Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerosoli
Uploaded by
Camytza CamyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerosoli
Uploaded by
Camytza CamyCopyright:
Available Formats
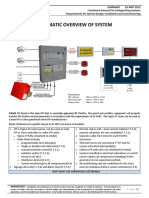
THE IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Keywords: impact, aerosols, environment
1. Introduction
Aerosols are formed by evaporation , weather turbulences with mechanical
effects on different surfaces , different types of emanations or even cosmic dust , collected
atmosphere, being defined as micro- particles in suspension in a gaseous environment [1].
Aerosols ( considered impurities of atmospheric air ) can be in particulate ( solid,
liquid ) or in the form of molecules ( gas or vapor ) being less than or heavier than air ,
nature is depending on the area in question ( industrial , urban , rural , volcanic etc.) [1].
2. Experimental
Measurement and monitoring of global beta aerosols are carried out through the
Environmental Radioactivity Station Botosani operating within NERSN ( substantial
national network of Environmental Radioactivity Surveillance ) in 1990 .
Within radioactive power plants menus for a standard environmental
radioactivity monitoring 11 hours / day , in which environmental factors are followed :
- AIR - by determining global beta activity of aerosols and atmospheric deposition
( wet and dry ) and continuous measurement of external gamma dose rate absorbed ;
- Water - the global beta activity determination Siret river water and drinking water ;
- Rainfall - by collecting and processing the samples for determination of tritium ;
- Vegetation ( with the sampling period April-October ) by determining global beta
activity ;
- SOL - ( sampling period April-October ) by determining global beta activity .
Environmental radioactivity monitoring network is realized through global
beta and dosimetric measurements on environmental factors. For global beta measurements
are used detection systems equipped with scintillation detector probe - type ND -304 and
GM detectors [2] .
Calibrating measurement is performed global beta sources (Sr -Y ) 90 . To
determine the gamma dose rate in air -type dosimeters are used IFIN - Tiexi provided with
GM detectors , and in 2007 the network was complemented by the acquisition within the
project PHARE 2003 / 005-551.04.11.01 . LOT 1 " of necessary equipment in order to create
a system for monitoring and reporting of radioactivity " of stations that monitor gamma dose
absorbed in automatic mode .
Fig.1. Measured aerosols
3. Results and Discussions
Radioactivity Station Botosani carry out annually a total of 5170
measurements of global beta and gamma radiation absorbed in the air. The share of
factor analysis on environmental monitoring is shown in the following chart:
Fig.2. The percentage of analysis on the environmental factor
4. Conclusions
The specific activity global aerosol samples measured immediately after
collection was within the normal range for this time , there are no breaches of the warning (10
Bq / m3) . The difference between the two aspirations that appears insignificant amount and are
due to temperature and humidity alternation of night and day between .
5. Acknowledgments
The work hazs been funded by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human
Resources Development 2007-2013 of the Ministry of European Funds through the Financial
Agreement POSDRU 187/1.5/S/155536.
6. References
[1] Meng Z.; Seinfeld J. H. (1994): Aerosol Science and Technology.
[2] Gallagher, M. W., Nemitz, E., Dorsey, J. R., Fowler, D., Sutton, M. A.,
Flynn, M. and Duyzer, J. H. (2002). Measurements and parameterisations of
small aerosol deposition velocities to grassland, arable crops, and forest:
Influence of surface roughness length on deposition. Journal of Geophysical
Research 107, 287-292.
2
You might also like
- Metoda ElectreDocument1 pageMetoda ElectreCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument1 pageCarsCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Traficul RutierDocument1 pageTraficul RutierCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Dsadadadvdvd Gfyfudaavfvdf Jhiiiuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuy77777777777 777777tccvcgDocument1 pageDsadadadvdvd Gfyfudaavfvdf Jhiiiuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuy77777777777 777777tccvcgCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Nutrient IDocument1 pageNutrient ICamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- AnalizaDocument1 pageAnalizaCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Traficul RutierDocument1 pageTraficul RutierCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Situatia TransportDocument1 pageSituatia TransportCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- Traficul RutierDocument1 pageTraficul RutierCamytza CamyNo ratings yet
- EM-ACE - Guidelines For Successful EM Applications - FinalDocument17 pagesEM-ACE - Guidelines For Successful EM Applications - Finalquantum16No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ASTM D4096-91 Determination of Total Suspended Particulate Matter in The Atmosphere (High-Volume Sampler Method)Document9 pagesASTM D4096-91 Determination of Total Suspended Particulate Matter in The Atmosphere (High-Volume Sampler Method)Fredi Cari Carrera100% (1)
- Macro Scale Modeling and Simulation of Two Phase Flow in Fibrous Liquid Aerosol FiltersDocument13 pagesMacro Scale Modeling and Simulation of Two Phase Flow in Fibrous Liquid Aerosol FilterssamandondonNo ratings yet
- Sponsored by TheDocument874 pagesSponsored by TheArmando HeilmannNo ratings yet
- Biennal Report On Hydrogen Safety - International Associaton For Hydrogen Safety - 2007Document118 pagesBiennal Report On Hydrogen Safety - International Associaton For Hydrogen Safety - 2007slumpNo ratings yet
- MSDS - PS 180 MDocument9 pagesMSDS - PS 180 MJahangeer KhanNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Air Package: Atlas CopcoDocument8 pagesTotal Quality Air Package: Atlas CopcoCastillo PercyNo ratings yet
- Safety Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesSafety Questions and Answersmiaicarba86% (50)
- Carbon Black: 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataDocument149 pagesCarbon Black: 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataabdulqadirNo ratings yet
- En 147Document20 pagesEn 147MohanNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Form 4 Exercise and ExamplesDocument6 pagesGas Laws Form 4 Exercise and ExampleszahidahoseinNo ratings yet
- Deltech DK60 and AboveDocument4 pagesDeltech DK60 and Abovesales-admin.bdgNo ratings yet
- AS 4487-2013 - Aerosols PDFDocument6 pagesAS 4487-2013 - Aerosols PDFĐức Huấn ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Aero MicrobiologyDocument28 pagesAero MicrobiologyMuhammad FatihNo ratings yet
- ISO DIS 29464-2023 Cleaning Air and Other Gases - TerminologyDocument51 pagesISO DIS 29464-2023 Cleaning Air and Other Gases - Terminologynhanhnafi5No ratings yet
- Bioglucanase HS: Trichoderma ReeseiDocument5 pagesBioglucanase HS: Trichoderma ReeseiRiyanNo ratings yet
- AEROSIL® For High Solid-Coatings: Technical Information 1197Document24 pagesAEROSIL® For High Solid-Coatings: Technical Information 1197rogerkid17No ratings yet
- Chamber-BasedDocument13 pagesChamber-BasedMicciNo ratings yet
- Progress in Developing Spray-Drying Methods For The Production of Controlled Morphology Particles - From The Nanometer To Submicrometer Size RangesDocument19 pagesProgress in Developing Spray-Drying Methods For The Production of Controlled Morphology Particles - From The Nanometer To Submicrometer Size RangesIyut PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Unit - I APCDocument37 pagesUnit - I APCMani DeepNo ratings yet
- Zinc Spray MSDSDocument4 pagesZinc Spray MSDSProject Sales CorpNo ratings yet
- ICENV 2015 EproceedingsDocument922 pagesICENV 2015 EproceedingsAhmad Anas Nagoor GunnyNo ratings yet
- Is 9462 1980Document7 pagesIs 9462 1980mishtinilNo ratings yet
- 1 WHO Oeh Airborne DustDocument246 pages1 WHO Oeh Airborne DustferzianNo ratings yet
- Articulo CientificoDocument7 pagesArticulo CientificoDaniel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kimre Aiche 2008Document12 pagesKimre Aiche 2008Marcelo PerettiNo ratings yet
- Iso 8573-4 2001Document6 pagesIso 8573-4 2001Gonzalo de LuisNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Delivery DevicesDocument68 pagesAerosol Delivery DevicesINGRID YISEL IDROBO AGREDONo ratings yet
- Diesel Fuel InjectionDocument5 pagesDiesel Fuel Injectiondamith21No ratings yet
- ENVR2020 Lecture 2 Fundamental Knowledge of Gases in The AtmosphereDocument29 pagesENVR2020 Lecture 2 Fundamental Knowledge of Gases in The AtmosphereAnson Kwun Lok LamNo ratings yet
- Trem CardDocument2 pagesTrem Cardasnandy100% (1)