Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learn Land Cover Classification with Landsat Imagery
Uploaded by
toarunaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learn Land Cover Classification with Landsat Imagery
Uploaded by
toarunaCopyright:
Available Formats
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3. Tutorials
The following is a basic tutorial about the use of the Semi-Automatic Classification
Plugin. However, visit the blog From GIS to Remote Sensing for new and updated
tutorials such as:
Estimation of Land Surface Temperature with Landsat Thermal Infrared Band;
Land Cover Classification of Cropland.
In this tutorial we are going to classify a Landsat image (single band rasters). Download
the sample dataset, which is a Landsat 8 image (a subset acquired in the South of Rome,
Italy) available from the U.S. Geological Survey. The following bands (each band is a
single 16 bit raster) are included in the file:
2 - Blue;
3 - Green;
4 - Red;
5 - Near-Infrared;
6 - Short Wavelength Infrared 1;
7 - Short Wavelength Infrared 2.
The Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin uses SAGA GIS for the classification process.
The SAGA algorithms work only with single band images as input. Therefore, if input is a
multi band raster (i.e. a single image file made of several bands), the Semi-Automatic
Classification Plugin automatically splits the input file to single band rasters, which takes
some time depending on raster size. In order to optimize the classification process
(especially for hyperspectral images), it is preferable to use single band rasters, or split
the image file to single bands, as explained here (point 1) .
3.1. Define the inputs
Required inputs are a multi band raster or single band rasters, and a training shapefile
for ROI creation. In this tutorial we are going to create a band set.
Start QGIS and load the raster bands; create a color composite (RGB=543) of the
sample data, which is useful for the photo interpretation, as explained here (point
2); start the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (if the docks of the are not
displayed, click the button Show docks in the main plugin interface);
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
1/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
In the plugin dock ROI creation click the button Band set besideSelect an image;
the tab Band set will open; click the button Select All, then Add rasters to set;
under Band set definition, order the band names in ascending order, from top to
bottom using the arrows (this is useful for the interpretation of spectral
signatures);
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
2/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
Now we need to create a training shapefile that will store ROIs (a polygon layer
that requires two fields ID_class and ROI_info in the attribute table); in the dock
ROI creation click the button New shapefile, and select where to save the shapefile
(for instance ROI.shp).
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
3/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
Hint: in order to use any shapefile (having different field names for ID and Information)
as training shapefile, it is possible to change the default field names in the tab Settings
of the main interface, according to the existing field names. When needed, the plugin
will add automatically other fields for the spectral signature calculation.
3.2. Create ROIs
ROIs are polygons delimiting a certain land cover class, which are required to train the
classification algorithm. Created ROIs are temporary polygons, which are placed inside
the group Class_temp_group (added automatically if missing) in the Layers panel. This
group should be moved to the bottom of the Layers panel; this way, only the last
created ROI will be displayed over the image (the previous ROIs will be automatically
hidden).
In order to create a ROI, in the dock ROI creation click the button + beside Create
a ROI (this activates the ROI pointer); ROIs are created by clicking on any pixel of
the image; click on the dark area in the South, which is the Lake Albano (use the
mouse scroll to zoom); after a few seconds the ROI polygon will appear over the
image (a semitransparent orange polygon);
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
4/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
It is possible to change the ROI creation parameters, in order to create a smaller
or lager ROI; change the Min ROI size value to 100, and the Max ROI width value to
150; in order to create a ROI at the same point clicked before, click the button
Redo ROI;
Now, check Rapid ROI on band and click the button Redo ROI; this way, ROIs can
be computed only on one selected band, saving time especially for
hyperspectral images; change the value to 4 beside Rapid ROI on band, and click
the button Redo ROI; as you can see, ROIs have different shapes depending on the
selected band;
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
5/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
Open the Settings tab of the main interface; under ROI style it is possible to
change colour and transparency of created ROIs as you wish.
3.3. Save the ROIs to shapefile
This step is required in order to save the created ROIs to the training shapefile.
Under ROI definition type a brief description of the ROI inside the field Information
(e.g. water); this description will not be used during the classification process, but it
is useful for distinguishing ROIs; the field ID (i.e. identifier of the class) is used as
reference for the land cover classification, therefore it is important that each
category has a unique ID value; ROIs sharing the same ID are treated as a single
ROI; now, leave the ID set to 1;
If the checkbox Calculate signature is checked, then the ROI spectral signature is
calculated while the ROI is saved; now, uncheck this checkbox (we are going to
calculate it later, from the Spectral signature tab);
In order to save the ROI to the training shapefile click the button Save ROI to
shapefile;
It is possible to delete the last saved ROI by clicking Undo save ROI.
3.4. Spectral signature plot
In the plugin main interface, select the tab ROI tools > Spectral signature, which
displays the plots of selected ROIs, and select the item water; it is possible to
calculate the ROI signature by clicking the button Calculate signature and
confirming;
If the checkox Plot is checked, then the plot will display the standard deviation
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
6/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
of each ROI; you can pan and zoom through the plot using the navigation toolbar
(provided by Matplotlib).
Hint: in the tab Settings of the main interface, it is possible to change the maximum
number of characters for ROIs of the plot legend (which is 15 by default).
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
7/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3.5. Scatter plot
The Scatterplot tab allows for the calculation of the ROI scatter plots, which are useful
to assess ROI separability choosing between two bands. Pixel values for two raster
bands are represented as points in the 2D space.
3.6. Multiple ROI creation at once
It is possible to create automatically ROIs given a list of point coordinates (X,
Y), class ID and ROI information (ROIs are created with the parameters defined in
the dock ROI creation); select the ROI tools tab > Multiple ROI creation and click
Add point to add a new line where you can fill the required fields; now select the
line (click the line number on the left) and click Remove highlighted points;
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
8/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
It is also possible to import a list of points, maybe from field survey; download
this text file, click the button Import and select the downloaded file;
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
9/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
In order to create and save the ROIs to the shapefile click Create and save ROIs (it
takes some time, depending on the number of points).
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
10/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3.7. Perform a classification preview
Classification preview is a rapid way to evaluate collected ROIs.
It is possible to choose between several classification algorithms (Maximum
Likelihood; Minimum Distance; Spectral Angle Mapping); now select Spectral Angle
Mapping;
Algorithm threshold allows you to leave unclassified pixels that meet a certain
rule: for Maximum Likelihood, pixels are unclassified if probability is less than
threshold (max 100); for Minimum Distance, pixels are unclassified if distance is
greater than threshold; for Spectral Angle Mapping, pixels are unclassified if
spectral angle distance is greater than threshold (max 90);
Preview size is the side of the classification preview (in pixel unit); setSize to 300;
click the button + under Classification preview and click on the image; similarly to
the ROI, click the button Redo to perform another classification preview at the
same point;
Created ROIs are displayed in the ROI list; double click on any item to zoom to the
corresponding ROI in the map; also, it is possible to delete selected ROIs using
the button Delete selected ROIs.
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
11/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3.8. Set a classification style
It is useful to create a classification style with labels that will be loaded for every
classification.
In the panel Layers, left click on a classification preview and selectProperties;
change the colours and labels of classes, according to the training ROIs; then,
create click Save style ... to save the .qml file (e.g. style.qml);
In the Classification dock, under Classification style click the button Select qml to
select the file style.qml; the next classification will be loaded with this style.
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
12/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
Hint: after adding a new class to the training shapefile, repeat the above steps to
overwrite the .qml file and update the classification style.
A large number of ROIs is required for a good classification. Download this training
shapefile , which contains several ROIs, and load it in QGIS.
The main output of a classification is a raster file .tif; click the button Perform
classification and select where to save the output (e.g. classification.tif); use the
classification style from this file zip ;
In addition to this raster, it possible to create the shapefile of the classification
by checking the checkbox Create vector; the shapefile will be saved with the same
name and in the same directory of the .tif file (it takes some minutes for the vector
creation, depending on your system spec);
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
13/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
If the checkbox Calculate accuracy is checked, than the error matrix is calculated
and saved as file .txt in the same directory of the .tif file (also, it is automatically
displayed in the tab of the plugin main interface Post processing > Accuracy); the
error matrix is calculated by comparing the classification to the training shapefile
used for the classification (see below Post processing tools);
It is possible to apply a mask shapefile to the classification; download this
shapefile , check the checkbox Apply mask and select the downloaded shapefile;
click the button Perform classification, and the classification will be saved along
with the error matrix and the vector output.
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
14/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3.9. Post processing tools
It is possible to assess the classification accuracy (implemented by GRASS GIS),
by comparing the classification to a reference shapefile (not necessarily the
training shapefile); now, select the tab Post processing > Accuracy of the plugin
main interface; select theclassification.tif beside Select a classification to assess
and select the ROI shapefile beside Select the reference shapefile; then click the
button Calculate error matrix and the matrix will be displayed; you can save the
error matrix by clicking the button Save error matrix to file;
It is useful to calculate the land cover change (through GDAL and Numpy)
between a reference classification raster and a new classification raster; download
this classification (pretend this is the last year classification); select the tab Post
processing > Land cover change of the plugin main interface, select the
downloaded classification as reference classification, and the classification.tif as
the new classification; click the button Calculate land cover change and select
where to save the raster of changes and the related table (i.e. a file .csv, whose
values are separated by tab); pixel values of the raster of changes (ChangeCode)
are described in the table, and each value represent a class of change from the
reference classification to the new classification;
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
15/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
16/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
If the checkbox Mask unchanged pixel is checked, then unchanged pixels will have
a value of 0 (Unclassified).
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
17/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
18/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
3.10. Advanced settings
It is worth mentioning also other advanced settings:
In the tab Settings of the plugin main interface it is possible to set the RAM used
for processing; set the Available RAM according to your computer spec (in
general, half of the system RAM is a good value);
if the checkbox Record events in a Log file is checked a Log file is created and
updated during the processes; the Log file is saved in the plugin directory (located
inside
your
user/home
directory,
.qgis2/python/plugins/SemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin),
with
the
name
__0semiautomaticclass.log;
several buttons allow for the testing of program installation such as: SAGA GIS,
GRASS GIS, and QGIS geoalgorithms;
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
19/20
12/9/2015
3.TutorialsSemiAutomaticClassificationPlugin2.5.1documentation
For more and updated tutorials please visit http://fromgistors.blogspot.com .
http://semiautomaticclassificationmanual.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Tutorials.html
20/20
You might also like
- Kruskal-Wallis Tests (Simulation)Document15 pagesKruskal-Wallis Tests (Simulation)scjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajNo ratings yet
- Potato Dextrose Agar (7149)Document2 pagesPotato Dextrose Agar (7149)Nelson MubaiNo ratings yet
- Quadrat SamplingDocument6 pagesQuadrat SamplingSabreena NordinNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Factors of Lake EcosystemDocument31 pagesPhysical and Chemical Factors of Lake EcosystemEllaine Larren RazonNo ratings yet
- Full Specification and Technical Data Sheet of Potato Dextrose AgarDocument2 pagesFull Specification and Technical Data Sheet of Potato Dextrose AgarKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- Units: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsDocument8 pagesUnits: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document72 pagesCH 02Handugan Quinlog NoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Power Point NotesDocument36 pagesChapter 7 Power Point Notesapi-285078865No ratings yet
- RNA Plant and Animal Virus Replication PDFDocument9 pagesRNA Plant and Animal Virus Replication PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- ScientificDocument1 pageScientificapi-190382013No ratings yet
- Intro To Biomechanics (TV)Document14 pagesIntro To Biomechanics (TV)lylyho91No ratings yet
- Chicken Anatomy Lab GuideDocument8 pagesChicken Anatomy Lab GuideKaryl GregorioNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesA Brief History of MicrobiologyVia Songcal100% (1)
- Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin For QGIS PDFDocument25 pagesSemi-Automatic Classification Plugin For QGIS PDFFlinkWebbNo ratings yet
- Zoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsDocument103 pagesZoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsTHUNDERCLASH_SILVEREYES139100% (3)
- Protozoa: General Properties and Medical ImportanceDocument73 pagesProtozoa: General Properties and Medical ImportanceUmer RasheedNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approaches To Phylogeny)Document26 pagesSystematic Approaches To Phylogeny)Mhi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Document68 pagesGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiNo ratings yet
- Frog DissectDocument5 pagesFrog DissectGeeklyGamer 02No ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Life Biological Principles and The Science of ZoologyDocument64 pagesLecture 1. Life Biological Principles and The Science of ZoologyLeopoldo ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- fFINAALS BIOCHEM 2019Document7 pagesfFINAALS BIOCHEM 2019Cathelyn C. MarianoNo ratings yet
- 09 Vertebrate Digestive SystemDocument74 pages09 Vertebrate Digestive SystemJohn Andre CruzNo ratings yet
- Ecology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument69 pagesEcology Multiple Choice QuestionsJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Animals ClassificationDocument10 pagesAnimals ClassificationVivek JainNo ratings yet
- SterilizationDocument7 pagesSterilizationdereje_kebebeNo ratings yet
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument24 pagesBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes Non ChordatesDocument76 pagesZoology Notes Non ChordatesAakash Dahiya100% (1)
- Long Questions: MSC-BOTANY, Model QuestionsDocument4 pagesLong Questions: MSC-BOTANY, Model QuestionsCDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Molecular Systematic of AnimalsDocument37 pagesMolecular Systematic of AnimalsMarlene Tubieros - InducilNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Cell and OsmosisDocument5 pagesLab 1 Cell and OsmosisyuwarajaNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function: C E L PDocument38 pagesAnimal Form and Function: C E L PJoshua Miguel Buno0% (1)
- Biodiversity Loss and Its ImpactsDocument94 pagesBiodiversity Loss and Its ImpactsSaif Mohammad100% (1)
- 9th Class Computer Chapter No. 1Document4 pages9th Class Computer Chapter No. 1Muhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Comparing DNA Sequences To Understand Evolutionary Relationships With BlastDocument3 pagesComparing DNA Sequences To Understand Evolutionary Relationships With Blastflyawayxx13No ratings yet
- Chapter 40 and 41 Objectives-1Document5 pagesChapter 40 and 41 Objectives-1Alex KirbyNo ratings yet
- Protocols For BioEditDocument24 pagesProtocols For BioEditHadi SastranegaraNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotsDocument19 pagesBiodiversity Hotspotsernawita ernawitaNo ratings yet
- MBB 125 RDR #1 Full Final - v2Document7 pagesMBB 125 RDR #1 Full Final - v2Flare16No ratings yet
- Bacterial Identification Lab Worksheet StudentDocument7 pagesBacterial Identification Lab Worksheet StudentmmparkerNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Comparative AnatomyDocument7 pagesComparative Anatomylife senceNo ratings yet
- Micro TaxonomyDocument29 pagesMicro TaxonomyGujulla RahulNo ratings yet
- A Maxent Model v7Document30 pagesA Maxent Model v7Sanjoy NingthoujamNo ratings yet
- VL 1. Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument8 pagesVL 1. Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesTrisha TioNo ratings yet
- National Income ConceptsDocument15 pagesNational Income Conceptsrinky_trivediNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics ManualDocument29 pagesCell Biology and Genetics ManualAyesha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Central Dogma - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument13 pagesQuiz On Central Dogma - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah TuringanNo ratings yet
- NMU Jalgaon Question Bank FYBSc Zoology Non-ChordatesDocument51 pagesNMU Jalgaon Question Bank FYBSc Zoology Non-ChordatesHassan Ahmed100% (2)
- MSC 1st Sem Model QuestionsDocument5 pagesMSC 1st Sem Model QuestionsCDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Class 11 Social Studies and Life Skill Education Model QuestionDocument2 pagesClass 11 Social Studies and Life Skill Education Model Questionprakasholi100% (1)
- Intro. Gen ZooDocument49 pagesIntro. Gen ZooEdward Ashley ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document11 pagesLab Report 1IrhamNiHazIqi100% (1)
- An Introduction To Phylogenetic Analysis - Clemson UniversityDocument51 pagesAn Introduction To Phylogenetic Analysis - Clemson UniversityprasadburangeNo ratings yet
- II. Cot AnalysisDocument32 pagesII. Cot AnalysisSuraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3.6 OsmosisDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 3.6 OsmosisFadhliana UzalliNo ratings yet
- Seagrass Species Distribution and Coverage in The Intertidal Zones of Bucas Grande Island, Surigao Del Norte, PhilippinesDocument4 pagesSeagrass Species Distribution and Coverage in The Intertidal Zones of Bucas Grande Island, Surigao Del Norte, PhilippinesChris CabugaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Zoology SyllabusDocument28 pagesM.Sc. Zoology Syllabusanurag kumarNo ratings yet
- Final Project Part 2 DashboardDocument6 pagesFinal Project Part 2 DashboardZubair AhmadNo ratings yet
- ABAP Report WizardDocument20 pagesABAP Report Wizardbskris8727No ratings yet
- UDA Online Application SystemDocument30 pagesUDA Online Application SystemtoarunaNo ratings yet
- Park Standards Guide for City DevelopmentDocument266 pagesPark Standards Guide for City DevelopmenttoarunaNo ratings yet
- Withstanding The Forces A Study of The Spatial ConfigurationDocument15 pagesWithstanding The Forces A Study of The Spatial ConfigurationtoarunaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Colombo's Spatial ConfigurationDocument17 pagesEvolution of Colombo's Spatial ConfigurationtoarunaNo ratings yet
- Katalog Optibelt Remenice PDFDocument128 pagesKatalog Optibelt Remenice PDFluky ivanNo ratings yet
- Iicep.1978.2758 Design and Construction of Kwai Chung Container Terminal, Hong Kong, Berth 1, 2 and 3 DiscussionDocument12 pagesIicep.1978.2758 Design and Construction of Kwai Chung Container Terminal, Hong Kong, Berth 1, 2 and 3 DiscussionChoy Chi WaiNo ratings yet
- Kareem Shagar Formation An Oil Field Located in Ras Gharib DevelopmentDocument53 pagesKareem Shagar Formation An Oil Field Located in Ras Gharib Developmentwisam alkhooryNo ratings yet
- Pipe Bending Machine Manual SmallDocument99 pagesPipe Bending Machine Manual SmallRajesh Kannan100% (2)
- Helical Gears: Gear DrivesDocument11 pagesHelical Gears: Gear DrivesNeil RubsNo ratings yet
- SS 18 Home ScienceDocument8 pagesSS 18 Home ScienceJaswant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sas Lesson - MathDocument6 pagesSas Lesson - Mathapi-280008473No ratings yet
- Pohnpei - About Nan MadolDocument20 pagesPohnpei - About Nan MadolSándor TóthNo ratings yet
- OAL - HCG Found Vaccine KenyaDocument31 pagesOAL - HCG Found Vaccine Kenyasdancer75100% (1)
- FDA AssignDocument9 pagesFDA AssignZhainna SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause Sentences SECOND 40Document2 pagesAdjective Clause Sentences SECOND 40sumiyaNo ratings yet
- CP SanitaryDocument2 pagesCP SanitaryMuthu ManiNo ratings yet
- MULTIGRADE DLP in MathDocument6 pagesMULTIGRADE DLP in Mathwinnie bugawit75% (4)
- Contractor Classification PDFDocument4 pagesContractor Classification PDFKendrick RickNo ratings yet
- Mdu 1Document3 pagesMdu 1Gaurang Agrawal0% (1)
- How to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeDocument4 pagesHow to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeKingwaKamencuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Post LabDocument7 pagesExperiment 2 Post LabM ReyNo ratings yet
- Excellence of Patience and Gratefulness - Ibnu Qayyim Al-DjawziyyahDocument474 pagesExcellence of Patience and Gratefulness - Ibnu Qayyim Al-DjawziyyahKarimMahamaneKarimou100% (1)
- News Lessons SnakebiteDocument5 pagesNews Lessons SnakebiteGuilherme SalvadoriNo ratings yet
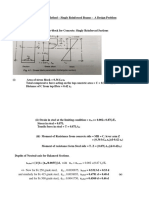
- Culvert Base Slabs: Slabs For Rectangular Portal Culvert Slabs For SATS Rectangular Portal CulvertDocument1 pageCulvert Base Slabs: Slabs For Rectangular Portal Culvert Slabs For SATS Rectangular Portal CulvertEphraim BarezNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation (Odd One Out) : Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced DifferentlyDocument2 pagesPronunciation (Odd One Out) : Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced Differentlyvo kelvin100% (1)
- Flexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMDocument12 pagesFlexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMKallem KiranmayiNo ratings yet
- Meditation GuideDocument168 pagesMeditation Guideaade100% (1)
- Industrial Gases and AcidsDocument5 pagesIndustrial Gases and AcidscarlNo ratings yet
- Open Foam SlidesDocument43 pagesOpen Foam SlidesjahidNo ratings yet
- SWIFT ChecklistDocument5 pagesSWIFT Checklistফয়সাল হোসেনNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment-1 ways to make lessons interestingDocument6 pagesDigital Assignment-1 ways to make lessons interestingSuhil IrshadNo ratings yet
- 12 Mounting and LabelingDocument1 page12 Mounting and LabelingEunice AndradeNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Manual Manuel de L'Utilisateur Manual Del OperadorDocument15 pagesOperator'S Manual Manuel de L'Utilisateur Manual Del OperadorCarlos SoutoNo ratings yet
- MCT-MST Summative Teaching Placement Assessment Rubric - EPC 4406 - 17 PagesDocument17 pagesMCT-MST Summative Teaching Placement Assessment Rubric - EPC 4406 - 17 PagesHuda HamadNo ratings yet