 With QP-1jaga67676734No ratings yet
- Project BankDocument8 pagesProject BankVARUN SINGH SHEKHAWATNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument26 pagesFlow MeasurementOmkar rodeNo ratings yet
- Friction and Its EffectsDocument39 pagesFriction and Its EffectsOmkar rodeNo ratings yet
- Viscous Flow in PipesDocument71 pagesViscous Flow in PipesAkmalFadzli100% (1)
- Laminar FlowDocument48 pagesLaminar Flowtimothyatambo383No ratings yet
- FRICTION AND ITS EFFECT ON FLUID FLOWDocument13 pagesFRICTION AND ITS EFFECT ON FLUID FLOWOmkar rodeNo ratings yet
- Streamline Flow: Laminar Flow and StreamlinesDocument5 pagesStreamline Flow: Laminar Flow and StreamlinesGowthamCoorgNo ratings yet
- Air Over A Two-Dimensional Studies Velocity Speed-Up, Roughness Effects and TurbulenceDocument20 pagesAir Over A Two-Dimensional Studies Velocity Speed-Up, Roughness Effects and TurbulenceGonKilNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer TheoryDocument2 pagesBoundary Layer TheoryHariz MiorNo ratings yet
- AE 2020: Low Speed AerodynamicsDocument51 pagesAE 2020: Low Speed AerodynamicsNatesan MahendranNo ratings yet
- Airflow Through Mine OpeningDocument6 pagesAirflow Through Mine Openingersunilsingh1No ratings yet
- Viscous Flow in Pipes PDFDocument71 pagesViscous Flow in Pipes PDFMuhammad Izzamir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Reynold Number QuestionDocument3 pagesReynold Number QuestionSyahdi RosliNo ratings yet
- Boundary LayerDocument10 pagesBoundary Layerعبدالمحسن علي ENo ratings yet
- Hydraulics & Hydrology (CVE 705)-Module 6Document52 pagesHydraulics & Hydrology (CVE 705)-Module 6mohammed adoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3-Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 3-Solutions PDFNickson KomsNo ratings yet
- Eme1122 CN4Document7 pagesEme1122 CN4MAENYA BRUCE OYONDINo ratings yet
- Types of Fluid Flow: Viscous vs Inviscid, Internal vs ExternalDocument5 pagesTypes of Fluid Flow: Viscous vs Inviscid, Internal vs ExternalkebasaNo ratings yet
- Question One: EZRA AHUMUZA AEBD 2004/HD16/2447UDocument31 pagesQuestion One: EZRA AHUMUZA AEBD 2004/HD16/2447UEzra AhumuzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 ConvectionDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 ConvectionSaiyam AjmeraNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mat 7Document14 pagesConcrete Mat 7Gert-Jan RoelevinkNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1: Course Notes: StaffDocument44 pagesHydraulics 1: Course Notes: StaffkristovNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Module 4 - Part1Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics - Module 4 - Part1Sk Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Lecture#4Document45 pagesLecture#4Babar KhattakNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Flow and Pipe Network AnalysisDocument18 pagesBoundary Layer Flow and Pipe Network AnalysisnkchandruNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 FLOW THROUGH PIPES Background TheoryDocument8 pagesExperiment No.1 FLOW THROUGH PIPES Background TheoryMradul YadavNo ratings yet
- Parala Maharaja Engineering College, Berhampur: 1. List Out The Advantages of Model AnalysisDocument10 pagesParala Maharaja Engineering College, Berhampur: 1. List Out The Advantages of Model AnalysisRohan KumarNo ratings yet
- (Khawaja Zain) (20-CE-121) (Transport Lab Copy)Document65 pages(Khawaja Zain) (20-CE-121) (Transport Lab Copy)Ali BahuNo ratings yet
- 1 Boundary Layer TheoryDocument14 pages1 Boundary Layer TheoryMoisés SolisNo ratings yet
- Boundary LayerDocument10 pagesBoundary LayerViwek MertiyaNo ratings yet
- LAB 3: PRESSURE LOSS IN PIPESDocument8 pagesLAB 3: PRESSURE LOSS IN PIPESLance HernandezNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer: (Arya Pradamansyah P, Achmad Rizkiawan, Ayu Annisa Febryana, Dewi Amalia, M DafaDocument7 pagesWater Hammer: (Arya Pradamansyah P, Achmad Rizkiawan, Ayu Annisa Febryana, Dewi Amalia, M DafaDimas FajarNo ratings yet
- Convection Heat Transfer Mechanisms and Flow RegimesDocument15 pagesConvection Heat Transfer Mechanisms and Flow RegimesYahia ZaghloulNo ratings yet
- CHE 333 Chapter 6 Fundamentals of ConvectionDocument47 pagesCHE 333 Chapter 6 Fundamentals of ConvectionEnesEmreTaşNo ratings yet
- Turbulence Measurements in Hydraulic JumpsDocument13 pagesTurbulence Measurements in Hydraulic JumpsBrandon LevineNo ratings yet
- Turbulator (Tipe Straight Tape Strip) TerhadapDocument8 pagesTurbulator (Tipe Straight Tape Strip) TerhadapMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law Explained for Groundwater FlowDocument19 pagesDarcy's Law Explained for Groundwater FlowAzman AzmanNo ratings yet
- TP 400levelDocument14 pagesTP 400levelEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MechDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank MechSandeep MoreNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Energy Gradients in Fluid FlowDocument75 pagesHydraulic and Energy Gradients in Fluid FlowJemima GnanaPushpamNo ratings yet
- I J Seas 20171208Document7 pagesI J Seas 20171208Anonymous PL6rbbNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument2 pagesCONCLUSION마비 니제시카No ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument1 pageCONCLUSION마비 니제시카No ratings yet
- Cours PG Chapitre 3-2 V.ANGDocument31 pagesCours PG Chapitre 3-2 V.ANGevident 2014No ratings yet
- T1.1b Flow of Heat - Forced ConvectionDocument17 pagesT1.1b Flow of Heat - Forced ConvectionMuhammad HussainNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer and Flow Control: Its Principles and ApplicationFrom EverandBoundary Layer and Flow Control: Its Principles and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Theory of Supersonic Viscous Gas FlowsFrom EverandAsymptotic Theory of Supersonic Viscous Gas FlowsVladimir NeylandNo ratings yet
- Dataset 26Document3 pagesDataset 26IndahPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Uji Bu Husni 40913Document2 pagesUji Bu Husni 40913IndahPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Ventilasi - Week 7Document20 pagesVentilasi - Week 7Rifky FarhanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionIndahPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Ventilasi Tambang: Teknik PertambanganDocument22 pagesVentilasi Tambang: Teknik PertambanganIndahPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument20 pagesCentrifugal PumpHENRYGALLEGOSNo ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Design and Theory - R. S. R. Gorla and A. A. KhanDocument179 pagesTurbomachinery Design and Theory - R. S. R. Gorla and A. A. KhanaliNo ratings yet
- Analysis of WCSPH Laminar Viscosity Models:, IncludingDocument26 pagesAnalysis of WCSPH Laminar Viscosity Models:, IncludingManuel AyalaNo ratings yet
- The Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, LubricationDocument43 pagesThe Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, Lubricationحسين مهديNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument61 pagesUnit IIHemanth Peddavenkatappa GariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document48 pagesChapter 9Ahmet KuralNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument1 pageWater HammerrosinniNo ratings yet
- The Drag Divergence Mach NumberDocument7 pagesThe Drag Divergence Mach NumberHasith SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Solving fluid equations with Navier-StokesDocument3 pagesSolving fluid equations with Navier-StokesositisNo ratings yet
- Rapidcast Pattern Plan: Advanced Manufacturing & Technology CentreDocument4 pagesRapidcast Pattern Plan: Advanced Manufacturing & Technology CentreDeepak DasNo ratings yet
- CE6451-Fluid Mechanics and Machinery QBDocument10 pagesCE6451-Fluid Mechanics and Machinery QBVignesh DuraiNo ratings yet
- Notes 4 (2023) Concepts of Fluid Kinematics and Internal FlowDocument26 pagesNotes 4 (2023) Concepts of Fluid Kinematics and Internal FlowVinn GTNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Ijthermalsci 2020 106573 PDFDocument10 pages10 1016@j Ijthermalsci 2020 106573 PDFzafira atifaNo ratings yet
- Brinkman EquationDocument5 pagesBrinkman EquationAdegbite Jamiu OyekanNo ratings yet
- Vincke Gear Pumps CatDocument48 pagesVincke Gear Pumps CatVelibor KaranovicNo ratings yet
- Pressure Control Design Guide SummaryDocument10 pagesPressure Control Design Guide SummaryMarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary and Study Guide for Control Volume Analysis Using EnergyDocument24 pagesChapter Summary and Study Guide for Control Volume Analysis Using Energykrntomboy25% (4)
- Flow Through Centrifugal & Axial Flow Compressors: A ComparisonDocument56 pagesFlow Through Centrifugal & Axial Flow Compressors: A ComparisonAzra H.No ratings yet
- 4th Sem Hydraulic MICROPROJECTDocument16 pages4th Sem Hydraulic MICROPROJECTOmkar Jambhale100% (1)
- Naval Engineering Modeling and Optimization Program (NEMO)Document54 pagesNaval Engineering Modeling and Optimization Program (NEMO)Leandro MeiliNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument18 pagesPumph.h.hussein.f92No ratings yet
- Total Hydrostatic Forces On Plane SurfaceDocument7 pagesTotal Hydrostatic Forces On Plane SurfaceJohnnette AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Predicting - How Could CFD Replaced Wind Tunnel TestDocument15 pagesWind Load Predicting - How Could CFD Replaced Wind Tunnel TestadiNo ratings yet
- DRLG 451 - Assignment #3 Well ControlDocument6 pagesDRLG 451 - Assignment #3 Well ControlnijamediaNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument205 pagesLectures On Computational Fluid Dynamicsalakozai Khan100% (1)
- Abu PembahasanDocument55 pagesAbu PembahasanshasaNo ratings yet
- Appendix-5: Design of UndersluiceDocument8 pagesAppendix-5: Design of UndersluicekkgbkjNo ratings yet
- Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, Topi-23460Document3 pagesGhulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, Topi-23460Saad RasheedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids 2 Marks (ALL-Units)Document22 pagesMechanics of Fluids 2 Marks (ALL-Units)rajapratyNo ratings yet
- Knudsen Number PDFDocument4 pagesKnudsen Number PDFBharath Reddy100% (1)