Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
Uploaded by
plokatz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
451 views3 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
451 views3 pagesPharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
Uploaded by
plokatzCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
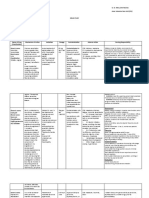
Name of the General
Specific Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Drug Action
• Antianginal Inhibits the movement • Angina • Contraindicated
AMLODI- • Antihyperte of calcium ions across pectoris due to with allergy to CNS: Dizziness, ASSESMENT:
PINE nsive the membranes of coronary artery amlodipine, impaired lightheadedness, headache, · History: Allergy to amlodipine, impaired hepatic or renal
BESYLATE • Calcium cardiac and arterial spasm hepatic or renal asthenia, fatigue, lethargy function, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, lactation, heart
channel muscle cells; inhibits (Prinzmetals’ function, sick sinus failure,
Norvasc blocker transmembrane variant angina) syndrome, heart CV: Peripheral edema, · Physical: Skin lesions, color, edema; P, BP, baseline ECG;
calcium flow, which · Chronic stable block (second or arrhymias peripheral perfusion, auscultation; R, adventitious sounds;
Dosage: 1 tab results in the angina, alone or third degree), and liver evaluation, GI normal output; LFT’s, renal function
10mg OD depression of impulse in combination lactation. Dermatologic: Flushing, tests, urinalysis
formation in with other drugs • Use cautiously withrash jaundice (yellowing of
specialized cardiac · Essential heart failure, the skin or eyes). INTERVENTIONS:
pacemaker cells, hypertension, pregnancy.
Pregnancy slowing of the alone or in GI: Nausea, abdominal Warning: Monitor patient carefully (BP, cardiac rhythm, and
category C velocity of conduction combination with discomfort output) while adjusting drug to therapeutic dose; use special
of the cardiac other anti- caution if patient has heart failure.
impulse, depression hypertensives Urinating more or less than · Monitor BP carefully if patient is also on nitrates.
of myocardial usual, or not at all; · Monitor cardiac rhythm regularly during stabilization of
contractility, and dosage and periodically during long term therapy.
dilation of coronary Fever, chills, body aches, · Administer drug without regard to meals.
arteries and arterioles flu symptoms; • Always remember and follow the 10 R’s of drug
and peripheral administration.
arterioles; these Tired feeling, muscle
effects lead to weakness, and pounding or TEACHING POINTS:
decreased cardiac uneven heartbeats; · Take with meals if upset stomach occurs.
work, decreased · You may experienced these side effects: Nausea, vomiting
cardiac oxygen chest pain; (eat frequent small meals); headache (adjust lightning, noise,
consumption, and in and temperature; medication may ordered)
patients with swelling, rapid weight gain; · Report irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of
vasospatic angina, the hands or feet, pronounced dizziness, constipation.
increased delivery of · Vomiting, diarrhea, or heavy sweating can cause you to
oxygen to cardiac become dehydrated. This can lead to very low blood
cells. pressure, electrolyte disorders, or kidney failure while you
are taking amlodipine and benazepril. Drink 6 to 8 full
glasses of water daily while you are taking this medication.
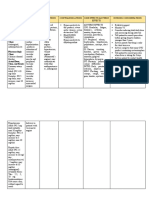
Name of the General
Specific Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Drug Action
MEFENAMIC • NSAID Anti- Relief of moderateContraindicated CNS: Headache, dizziness, BEFORE:
ACID inflammatory, pain when therapy with somnolence, insomnia, • Assess for history of allergies, renal, hepatic, CV,GI
analgesic and will not exceed 1 hypersensitivity to fatigue, tiredness, tinnitus, conditions; pregnancy; lactation
Apo- antipyretic week. mefenamic acid, ophthalmic effects • Assess the physical for skin color and lesions; orientation,
Mefenamic, activities related Treatment of aspirin allergy, and Dermatologic: Rash, reflexes, opthalmolgic, and andiometric evaluation,
ponstel to inhibition of primary as treatment of prurotus, sweating, dry peripheral sensation; P, edema R, adventitious sounds,; renal
prostaglandin dysmenorrhea. preoperative pain mucous function tests, serum electrolytes, stool guaiac
synthesis; exact with coronary artery membranes,stomatitis
500 mg 1 cap mechanisms of bypass grafting. DURING:
3x/day action are not GI: nausea, dyspepsia, GI • Be aware that patient may be at increase risk for CV events,
known. Use cautiously with pain, diarrhea, vomiting, GI bleeding, monitor accordingly.
Pregnancy asthma, renal or constipation, flatulence • Give the milk or food to decrease GI upset.
category C hepatic impairment, • Arrange for periodic ophthalmologic examinations during
peptic ulcer disease, GU: Dysuria, renal long-term therapy.
GI bleeding, impairment
• If overdose occurs, institute emergence procedures-
hypertension heart
supportive therapy and induced emesis, activated charcoal,
failure, pregnancy Hematologic: bleeding,
and/or an osmotic cathartic
lactation. platelet inhibition wiyh
higher doses, neutropenia, • Do not exceed 1 week therapy
eosinophilia, leukopenia, • Always remember and practice the 10 R’s
pancytopenia,
thrombocytopenia, AFTER:
agranulocytosis, • Take drug with food; take only the prescribed dosage and
granulocytopenia, aplastic teach not to take the drug longer than 1 week
anemia, decrease Hgb or Hct, • Discontinue drug and consult health care provider if rash,
bone marrow depression, diarrhea, or digestive problems occur.
menorrhagia • Dizziness or drowsiness can occur ( so avoid driving and
using dangerous machinery )
Respiratory: Dyspnea, • Report sore throat, fever, rash, itching, weight gain, swelling
hemoptysis, pharyngitis, in the ankles or fingers, changes in vision; cephalexin.
bronchospasm, rhinitis
• Other: Peripheral edema,
anaphylactoid reactions to
anaphylactic shock
You might also like
- Faith HealingDocument23 pagesFaith Healingcreamyfrappe0% (1)
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Soap NotesDocument4 pagesSoap NotesLatora Gardner Boswell100% (3)
- Problems and Remedies For MarsDocument4 pagesProblems and Remedies For MarsSunil RupaniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyJoseph Dann Enero Jr.100% (3)
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fall Prevention Presentation1Document26 pagesFall Prevention Presentation1pam937100% (1)
- Free Dive Training Schedules - Land and Pool Based Training SessionsDocument10 pagesFree Dive Training Schedules - Land and Pool Based Training Sessionssjf540100% (1)
- Nursing Note Sample 17Document6 pagesNursing Note Sample 17Lanzen Dragneel100% (1)
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahNo ratings yet
- Note: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: AmlodipineDocument4 pagesNote: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: Amlodipineanette katrinNo ratings yet
- The Case of Mouthwash MarketDocument6 pagesThe Case of Mouthwash MarketAce ReytaNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor / Company Name Stall Name AreaDocument56 pagesExhibitor / Company Name Stall Name AreaJyotsna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilpinksapphire929100% (2)
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Clinical Skill ChecklistDocument2 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation Clinical Skill ChecklistCarissa TirtaniaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocument4 pagesDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- MS Drug Study 1Document6 pagesMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Laranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Document5 pagesLaranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Gerard Louise Esmao RNNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesphoebeNo ratings yet
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors - AlzheimersDocument1 pageCholinesterase Inhibitors - AlzheimerscpboilergirlNo ratings yet
- ARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)Document2 pagesARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)SHIELA MAE ARCHEDERANo ratings yet
- Drug Study AlzheimersDocument12 pagesDrug Study Alzheimersella retizaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument12 pagesDrugsJean RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument5 pagesDrug Study orRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNicole Rachelyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMarc Daryl MendozaNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Tolleno Drug Study LONGDocument9 pagesTolleno Drug Study LONGHannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: RLE DutyDocument12 pagesCase Study: RLE DutyEsther Ellise AbundoNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument2 pagesAMLODIPINEMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument10 pagesCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D InsipidusDocument7 pagesDrug Study D InsipidusAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Diclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)Document3 pagesDiclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyizzieliciousNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyZek ComidoyNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- CNS: Headache, InsomniaDocument5 pagesCNS: Headache, InsomniaDave FagaritaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AhhhahahhaDocument11 pagesDrug Study AhhhahahhaShiela Mae Llarenas LoretoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsKookie JunNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolDocument3 pagesPedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolKuro HanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studydana100% (2)
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBesael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Comparing Different Approaches To CounsellingDocument7 pagesComparing Different Approaches To CounsellingTim RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Non-Suicidal Self-Injury (NSSI) and Suicide: Criteria DifferentiationDocument7 pagesNon-Suicidal Self-Injury (NSSI) and Suicide: Criteria DifferentiationTututWidyaNurAnggrainiNo ratings yet
- How To Rid The Body of CandidaDocument2 pagesHow To Rid The Body of Candidaradio53fingerNo ratings yet
- Scripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Document68 pagesScripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Zdravko GrubacNo ratings yet
- Speck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsDocument134 pagesSpeck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsSimona Mariana DutuNo ratings yet
- Vaccination List: Name Anti-Hbs Vaccine To GIVE Hepa-B (PHP 340/dose)Document10 pagesVaccination List: Name Anti-Hbs Vaccine To GIVE Hepa-B (PHP 340/dose)Manuel Florido ZarsueloNo ratings yet
- Parecoxib PDFDocument7 pagesParecoxib PDFawardani13No ratings yet
- Soa New DocumentsDocument1 pageSoa New Documentsjhoy visitacionNo ratings yet
- Patient Profile-C in The WDocument17 pagesPatient Profile-C in The WPj TignimanNo ratings yet
- Álvarez Et Al (2011) ChildabuseDocument6 pagesÁlvarez Et Al (2011) ChildabuseAra Moreno EscaladaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceDocument7 pagesElectronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceKhalil ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cold Chain Medication List 2021Document13 pagesCold Chain Medication List 2021sumaiyakhan880No ratings yet
- LO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Document38 pagesLO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Alan Dwi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 05 2019 Pediatric Infectious Diseases LAYOUT R3Document58 pages05 2019 Pediatric Infectious Diseases LAYOUT R3khalid alharbiNo ratings yet
- Recommendations From The Guideline For Pcos-NoprintDocument16 pagesRecommendations From The Guideline For Pcos-NoprintpopasorinemilianNo ratings yet
- ÁdadDocument24 pagesÁdadFùq Tất ỨqNo ratings yet
- Management of Acquired Maxillary Defects Partially Edentlous PDFDocument129 pagesManagement of Acquired Maxillary Defects Partially Edentlous PDFRamy Khalifa AshmawyNo ratings yet
- Burns Secret TestDocument2 pagesBurns Secret TestChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Various Kinds of Leave Admissible To Tamil Nadu Government ServantsDocument16 pagesVarious Kinds of Leave Admissible To Tamil Nadu Government Servantssankkitha100% (1)
- Reiki Is A Great Tool For Stress Reduction and Relaxation (!)Document16 pagesReiki Is A Great Tool For Stress Reduction and Relaxation (!)vaniaNo ratings yet
- Ethnobotany and EthnopharmacologyDocument29 pagesEthnobotany and EthnopharmacologyJohn CaretakerNo ratings yet