Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerodynamic Force
Uploaded by
Viswanathan SrkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerodynamic Force
Uploaded by
Viswanathan SrkCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerodynamic force
Aerodynamic force
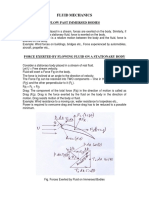
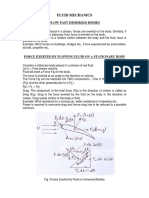
Aerodynamic force is the resultant force exerted on a body by the air
(or some other gas) in which the body is immersed, and is due to the
relative motion between the body and the fluid. An aerodynamic force
arises from two causes: [1] [2] [3]
the force due to the pressure on the surface of the body
the force due to viscosity, also known as skin friction
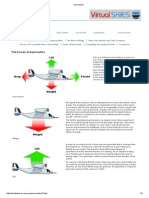
Forces on an aerofoil.
When a body is exposed to the wind it experiences a force in the direction in which the wind is moving. This is an
aerodynamic force. When a body is moving in air or some other gas the aerodynamic force is usually called drag.
When an airfoil or a wing or a glider is moving relative to the air it generates an aerodynamic force that is partly
parallel to the direction of relative motion, and partly perpendicular to the direction of relative motion. This
aerodynamic force is commonly resolved into two components:[4] [5]
Drag is the component parallel to the direction of relative motion.
Lift is the component perpendicular to the direction of relative motion.
The force created by a propeller or a jet engine is called thrust and it is also an aerodynamic force. The aerodynamic
force on a powered airplane is commonly resolved into three components:[6] [7]
thrust, lift and drag
The only other force acting on a glider or powered airplane is its weight. (Weight is a body force, not an
aerodynamic force.)
See also
Optical lift
References
Hurt, H.H.Jr. Aerodynamics for Naval Aviators. A National Flightshop Reprint, Clearwater, Florida (1979)
Clancy, L.J. (1975). Aerodynamics. Pitman Publishing Limited, London. ISBN 0 273 01120 0
Massey, B.S. Mechanics of Fluids, 2nd Edition. Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., London (1970) Library of Congress
Catalog Card No. 67-25005
Notes
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
Hurt, H.H.Jr. Aerodynamics for Naval Aviators. p.29
Clancy, L.J. Aerodynamics. Section 4.10
Massey, B.S. Mechanics of Fluids, section 10.8.2
Hurt, H.H.Jr. Aerodynamics for Naval Aviators. p.14
Clancy, L.J. Aerodynamics. Section 5.3
Hurt, H.H.Jr. Aerodynamics for Naval Aviators. Fig 2.20
Clancy, L.J. Aerodynamics. Section 14.2
Article Sources and Contributors
Article Sources and Contributors
Aerodynamic force Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=408257624 Contributors: Bahar101, BatteryIncluded, Crowsnest, Dolphin51, Favonian, Lechatjaune, Malcolma,
NegativeSpace, R'n'B, Sergey Khantsis, SpiderMum, 12 anonymous edits
Image Sources, Licenses and Contributors
Image:aeroforces.svg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Aeroforces.svg License: Public Domain Contributors: Amada44, Kadellar, Lechatjaune, Mo7amedsalim,
WikipediaMaster
License
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
http:/ / creativecommons. org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3. 0/
You might also like
- Aerodynamics (Embry Riddle)Document10 pagesAerodynamics (Embry Riddle)Tariq TaeemNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers in AerodynamicsDocument16 pagesQuestions and Answers in AerodynamicsD.Viswanath85% (27)
- 90 Series Variable Pumps and Motors Repair Manual PDFDocument54 pages90 Series Variable Pumps and Motors Repair Manual PDFsssydorenko100% (3)
- Lesson 1 Basic Aerodynamics & IntroductionDocument31 pagesLesson 1 Basic Aerodynamics & Introductionaahsan345100% (1)
- Physics of Flight/ Essay / PaperDocument11 pagesPhysics of Flight/ Essay / PaperAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- How To Size A Control Valve For Liquid and Gas Applications Usi PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Size A Control Valve For Liquid and Gas Applications Usi PDFv noteNo ratings yet
- BASIC AERODYNAMICS TRAININGDocument57 pagesBASIC AERODYNAMICS TRAININGKabir ShariffNo ratings yet
- 745C Hydraulic SchematicsDocument15 pages745C Hydraulic SchematicsMoataz SamiNo ratings yet
- Glider HandbookDocument20 pagesGlider Handbookjilu100% (1)
- Technical Reference Guide Fastenal K Factor and MoreDocument62 pagesTechnical Reference Guide Fastenal K Factor and Moredlight0No ratings yet
- Theory of Flight Components and ForcesDocument124 pagesTheory of Flight Components and ForcesReem Rodriguez100% (2)
- Weymouth and Panhandle Equations For Gas PipelinesDocument4 pagesWeymouth and Panhandle Equations For Gas PipelinessgrsthNo ratings yet
- Moneylife 12 November 2015Document68 pagesMoneylife 12 November 2015Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering GATE 2020 SolutionsDocument33 pagesPetroleum Engineering GATE 2020 SolutionsGate Aiots Petroleum AdminNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Force - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesAerodynamic Force - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHareshVaniyaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Basics ExplainedDocument8 pagesAerodynamics Basics ExplainedAib BDNo ratings yet
- Design and AnalysisDocument30 pagesDesign and AnalysisQasim ElectricwalaNo ratings yet
- AeroDynamics of Basic AircraftDocument16 pagesAeroDynamics of Basic AircraftRahat RahmanNo ratings yet
- Aerofoil Lift Coefficient StallingDocument4 pagesAerofoil Lift Coefficient Stallinganurag1_mehtaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Forces of FlightDocument10 pagesAerodynamics Forces of FlightApoloNo ratings yet
- AeroDocument24 pagesAerox7w34TNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics ForcesDocument19 pagesAerodynamics ForcesTesh Si100% (1)
- Flight - Study GuideDocument2 pagesFlight - Study Guidedmccloy28No ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument3 pagesFundamentalsnkjwbnbbtqNo ratings yet
- Week 10Document15 pagesWeek 10Salem KanaanNo ratings yet
- TASK 11 QUESTIONNAIRE 2 - ArcentalesJosueDocument6 pagesTASK 11 QUESTIONNAIRE 2 - ArcentalesJosueMICAELA VALENTINA GUTIERREZ MINDANo ratings yet
- Aeronautics: The Forces of AeronauticsDocument3 pagesAeronautics: The Forces of AeronauticsBaldev RamNo ratings yet
- Airfoil 1218496305090018 8Document23 pagesAirfoil 1218496305090018 8Yousef AsmarNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Aerodynamics For FlyingDocument47 pagesChap 4 - Aerodynamics For Flyingdada1020chapmanNo ratings yet
- Safari - Jan 2, 2024 at 11:22 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Jan 2, 2024 at 11:22 PMsyansyncNo ratings yet
- Safari - Jan 2, 2024 at 5:15 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Jan 2, 2024 at 5:15 PMsyansyncNo ratings yet
- Introduction To R.C. GlidersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To R.C. GlidersBala SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Aerospace EngineeringDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Aerospace Engineeringleslie dNo ratings yet
- CFD analysis of airplane airfoil using AnsysDocument11 pagesCFD analysis of airplane airfoil using AnsysumairNo ratings yet
- Stem Lesson Ld04 Aerodynamics SarradetDocument19 pagesStem Lesson Ld04 Aerodynamics SarradetYadana1No ratings yet
- Lift (Force) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument6 pagesLift (Force) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchManoj PradhanNo ratings yet
- Parasitic DragDocument3 pagesParasitic Dragphutd09No ratings yet
- Parasitic Drag Types and ComponentsDocument3 pagesParasitic Drag Types and Componentsphutd09No ratings yet
- Fhe Four Forces V2Document16 pagesFhe Four Forces V2jalal mustafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Aerodynamics ForcesDocument51 pagesIntroduction to Aerodynamics ForcesYadanaNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument25 pagesAerodynamicsMary Juanna T. MacandogNo ratings yet
- Background on Air and AerodynamicsDocument5 pagesBackground on Air and AerodynamicsbadamsmithNo ratings yet
- Principles of Major Flight IntroductionDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Major Flight IntroductionIvan GluhenkiyNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Principles For Aircraft: A StudyDocument9 pagesAerodynamic Principles For Aircraft: A StudyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- MECN 3350 - Aircraft Design and Performance - Module 1 - Unit 1.1 - Lesson 1.1.2Document54 pagesMECN 3350 - Aircraft Design and Performance - Module 1 - Unit 1.1 - Lesson 1.1.2Jose A Rosado LopezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Flight: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Flight: Learning ObjectivesAshmi ShajiNo ratings yet
- Drag in AerodynamicsDocument3 pagesDrag in AerodynamicssarfraazNo ratings yet
- Aircraft FlightDocument4 pagesAircraft FlightNirmal JayanthNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragDocument4 pagesBernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragABHIJEETNo ratings yet
- Theory of Flight: Lift Drag Weight ThrustDocument8 pagesTheory of Flight: Lift Drag Weight ThrustJames Leonard Marquez BautistaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Fundamentals ExplainedDocument1 pageAerodynamics Fundamentals Explainedmamaadam02No ratings yet
- Aerodynamics - Academic BlogDocument25 pagesAerodynamics - Academic Bloghassaanshahid2003No ratings yet
- Flow Past Immersed BodiesDocument13 pagesFlow Past Immersed BodiesBalaguruNo ratings yet
- 11a. Flow Past Immersed BodiesDocument11 pages11a. Flow Past Immersed Bodiessanyam KanungaNo ratings yet
- Aero Lec 1Document46 pagesAero Lec 1maya2001.tareqNo ratings yet
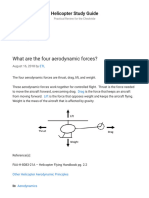
- Aerodynamic Force - Helicopter Study GuideDocument2 pagesAerodynamic Force - Helicopter Study GuideИстребитель ПилотNo ratings yet
- Missile ForcesDocument4 pagesMissile ForcesPrasanna Balaji100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document30 pagesPresentation 1Kaleab TekabeNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis of Blended Wing Body Aircraft: Department of Mechanical Engineering, NIE 1Document56 pagesForce Analysis of Blended Wing Body Aircraft: Department of Mechanical Engineering, NIE 1BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Parasitic DragDocument4 pagesParasitic DragsarfraazNo ratings yet
- Air and Aerodynamic Vocabulary TermsDocument3 pagesAir and Aerodynamic Vocabulary TermsQurat-Ul-Ain JaferiNo ratings yet
- Rocket ResearchDocument11 pagesRocket Researchapi-433751053No ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument10 pagesAerodynamicsCarlos Castillo PalmaNo ratings yet
- Ringka, Dzharl - Activity 1Document3 pagesRingka, Dzharl - Activity 1Dzharl RingkaNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay 103 1Document1 pageAraldite Ay 103 1Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Passivate Stainless Steel PartsDocument2 pagesPassivate Stainless Steel PartsViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Tables of International Standards, A ComparisonDocument22 pagesTables of International Standards, A ComparisonViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Contract Review Rev2 1208Document19 pagesContract Review Rev2 1208Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFDocument4 pagesAraldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- A 240 - A 240M - 04 - Qti0mc0wnaDocument12 pagesA 240 - A 240M - 04 - Qti0mc0wnaViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- GLORIA MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CORP. EVERCUT 316 STAINLESS STEEL SPECIFICATIONDocument1 pageGLORIA MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CORP. EVERCUT 316 STAINLESS STEEL SPECIFICATIONViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- GLORIA MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CORP. EVERCUT 316 STAINLESS STEEL SPECIFICATIONDocument1 pageGLORIA MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CORP. EVERCUT 316 STAINLESS STEEL SPECIFICATIONViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Antelope 21 December 2015Document3 pagesAntelope 21 December 2015Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFDocument4 pagesAraldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Araldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFDocument4 pagesAraldite Ay103 1hy991 PDFViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SW InsightDocument13 pagesSW InsightViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SW DailyDocument32 pagesSW DailyViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- SSWWWWDocument6 pagesSSWWWWViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Wi 2015 12Document64 pagesWi 2015 12Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- For The First Time in India, Electrodes Put in Australian Man's Brain To Curb Depression - The Times of IndiaDocument6 pagesFor The First Time in India, Electrodes Put in Australian Man's Brain To Curb Depression - The Times of IndiaViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Create Shaper Tool Head Assembly and Exploded View in CADDocument6 pagesCreate Shaper Tool Head Assembly and Exploded View in CADjagadeesh01No ratings yet
- Ex 4 BDocument1 pageEx 4 BViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Project1 - Diagram1Document1 pageProject1 - Diagram1Viswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- GateDocument6 pagesGateParveen SwamiNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 BDocument1 pageEx 3 BViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 4 ADocument3 pagesEx 4 AViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 ADocument2 pagesEx 3 AViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 ADocument2 pagesEx 2 AViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 4 ADocument3 pagesEx 4 AViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 BDocument1 pageEx 1 BViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Working Mind and The Thinking Mind - Lifestyle Article On SpeakingtreeDocument3 pagesWorking Mind and The Thinking Mind - Lifestyle Article On SpeakingtreeViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 ADocument2 pagesEx 1 AViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Euler Equation PDFDocument2 pagesEuler Equation PDFAlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 02 Name of The Experiment: Calibration of Orifice Meter ObjectivesDocument8 pagesExperiment No.: 02 Name of The Experiment: Calibration of Orifice Meter ObjectivesMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Gala Balancing ValveDocument36 pagesGala Balancing ValveMazhar Qayyum QadriNo ratings yet
- Robust Wax Deposition Modeling Incorporating NonDocument4 pagesRobust Wax Deposition Modeling Incorporating Nonabhay.singhNo ratings yet
- Stability Prediction On Armor Blocks For Submerged Breakwater by Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument14 pagesStability Prediction On Armor Blocks For Submerged Breakwater by Computational Fluid DynamicsHaryo ArmonoNo ratings yet
- Formation of a Weak Vortex StudyDocument17 pagesFormation of a Weak Vortex StudyBharath kumarNo ratings yet
- ANSYS CFX Tutorial Laminar Flow in A Rectangular DuctDocument17 pagesANSYS CFX Tutorial Laminar Flow in A Rectangular DuctShafiul AzamNo ratings yet
- Turbulence Notes Fluent-V6.3.06 PDFDocument49 pagesTurbulence Notes Fluent-V6.3.06 PDFthanakorn vichiensamuthNo ratings yet
- Wind Load ExcelDocument30 pagesWind Load Excelkim suarezNo ratings yet
- TFP1221 08 2015Document4 pagesTFP1221 08 2015JoshuaNo ratings yet
- p1 IntroductionDocument55 pagesp1 IntroductionJala GergesNo ratings yet
- Porosidad de La Fractura de PbuDocument14 pagesPorosidad de La Fractura de PbuAnonymous 9lckaf9st6No ratings yet
- Rwind Simulation Manual enDocument93 pagesRwind Simulation Manual enJEMAYERNo ratings yet
- 3-Turbulent Flow PDFDocument16 pages3-Turbulent Flow PDFAbhinav AbhiNo ratings yet
- Pump Hm250 FHC-S C5 Performance Curve: 600mm 600mm Full Closed 73mm High Chrome High ChromeDocument1 pagePump Hm250 FHC-S C5 Performance Curve: 600mm 600mm Full Closed 73mm High Chrome High ChromeJoão Paulo Augusto MacedoNo ratings yet
- NFPA-20-fire Pump ReliefDocument3 pagesNFPA-20-fire Pump ReliefhossameldeenNo ratings yet
- Procedure SDI TestDocument2 pagesProcedure SDI TestChairul ImamNo ratings yet
- Gasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 2: Linearized Flow EquationsDocument47 pagesGasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 2: Linearized Flow EquationsPythonraptorNo ratings yet
- Petroleum MCQs-1Document19 pagesPetroleum MCQs-1Hikmatullah khanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Technology For Ion Sources: April 2014Document41 pagesVacuum Technology For Ion Sources: April 2014RenatoNo ratings yet
- IIT MM2080 Final Exam: Principles of Extractive MetallurgyDocument4 pagesIIT MM2080 Final Exam: Principles of Extractive MetallurgynewteamNo ratings yet
- MASTERS OF SCIENCE THESIS by Abraham TayeDocument78 pagesMASTERS OF SCIENCE THESIS by Abraham TayeabrahamNo ratings yet
- Review-Vortex Shedding Lock-On and Flow Control in Bluff Body WakesDocument12 pagesReview-Vortex Shedding Lock-On and Flow Control in Bluff Body Wakes李智No ratings yet
- Alistair Doig - Some Metallurgical Aspects of Shaped Charge LinersDocument3 pagesAlistair Doig - Some Metallurgical Aspects of Shaped Charge LinersGhoree23456No ratings yet