Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Constructions: Learn About The Math
Uploaded by
joeynagaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometric Constructions: Learn About The Math
Uploaded by
joeynagaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 10
You will need
Geometric
Constructions
a ruler
a compass
a protractor
c GOAL
Construct various geometric shapes based on given information.
Learn about the Math
Raven needs to construct a triangle, where one side
measuring 5 cm is contained between a 30 angle and
a 50 angle.
can Raven accurately draw a complete triangle
? How
based on this information?
A. Use a ruler to draw a line segment measuring 5 cm.
B. Using a protractor, draw a second leg of the triangle,
forming a 30 angle with the first leg.
C. Use the protractor again to draw the third leg of the triangle,
forming a 50 angle with the original 5 cm line segment and
connecting to the line segment drawn in part B.
D. Using what you already know about triangles, what must
the measure of the third angle of this triangle equal?
E. Use your protractor to measure the third angle to see if it is
equal to your answer for step D.
Reflecting
1. What information must you have to draw a square?
2. What information must you have to draw a regular
pentagon?
3. What instruments might be helpful in constructing a
geometric shape?
Copyright 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Reproduction permitted for classrooms
10B Geometric Constructions
Work with the Math
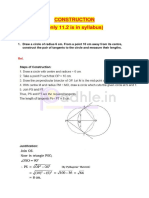
Example 1: Drawing a square
Draw a square with sides measuring 2 cm.
Angeles Solution
I will first recall what I already know about any square. I know that a
square has four equal side lengths and contains four right angles.
I will use a ruler to draw a line segment measuring 2 cm.
I will then draw three more segments of equal length,
connecting them with 90 angles. I can check the
measure of the side lengths with my ruler and the
angle measures with a protractor.
Example 2: Drawing a rhombus
Draw a rhombus whose diagonals measure 7 cm and 4 cm.
Kurts Solution
I first recall what I already know about a rhombus. I know that a rhombus
has four equal side lengths and the pairs of sides are parallel. I also know
that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors to each other.
I draw two dashed line segments perpendicular to each other, crossing at the
midpoints of each segment. I use my ruler to make certain that one of them has a
length of 7 cm and the other has a length of 4 cm and to make sure they cross at
the midpoints. I use my protractor to make certain the two lines cross to form four
90 angles. I then connect the ends of these lines to form a rhombus. I use my
ruler to measure the outside lines to make sure I have four equal line segments.
4 cm
7 cm
Nelson Mathematics Secondary Year Two, Cycle One
Reproduction permitted for classrooms
Copyright 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Example 3: Drawing a triangle
Draw a triangle with angles measuring 40 and 60 and the side between
the given angles measuring 4 cm.
Maggies Solution
First I draw a line segment 4 cm long using my ruler. Then at the left end of
the segment I use my protractor to measure a 40 angle and draw the other
segment for that angle. At the right end of the segment I use my protractor to
measure a 60 angle and draw the other segment for that angle. I will make
sure that the two segments I have drawn intersect each other. This point of
intersection will be the third vertex of the triangle. The angle at this vertex
should measure 180 2 40 2 60 5 80. I can use my protractor to measure
this angle as a way to check that I have done the construction properly.
40
60
4 cm
Checking
4. Use a compass to construct a circle
with a diameter of 4 cm.
Practising
5. Construct a rectangle with a length of
4 cm and a width of 2 cm.
6. Construct a regular pentagon with a
side length of 3 cm.
7. Construct a circle with radius 1 cm.
8. Draw a horizontal line segment
measuring 5 cm and its perpendicular
bisector.
9. Construct a rhombus with diagonals
measuring 8 cm and 6 cm.
10. Draw two parallel line segments
measuring 3 cm in length.
Copyright 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Reproduction permitted for classrooms
11. Draw a 40 angle; then draw an
angle bisector of that angle.
12. Construct a right triangle, with legs
measuring 3 cm and 4 cm.
13. Construct a triangle with angles
measuring 50 and 70 and the side
between them measuring 5 cm.
14. Construct an equilateral triangle with
side length 6 cm.
C
Extending
15. Write a description of a geometric
shape for a classmate to draw. Try to
provide only as much information as
is necessary for your classmate to
draw the shape. Trade problems with
a classmate and attempt to draw the
shape that the other has described.
10B Geometric Constructions
You might also like
- Practice BookDocument20 pagesPractice BookWeteachNo ratings yet
- EE ReviewerDocument14 pagesEE Reviewerjoeynaga83% (6)
- How to Create a Bell Curve in ExcelDocument12 pagesHow to Create a Bell Curve in ExceljoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Construction and LociDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Construction and LociAtif Muhammad100% (1)
- Tiny ES6 Notebook Curated JavaScript ExamplesDocument100 pagesTiny ES6 Notebook Curated JavaScript ExamplesJesus Leon Cordero100% (1)
- Construction of QuadrilateralsDocument93 pagesConstruction of QuadrilateralsChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Shear-Transfer Strength of Reinforced Concrete PDFDocument11 pagesShear-Transfer Strength of Reinforced Concrete PDFPremasiri KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- IB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8Document62 pagesIB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8aa1cc2100% (3)
- Alarp-Comah 2003Document18 pagesAlarp-Comah 2003kenoly123No ratings yet
- Performance Prediction and Analytics of Fuzzy, Reliability and Queuing Models Theory and Applications by Kusum Deep, Madhu Jain, Said Salhi PDFDocument282 pagesPerformance Prediction and Analytics of Fuzzy, Reliability and Queuing Models Theory and Applications by Kusum Deep, Madhu Jain, Said Salhi PDFSazzadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functional Programming Using Haskell - Richard BirdDocument222 pagesIntroduction To Functional Programming Using Haskell - Richard BirdSaptarshi S Mohanta75% (4)
- Maths Module 7: GeometryDocument16 pagesMaths Module 7: GeometryRonnie Smith100% (1)
- X - Standard Mathematics ConstructionsDocument30 pagesX - Standard Mathematics ConstructionsjackNo ratings yet
- Shapes of Constant WidthDocument4 pagesShapes of Constant WidthchessgeneralNo ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Drawing Circles with Different Radii Using a CompassDocument18 pagesDrawing Circles with Different Radii Using a CompassRiza GusteNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Constructions ExercisesDocument3 pagesYear 8 Constructions Exercisesr2933478No ratings yet
- Year 8 Constructions ExercisesDocument3 pagesYear 8 Constructions ExercisesKarl JonssonNo ratings yet
- Constructing triangles PixiPPtDocument7 pagesConstructing triangles PixiPPtAdrian GasmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Seven ThirdDocument10 pagesMathematics Seven ThirdJEWEL LUCKY LYN GUINTONo ratings yet
- Mathematics7 q3 Week8and9 v4Document11 pagesMathematics7 q3 Week8and9 v4Rick Jones Abella BuicoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration and Practical GeometryDocument12 pagesMensuration and Practical Geometrydocuments unaisNo ratings yet
- Constructing Circles and Polygons with a CompassDocument6 pagesConstructing Circles and Polygons with a CompassShahrazad8No ratings yet
- yr10 td plan wk8 9 10Document19 pagesyr10 td plan wk8 9 10Chilekezi DanielNo ratings yet
- LeaP Math G7 Week 8 Q3Document10 pagesLeaP Math G7 Week 8 Q3Reymart PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Constructing Regular PolygonsDocument14 pagesModule 7 Constructing Regular PolygonsKeziah Cheluj GamengNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Constructing Regular Polygons 1Document15 pagesModule 7 Constructing Regular Polygons 1Andrie Dagta ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document6 pagesUnit - 1anjaiah_19945No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Geometrical ConstractionDocument38 pagesLecture 2 - Geometrical Constractionmmarybenson11No ratings yet
- HW Chapter 6Document12 pagesHW Chapter 6crampingpaul100% (1)
- ConstructionsDocument1 pageConstructionsTeereg VINo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 68-LMDocument4 pagesQ3 Lesson 68-LMCHRISTINE A. DIAZNo ratings yet
- For #'S 3-4: The Choices Are:: MATH014 Long Quiz MULTIPLE CHOICE: (2 Points Each)Document2 pagesFor #'S 3-4: The Choices Are:: MATH014 Long Quiz MULTIPLE CHOICE: (2 Points Each)AloneNo ratings yet
- Applications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Document20 pagesApplications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Dipak KumarNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction Notes: Click On The Title To View A TutorialDocument43 pagesGeometric Construction Notes: Click On The Title To View A TutorialPetru TudoranNo ratings yet
- Drawing Triangle N Their LinesDocument7 pagesDrawing Triangle N Their LinesYurizkaMeliaSariNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTIONS Class 10Document7 pagesCONSTRUCTIONS Class 10Reeta StoreNo ratings yet
- Construction of Geometrical FiguresDocument3 pagesConstruction of Geometrical Figuresjoseph42No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremaDocument5 pagesPythagoras TheoremaCailyn SalimNo ratings yet
- Practical Geometry NotesDocument6 pagesPractical Geometry NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Module 15 Motion and MeasurementDocument3 pagesModule 15 Motion and Measurementakshitbn303No ratings yet
- Constructions Class XDocument4 pagesConstructions Class XDsr dNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument9 pagesConstructionsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Math II - Unit 2-Right Triangle Trig Lessons 1-13Document60 pagesMath II - Unit 2-Right Triangle Trig Lessons 1-13Kelvin LaiNo ratings yet
- dpp6 BuniyadDocument1 pagedpp6 BuniyadVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Square Root SpiralDocument2 pages3 Square Root SpiralSawarSagwalNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Revision NotesDocument7 pagesClass 6 Maths Chapter 14 Revision NotesNeha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Materials and Principles of ConstructionDocument7 pagesUnit - 4: Materials and Principles of ConstructionShriya MadooriNo ratings yet
- Construction of PolygonDocument57 pagesConstruction of Polygoniam whatiamNo ratings yet
- Practical Geometry Assignment 4Document1 pagePractical Geometry Assignment 4Vanya bajajNo ratings yet
- Line and Angle Bisectors TaskDocument2 pagesLine and Angle Bisectors TaskIslastoveNo ratings yet
- 2.28 Trig ApplicationsDocument19 pages2.28 Trig Applicationshazel_enaNo ratings yet
- 10th Geometrical ConstructionDocument2 pages10th Geometrical Constructionapi-242227794100% (1)
- Merestuinya Demi Kecemerlangan SATU Malaysia: Ambo SekeluargaDocument6 pagesMerestuinya Demi Kecemerlangan SATU Malaysia: Ambo SekeluargaAziz MamatNo ratings yet
- Discovering Congruent Triangles ActivityDocument7 pagesDiscovering Congruent Triangles ActivityMd YusofNo ratings yet
- Tri An GlenDocument16 pagesTri An Glenapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Measuring FieldsDocument13 pagesMeasuring FieldsRed GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Discovering Congruent Triangles Activity: Grading CriteriaDocument6 pagesGeometry - Discovering Congruent Triangles Activity: Grading CriteriaCatherine San JuanNo ratings yet
- ED Lecture NotesDocument27 pagesED Lecture NotesHaritha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9: Content Booklet: Targeted Support MathematicsDocument52 pagesGrade 9: Content Booklet: Targeted Support MathematicsCuchatte JadwatNo ratings yet
- Trig applications for real-life problemsDocument19 pagesTrig applications for real-life problemsCharry DawnNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Geometry Study GuideDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Geometry Study Guides9120362No ratings yet
- Classifying Triangles: Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 7 GradeDocument39 pagesClassifying Triangles: Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 7 Gradejun bonifacioNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document3 pagesHandout 1sunil varma0% (1)
- Victor RC-T1MDDocument14 pagesVictor RC-T1MDjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- LM386 AmplifierDocument3 pagesLM386 AmplifierjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Electric Fan With RemoteDocument2 pagesElectric Fan With RemotejoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Impedance and Phase AngleDocument5 pagesImpedance and Phase AnglejoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Insert Logo Word DocDocument1 pageInsert Logo Word DocjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- MHL Mobile DevicesDocument5 pagesMHL Mobile DevicesjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Resistor Color CodeDocument4 pagesResistor Color CodejoeynagaNo ratings yet
- MT InCarrierDocument4 pagesMT InCarrierjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Exp12 13 DataDocument2 pagesExp12 13 DatajoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Canon MP258 error code guideDocument2 pagesCanon MP258 error code guidejoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Resistor Color CodeDocument4 pagesResistor Color CodejoeynagaNo ratings yet
- MT InStripDocument2 pagesMT InStripjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- Pinout Description For Main Usb ConnectorsDocument3 pagesPinout Description For Main Usb ConnectorsjoeynagaNo ratings yet
- All About ScrewsDocument20 pagesAll About Screwshon choong chongNo ratings yet
- Review Basic MathsDocument16 pagesReview Basic MathsKaleeswaran EinsteinNo ratings yet
- Modeling of The Dynamics of Rotors of An Energy Gas Turbine Installation Using An Analytical Method For Analyzing Active Magnetic Bearing CircuitsDocument6 pagesModeling of The Dynamics of Rotors of An Energy Gas Turbine Installation Using An Analytical Method For Analyzing Active Magnetic Bearing Circuitsshamiul himelNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W3Document13 pagesDLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W3Maricar SilvaNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn Group Assignment G3Document47 pagesDiff Eqn Group Assignment G3i RareNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 Demo 2013 PDFDocument24 pagesSAP2000 Demo 2013 PDFLi Yin Ting TerryNo ratings yet
- Small Craft Power PredictionDocument32 pagesSmall Craft Power Predictionaeromexpower2009No ratings yet
- Fast Floating Point Square Root: Thomas F. Hain, David B. MercerDocument7 pagesFast Floating Point Square Root: Thomas F. Hain, David B. MercerValentina NigaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Experimental Errors and Acoustics (Ver10182020) - UnlockedDocument8 pagesActivity 3 Experimental Errors and Acoustics (Ver10182020) - UnlockednyorkNo ratings yet
- 116102038Document3 pages116102038SantoshNo ratings yet
- Symmetry in Art and ArchitectureDocument59 pagesSymmetry in Art and ArchitectureIIRemmyIINo ratings yet
- The Black and Scholes ModelDocument2 pagesThe Black and Scholes ModelnobuyukiNo ratings yet
- MA Sample Paper 2 UnsolvedDocument8 pagesMA Sample Paper 2 UnsolvedHoneyNo ratings yet
- Geology of Radon in The United States: January 1992Document17 pagesGeology of Radon in The United States: January 1992Stefan StefNo ratings yet
- Distillation Version 3Document4 pagesDistillation Version 3Toru Lucis CaelumNo ratings yet
- Trainer: Class 2Document13 pagesTrainer: Class 2Kavita PatilNo ratings yet
- Normal Subgroup: You Can Enter A Subtitle Here If You Need ItDocument20 pagesNormal Subgroup: You Can Enter A Subtitle Here If You Need ItBujur KetarenNo ratings yet
- Ripple Carry and Carry Lookahead Addition and Subtraction CircuitsDocument19 pagesRipple Carry and Carry Lookahead Addition and Subtraction CircuitsSurya KanthNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 14 OscillationsDocument19 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 14 Oscillationsnc5836795No ratings yet
- Effective Pandas SampleocrDocument13 pagesEffective Pandas SampleocrrandallNo ratings yet
- Pubali Bank Limited: Post NameDocument6 pagesPubali Bank Limited: Post NametitoNo ratings yet
- Discrete Phase Modelling - CombustionDocument63 pagesDiscrete Phase Modelling - CombustionFabian Andrey DiazNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC 1998 Free-Response QuestionsDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC 1998 Free-Response QuestionsepoxytocinNo ratings yet
- Discontinuous GalerkinDocument17 pagesDiscontinuous GalerkinAnna ShcherbachevaNo ratings yet
- Python Lab Cycle - ITDocument4 pagesPython Lab Cycle - ITeswar jrNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics ExamDocument3 pagesAtomic Physics Examvasudevan m.vNo ratings yet
- Cinema Fiction Vs Physics Reality Ghosts, Vampires and Zombies PDFDocument13 pagesCinema Fiction Vs Physics Reality Ghosts, Vampires and Zombies PDFnknknklNo ratings yet