Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1ge PDF
Uploaded by
Joko SukarionoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1ge PDF
Uploaded by
Joko SukarionoCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Engine model
Item
RF8
RG8
Type
Diesel
Cooling method
Water cooled
Number of cylinders and cylinder arrangement
V8, vertical
V10, vertical
Stroke cycle
Combustion chamber
Direct fuel injection
Valve mechanism
Overhead valve, gear driven, center camshaft
Cylinder liner
Wet
Bore x stroke
[mm]
138.0 x 142.0
142 x 142
Compression ratio
[kg/cm2-rpm]
Minimum engine speed under no-load conditions
Intake valve timing
Exhaust valve timing
Valve clearance
[mm]
[rpm]
31.0 - 200
550 - 570
460 - 480
450 - 550
Open
14 B.T.D.C.
18 B.T.D.C.
14 B.T.D.C.
Closed
44 A.B.D.C.
64 A.B.D.C.
44 A.B.D.C.
Open
52 B.B.D.C.
Closed
20 A.T.D.C.
Intake
0.3 - 0.4
Exhaust
0.5 - 0.6
Ignition system
Compression ignition
Fuel injection timing [B.T.D.C.]
Conventional type
nozzle
17
Two-spring type nozzle
(Taiwan only)
18
10.5
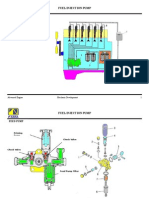
Fuel feed pump
Fuel injection nozzle Fuel injection pump
1R-1L-5R-5L-2R2L-3R-3L-4R-4L
Plunger type
Main
Fuel filter
Fuel system
18
1R-1L-4R-4L3L-2R-2L-3R
Ignition order
Cartridge type
Primary
Filter paper
Type
Bosch
Plunger diameter
[mm]
12.0
Plunger lead
22+45
Cam lift
[mm]
11.0
Governor
12.0
11.0
Centrifugal
Timer
Centrifugal
Nozzle holder
Flange type
Nozzle
Multi-jet
Number of injection
nozzle holes
Conventional type
Two-spring type
Conventional type
Injection pressure
[kg/cm2] Two-spring type
Over flow valve opening pressure
220
180 - 220
Injection pump outlet
[kg/cm2] Fuel filter
Voltage [V] x
Current [A] x Number
180 - 230
180 - 220
1.6
1.3 0.2
Type
Air heater
135.0 x 132.0
17.3 : 1
Cylinder compression
Intake system
RE10
Ribbon
Standard
22.5 x 85 x 2
22 - 85 x 2
22.5 x 85 x 2
Optional
22.5 x 170 x 2
22.5 x 170 x 2
1 3
GENERAL
Engine model
Item
RF8
RG8
Type
Forced circulation
Type
Lubricating system
Oil pump
Gear pump
Amount of discharge
Safety valve opening pressure
Type
Oil filter
[!/rpm]
160/2500
160/2200
180/2500
[kg/cm2]
10.8
11.0
10.8
Full-flow type
Paper filter
By-pass type
Laminated filter plate type
Method of replacement
Disassembly
Short valve opening pressure
[kg/cm2]
1.2
Type
Oil cooler
Built-in, water cooled
Number of cores
10
Short valve opening pressure
Lubrication oil capacity
12
[kg/cm2]
[kg/cm2]
Regulator valve opening pressure
2.0
4.3
4.5
[!]
Cooling system
Corrugated fin
Taiwan
600 or 670
[mm] Except Taiwan
700
Outside diameter of cooling fan
Water pump
Valve port diameter
Valve opening temperature
Auxiliary equipment
Electrical system
Valve lift/temperature
Wax-pellet type
[mm/C]
76.5, 82
Output
More
than 10/95,
100
Shift type
[V-kw]
24-6
24-7
AC, diode-rectified
Output
24-40 or 24-50
IC-transistor type
Type
Reciprocating type
Cooling system
Water-cooled
Type
Regulating pressure
82, 88
More than 10/90, 95
Type
Allowable maximum torque
Engine rear PTO
50
[C]
Regulator
Hydraulic pump
[mm]
Type
Air compressor
670
Centrifugal, belt-driven type
Type
Alternator
39
Forced-circulation type
Radiator type
Starting motor
4.3
34
Cooling system
Thermostat
RE10
Vane, Gear driven
[kg/cm2]
[kgm]
Direction of rotation
135, 105
30.0
Clockwise (as viewed from the rear)
Gear ratio (PTO: crankshaft)
1.0
1 4
24-8
GENERAL
LUBRICATION
RECOMMENDED FUEL AND LUBRICANTS
Lubricant
Specifications
Remarks
Engine oil
API CC or CD
For Viscosity Number, refer
to the undermentioned.
Power steering fluid
DEXRONR or DEXRONR II
GM ATF type
Bearing grease
NLGI No. 2
Lithium soap base
Antifreeze
Above 20F ( 7C)
2-D Diesel fuel or equivalent
blended diesel fuel
Below 20F ( 7C)
1-D Diesel fuel or equivalent
blended diesel fuel
Fuel
Ethylene glycol base
Check with the service establishment to be sure you get
the properly blended fuel.
RECOMMENDED SAE VISCOSITY NUMBER
Use oil having the proper viscosity beforehand which meets
temperatures forecast for areas where you are planning to
drive.
CAPACITIES (APPROXIMATELY)
Item
Engine oil pan
Engine oil
Total
Liter
RF8 & RG8
engines
24
RE10 engine
29
RF8 & RG8
engines
34
RE10 engine
39
Power steering system fluid
Cooling system
7.2
RF8 & RG8
engines
42
RE10 engine
47
NOTE:
Capacities shown are for reference only. When filling,
observe the specified level.
1 6
EGE1-005
GENERAL
PRECAUTIONS
PREPARATION
When doing maintenance work on each section of the engine, the following points should be strictly
observed:
Park the vehicle in a level spot. If the area is not level, it will not be possible to perform oil inspections
properly; it is also dangerous, since the vehicle may suddenly begin rolling down the incline.
Set the parking brake to lock the wheels in place and chock both the front and rear wheels.
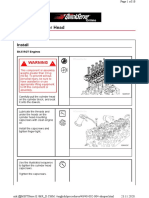
Do not perform maintenance operations while the engine is still hot. Wait for it to cool first.
Set the gearshift to neutral.
Make sure the key is in the OFF position. When doing work on the electrical system, disconnect the
battery cable from the negative terminal of the battery as well.
When starting the engine to perform maintenance operations, be particularly careful not to touch any
of the rotating parts. Also, make sure the area is well-ventilated when running the engine.
GENERAL REMARKS REGARDING DISASSEMBLY OPERATIONS
Establishing conditions prior to disassembly
Before starting to disassemble, check the nature of the problem to see if disassembly is really required. For
example, if the problem is in the engine, is there any abnormal noise? insufficient output? oil leakage? As
a result of disassembly and inspection, the cause of the trouble can be accurately determined.
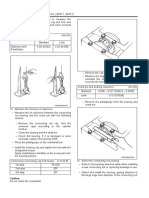
Disassembly
When disassembling complicated assemblies, stamp parts that have no effect on the assembly functional
and use matching marks in order to make reassembly easier. Also, when repairing the electrical system,
be sure to remove the cable from the negative terminal of the battery first.
Inspection during disassembly
Each time you remove a part, inspect that part for correct assembly, cleanliness, wear, damage and so on.
High efficiency cannot be obtained if all parts are disassembled prior to inspection.
Arrangement of disassembled parts
After disassembly, lay the parts down in the proper order so they will not get mixed up. Replace all packing
materials, gaskets, split pins and so on with new ones.
Make sure your hands are clean before handling V-belts, rubber items and electrical components that are
sensitive to water and oil. Place these parts in a different location from components that are covered with
engine oil.
Cleaning disassembled parts
Clean or wash all parts before starting reassembly.
If disassembled parts are not cleaned before reassembly, it will be impossible to judge which parts are
good and which are bad and discover part defects. In addition, foreign matter may adhere to the parts
during reassembly and contaminate the engine, adversely affecting performance and possibly leading to
engine trouble. Be sure to maintain the proper degree of cleanliness during repair operations.
Reassembly
During reassembly, be sure to use the right procedure to assemble the right part with the right standard
(tightening torque, adjustment value, etc.). Also, do not forget to apply oil or grease where required.
Adjustment and operation check
Adjust parts to the specified standard value, using a gauge or tester. Ultimately it would be most efficient
to operate or perform an inspection each time the assembly operation is performed.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING
Each component part must be cleaned of dirty oil, oil sludges, scale, carbon, old gasket or adhesives
attached to it.
Cleaning methods are: high temperature steam cleaning, light oil cleaning, acid or alkaline solution
cleaning, neutral detergent cleaning, trichlene solution steam cleaning, and magnas fluid cleaning.
In cleaning, unexpected crack or damage may often be found. It is important, therefore, to take sufficient
care during cleaning not to overlook any defect on a part.
1 7
GENERAL
Cleaning metal parts
Cleaning with light oil
Light oil features minimal permeability and solubility for matter adhered to the surface of the parts, and is
therefore most suitable for cleaning parts with sliding surfaces or finely finished surfaces. For other
portions, use a wire brush, a wooden spatula, or a piece of metal plate to scrape off foreign matter. Perform
this preliminary cleaning before conducting final cleaning.
Cleaning with alkaline fluid
For those parts composed of a single kind of material such as copper, cast iron, and aluminum, alkaline
cleaning fluid may be used. However, for a metal product composed of two or more materials, such as
bearing shell and bushing, cleaning with light oil, trichlene solvent, steam, or magnas fluid is recommended, because electrolytic corrosion may occur due to ionization in these type parts.
Note:
When handling alkaline fluid, prepare a boric acid solution so that if cleaning fluid accidentally
falls on to the skin or clothes, or splashes into the eyes, it can be quickly neutralized.
Cleaning rubber products
When cleaning rubber parts, use alcohol to remove foreign matter. Never use light oil, lamp oil or any other
mineral oil.
Cleaning oil line
Pass a wire through the oil line in each part to make sure the line is not clogged, then squirt cleaning fluid
from the nozzle to clean.
Rustproofing
When parts have been cleaned and the grease has been completely removed, coat the surfaces with clean
oil to prevent the part from rusting.
INSPECTION
During inspection, use measuring instruments in accordance with the maintenance standards and
make pass/fail determinations accurately. When the values exceed the repair limit or wear limit, be sure
to repair the part or replace it with a new one. When the standards for determining whether or not the
part should be replaced are shown by clearances, replace the corresponding part or the whole of the
assembly as needed.
Even if the measured values are within the wear limit, in some cases it would be better to replace the
part from the standpoint of preventive maintenance.
When inspecting parts, be sure to check the external appearance as well, either through visual
inspection, red check or the like. When the problems listed below are observed in an external
appearance check, the part should be repaired or replaced.
If even one of the following damages is noted during inspection, be sure to repair or replace the
corresponding part with a new one. In addition, note that, in principle, all rubber parts such as O-rings, oil
seals and the like should be replaced with new ones.
External appearance check items
Uneven wear
Stepped wear
Damage
Cracks
Deformation
Aging (spring, etc.)
Warping
Loose fits
Abnormal noise (from bearings, etc.)
Discoloration (from engine seizure, etc.)
Rust
Surface hardening
1 8
You might also like
- m57 Common RailDocument13 pagesm57 Common RailMartin Hani100% (4)
- Spare Parts V2403 M Di e PDFDocument50 pagesSpare Parts V2403 M Di e PDFdaniel100% (12)
- Engine Specs Specification (Engine Mechanical (H4Dotc 2.5L Dohc Turbo) : General Description)Document14 pagesEngine Specs Specification (Engine Mechanical (H4Dotc 2.5L Dohc Turbo) : General Description)Cristobal MedinaNo ratings yet
- Adjust Valve EC200DDocument5 pagesAdjust Valve EC200DHeru Hoo0% (1)
- SK450 - SK450 SK480 - SK480: Hydraulic ExcavatorsDocument12 pagesSK450 - SK450 SK480 - SK480: Hydraulic Excavatorsanon_485665212No ratings yet
- D155A-2 # 57001 Up SEBM018602 PDFDocument462 pagesD155A-2 # 57001 Up SEBM018602 PDFJoko Sukariono100% (6)
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDocument34 pagesSheet Metal Forming ProcessesIzi100% (12)
- Vortex X10 Settings CRF250R - 18Document1 pageVortex X10 Settings CRF250R - 18Filipe FavarelliNo ratings yet
- Quincy 106 y 108Document45 pagesQuincy 106 y 108nelsonp12No ratings yet
- Series: Swash-Plate Type Axial Piston Double PumpDocument11 pagesSeries: Swash-Plate Type Axial Piston Double PumpanandsubbiahNo ratings yet
- Demo PB GD510R-1Document7 pagesDemo PB GD510R-1Shop ManualNo ratings yet
- Valve Clearance Check and AdjustmentDocument3 pagesValve Clearance Check and AdjustmentRodrigo MuñozNo ratings yet
- Lessp13700 PC130F-7 PDFDocument14 pagesLessp13700 PC130F-7 PDFArdika GandhyNo ratings yet
- Brochure Ec210b Prime t3 en 30 20000465 CDocument20 pagesBrochure Ec210b Prime t3 en 30 20000465 CJumansyah Hamid100% (2)
- اطلاعات موتور Mitsubishi 8dc10Document1 pageاطلاعات موتور Mitsubishi 8dc10ali4299100% (1)
- Memahami Code NissanDocument11 pagesMemahami Code Nissananggie100% (1)
- SH210-5/SH210LC-5 Hydraulic ExcavatorDocument12 pagesSH210-5/SH210LC-5 Hydraulic ExcavatorpurwadiNo ratings yet
- Toyota Engine W04D (130HT)Document216 pagesToyota Engine W04D (130HT)Suryana Iskandar100% (1)
- Check List Generic Wheel Loader Caterpillar 938FDocument3 pagesCheck List Generic Wheel Loader Caterpillar 938FFrans Metin100% (1)
- Mitsubishi 6D16 A54727 Parts Catalogue (MG330) PDFDocument897 pagesMitsubishi 6D16 A54727 Parts Catalogue (MG330) PDFTharindu ManamperyNo ratings yet
- Accelerator Control, Fuel & Exhaust Systems: GI MADocument12 pagesAccelerator Control, Fuel & Exhaust Systems: GI MAaymendabNo ratings yet
- Nissan CD17Document3 pagesNissan CD17jose luis calixto requisNo ratings yet
- CDS11309 Toyota Hilux 1KD 2012 KitDocument14 pagesCDS11309 Toyota Hilux 1KD 2012 KitNelly AprianaNo ratings yet
- H D C 2Kd M STD: Ilux Ouble Abin AnualDocument3 pagesH D C 2Kd M STD: Ilux Ouble Abin AnualSalehe abdallah100% (1)
- Huafengdongli 495 4100 Series OperationmanualDocument73 pagesHuafengdongli 495 4100 Series OperationmanualHoang Vien DuNo ratings yet
- 002-004 Cylinder Head Cummins 6BTA5.9 G2Document10 pages002-004 Cylinder Head Cummins 6BTA5.9 G2AleksaNo ratings yet
- DX700LC PDFDocument20 pagesDX700LC PDFA Ramos GabyNo ratings yet
- Top Causes of An ECM FailureDocument2 pagesTop Causes of An ECM FailuredubimouNo ratings yet
- 388 488 ENGINE Maintenance ManalDocument62 pages388 488 ENGINE Maintenance Manalluis gomezNo ratings yet
- Armado Transmision D6GDocument23 pagesArmado Transmision D6GServimaquinaria Millan Sac0% (1)
- Komatsu PC200-7 Error Code On The Monitor, CMP Technology Co., LimitedDocument5 pagesKomatsu PC200-7 Error Code On The Monitor, CMP Technology Co., Limitedkiagengbrantas heavyequipmentNo ratings yet
- ERROR CA272 & CA559 Problem IMV Open Error & Low PressureDocument16 pagesERROR CA272 & CA559 Problem IMV Open Error & Low Pressureahmad hidayatNo ratings yet
- Bomag bw212 Full-Product-Guide - PRE101334 - 1803 PDFDocument364 pagesBomag bw212 Full-Product-Guide - PRE101334 - 1803 PDFmartin marsayNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification CWB6BLLDN2-6X4Document1 pageTechnical Specification CWB6BLLDN2-6X4Muhaimin100% (2)
- Transmission System: Transmission Proper Transmission LinkageDocument106 pagesTransmission System: Transmission Proper Transmission Linkageirwan yuniardi100% (1)
- Manual Hitachi 130Document20 pagesManual Hitachi 130yoharamyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit DiagramDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuit DiagramVOk Boy Nuar100% (2)
- D31P-20 Komatsu S4D102EDocument3 pagesD31P-20 Komatsu S4D102Esrabesh basnetNo ratings yet
- 3054c Pistons and Connecting Rods - RemoveDocument4 pages3054c Pistons and Connecting Rods - RemoveAlissontrin100% (1)
- Hino J08c Engine ManualDocument2 pagesHino J08c Engine ManualMichel Mejia durandNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Bulldozers D D60P-6 Cummins Nh220-Ci: Normal ModerateDocument3 pagesKomatsu Bulldozers D D60P-6 Cummins Nh220-Ci: Normal Moderatesrabesh basnet50% (2)
- Hitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebDocument8 pagesHitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebridofambudiNo ratings yet
- Kamatsu PC270 - 270LC-8 - 2Document7 pagesKamatsu PC270 - 270LC-8 - 2Piotr Gabryś Hi-this100% (1)
- Piston and Rings: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument9 pagesPiston and Rings: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenalonsoNo ratings yet
- d3g d4g d5g Eng PDFDocument20 pagesd3g d4g d5g Eng PDFDhee DoodzNo ratings yet
- QuickServe Online - (3666087) A B3.9, B4.5, B4.5 RGT, and B5.9 Service ManualDocument7 pagesQuickServe Online - (3666087) A B3.9, B4.5, B4.5 RGT, and B5.9 Service ManualshashirajNo ratings yet
- Valve Clearance CheckDocument1 pageValve Clearance Checkau7usaNo ratings yet
- 6D114-3 Seccion20 STD Value A4Document41 pages6D114-3 Seccion20 STD Value A4Wr Sb100% (1)
- New Fuso Fighter FK FM FN Brochure 2015Document8 pagesNew Fuso Fighter FK FM FN Brochure 2015ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Cummins Injector Install ProcedureDocument15 pagesCummins Injector Install ProcedureLawrence Shafer100% (6)
- C15 and C18 - Finding Top Center Position For No. 1 Piston - Caterpillar Engines TroubleshootingDocument3 pagesC15 and C18 - Finding Top Center Position For No. 1 Piston - Caterpillar Engines Troubleshootingmohd arif fahmi mohamad saleh100% (1)
- Service Manual Common Rail System Isuzu 4HK1 6HK1Document20 pagesService Manual Common Rail System Isuzu 4HK1 6HK1Văn Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- At 300Document11 pagesAt 300mne79054No ratings yet
- Disassembly Cylinder Head 920 Wheel LoaderDocument7 pagesDisassembly Cylinder Head 920 Wheel LoaderAmir Bambang YudhoyonoNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat 320D L Excavator (Prefix A9F) Service Repair Manual (A9F00001 and Up)Document23 pagesCaterpillar Cat 320D L Excavator (Prefix A9F) Service Repair Manual (A9F00001 and Up)kfmuseddk0% (1)
- 1A-108 Engine Mechanical (4Hk1, 6Hk1) : CautionDocument1 page1A-108 Engine Mechanical (4Hk1, 6Hk1) : CautionВладимир Швед100% (1)
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: C7.1 Industrial EngineDocument144 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual: C7.1 Industrial EngineAlonso FernandoNo ratings yet
- Manual Engine TritonDocument6 pagesManual Engine Tritonryan pentol100% (2)
- Low Idle RPM AdjustDocument4 pagesLow Idle RPM AdjustSteven ManuputtyNo ratings yet
- Silentpiler f101Document3 pagesSilentpiler f101Nguyen The PhatNo ratings yet
- SEM C Series Catalogue LOW REZDocument16 pagesSEM C Series Catalogue LOW REZAnonymous M5F3h2NR3f50% (2)
- Isuzu Engine ValveDocument4 pagesIsuzu Engine ValveAnthony Carson100% (1)
- Technical Data-OM471LA.E5-2-360 kW-2400 Nm-D471.945-Off Highway US Tier 4 (With DPF)Document6 pagesTechnical Data-OM471LA.E5-2-360 kW-2400 Nm-D471.945-Off Highway US Tier 4 (With DPF)Samuel SQNo ratings yet
- 4bc2 Injection Pump PDFDocument1 page4bc2 Injection Pump PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Kohler 18 Ch620Document88 pagesKohler 18 Ch620michaelmvNo ratings yet
- N Step 1 NissanDocument1,415 pagesN Step 1 NissanJoko Sukariono100% (9)
- What Is An Informal LetterDocument10 pagesWhat Is An Informal LetterJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- 4fuel Injection PumpDocument9 pages4fuel Injection PumpJoko Sukariono100% (2)
- SEKN5003 R KIT For New Connector PDFDocument23 pagesSEKN5003 R KIT For New Connector PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- SEKN5005 Deutsch C TIPS PDFDocument7 pagesSEKN5005 Deutsch C TIPS PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- Introduction and General Service SafetyDocument47 pagesIntroduction and General Service SafetyJoko Sukariono100% (2)
- (CRI) Engine Fuel Filters PDFDocument7 pages(CRI) Engine Fuel Filters PDFJoko Sukariono100% (1)
- Harness Checker Box PDFDocument2 pagesHarness Checker Box PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- At04222a2filter PDFDocument8 pagesAt04222a2filter PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- III. ENGINE DIESEL (Engine System) PDFDocument75 pagesIII. ENGINE DIESEL (Engine System) PDFJoko Sukariono100% (4)
- Cri Fuel System Thiess PDFDocument11 pagesCri Fuel System Thiess PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- II. ENGINE DIESEL (Komponen Engine) PDFDocument34 pagesII. ENGINE DIESEL (Komponen Engine) PDFJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- A4 SEBM024301 (T&A Troubleshooting) PDFDocument330 pagesA4 SEBM024301 (T&A Troubleshooting) PDFJoko Sukariono100% (2)
- Off LeakDocument26 pagesOff LeakPatriciaH20No ratings yet
- 062 - R - 301 - 302 - 303 ManuelDocument303 pages062 - R - 301 - 302 - 303 Manuelshinki31000No ratings yet
- E000Document4 pagesE000Nazael DiazNo ratings yet
- OverhaulDocument10 pagesOverhaularhamNo ratings yet
- Spare Part ListDocument23 pagesSpare Part ListCarloAugentiNo ratings yet
- Service and Maintenance Manual: Models 800S 810SJ 860SJDocument516 pagesService and Maintenance Manual: Models 800S 810SJ 860SJ云大豪No ratings yet
- 909J e 959J Parts BookDocument405 pages909J e 959J Parts BookGabriely MuriloNo ratings yet
- Discovery 3.0 Litre V6 Diesel (10my Eu5) On-Board Diagnostics Engine Management SystemDocument70 pagesDiscovery 3.0 Litre V6 Diesel (10my Eu5) On-Board Diagnostics Engine Management SystemVladimirAgeevNo ratings yet
- Esquematico Chevrolet s10 Xtreme 2002Document5 pagesEsquematico Chevrolet s10 Xtreme 2002Raul RossyNo ratings yet
- Engine NomenclatureDocument18 pagesEngine NomenclatureAlonso Trancon ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel TurbineDocument6 pagesPelton Wheel Turbinesmh khanNo ratings yet
- P700e5 BrochureDocument4 pagesP700e5 BrochureahmedalgaloNo ratings yet
- Valve Refacing and Valve Seat Grinding and Checking of Leakage of ValvesDocument6 pagesValve Refacing and Valve Seat Grinding and Checking of Leakage of ValvesNandakumar BasavarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4ゞ『HaiDerツ98〆No ratings yet
- Sperre HL2 90Document1 pageSperre HL2 90Eslam MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Omohi: Made in ApanDocument10 pagesOmohi: Made in ApanWilmer VasquezNo ratings yet
- 6 Wheeler & Trucks Engine OhDocument12 pages6 Wheeler & Trucks Engine Ohhajj basitNo ratings yet
- The New Mercedes Benz Four Cylinder Diesel Engine For Passenger CarsDocument8 pagesThe New Mercedes Benz Four Cylinder Diesel Engine For Passenger CarsBobCavNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Table of ContentDocument17 pages4 Stroke Table of ContentMussardNo ratings yet
- Spare Part Request List Doosan PU086TIDocument12 pagesSpare Part Request List Doosan PU086TIPak ItamNo ratings yet
- Industrial Diesel Engine: TNV DI SeriesDocument2 pagesIndustrial Diesel Engine: TNV DI SeriesJohn GarnetNo ratings yet
- Parts List of Engine Assy of BD-65 (DZ-00535)Document1 pageParts List of Engine Assy of BD-65 (DZ-00535)CwsNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Power Plant: Submitted By-Hiten (2K19/EE/113) Khursheed Aqueeb (2K19/EE/135)Document16 pagesGas Turbine Power Plant: Submitted By-Hiten (2K19/EE/113) Khursheed Aqueeb (2K19/EE/135)2k19ee113 HitenNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Scorpio SC DC NEF LHDDocument508 pagesService Manual Scorpio SC DC NEF LHDAlex Bravo100% (1)
- FM Module I - Turbines - Note - PPTDocument52 pagesFM Module I - Turbines - Note - PPT916 Maneesh nn ME BNo ratings yet
- 2021 Yam Gytr Acc Supersport Eu-En v2Document28 pages2021 Yam Gytr Acc Supersport Eu-En v2Lillo VetroNo ratings yet